目录
(2)工作机制
举例:分类向银行提出贷款的顾客是否可以贷款。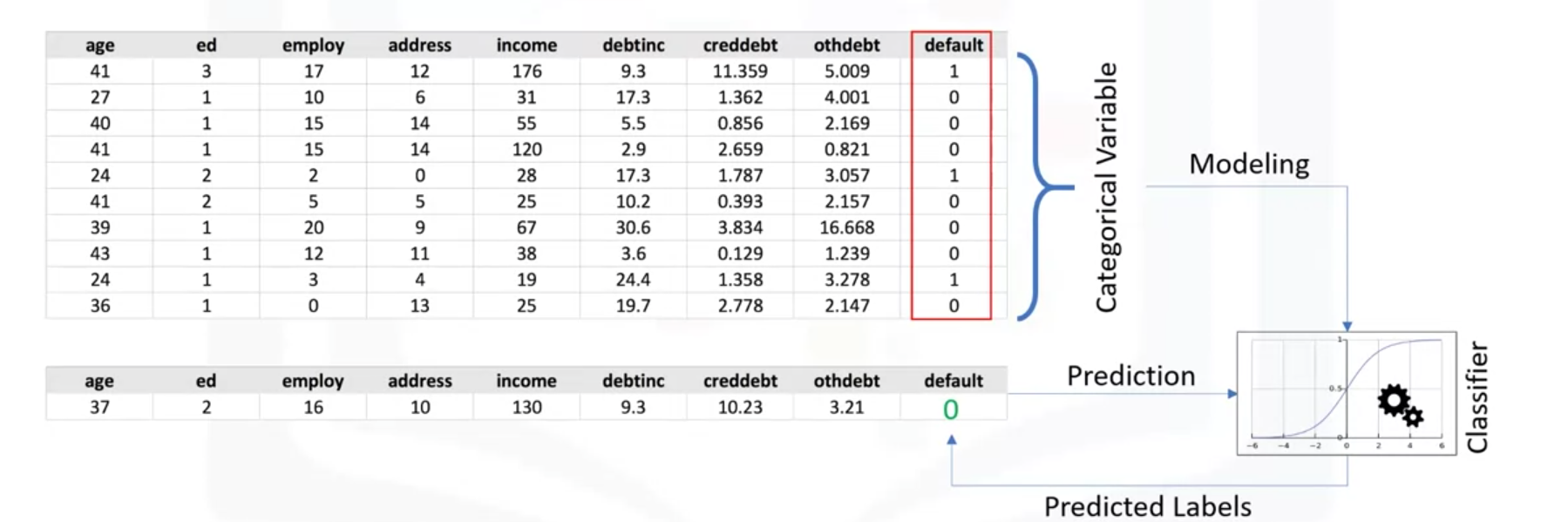
(3)应用
- 邮箱过滤
- 语音识别
- 手写识别
- 生物识别
- 文件识别
(4)分类算法
- 决策树(Decision Trees)
- 朴素贝叶斯(Naive bayes)
- 线性判别分析(linear discriminant nanlysis)
- K-邻近(K-nearst Neighbor)
- 逻辑回归(Logistic regression)
- 神经网络(Neural Networ)
- 支持向量机(Support Vector Machine,SVM)
2 K-邻近
2.1 简介
是一种是分类算法,采用一些已经标签的点去标记未标签的点。这个算法的原理是基于相似度.
