命令查看
127.0.0.1:6379> lpush k3 data1(integer) 1127.0.0.1:6379> lpush k3 data2(integer) 2127.0.0.1:6379> lpush k3 data3(integer) 3127.0.0.1:6379> lpush k3 data4(integer) 4127.0.0.1:6379> lrange k3 0 101) "data4"2) "data3"3) "data2"4) "data1"127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding k3"quicklist"
我们可以看到实现List数据类型的数据结构是quicklist。
实际上在以前版本, Redis 中链表的内部实现可不是一个简单的双向链表.在数据量较少的时候它的底层存储结构为一块连续内存,称之为ziplist(压缩列表).当数据量较多的时候将会变成链表的结构.后来因为链表需要 prev 和 next 两个指针占用内存很多,改用 ziplist+链表的混合结构,称之为 quicklist(快速链表)。
在新的版本中 Redis 链表统一使用 quicklist来存储。
链表LinkedList
/* Node, List, and Iterator are the only data structures used currently. *///定义链表节点的结构体typedf struct listNode{//前一个节点struct listNode *prev;//后一个节点struct listNode *next;//当前节点的值的指针void *value;}listNode;
这个结构体上面有一句注释,表名和这个结构体是当前使用的唯一数据结构。pre指向前一个节点,next指针指向后一个节点,value保存着当前节点对应的数据对象。listNode的示意图如下所示: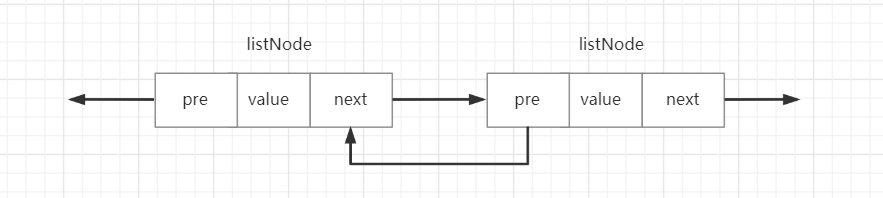
链表的结构如下:
typedf struct list{//头指针listNode *head;//尾指针listNode *tail;//节点拷贝函数void *(*dup)(void *ptr);//释放节点函数void *(*free)(void *ptr);//判断两个节点是否相等的函数int (*match)(void *ptr,void *key);//链表长度unsigned long len;}
head指向链表的头节点,tail指向链表的尾节点,dup函数用于链表转移复制时对节点value拷贝的一个实现,一般情况下使用等号足以,但在某些特殊情况下可能会用到节点转移函数,默认可以给这个函数赋值NULL即表示使用等号进行节点转移。free函数用于释放一个节点所占用的内存空间,默认赋值NULL的话,即使用Redis自带的zfree函数进行内存空间释放。match函数是用来比较两个链表节点的value值是否相等,相等返回1,不等返回0。len表示这个链表共有多少个节点,这样就可以在O(1)的时间复杂度内获得链表的长度。
图示如下: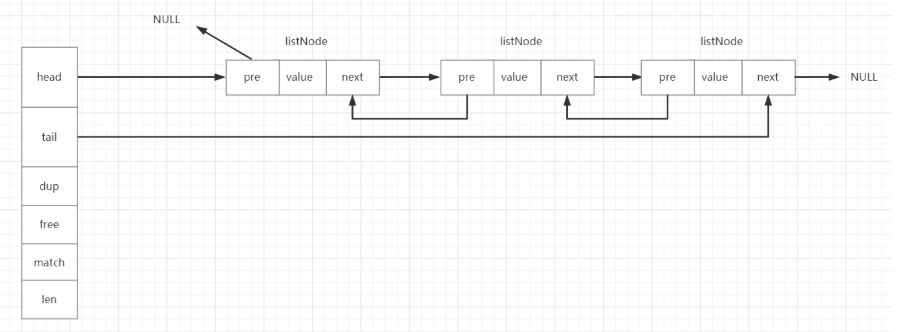
压缩列表ziplist
Redis的zipList结构如下所示:
typedf struct ziplist<T>{//压缩列表占用字符数int32 zlbytes;//最后一个元素距离起始位置的偏移量,用于快速定位最后一个节点int32 zltail_offset;//元素个数int16 zllength;//元素内容T[] entries;//结束位 0xFFint8 zlend;}ziplist
zipList的结构如下所示: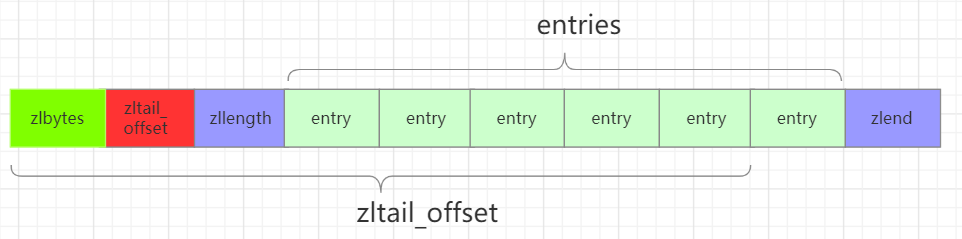
