前言
objc_msgSend是用汇编写的:
- 因为在C语言中不可能通过写一个函数来保留未知的参数并且跳转到一个任意的函数指针。C语言没有满足做这件事情的必要特性。
- objc_msgSend必须够快。
位说明
在objc_msgSend(下)中我们知道cache_t结构体中_bucketsAndMaybeMask指针中高16位是mask,低48位是buckets_t指针,在mask中,还预留的maskZeroBits 4位供msgSend操作,用来判断cache_t中是否有preopt_cache_t(共享缓存) ```cpp // _bucketsAndMaybeMask is a buckets_t pointer in the low 48 bits // _maybeMask is unused, the mask is stored in the top 16 bits.
// How much the mask is shifted by. static constexpr uintptr_t maskShift = 48;
// Additional bits after the mask which must be zero. msgSend
// takes advantage of these additional bits to construct the value
// mask << 4 from _maskAndBuckets in a single instruction.
static constexpr uintptr_t maskZeroBits = 4;
<a name="lCiIQ"></a>### 汇编流程承接[objc_msgSend(下)](https://www.yuque.com/raindykukude/fwbpv1/tfcxyk)汇编流程,在bucket对比都为命中情况下,汇编执行以下流程,p13直接定位到mask位置的bucket,即capacity-1位置,最后一个bucket是首地址。```cpp#elif CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_HIGH_16add p13, p10, p11, LSR #(48 - (1+PTRSHIFT))// p13 = buckets + (mask << 1+PTRSHIFT)
判断共享缓存中是否包含
add p12, p10, p12, LSL #(1+PTRSHIFT)// p12 = first probed bucket
接着从后向前进行遍历对比,有找到,则跳转2 cacheHit,否则判断是否大于first_probed,如果是即跳出
4: ldp p17, p9, [x13], #-BUCKET_SIZE // {imp, sel} = *bucket--cmp p9, p1 // if (sel == _cmd)b.eq 2b // goto hitcmp p9, #0 // } while (sel != 0 &&ccmp p13, p12, #0, ne // bucket > first_probed)b.hi 4b
慢速查找流程
在cache_t缓存未查找到后,会调用__objc_msgSend_uncached,此时主要两个流程:
- MethodTableLookup 重点
TailCallFunctionPointer x17 跳转函数 ```cpp STATIC_ENTRY objc_msgSend_uncached UNWIND objc_msgSend_uncached, FrameWithNoSaves