- A method for classifying cases based on their similarity to other cases
- Cases that are near each other are said to be “beighbors”
- Based on simiar cases with same class labels are near each other
如下图根据个别自变量age和Income去判别类别。方法是去找最邻近的那个点。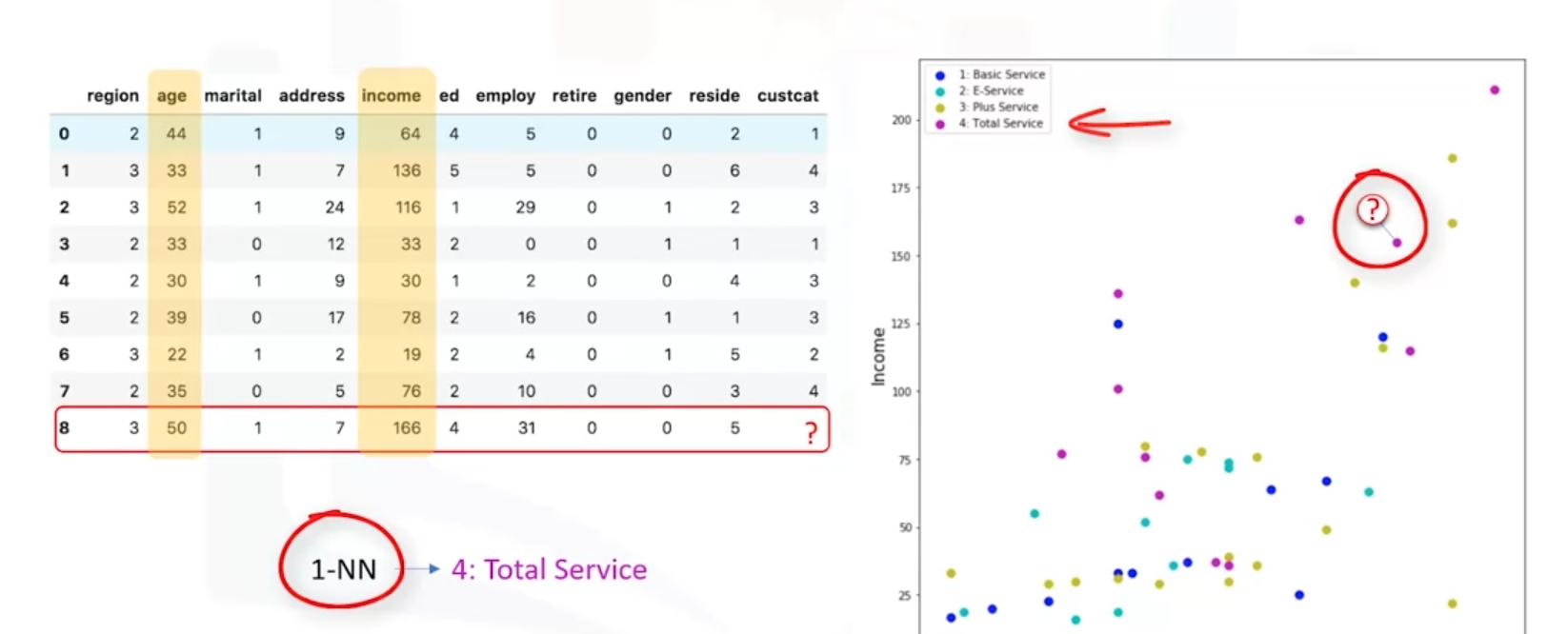
