二叉树分类
满二叉树
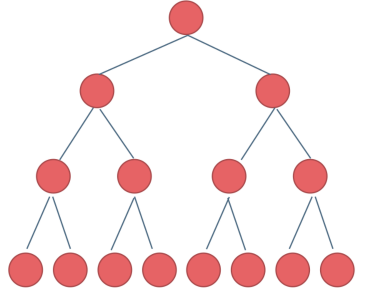
完全二叉树
除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置(优先级队列其实是一个堆,堆就是一棵完全二叉树,同时保证父子节点的顺序关系)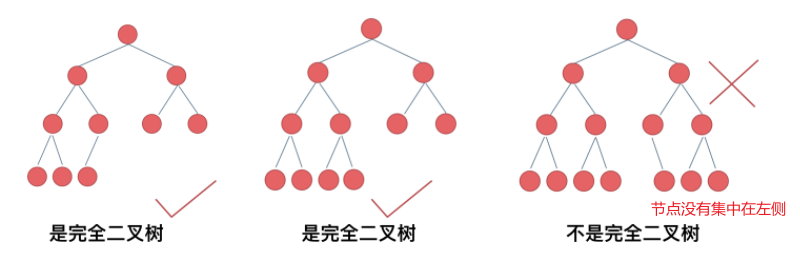
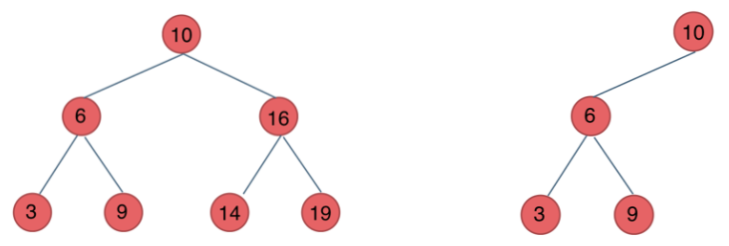
二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树是一个有序树。
- 每一个节点有一个值,不允许重复
- 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
- 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
- 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树
代码模板如下:
#ifndef BST_H#define BST_H#include <iostream>template <typename T>class BST; //前置声明template <typename T>class Element{public:T key; //将键值单独一个类放置,方便扩展数据结构};template <typename T>class BstNode{friend class BST<T>; //友元类,可以访问私有成员public:Element<T> data;private:BstNode *leftChild;BstNode *rightChild;};template <typename T>class BST{public:BST(BstNode<T> *init = 0){root = init;}bool insertKey(const Element<T> &ele); //插入数据BstNode<T> *search(const Element<T> &ele);BstNode<T> *search(BstNode<T> *start, const Element<T> &ele); //递归查找数据BstNode<T> *forSearch(const Element<T> &ele); //迭代查找数据void display(){if (root)display(root);elsestd::cout << "no nodes" << std::endl;}void display(BstNode<T> *node); //显示节点数据private:BstNode<T> *root;};template <typename T>void BST<T>::display(BstNode<T> *node){if (!node){return;}//显示当前节点及其左右子树的keystd::cout << "data.key: " << node->data.key << std::endl;if (node->leftChild){display(node->leftChild);}if (node->rightChild){display(node->rightChild);}}template <typename T>bool BST<T>::insertKey(const Element<T> &ele){BstNode<T> *p = root;BstNode<T> *q = nullptr; // q为p的父节点//插入之前需要先查找,找到合适的位置while (p){q = p; // p改变之前,q指向当前节点if (ele.key == p->data.key){return false; //值重复,失败返回}else if (ele.key < p->data.key){//小于,继续查找当前节点左子树p = p->leftChild;}else{//大于,继续查找当前节点右子树p = p->rightChild;}}//循环结束,合适的位置就是qp = new BstNode<T>; //创建新节点p->leftChild = nullptr;p->rightChild = nullptr;p->data = ele;if (!root)root = p; //没有根节点,p就是根节点else if (ele.key < q->data.key){q->leftChild = p;}else{q->rightChild = p;}return true;}template <typename T>BstNode<T> *BST<T>::search(const Element<T> &ele){if (root)return