1、离散/连续随机变量、概率函数
- 对于随机变量,均有概率,即有对应的分布特征。
- Probability Distribution(概率分布)
- Specifies the probabilities of the possible outcomes of a random variable.
- Discrete/Continuous random variables(离散/连续随机变量)
- Discrete random variables(离散随机变量)
- take on at most a countable number of possible outcomes but do not necessarily to be limited.
- 取值可数
- Continuous random variables(连续随机变量)
- cannot describe the possible outcomes of a continuous random variable
with a list
because the outcome
not in the list, would always be possible.
- 取值不可数
- 特征:
(even though
can happen)
(计算概率时通常是计算区间的概率)
- cannot describe the possible outcomes of a continuous random variable
- Discrete random variables(离散随机变量)
- Probability function(概率函数
)
- For discrete random variables
- Probability density function(PDF,概率密度函数
)
- For continuous random variable commonly.
- 用密度函数图形的面积表示概率(以下为正太分布的概率密度函数)
- Cumulative probability function(CPF,累积概率函数
)
2、概率分布:离散分布(2 种)
(1)Discrete uniform distribution(离散均匀分布)
- A known, finite number of outcomes equally likely to happen.(取值确定、取值概率相等)
- Every one of
outcomes has equal probability
如:Rolling a dice will have 6 possible outcomes as
,the probability of each outcome is 0.167
(2)Binomial distribution(二项式分布)
Bernoulli random variable(伯努利随机变量)
- 一个事件只有两种结果的情况(如抛硬币,结果只能是正面 or 反面)
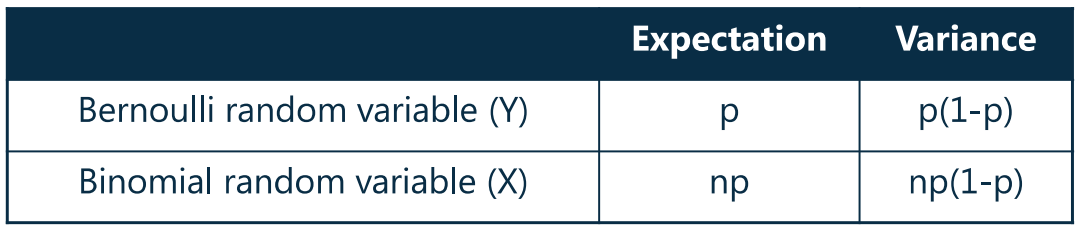
- Binomial random variable(二项式随机变量)
- the probability of
successes in
trails
- 如:计算抛
次硬币,有
次正面朝上(假设代表成功)的概率(每次实验都相互独立,且每次实验均只能有两种结果)
次实验
次成功,成功的概率用
表示
次不成功
- 公式原理:从
次实验中挑选出
次(即:
),乘以其概率
,剩下的
次均为不成功的,其概率为
,相乘即为所求概率。
- 应用:可应用到预测生孩子判断性别概率上,如:医院里当天生
个孩子,求生出
个男孩的概率
- the probability of
- 伯努利随机变量 vs 二项式随机变量
- 相同点:事件均只有两种结果
- 不同点:
- 伯努利随机变量中,只做一次实验
- 二项式随机变量中,做了 n 次实验
- Expectations(期望)、variances(方差)【了解,不太考,推导见视频】
3、概率分布:连续分布(3 种)
(1)Continuous Uniform Distribution(连续均匀分布)
- All intervals of the same length on the Continuous Uniform Distribution’s support are equally probable.
- The support is defined by the two parameters,
and
, which are its minumum and maximum values.
- The support is defined by the two parameters,
特征:
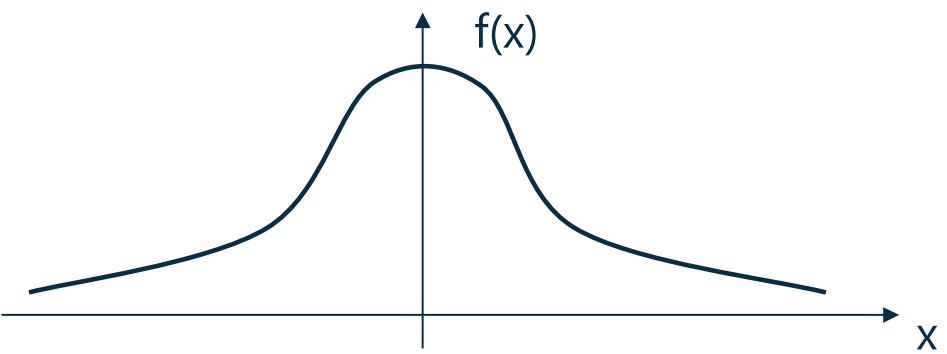
特征:
(决定正太分布的变量:均值和方差)
- Symmetrical distribution:skewness=0, kurtosis=3
- 密度函数的图形形状对称
- A linear combination of normally distributed random variables is also normally distributed.