2.2 算法过程
(1)为K找到一个值
(2)计算未知点与所有已知点的距离(相似度)
(3)在训练数据中找到与未知点最邻近的K的观察值(Select the K-observations in the training data that are nearest to unknown data point)
(4)Predict the response of the unknown data point using the most popular response value from the K-nearest neighbors
问题是:如何选择一个正确的K,如何计算距离
2.3 选择一个正确的K值
过低的K值可能会导致模型的高复杂度,也会导致模型过拟合。方法是在不同K值下计算模型的准确率,选择最佳准确率的K值。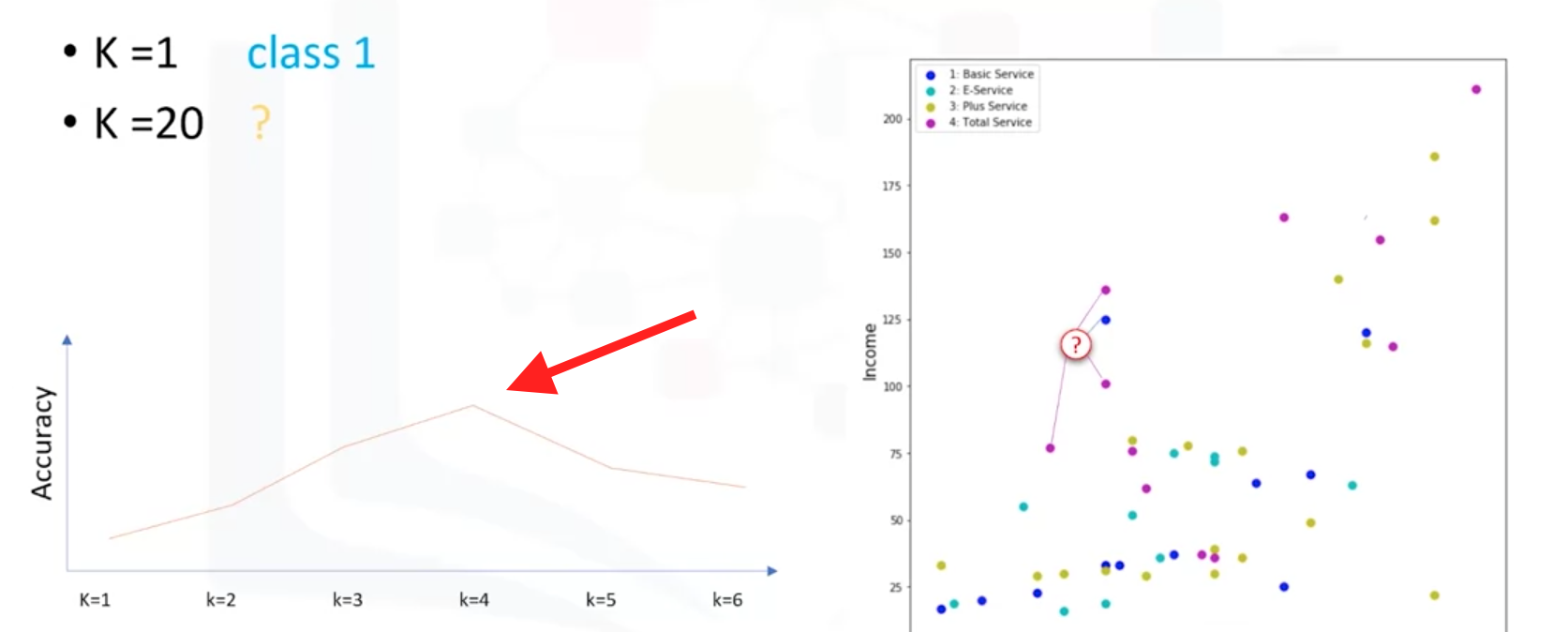
3 分类评估指标
(1)分类准确率Classification accuracy
(2)Jaccard Index
说白了就是如下两个圆圈重叠是大小。越大越好。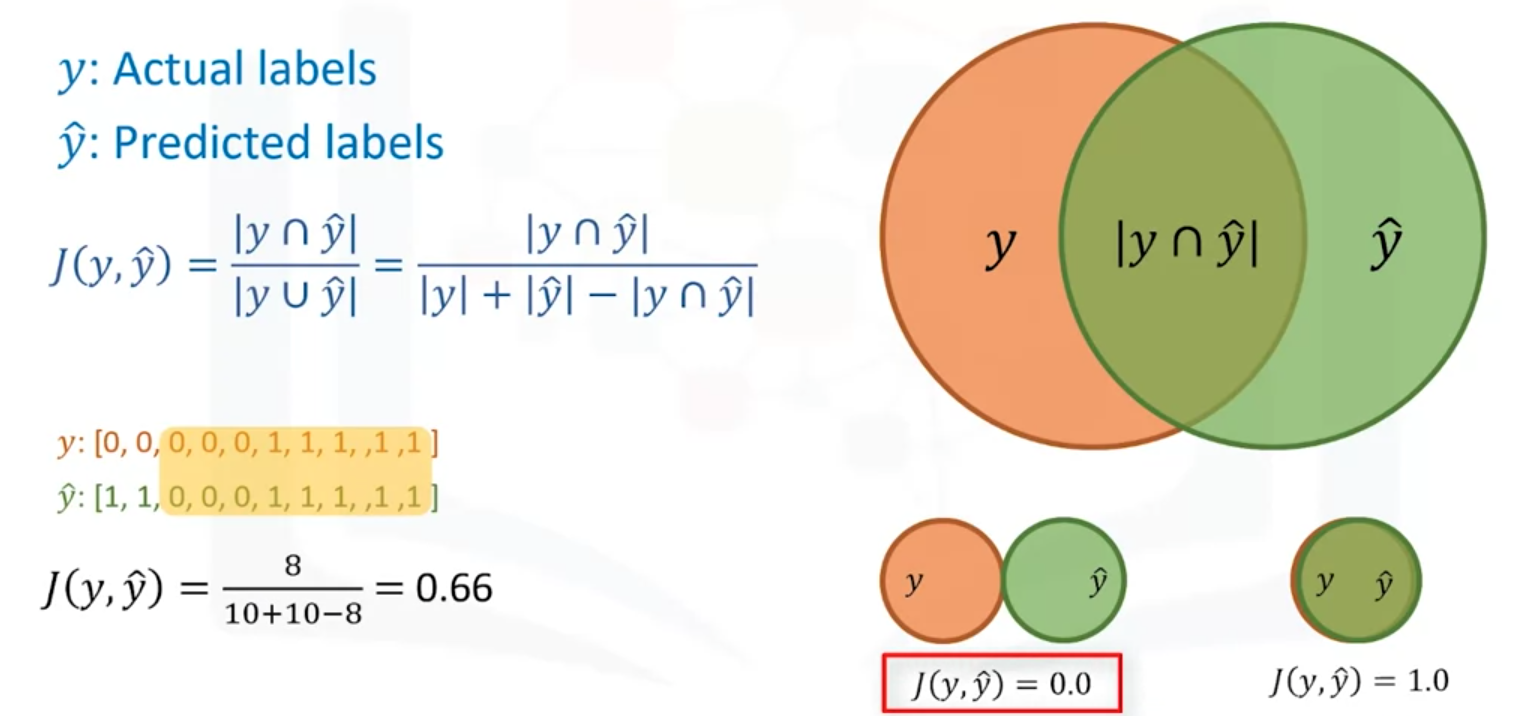