search(root, ele);elsereturn nullptr;}template <typename T>BstNode<T> *BST<T>::search(BstNode<T> *start, const Element<T> &ele){if (!start)return nullptr;if (start->data.key == ele.key){return start;}else if (start->data.key > ele.key){return search(start->leftChild, ele);}else{return search(start->rightChild, ele);}}template <typename T>BstNode<T> *BST<T>::forSearch(const Element<T> &ele){for (BstNode<T> *n = root; n != nullptr;){if (ele.key == n->data.key){return n;}else if (ele.key < n->data.key){n = n->leftChild;}else{n = n->rightChild;}}return nullptr;}#endif // BST_H
平衡二叉搜索树
被称为AVL(Adelson-Velsky and Landis)树,且具有以下性质:它是一棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树也是一棵平衡二叉树。
C++中map、set、multimap,multiset的底层实现都是平衡二叉搜索树,所以map、set的增删操作时间时间复杂度是logn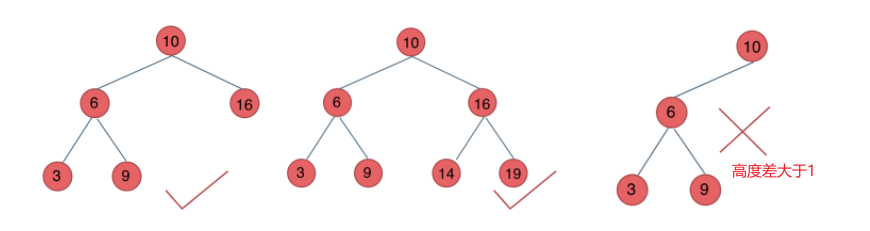
二叉树存储方式
二叉树可以链式存储,也可以顺序存储。链式存储方式就用指针, 顺序存储的方式就是用数组。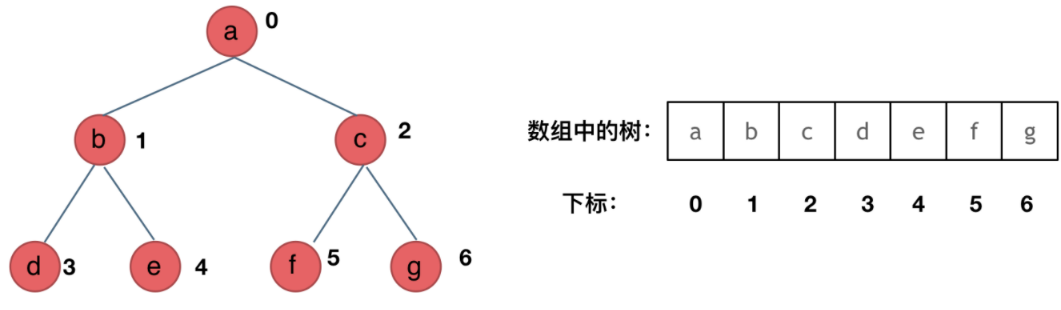
用数组来存储二叉树如何遍历的呢?如果父节点的数组下标是 i,那么它的左孩子就是 i 2 + 1,右孩子就是 i 2 + 2。
二叉树如何遍历
遍历方式分类
- 深度优先遍历
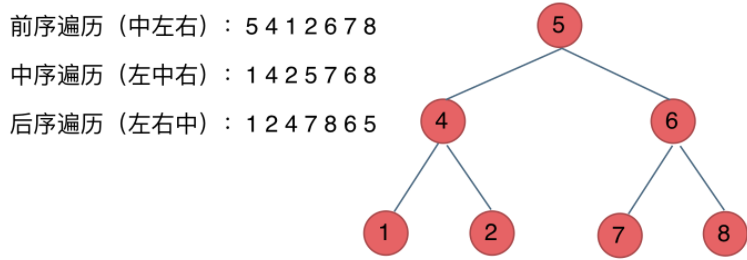
- 前序遍历(递归法,迭代法):中左右
- 中序遍历(递归法,迭代法):左中右
- 后序遍历(递归法,迭代法):左右中
- 广度优先遍历
- 层次遍历(迭代法)
递归遍历模板
可以根据下面的模板试试leetcode94,144,145
#ifndef BINARY_TREE_HPP
#define BINARY_TREE_HPP
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
template <typename T>
class TreeNode
{
public:
TreeNode(T val) : data(val), leftChild(nullptr), rightChild(nullptr) {}
T data;
TreeNode<T> *leftChild;
TreeNode<T> *rightChild;
};
template <typename T>
class BinaryTree
{
public:
//二叉树的遍历操作
void InOrder(TreeNode<T> *currentNode); //中序遍历:左子树-节点-右子树
void PreOrder(TreeNode<T> *currentNode); //前序遍历 节点-左子树-右子树
void PostOrder(TreeNode<T> *currentNode); //后续遍历 左子树-右子树-节点
void LevelOrder(TreeNode<T> *currentNode); //层序遍历, 一层一层显示value
void showNodeValue(TreeNode<T> *currentNode);
TreeNode<T> *root;
};
template <typename T>
void BinaryTree<T>::InOrder(TreeNode<T> *currentNode)
{
if (currentNode)
{
//左子树递归
InOrder(currentNode->leftChild);
//显示当前节点
showNodeValue(currentNode);
//右子树递归
InOrder(currentNode->rightChild);
}
}
template <typename T>
void BinaryTree<T>::PreOrder(TreeNode<T> *currentNode)
{
if (currentNode)
{
//显示当前节点