// THIS IS NOT A CALLABLE C FUNCTION // Out-of-band p15 is the class to search
MethodTableLookup TailCallFunctionPointer x17
END_ENTRY __objc_msgSend_uncached
- TailCallFunctionPointer是简单一个跳转到$0```cpp.macro TailCallFunctionPointer// $0 = function pointer valuebr $0.endmacro
MethodTableLookup中会调用_lookUpImpOrForward,必然会返回一个imp值,因为x0即可以作为参数传递,亦可以作为下个函数的返回值,
mov x17, x0中x0存储了IMP并返回给了x17。进一步查看_lookUpImpOrForward ```cpp .macro MethodTableLookupSAVE_REGS MSGSEND
// lookUpImpOrForward(obj, sel, cls, LOOKUP_INITIALIZE | LOOKUP_RESOLVER) // receiver and selector already in x0 and x1 mov x2, x16 mov x3, #3 bl _lookUpImpOrForward
// IMP in x0 mov x17, x0
RESTORE_REGS MSGSEND
.endmacro
<a name="kWBjQ"></a>## lookUpImpOrForward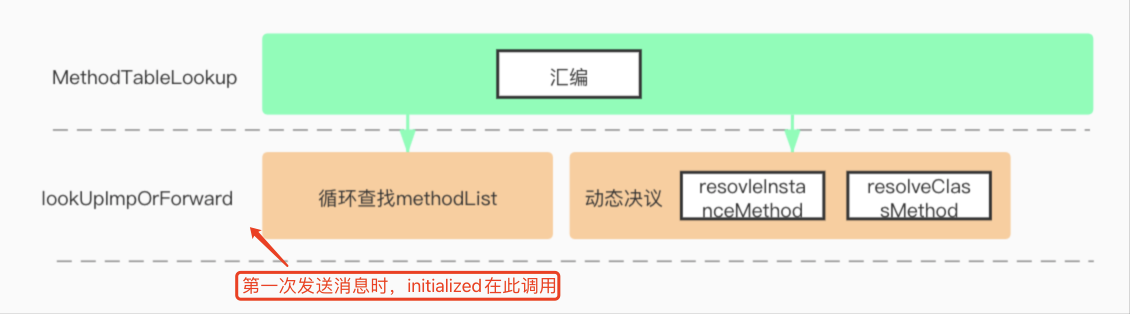- **_lookUpImpOrForward是用C++编写,开始慢速查找,不断遍历method_list过程,慢速流程,目标找到imp,**```cppIMP lookUpImpOrForward(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)checkIsKnownClass(cls);
checkIsKnownClass注册类(有很多相关的表),判断当前class是否已注册到缓存表allocatedClasses中,实际有很多注册表
static boolisKnownClass(Class cls){if (fastpath(objc::dataSegmentsRanges.contains(cls->data()->witness, (uintptr_t)cls))) {return true;}auto &set = objc::allocatedClasses.get();return set.find(cls) != set.end() || dataSegmentsContain(cls);}
realizeAndInitializeIfNeeded_locked中主要对对象、类、元类建立关系,可以参考经典的isa走位图,所有关联的对象都会初始化完毕,其意义就是找方法imp,也是为下一步for循环做准备
- 其中父类 - 子类是双向链表的关系,通过子类,初始化父类,再设置父类的childrenClass是当前类
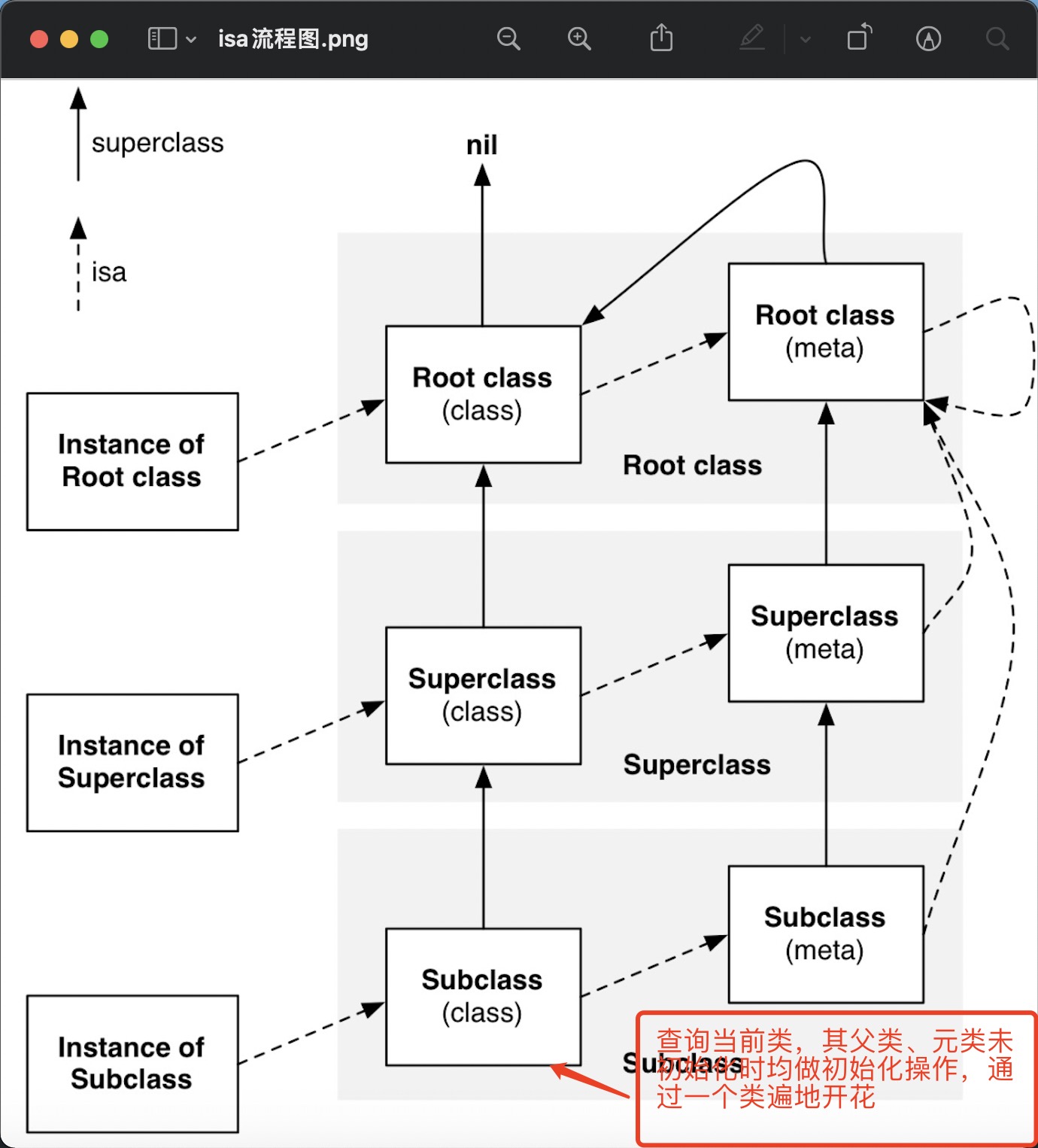
realizeAndInitializeIfNeeded_lockedstatic Class realizeClassWithoutSwift(Class cls, Class previously)cls->setSuperclass(supercls);cls->initClassIsa(metacls);