(3)F1-score
F1分数度量,在《机器学习-周志华》书的32-32页详解。Confusion matrix 是混淆矩阵。
Precision又称为查准率
Recall又称为查全率
F1-score越高准确率越高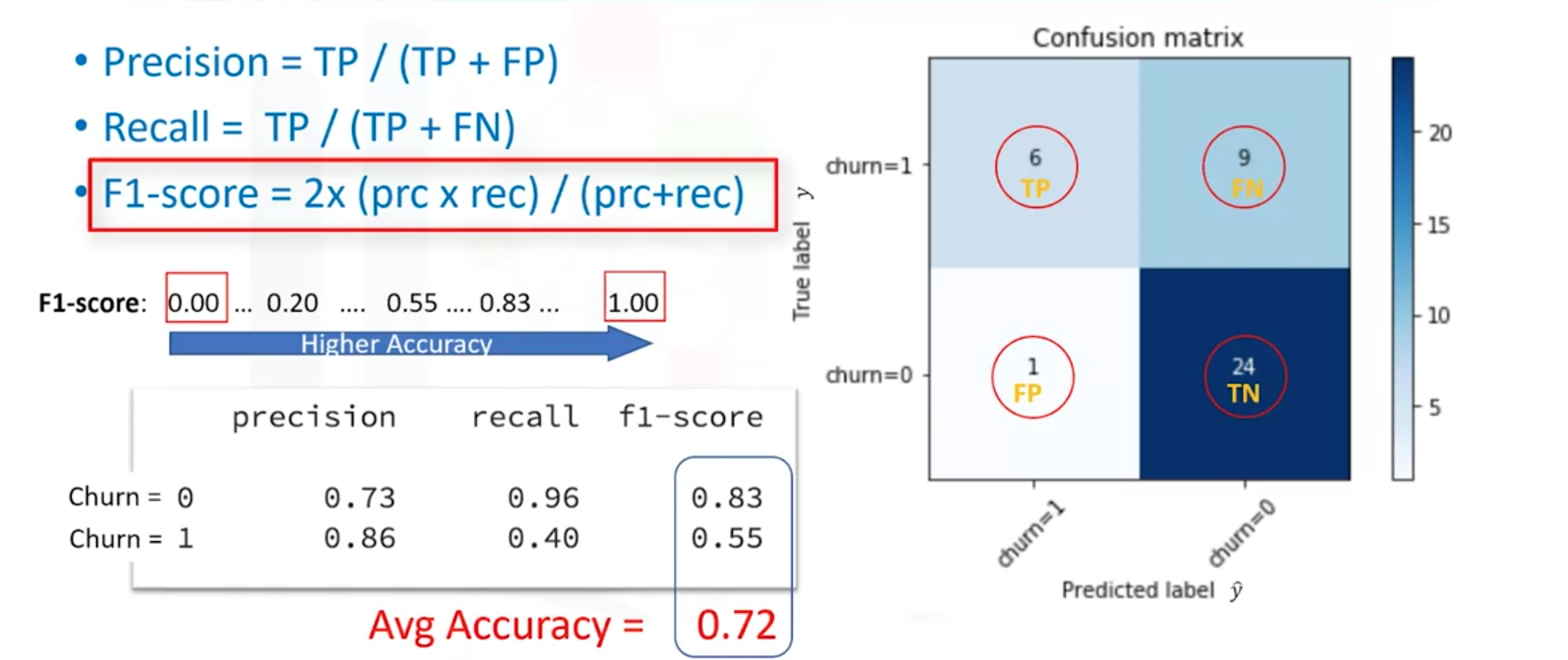
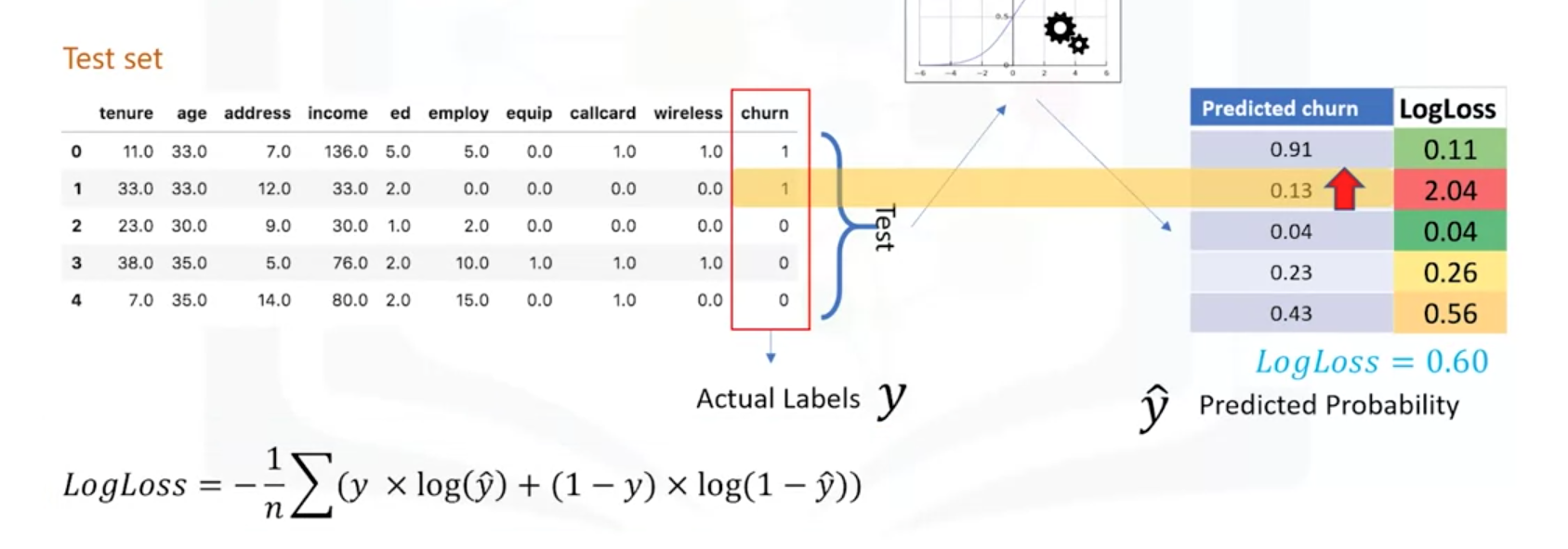
(4)Log Loss
在输出概率是0~1之间去评价分类器的好坏。
如下举例计算Log loss。
Log loss越小越好。