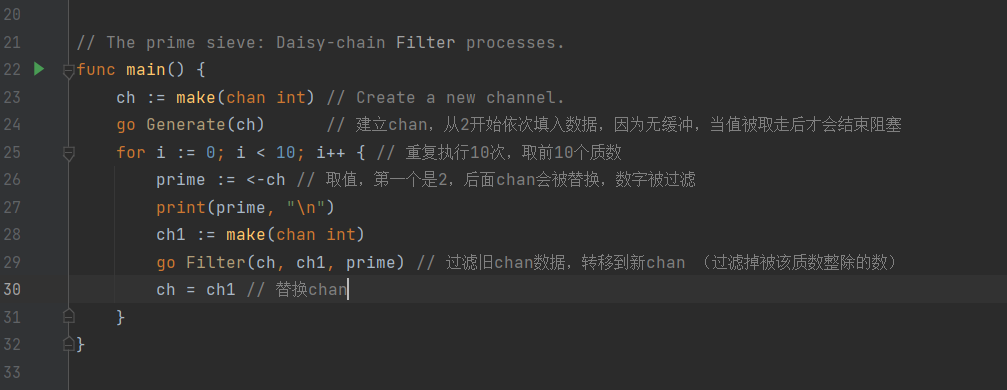
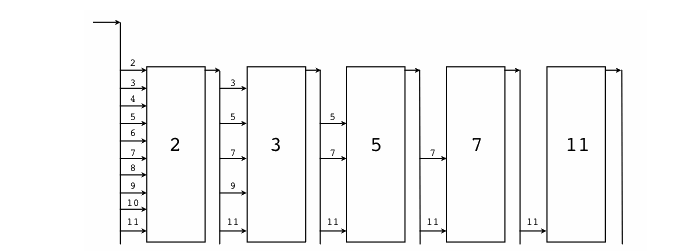
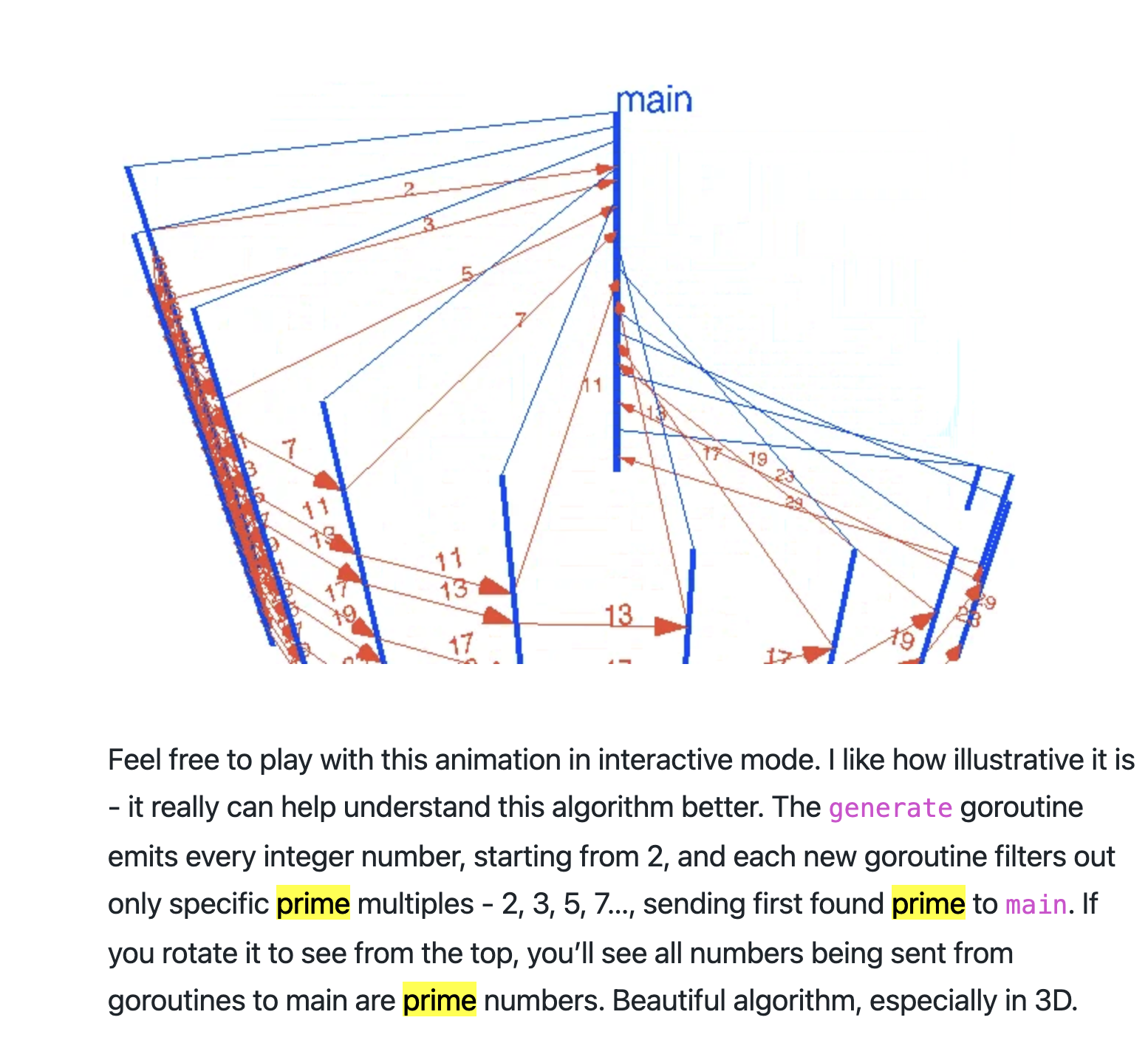
// A concurrent prime sievepackage mainimport "fmt"// Send the sequence 2, 3, 4, ... to channel 'ch'.func Generate(ch chan<- int) {for i := 2; ; i++ {ch <- i // Send 'i' to channel 'ch'.}}// Copy the values from channel 'in' to channel 'out',// removing those divisible by 'prime'.func Filter(in <-chan int, out chan<- int, prime int) {for {i := <-in // Receive value from 'in'.if i%prime != 0 {out <- i // Send 'i' to 'out'.