注意到zltail_offset这个参数,有了这个参数就可以快速定位到最后一个entry节点的位置,然后开始倒序遍历,也就是说zipList支持双向遍历。
下面是entry的结构:
typede struct entry{//前一个entry的长度int<var> prelen;//元素类型编码int<var> encoding;//元素内容optional byte[] content;}entry
prelen保存的是前一个entry节点的长度,这样在倒序遍历时就可以通过这个参数定位到上一个entry的位置。encoding保存了content的编码类型。content则是保存的元素内容,它是optional类型的,表示这个字段是可选的。当content是很小的整数时,它会内联到content字段的尾部。entry结构的示意图如下所示: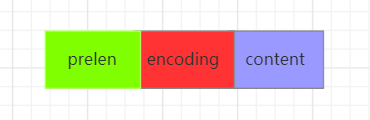 :::info
好了,那现在我们思考一个问题,为什么有了
:::info
好了,那现在我们思考一个问题,为什么有了linkedList还有设计一个zipList呢?就像zipList的名字一样,它是一个压缩列表,是为了节约内存而开发的。相比于linkedList,其少了pre和next两个指针。在Redis中,pre和next指针就要占用16个字节(64位系统的一个指针就是8个字节)。另外,linkedList的每个节点的内存都是单独分配,加剧内存的碎片化,影响内存的管理效率。与之相对的是,zipList是由连续的内存组成的,这样一来,由于内存是连续的,就减少了许多内存碎片和指针的内存占用,进而节约了内存。
:::
zipList遍历时,先根据zlbytes和zltail_offset定位到最后一个entry的位置,然后再根据最后一个entry里的prelen时确定前一个entry的位置。
连锁更新
上面说到了,entry中有一个prelen字段,它的长度要么是1个字节,要么都是5个字节:
- 前一个节点的长度小于254个字节,则
prelen长度为1字节; - 前一个节点的长度大于254字节,则
prelen长度为5字节;
假设现在有一组压缩列表,长度都在250~253字节之间,突然新增一个entry节点,这个entry节点长度大于等于254字节。由于新的entry节点大于等于254字节,这个entry节点的prelen为5个字节,随后会导致其余的所有entry节点的prelen增大为5字节。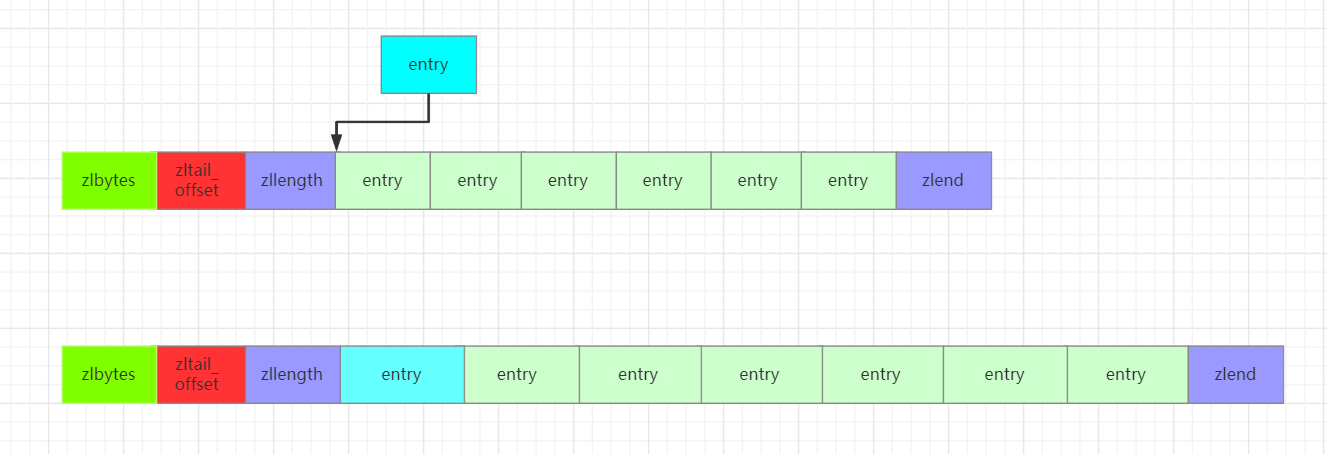
同样地,删除操作也会导致出现连锁更新这种情况,假设在某一时刻,插入一个长度大于等于254个字节的entry节点,同时删除其后面的一个长度小于254个字节的entry节点,由于小于254的entry节点的删除,大于等于254个字节的entry节点将会与后面小于254个字节的entry节点相连,此时就与新增一个长度大于等于254个字节的entry节点时的情况一样,将会发生连续更新。发生连续更新时,Redis需要不断地对压缩列表进行内存分配工作,直到结束。
linkedList与zipList的对比
- 当列表对象中元素的长度较小或者数量较少时,通常采用
zipList来存储;当列表中元素的长度较大或者数量比较多的时候,则会转而使用双向链表linkedList来存储。 - 双向链表
linkedList便于在表的两端进行push和pop操作,在插入节点上复杂度很低,但是它的内存开销比较大。首先,它在每个节点上除了要保存数据之外,还有额外保存两个指针;其次,双向链表的各个节点都是单独的内存块,地址不连续,容易形成内存碎片。 zipList存储在一块连续的内存上,所以存储效率很高。但是它不利于修改操作,插入和删除操作需要频繁地申请和释放内存。特别是当zipList长度很长时,一次realloc可能会导致大量的数据拷贝。快速列表quicklist
