题目
15 三数之和
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
思路
哈希去重超时了
看到题目里要求不能包含重复元组,首先会想到用map或set去重。但问题是我们需要给a,b,c三个值去重,代码处理就非常耗时,即使用上了双指针,如下代码还是运行超时了:
class Solution{public:vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int> &nums){sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());vector<vector<int>> result;unordered_map<int, int> numa; //用于对第一个数a去重for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){if (nums[i] > 0)break;auto it = numa.find(nums[i]);if (it == numa.end()){numa.insert({nums[i]}, i); //当前map不存在}else{continue;}unordered_map<int, int> numb;unordered_map<int, int> numc;int b = it->second + 1;int c = nums.size() - 1;while (nums[slow] <= 0 && nums[right] >= 0){auto itb = numb.find(nums[b]);if (itb == numb.end()){numb.insert({nums[b]}, b); //当前map不存在}else{continue;}auto itc = numc.find(nums[c]);if (itc == numc.end()){numc.insert({nums[c]}, c); //当前map不存在}else{continue;}int sum = nums[i] + nums[b] + nums[c];if (sum == 0){result.push_back({nums[i], nums[slow], nums[right]});}else if (sum < 0)slow++;elseright--;}}return result;}};
手动去重+双指针
其实这道题目使用哈希法并不十分合适,可以先对nums进行排序,然后手动去重(保证在遍历时不会用到相同的值进行加法运算)。在配合双指针法,效率有很大提升:
双指针法图示: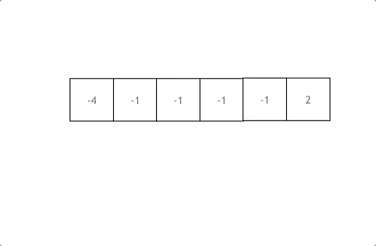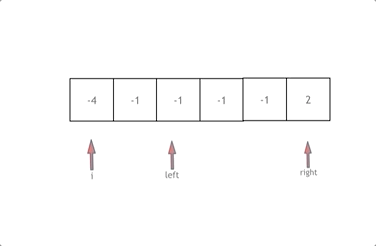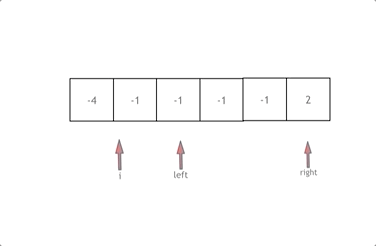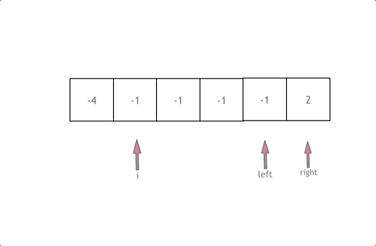
- 首先将数组排序,然后有一层for循环,i从下标0的地方开始,同时定一个下标left 定义在i+1的位置上,定义下标right 在数组结尾的位置上。
- 在数组中找到 abc 使得a + b +c =0,我们这里相当于 a = nums[i] b = nums[left] c = nums[right]。
- 如果nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > 0 就说明 此时三数之和大了,因为数组是排序后了,所以right下标就应该向左移动,这样才能让三数之和小一些。
如果 nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] < 0 说明 此时 三数之和小了,left 就向右移动,才能让三数之和大一些,直到left与right相遇为止。
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int> &nums) { vector<vector<int>> ans; if (nums.size() < 3) return ans; int n = nums.size(); sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); // 枚举 a for (int first = 0; first < n; ++first) { // a需要和上一次枚举的数不相同 if (first > 0 && nums[first] == nums[first - 1]) { continue; } // c 对应的指针初始指向数组的最右端 int third = n - 1; int target = -nums[first]; // 枚举 b for (int second = first + 1; second < n; ++second) { // b需要和上一次枚举的数不相同 if (second > first + 1 && nums[second] == nums[second - 1]) { continue; } // 需要保证 b 的指针在 c 的指针的左侧 while (second < third && nums[second] + nums[third] > target) { --third; } // 如果指针重合,随着 b 后续的增加 // 就不会有满足 a+b+c=0 并且 b<c 的 c 了,可以退出循环 if (second == third) { break; } if (nums[second] + nums[third] == target) { ans.push_back({nums[first], nums[second], nums[third]}); } } } return ans; } };leetcode18
18 四数之和
与三数之和类似,只不过变成了四个数的和。所以这里写在了一起,解析思路是一样的,四个数也没法用set去重了。还是和三数之和差不多,这次遍历a,b两个数并手动去重,然后c,d两个数用双指针来遍历class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> fourSum(vector<int> &nums, int target) { vector<vector<int>> ans; if (nums.size() < 4) return ans; int n = nums.size(); sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); //在三数之和的基础上再加一层for循环 // 枚举 a for (int first = 0; first < n; ++first) { // a需要和上一次枚举的数不相同 if (first > 0 && nums[first] == nums[first - 1]) { continue; } //枚举b for (int second = first + 1; second < n; second++) { // b需要和上一次枚举的数不相同 if (second > (first + 1) && nums[second] == nums[second - 1]) { continue; } // d 对应的指针初始指向数组的最右端 int fourth = n - 1; int tmp = target - nums[first] - nums[second]; // 枚举 c for (int third = second + 1; third < n; ++third) { // c需要和上一次枚举的数不相同 if (third > (second + 1) && nums[third] == nums[third - 1]) { continue; } // 需要保证 c 的指针在 v 的指针的左侧 while (third < fourth && nums[third] + nums[fourth] > tmp) { --fourth; } // 如果指针重合,可以退出循环 if (fourth == third) { break; } if (nums[third] + nums[fourth] == tmp) { ans.push_back({nums[first], nums[second], nums[third], nums[fourth]}); } } } } return ans; } };