}}}// The prime sieve: Daisy-chain Filter processes.func main() {ch := make(chan int) // Create a new channel.go Generate(ch) // Launch Generate goroutine. 建立chan 从2开始依次填入数据,因为无缓冲, 当值被取走后才会结束阻塞for i := 0; i < 10; i++ { //重复执行10次 取前10个质数prime := <-ch //取值 第一个是2 后面chan会被替换 ,数字被过滤fmt.Println(prime)ch1 := make(chan int)go Filter(ch, ch1, prime) //过滤旧chan数据 转移到新chan (过滤掉被该质数整除的数)ch = ch1 //替换chan}}
package mainfunc main() {// create new channel of type intch := make(chan int)// start new anonymous goroutinego func() {// send 42 to channelch <- 42}()// read from channel<-ch}

package mainimport "time"func timer(d time.Duration) <-chan int {c := make(chan int)go func() {time.Sleep(d)c <- 1}()return c}func main() {for i := 0; i < 24; i++ {c := timer(1 * time.Second)<-c}}
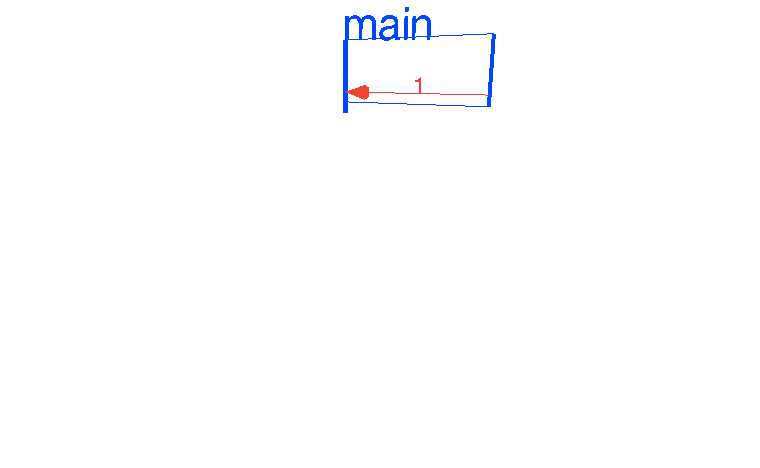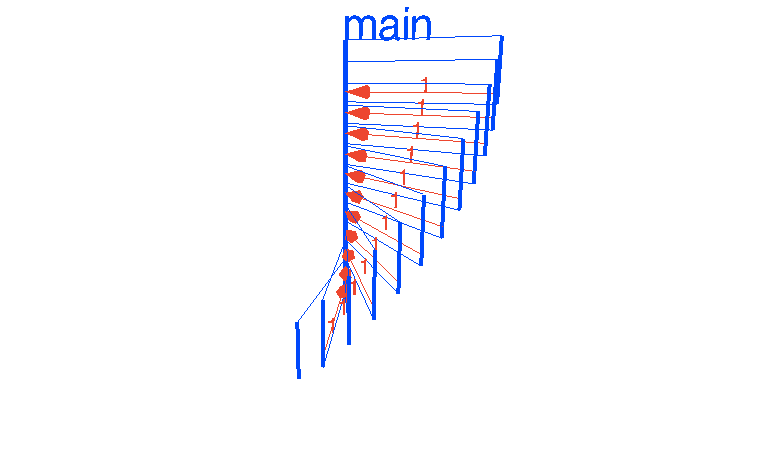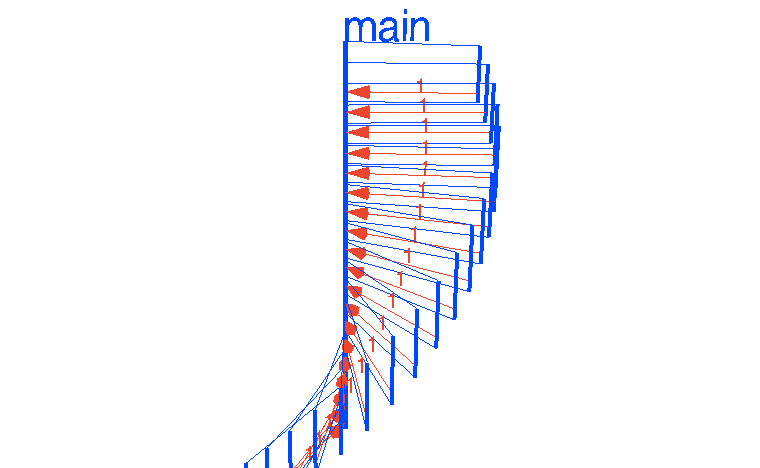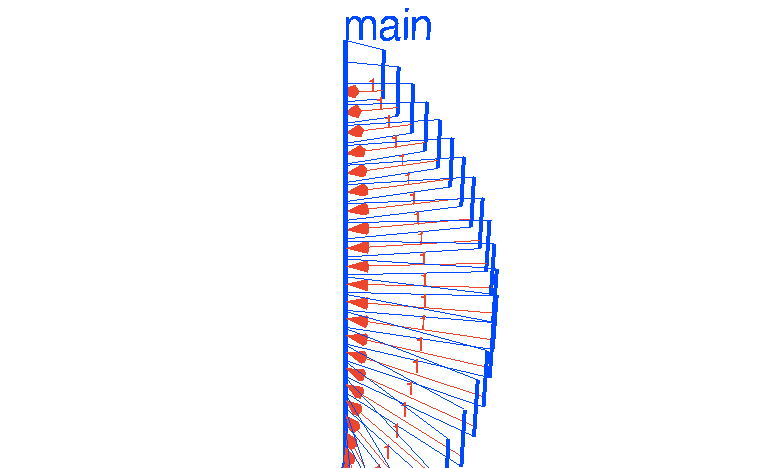