在Redis3.2版本之后,list的底层实现方式又多了一种,quickList。qucikList是由zipList和双向链表linkedList组成的混合体。它将linkedList按段切分,每一段使用zipList来紧凑存储,多个zipList之间使用双向指针串接起来。示意图如下所示: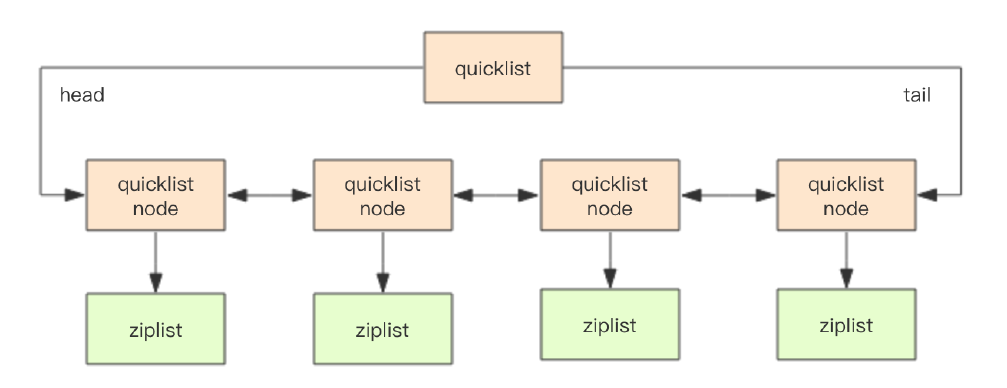
节点quickListNode的定义如下:https://github.com/redis/redis/blob/unstable/src/quicklist.h
typedef struct quicklistNode {//前一个节点struct quicklistNode *prev;// 后一个节点struct quicklistNode *next;// 压缩列表unsigned char *zl;// 压缩列表的大小unsigned int sz; /* ziplist size in bytes */// 压缩列表中item的数量unsigned int count : 16; /* count of items in ziplist */// 编码形式 存储 ziplist 还是进行 LZF 压缩储存的zipListunsigned int encoding : 2; /* RAW==1 or LZF==2 */unsigned int container : 2; /* NONE==1 or ZIPLIST==2 */unsigned int recompress : 1; /* was this node previous compressed? */unsigned int attempted_compress : 1; /* node can't compress; too small */unsigned int extra : 10; /* more bits to steal for future usage */} quicklistNode;
quickList的定义如下所示:
typedf struct quicklist{//指向头结点quicklistNode* head;//指向尾节点quicklistNode* tail;//元素总数long count;//quicklistNode节点的个数int nodes;//压缩算法深度int compressDepth;...}quickList
上述代码简单地表示了quickList的大致结构,为了进一步节约空间,Redis还会对zipList进行压缩存储,使用LZF算法进行压缩,可以选择压缩深度。
每个zipList可以存储多少个元素
想要了解这个问题,就得打开redis.conf文件了。在DVANCED CONFIG下面有着清晰的记载。
# Lists are also encoded in a special way to save a lot of space.# The number of entries allowed per internal list node can be specified# as a fixed maximum size or a maximum number of elements.# For a fixed maximum size, use -5 through -1, meaning:# -5: max size: 64 Kb <-- not recommended for normal workloads# -4: max size: 32 Kb <-- not recommended# -3: max size: 16 Kb <-- probably not recommended# -2: max size: 8 Kb <-- good# -1: max size: 4 Kb <-- good# Positive numbers mean store up to _exactly_ that number of elements# per list node.