- 如果
和
均服从正太分布,则他们的线性组合也符合正太分布
- 如果
- The tails get thin and go to zero but extend iinfinitely, asympotic(渐近)
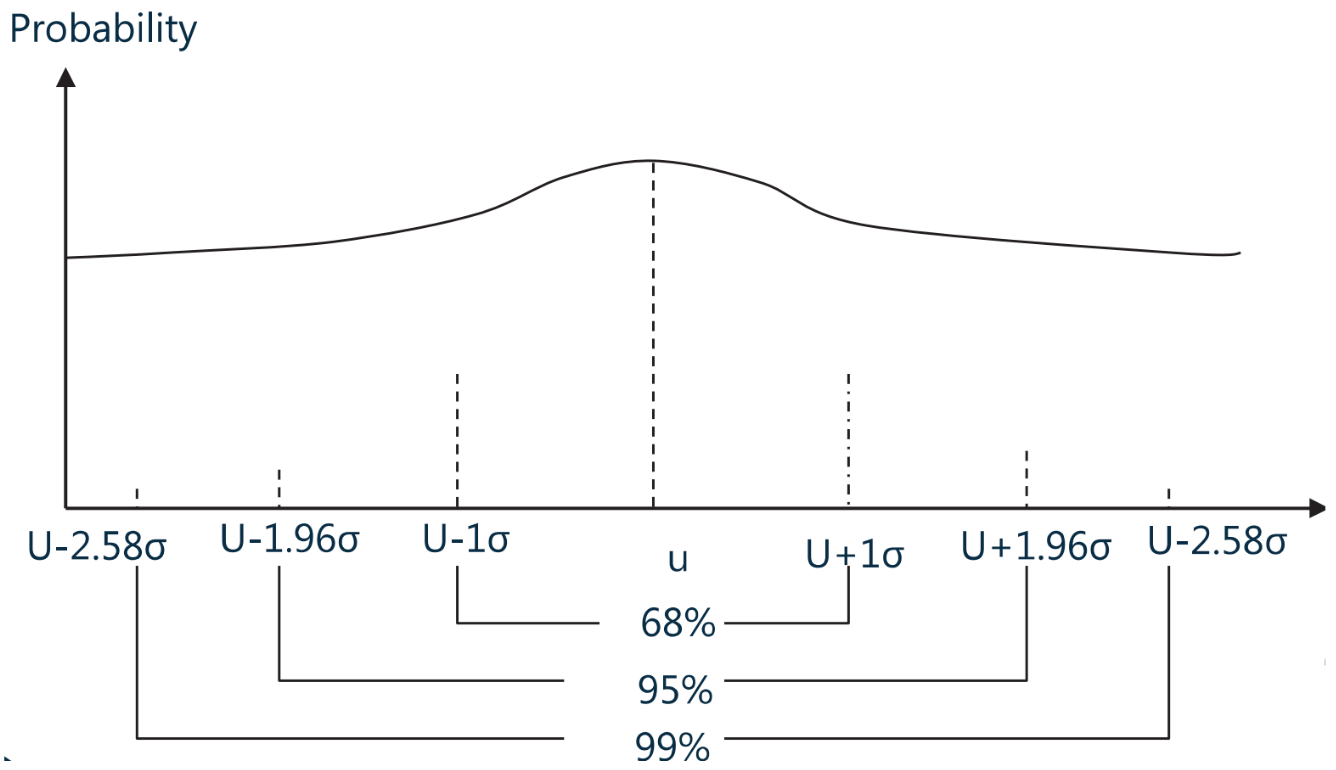
(a)Confidence intervals(置信区间,正太分布的置信区间)
置信区间:个体落在某个区间的概率有多大(一个区间对应一个概率)
- 68% confidence interval is
- 90% confidence interval is
- 95% confidence interval is
- 99% confidence interval is
之前讲过的切比雪夫不等式对于任何分布均成立,其含义为:
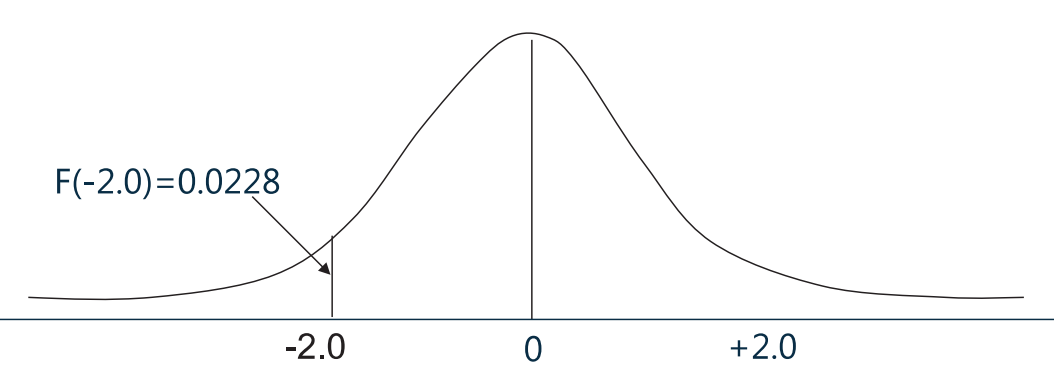