showNodeValue(currentNode);
//左子树递归
PreOrder(currentNode->leftChild);
//右子树递归
PreOrder(currentNode->rightChild);
}
}
template <typename T>
void BinaryTree<T>::PostOrder(TreeNode<T> *currentNode)
{
if (currentNode)
{
//左子树递归
PostOrder(currentNode->leftChild);
//右子树递归
PostOrder(currentNode->rightChild);
//显示当前节点
showNodeValue(currentNode);
}
}
template <typename T>
void BinaryTree<T>::LevelOrder(TreeNode<T> *currentNode)
{
//层序遍历无法使用递归法实现
}
template <typename T>
void BinaryTree<T>::showNodeValue(TreeNode<T> *currentNode)
{
std::cout << currentNode->data;
}
#endif
迭代遍历模板
#ifndef BINARY_TREE_HPP
#define BINARY_TREE_HPP
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
template <typename T>
class TreeNode
{
public:
TreeNode(T val) : data(val), leftChild(nullptr), rightChild(nullptr) {}
T data;
TreeNode<T> *leftChild;
TreeNode<T> *rightChild;
};
template <typename T>
class BinaryTree
{
public:
//二叉树的遍历操作
void InOrder(TreeNode<T> *currentNode); //中序遍历:左子树-节点-右子树
void PreOrder(TreeNode<T> *currentNode); //前序遍历 节点-左子树-右子树
void PostOrder(TreeNode<T> *currentNode); //后续遍历 左子树-右子树-节点
void LevelOrder(TreeNode<T> *currentNode); //层序遍历, 一层一层显示value
void showNodeValue(TreeNode<T> *currentNode);
TreeNode<T> *root;
};
template <typename T>
void BinaryTree<T>::InOrder(TreeNode<T> *currentNode)
{
std::stack<TreeNode<T> *> st;
if (root != NULL)
st.push(root);
while (!st.empty())
{
TreeNode<T> *node = st.top();
if (node != NULL)
{
st.pop(); // 将该节点弹出,避免重复操作,下面再将右中左节点添加到栈中
if (node->right)
st.push(node->right); // 添加右节点(空节点不入栈)
st.push(node); // 添加中节点
st.push(NULL); // 中节点访问过,但是还没有处理,加入空节点做为标记。
if (node->left)
st.push(node->left); // 添加左节点(空节点不入栈)
}
else
{ // 只有遇到空节点的时候,才将下一个节点放进结果集
st.pop(); // 将空节点弹出
node = st.top(); // 重新取出栈中元素
st.pop();
//显示当前节点
showNodeValue(node);
}
}
}
template <typename T>
void BinaryTree<T>::PreOrder(TreeNode<T> *currentNode)
{
std::stack<TreeNode<T> *> st;
if (root != NULL)
st.push(root);
while (!st.empty())
{
TreeNode<T> *node = st.top();
if (node != NULL)
{
st.pop();
if (node->right)
st.push(node->right); // 右
if (node->left)
st.push(node->left); // 左
st.push(node); // 中