package mainimport "time"func main() {var Ball inttable := make(chan int)go player(table)go player(table)table <- Balltime.Sleep(1 * time.Second)<-table}func player(table chan int) {for {ball := <-tableball++time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond)table <- ball}}
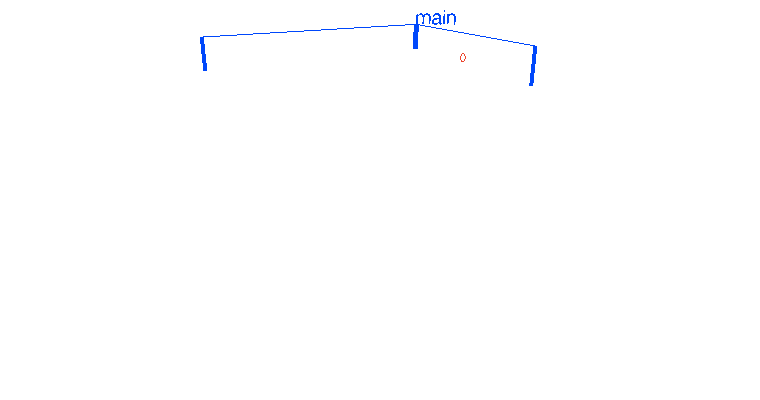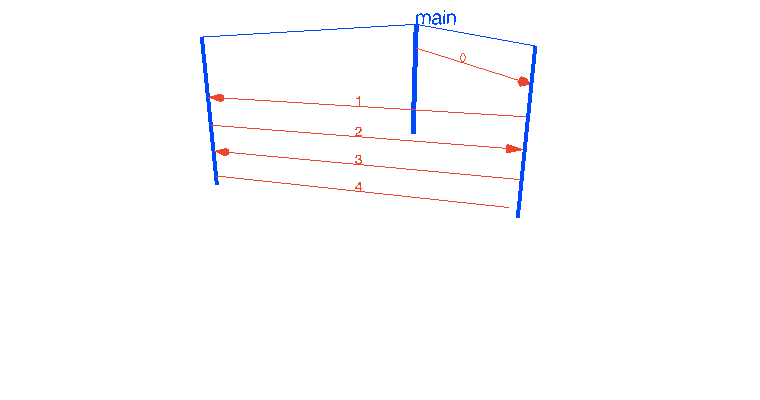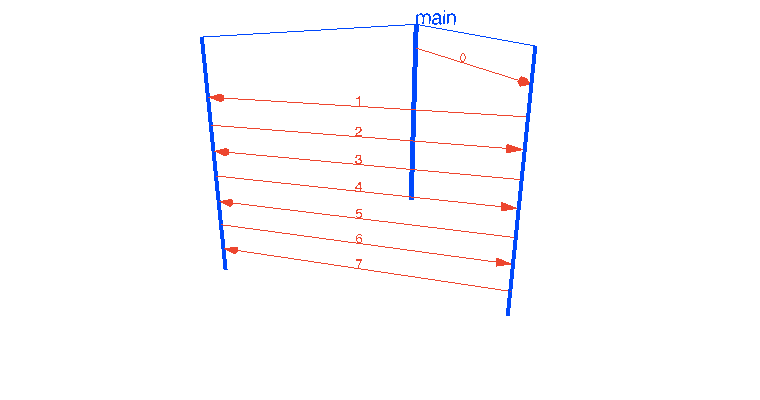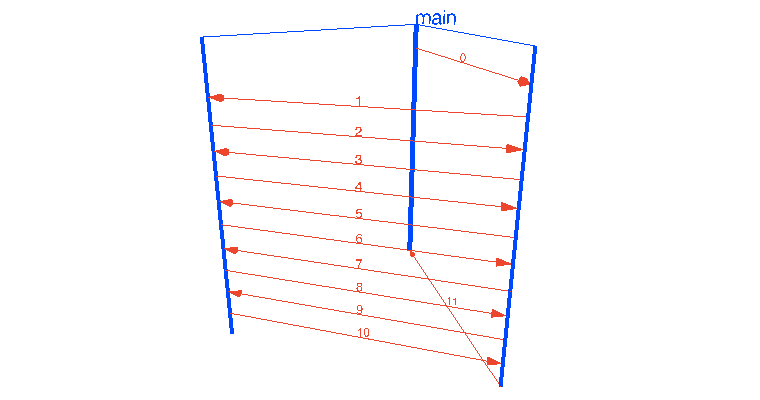
go player(table)go player(table)go player(table)

参考:https://www.cloudbees.com/blog/visualizing-concurrency-go