标准正太分布:
or
- standardization(普通正太分布的标准化):
- 如果
,则
- 推导:
- 如果
,则:
- 如果
,则:
(一组数据同时加上一个数,不会影响其离散程度)
- 如果
- 如果
- 为什么要进行标准化?
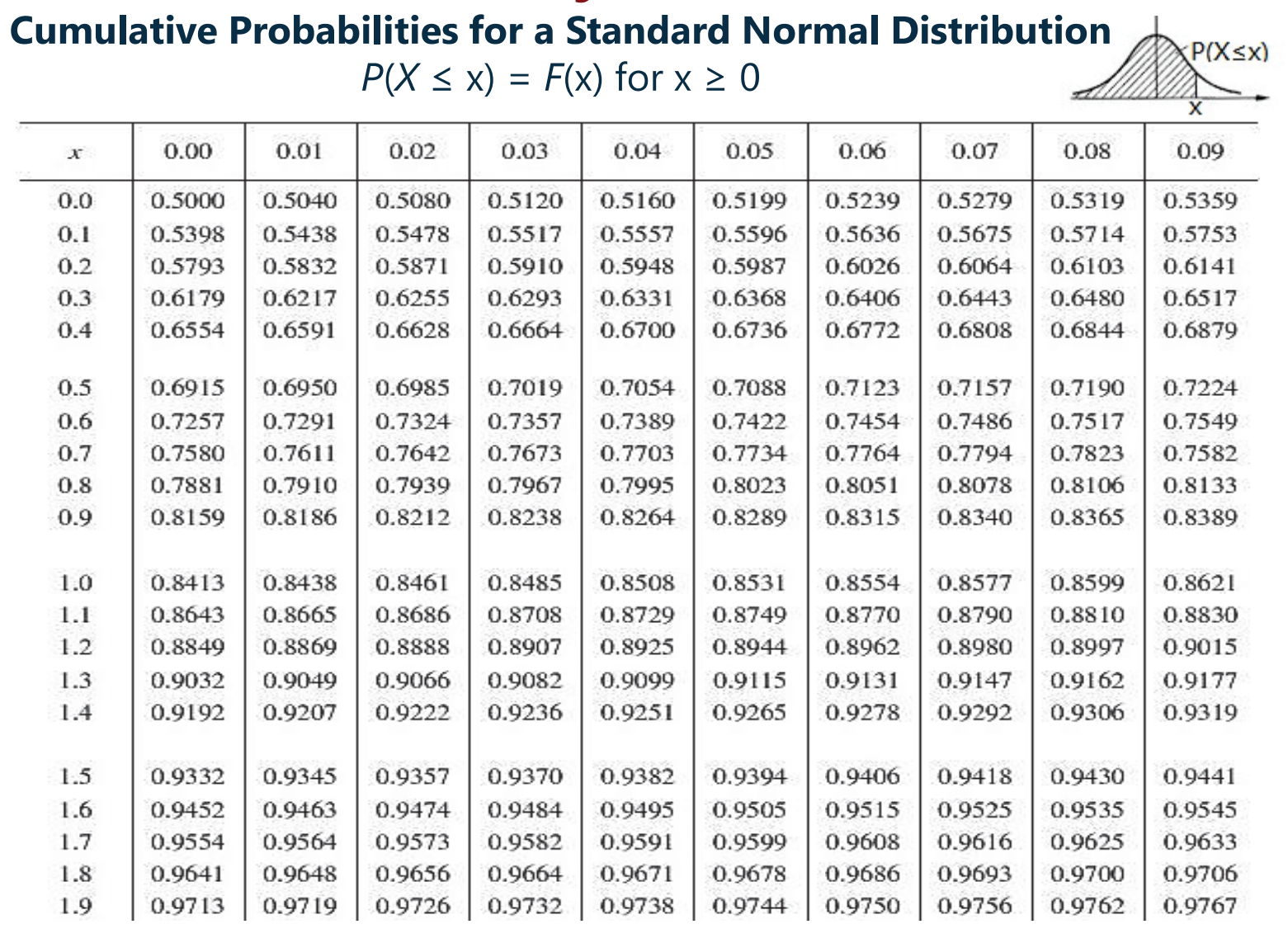
- 方便查表(Z-table 表);统计学家不可能做无数个正太分布表。
- Z-table 表如下(每个数值均为累积概率,只给出了
的部分,另外一部分对称):
- 方便查表(Z-table 表);统计学家不可能做无数个正太分布表。
常见考法:
Shortfall risk
:threshold level return、minimum return required
- 如果
,出现这种情况的概率(
),即为 Shortfall risk
- 即:基金经理做投资的回报率小于客户最底要求回报率的风险
