一、什么是“异步调用”?
“异步调用”对应的是“同步调用”;
同步调用 指程序按照定义顺序依次执行,每一行程序都必须等待上一行程序执行完成之后才能执行;
异步调用 指程序在顺序执行时,不等待异步调用的语句返回结果就执行后面的程序。
二、同步调用
通过一个简单示例来直观的理解什么是同步调用
2.1、SyncController: 调用入口
package com.wells.demo.sync.controller;import com.wells.demo.async.controller.DefaultAsyncController;import com.wells.demo.sync.service.SyncService;import org.slf4j.Logger;import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;/*** Description 同步调用Service* Created by wells on 2020-07-15 09:45:01*/@RestController@RequestMapping(value = "sync")public class SyncController {Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DefaultAsyncController.class);@Autowiredprivate SyncService syncService;@GetMapping(value = "/execute/task")public String executeTask() throws InterruptedException {logger.info("sync request start");long start = System.currentTimeMillis();syncService.executeTaskOne();syncService.executeTaskTwo();long end = System.currentTimeMillis();logger.info("sync request end, cost:{}", (end - start));return "success";}}
2.2、Service
package com.wells.demo.sync.service;import org.slf4j.Logger;import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** Description* Created by wells on 2020-07-15 09:44:50*/@Servicepublic class SyncService {Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SyncService.class);public void executeTaskOne() throws InterruptedException {logger.info("executeTaskOne request start");TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);logger.info("executeTaskOne request end");}public void executeTaskTwo() throws InterruptedException {logger.info("executeTaskTwo request start");TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);logger.info("executeTaskTwo request end");}}
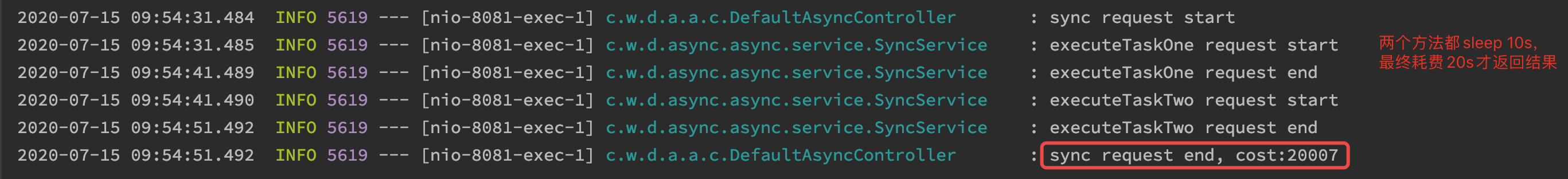
2.3、调用结果
2.4、代码示例
三、异步调用
上述的同步调用虽然顺利的执行完了三个任务,但是可以看到执行时间比较长,若这三个任务本身之间不存在依赖关系,可以并发执行的话,同步调用在执行效率方面就比较差,可以考虑通过异步调用的方式来并发执行。
在Spring Boot中,我们只需要通过使用 @Async 注解就能简单的将原来的同步函数变为异步函数,Service类改在为如下模式:
3.1、Application
通过 @EnableAsync 开启异步
package com.wells.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.service.Contact;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@SpringBootApplication
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
// 开启Schedule注解
@EnableScheduling
// 开启异步注解
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AsyncApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.wells.demo.quartz"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("Spring Boot Quartz")
.description("更多Spring Boot相关文章请关注:https://www.yuque.com/wells/micro.service")
.contact(new Contact("wells", "", ""))
.version("2.0")
.build();
}
}
3.2、DefaultAsyncController: 调用入口,也可通过Springboot Test调用
package com.wells.demo.async.controller;
import com.wells.demo.async.service.DefaultAsyncService;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* Description 异步调用Service
* Created by wells on 2020-07-15 09:26:38
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "default/async")
public class DefaultAsyncController {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DefaultAsyncController.class);
@Autowired
private DefaultAsyncService defaultAsyncService;
@GetMapping(value = "/execute/task")
public String executeTask() throws InterruptedException {
logger.info("default async request start");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
defaultAsyncService.executeTaskOne();
defaultAsyncService.executeTaskTwo();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
logger.info("default async request end, cost:{}", (end - start));
return "success";
}
}
3.3、DefaultAsyncService: 通过 @Sync 实现异步
注意: @Async所修饰的函数不要定义为static类型,这样异步调用不会生效
package com.wells.demo.async.service;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* Description
* Created by wells on 2020-07-15 09:36:29
*/
@Service
public class DefaultAsyncService {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DefaultAsyncService.class);
@Async
public void executeTaskOne() throws InterruptedException {
logger.info("executeTaskOne request start");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
logger.info("executeTaskOne request end");
}
@Async
public void executeTaskTwo() throws InterruptedException {
logger.info("executeTaskTwo request start");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
logger.info("executeTaskTwo request end");
}
}
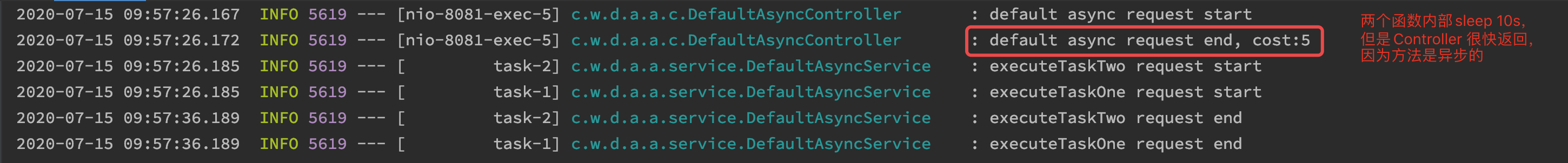
3.4、调用结果
3.5、代码示例
四、异步回调
为了让 executeTaskOne、executeTaskTwo 能正常结束,假设我们需要统计一下两个任务并发执行共耗时多少,这就需要等到上述两个个函数都完成调动之后记录时间,并计算结果。
4.1、AsyncCallbackController: 调用入口
package com.wells.demo.callback.controller;
import com.wells.demo.callback.service.AsyncCallbackService;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
/**
* Description 异步调用Service
* Created by wells on 2020-07-15 09:26:38
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "async/callback")
public class AsyncCallbackController {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AsyncCallbackController.class);
@Autowired
private AsyncCallbackService asyncCallbackService;
@GetMapping(value = "/execute/task")
public String executeTask() throws InterruptedException {
List<Future<String>> futureList = new ArrayList<Future<String>>();
logger.info("async callback request start");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Future<String> f1 = asyncCallbackService.executeTaskOne();
Future<String> f2 = asyncCallbackService.executeTaskTwo();
futureList.add(f1);
futureList.add(f2);
futureList.forEach(future -> {
try {
System.out.println(future.get());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
logger.info("async callback request end, cost:{}", (end - start));
return "success";
}
}
4.2、Service
package com.wells.demo.callback.service;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* Description
* Created by wells on 2020-07-15 09:36:29
*/
@Service
public class AsyncCallbackService {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AsyncCallbackService.class);
@Async
public Future<String> executeTaskOne() throws InterruptedException {
logger.info("executeTaskOne request start");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
logger.info("executeTaskOne request end");
return new AsyncResult<>("task on execute success");
}
@Async
public Future<String> executeTaskTwo() throws InterruptedException {
logger.info("executeTaskTwo request start");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
logger.info("executeTaskTwo request end");
return new AsyncResult<>("task on execute success");
}
}