st.push(NULL);
}
else
{
st.pop();
node = st.top();
st.pop();
//显示当前节点
showNodeValue(node);
}
}
}
template <typename T>
void BinaryTree<T>::PostOrder(TreeNode<T> *currentNode)
{
std::stack<TreeNode<T> *> st;
if (root != NULL)
st.push(root);
while (!st.empty())
{
TreeNode<T> *node = st.top();
if (node != NULL)
{
st.pop();
st.push(node); // 中
st.push(NULL);
if (node->right)
st.push(node->right); // 右
if (node->left)
st.push(node->left); // 左
}
else
{
st.pop();
node = st.top();
st.pop();
//显示当前节点
showNodeValue(node);
}
}
}
template <typename T>
void BinaryTree<T>::LevelOrder(TreeNode<T> *currentNode)
{
std::queue<TreeNode<T> *> que;
if (root != NULL)
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty())
{
int size = que.size();
// 这里一定要使用固定大小size,不要使用que.size(),因为que.size是不断变化的
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
TreeNode<T> *node = que.front();
que.pop();
showNodeValue(node);
if (node->left)
que.push(node->left);
if (node->right)
que.push(node->right);
}
}
}
template <typename T>
void BinaryTree<T>::showNodeValue(TreeNode<T> *currentNode)
{
std::cout << currentNode->data;
}
#endif
红黑树—自平衡二叉查找树
红黑规则
红黑树(Red–black tree)是一种自平衡二叉查找树。红黑树特征:节点有颜色,插入和删除节点是要遵守红黑规则:
- 每一个节点不是红色就是黑色
- 根节点是黑色
- 如果节点是红色,则它的子节点必须是黑的。即红色不能相邻
- 从根到叶子节点的每条路经,必须包含相同数目的黑色节点
如果当前二叉树不符合红黑规则,有两种自我修正方式:
- 改变节点的颜色
- 旋转
旋转
旋转分为单旋转和双旋转,应用于下面场景:
代码模板
红黑树代码讲解:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av31763085/?p=28 ```cppifndef REDBLACKTREE_H
define REDBLACKTREE_H
include “except.h”
template
template
//红黑树
template
RedBlackTree(const T &negInf);
~RedBlackTree();
void insert(const T &x);
void rotateWithLeftChild(Node *&K2) const; //单旋转,向右
void rotateWithRightChild(Node *&k1) const; //单旋转,向左
void doubleRotateWithLeftChild(Node *&K2) const; //双旋转
void doubleRotateWithRightChild(Node *&k1) const; //双旋转
void handleReorient(const T &item); //平滑处理
RedBlackNode<T> *rotate(const T &item, Node *parent); //旋转函数
bool isEmpty();
void makeEmpty();
void deleteNodes(Node *start); //删除从start开始往后所有节点
bool find(const T &x, Node *node);
bool findMin(T &value);
bool findMax(T &value);
// private: //just for test