越小越好
- Roy’s safety-first criterion
- 类似夏普比率,但此处的基准是
(客户要求的最低回报率),而夏普比率的基准为
(无风险回报率)
越大越好
Maximize S-F-Ratio
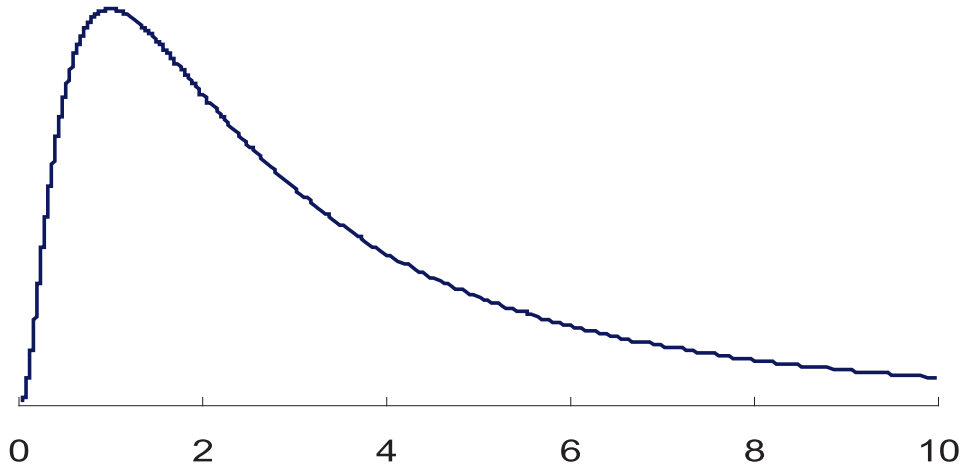
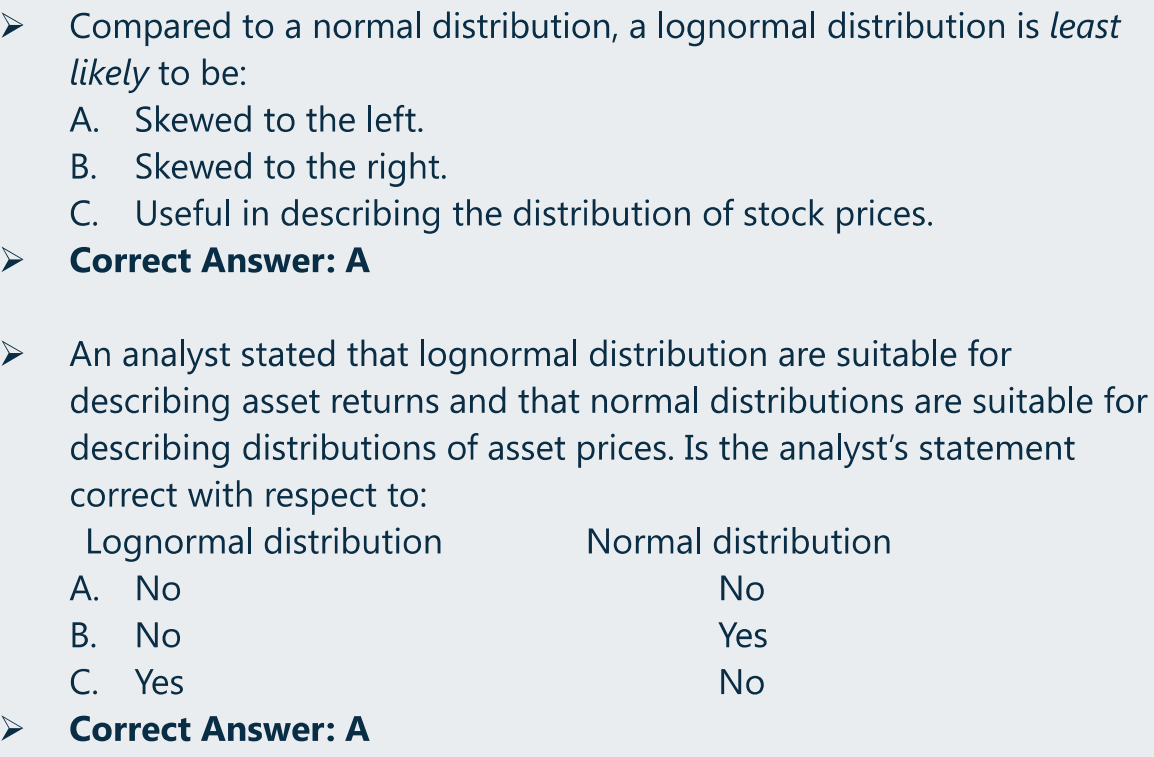
If
is normal, then
is lognormal.
- 如果
是正太分布,则
服从对数正太分布(注意:不能颠倒说法)
- 如果
- 特点:Right skewed(右偏).
- 考试时,可能会与偏度的相关概念与特性结合起来考
- The values of random variables that follow lognormal distribution are always be positive, so it is useful for modeling asset prices.