# The highest performing option is usually -2 (8 Kb size) or -1 (4 Kb size),# but if your use case is unique, adjust the settings as necessary.list-max-ziplist-size -2
quickList内部默认单个zipList长度为8k字节,即list-max-ziplist-size的值设置为-2,超出了这个阈值,就会重新生成一个zipList来存储数据。根据注释可知,性能最好的时候就是就是list-max-ziplist-size为-1和-2,即分别是4kb和8kb的时候,当然,这个值也可以被设置为正数,当list-max-ziplist-szie为正数n时,表示每个quickList节点上的zipList最多包含n个数据项。
压缩深度
上面提到过,quickList中可以使用压缩算法对zipList进行进一步的压缩,这个算法就是LZF算法,这是一种无损压缩算法,具体可以参考这里。使用压缩算法对zipList进行压缩后,zipList的结构如下所示:
typedf struct ziplist_compressed{//元素个数int32 size;//元素内容byte[] compressed_data}
此时quickList的示意图如下所示: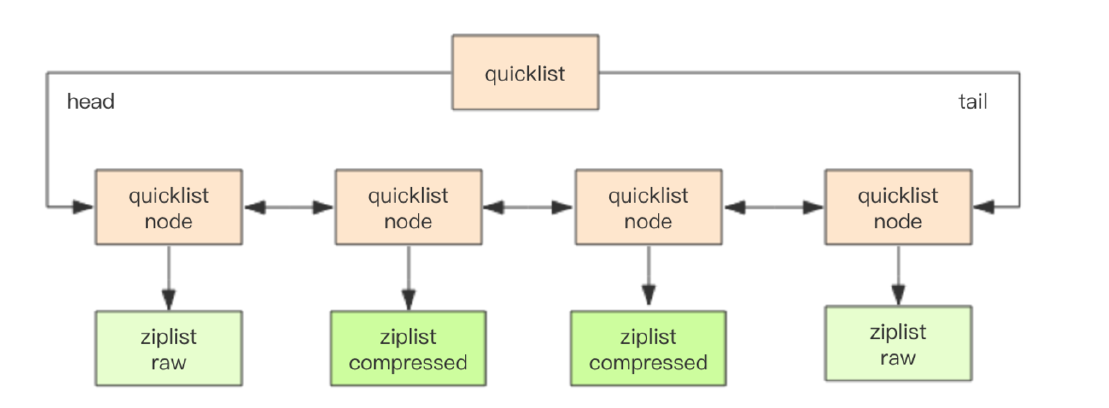
当然,在redis.conf文件中的DVANCED CONFIG下面也可以对压缩深度进行配置。
# Lists may also be compressed.# Compress depth is the number of quicklist ziplist nodes from *each* side of# the list to *exclude* from compression. The head and tail of the list# are always uncompressed for fast push/pop operations. Settings are:# 0: disable all list compression# 1: depth 1 means "don't start compressing until after 1 node into the list,# going from either the head or tail"# So: [head]->node->node->...->node->[tail]# [head], [tail] will always be uncompressed; inner nodes will compress.# 2: [head]->[next]->node->node->...->node->[prev]->[tail]# 2 here means: don't compress head or head->next or tail->prev or tail,# but compress all nodes between them.# 3: [head]->[next]->[next]->node->node->...->node->[prev]->[prev]->[tail]# etc.list-compress-depth 0
通过list-compress-depth配置.默认情况下quicklist 的压缩深度是 0,也就是不压缩.配置为 1 的话代表从头/尾开始第 1 个ziplsit 进行压缩。
总结