Node *header; //指向root根节点的指针
Node *nullNode; //无子节点
Node *current;
Node *parent; //父节点
Node *grand; //祖父节点
Node *great; //曾祖父节点
};
//红黑树节点
template
template
//构造函数指定header为负无穷大
header = new Node(neginf);
header->left = header->right = nullNode;
}
template
template
current = x < current->element ? current->left : current->right;
//检查:如果当前节点,左右儿子节点都是红色,需要处理
if (current->left->color == RED && current->right->color == RED)
{
handleReorient(x);
}
}
if (current != nullNode)
throw DuplicateItemException();
current = new Node(x, nullNode, nullNode);
if (x < parent->element)
parent->left = current;
else
parent->right = current;
//自动平滑当前树,变为红黑树(重点)
handleReorient(x);
}
//向右旋转
template
//向左旋转
template
template
template
template
if (parent->color == RED)
{
grand->color = RED;
if ((item < grand->element) != (item < parent->element))
{
parent = rotate(item, grand); //单旋转
}
current = rotate(item, great); //双旋转
current->color = BLACK;
}
header->right->color = BLACK;
}
/*
- 左子树向右转—LL
- 左子树向左转—LR
- 右子树向右转—RL
- 右子树向左转—RR
/
template
RedBlackNode RedBlackTree::rotate(const T &item, Node *parent) { if (item < parent->element) {
} else {item < parent->left->element ? rotateWithLeftChild(parent->left) : rotateWithRightChild(parent->left); return parent->left;
} }item < parent->right->element ? rotateWithLeftChild(parent->right) : rotateWithRightChild(parent->right); return parent->right;
template
template
template
template
nullNode->element = x;
Node *start = header->right;
for (;;)
{
if (x < start->element)
{
start = start->left;
}
else if (x > start->element)
{
start = start->right;
}
else if (start != nullNode)
{
node->element = start->element;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
}
template
//一直向左查找最小
Node *node = header->right;
while (node->left != nullNode)
{
node = node->left;
}
value = node->element;
return true;
}
template
//一直向左查找最小
Node *node = header->right;
while (node->right != nullNode)
{
node = node->right;
}
value = node->element;
return true;
}
endif // REDBLACKTREE_H
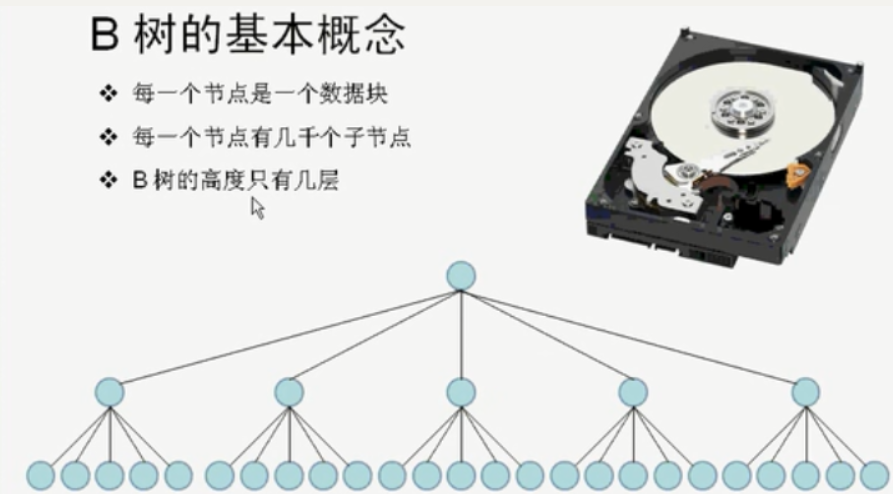
B树
B树和红黑树类似,但可以有多个子节点,对减少磁盘IO操作次数有显著作用。B树主要用途如下:
- 实现文件系统:btrfs
- 实现数据库系统的数据文件和索引文件