- 资产价格(P)总是大于 0 的,因此实际应用中总是假设资产价格符合对数正太分布。
- 而 Return 可以小于 0 或大于 0,与正太分布的特性相似,故实际应用中假设 Return 是符合正太分布的。
4、Monte Carlo simulation、Historical simulation
- 离散(Discrete)
- 连续(Continuous)
(持有一年)
(持有 T 年)
- Monte Carlo simulation
- generate a large number of random samples from specified probability distribution(s) to represent the operation of risk in the system.
- It is used in planning, in financial risk management, and in valuing complex securities.
- Limitations:
- The operating of Monte Carlo simulation is very complex and we must assume a parameter distribution in advance.
- Monte Carlo simulation provides only statistical estimates, not exact results.
Historical simulation
- repeat sampling from a historical data series.
- grounded in actual data but can reflect only risks represented in the sample historical data.
- Compared with Monte Carlo simulation, historical simulation does not lend itself to “what if” analyses.
5、例题
(1)离散/连续随机变量、概率函数、概率分布
(a)离散型随机变量的概率分布

(b)连续均匀分布、累积分布函数

(c)概率分布的理解:离散均匀分布

(d)二项式分布求概率公式

(e)二项式分布:求期望 E(X)

(f)二项式分布:概念理解

(2)连续分布
(a)连续均匀分布

(b)正太分布:Confidence intervals
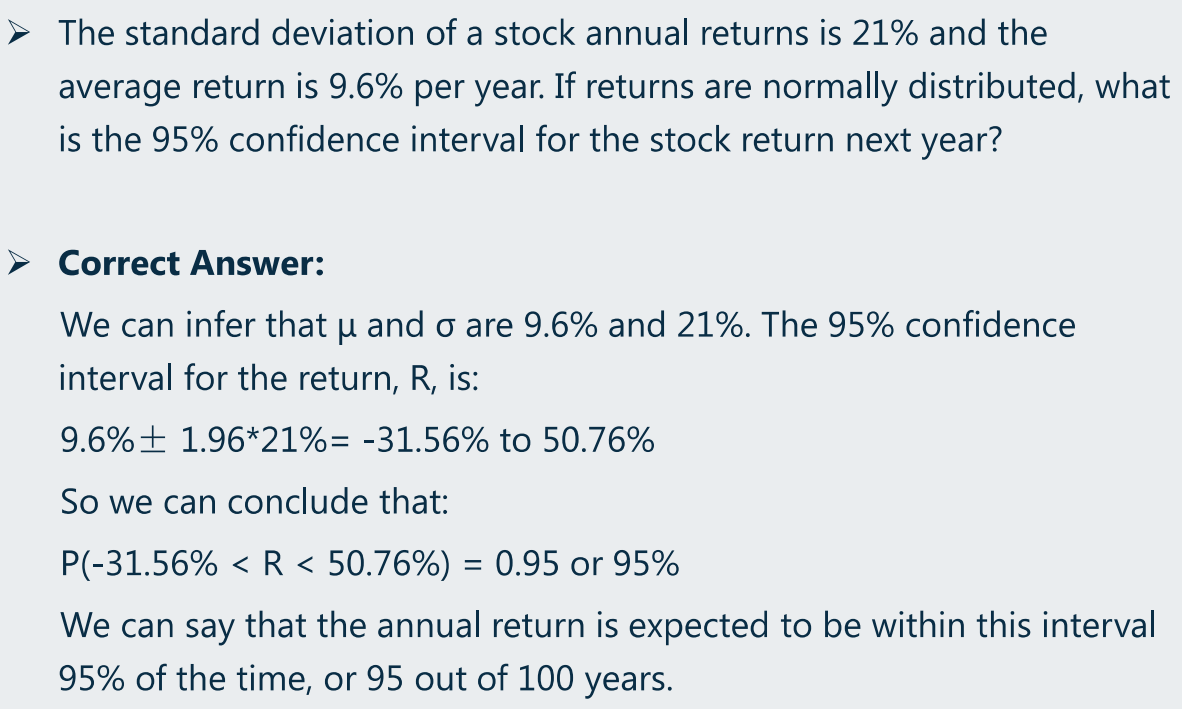