- for (unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();;) {} 是一个死循环,直到出现break或者goto跳出
CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES 代表去共享缓存查找,因为当执行遍历时,可能某个方法正在写入
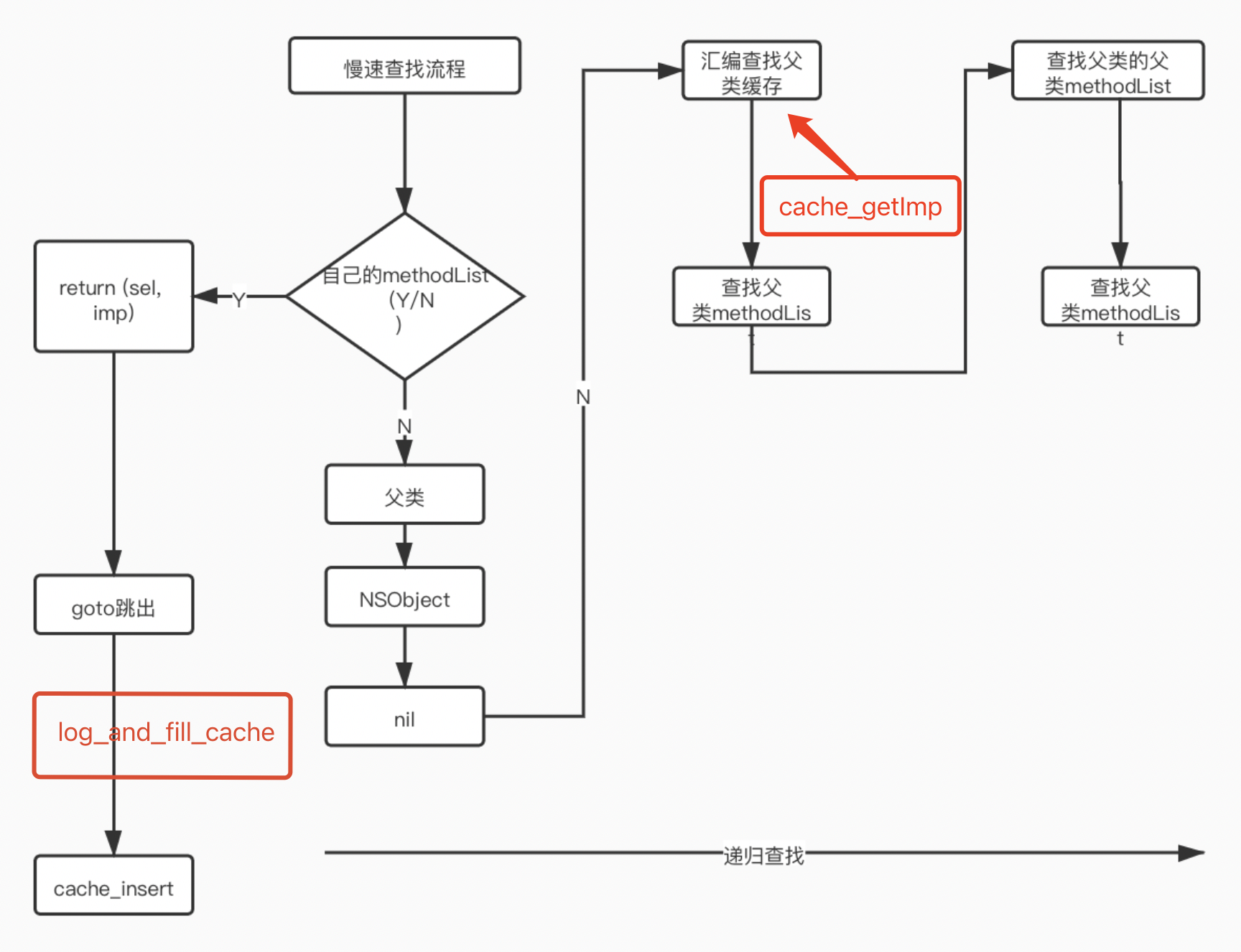
for (unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();;) { // for死循环if (curClass->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache(/* strict */true)) {#if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES //共享缓存找一波,调用函数是可能某个方法正在写入imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);if (imp) goto done_unlock;curClass = curClass->cache.preoptFallbackClass();#endif} else {// curClass method list.Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);//二分查找if (meth) {imp = meth->imp(false);goto done; // 跳出循环}// 父类if (slowpath((curClass = curClass->getSuperclass()) == nil)) {// No implementation found, and method resolver didn't help.// Use forwarding.imp = forward_imp;break;}}// Halt if there is a cycle in the superclass chain.if (slowpath(--attempts == 0)) {_objc_fatal("Memory corruption in class list.");}// Superclass cache. 父类的快速查找imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);if (slowpath(imp == forward_imp)) {// Found a forward:: entry in a superclass.// Stop searching, but don't cache yet; call method// resolver for this class first.break;}if (fastpath(imp)) {// Found the method in a superclass. Cache it in this class.goto done;}}// No implementation found. Try method resolver once.if (slowpath(behavior & LOOKUP_RESOLVER)) {behavior ^= LOOKUP_RESOLVER;return resolveMethod_locked(inst, sel, cls, behavior);}done:if (fastpath((behavior & LOOKUP_NOCACHE) == 0)) {#if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHESwhile (cls->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache(/* strict */true)) {cls = cls->cache.preoptFallbackClass();}#endif// 查找到流程,填充缓存,cache_insertlog_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);}
遍历methodList,数据量非常庞大,这里用了二分查找,提高效率(以下写法很牛逼)
- 初始count为list的长度,条件判断为不等于0,然后count>>=1,右移一位相当于除以2
- 初始probe = base(0) + count >>=2 得到中位数
判断sel与传入的sel是否匹配
- 如果匹配时,这里存在分类情况,进行probe—,判断其前一个是否是同名方法,如果是代表是分类方法,执行分类方法
- 不匹配时,count—,再二分拿到新中位数 ```cpp ALWAYS_INLINE static method_t findMethodInSortedMethodList(SEL key, const method_list_t list, const getNameFunc &getName) { ASSERT(list);
auto first = list->begin(); auto base = first; decltype(first) probe;
uintptr_t keyValue = (uintptr_t)key; uint32_t count; // 例如初始为8 二进制1000 位移1位后 0100 为 4 // count = 8
// probe = 0 + 4 = 4
// count = 7, base = 5 // 0111 >> 0011 为 3 , probe = 5 + 3 = 8 // 取值范围 5-8, 6 或者 7 // 3 >> 1 = 1 for (count = list->count; count != 0; count >>= 1) { probe = base + (count >> 1);
// 得到sel uintptr_t probeValue = (uintptr_t)getName(probe);
// 判断sel与传入sel是否匹配 if (keyValue == probeValue) {
// 如果有分类,优先分类方法while (probe > first && keyValue == (uintptr_t)getName((probe - 1))) {probe--;}// 查找到则返回return &*probe;
}
// 未满足上述条件,base = 4 + 1 = 5, count= 8-1 = 7 if (keyValue > probeValue) {
base = probe + 1;count--;
} }
流程图
需要注意,cache_getImp与lookUpImpCache有一点不同,这里找不到直接return nil,然后在代码循环中接着找父类
- 类能运行对象方法吗?(NSObject中定义了方法)
- 可以,根据类的走位图,查找类 -> 元类 -> 元类的父类 -> 根元类 -> NSObject 调用