(c)正太分布:基于区间范围计算均值和标准差
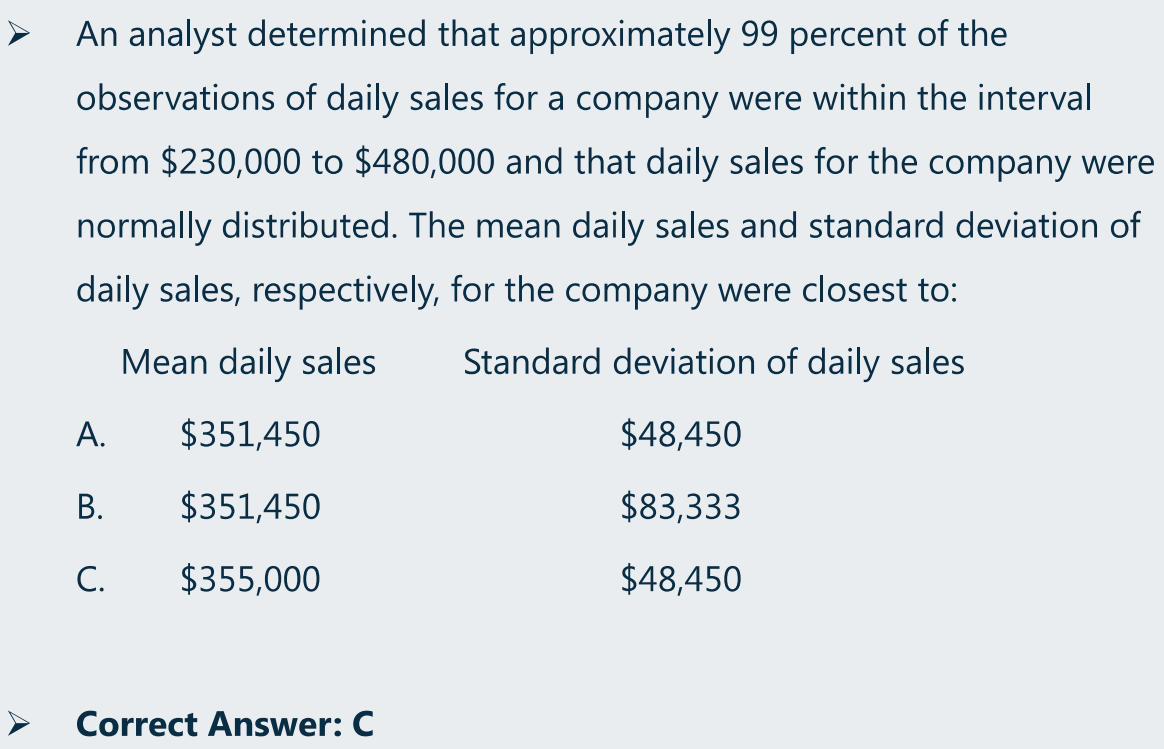
(d)标准正太分布:概率计算
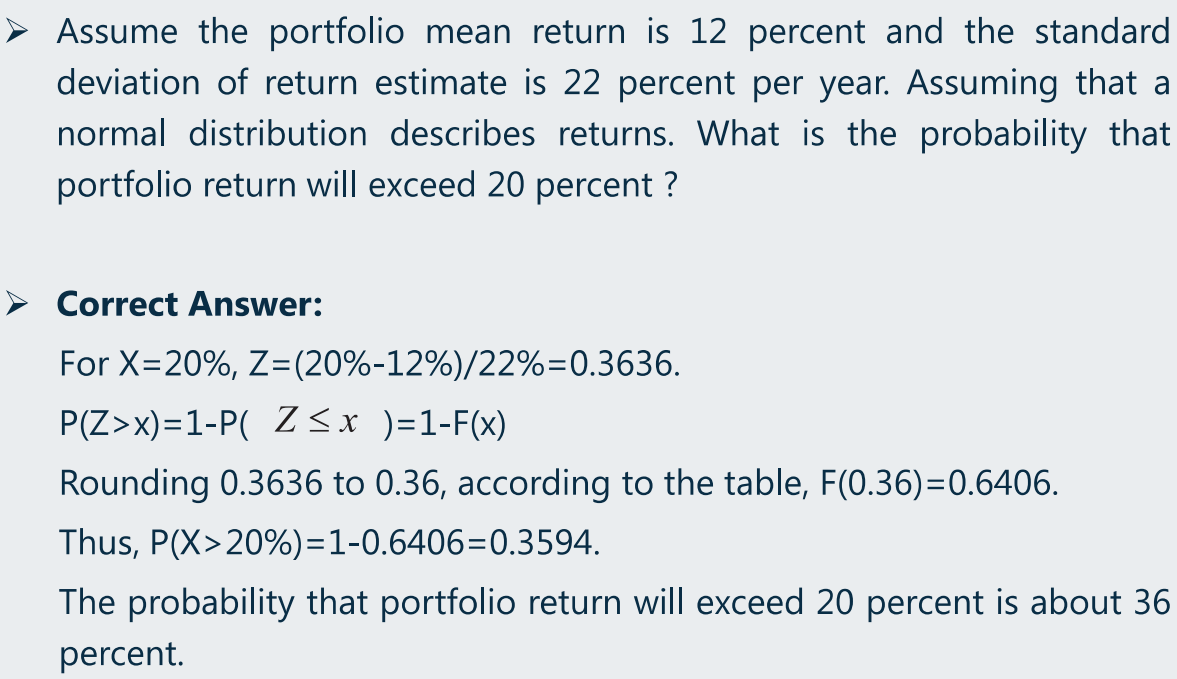
(e)Shortfall risk、Roy’s safety-first criterion、Maximize S-F-Ratio
Roy’s safety-first criterion 计算与比较
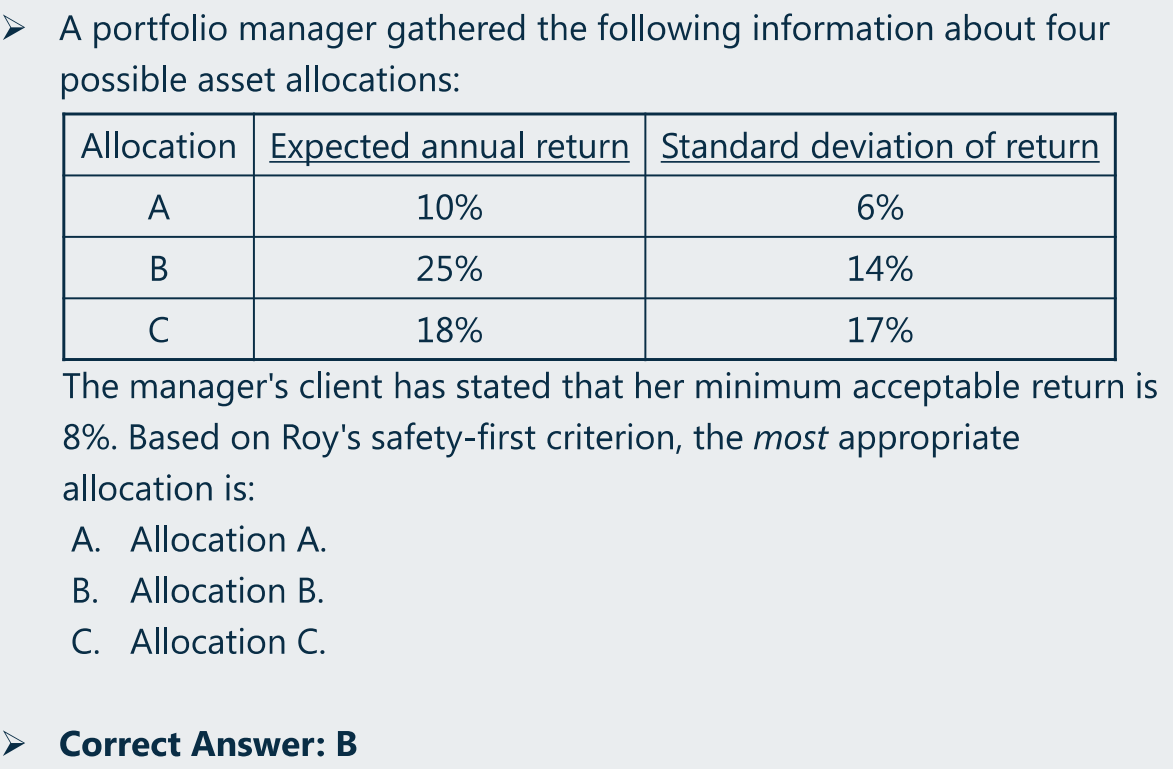
(求解取最大值即可)
Shortfall risk 的理解、Roy’s safety-first criterion 计算与比较、正太分布概率计算
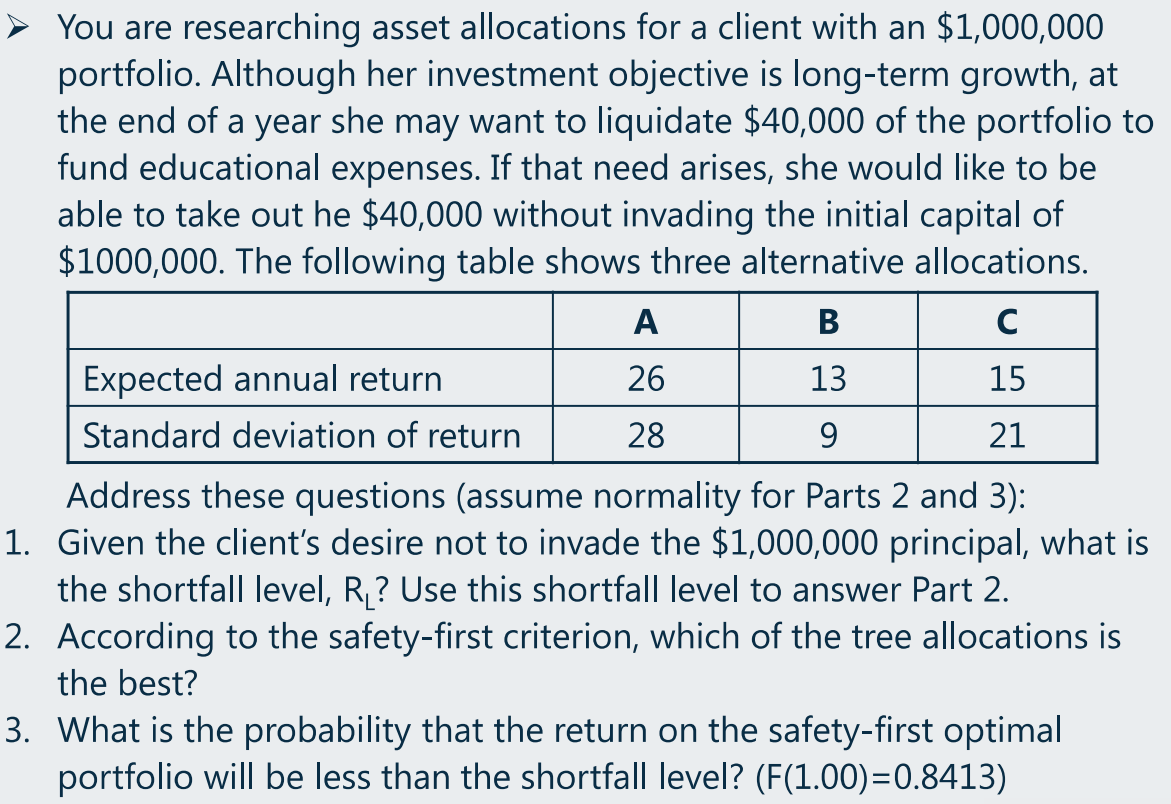

(f)对数正太分布
(3)Monte Carlo simulation