RDD
转换:功能的补充和封装,将旧的的RDD包装成新的RDD
行动:触发任务的调度和作业的执行
RDD根据数据处理方式不同将算子整体分为
Value类型、双Value类型、Key-Value类型
一 Value
1.Map()
函数签名: def map( f : T => U ) : RDD[U]
val sparkConf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("R")val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(sparkConf)val rdd: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas/apache.log")val mapRDD: RDD[String] = rdd.map(line => {val datas: Array[String] = line.split(" ")datas(6)})mapRDD.collect().foreach(print)sc.stop()
数据源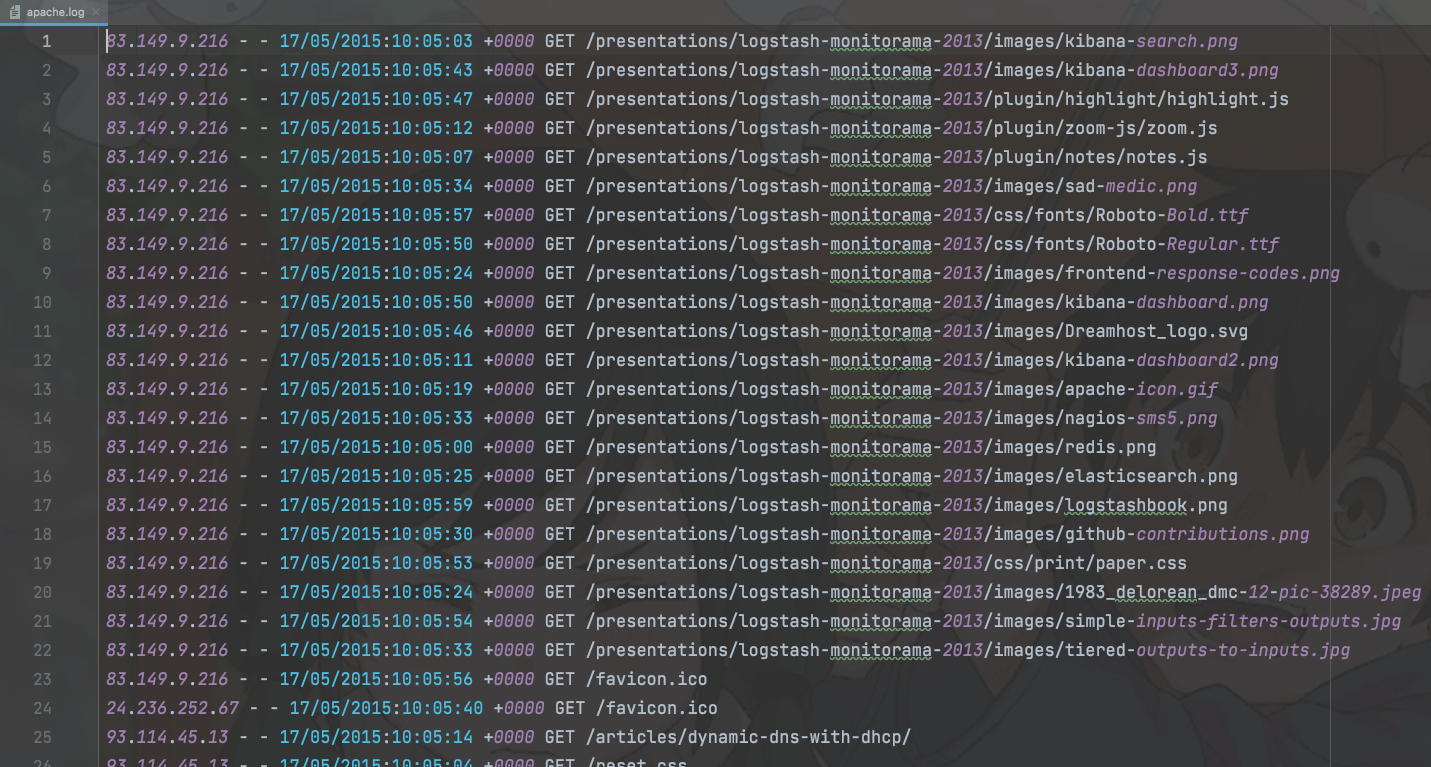
输出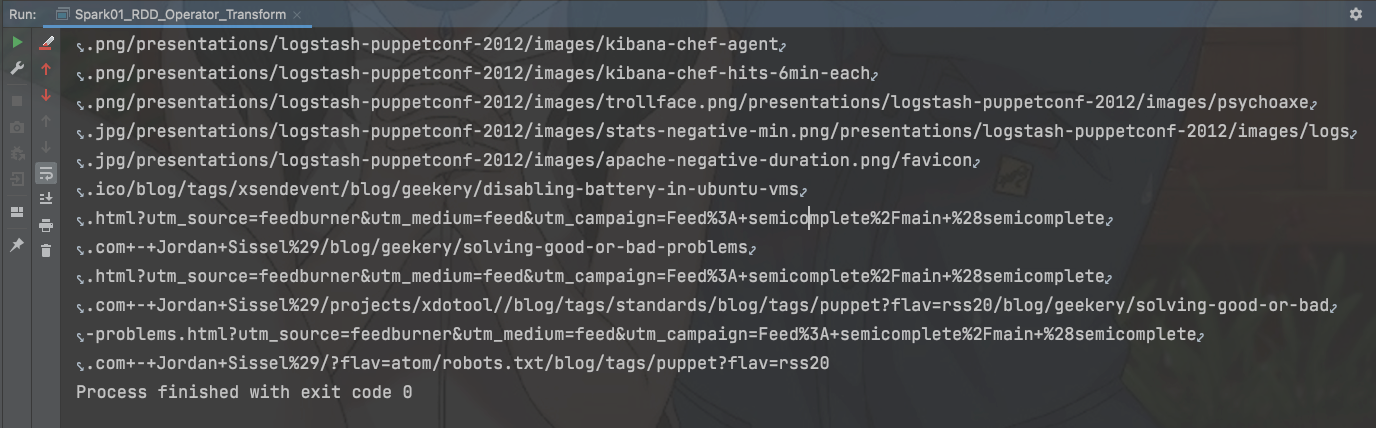
2.mapPartitions()
函数签名 def mapPartitionsU:ClassTag :RDD[U]
是以分区为单位进行数据转换操作,会将整个分区的数据加载到内存进行操作
例子:
1.每个分区过滤
val rdd: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas/1.txt")val mapRDD: RDD[String] = rdd.mapPartitions(iter => {iter.filter( item => item.toInt % 2 == 0)})mapRDD.collect().foreach(print)sc.stop()
2.每个分区最大值
val sparkConf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("R")val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(sparkConf)val rdd: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas/3.txt")val mapRDD: RDD[Int] = rdd.mapPartitions(iter => {//iter.filter( item => item.toInt % 2 == 0)val arr: Iterator[Int] = iter.map(item => item.toInt)List(arr.max).iterator})mapRDD.collect().foreach(println)sc.stop()
3.mapPartitionsWithIndex()
函数签名 def mapPartitionsWithIndexU:ClassTag => Iterator[U] , preservesPartitionsing : Boolean = false ) :RDD[U]
第一个参数是分区编号(从0开始)
val sparkConf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("R")val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(sparkConf)val rdd: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas/3.txt")val mapRDD: RDD[String] = rdd.mapPartitionsWithIndex((index, iter) => {if (index == 0) {iter} else {Nil.iterator}})mapRDD.collect().foreach(println)sc.stop()
4.flatMap()
函数签名 def flatMap( f: T => TraversableOnce[U] ) : RDD[U]
泛型T 是类泛型
先map再flatten
val rdd: RDD[List[Int]] = sc.makeRDD(List(List(1,2),List(3,4)))val rddMap: RDD[Int] = rdd.flatMap(arr => arr)rddMap.collect().foreach(println)
模式匹配
val rdd: RDD[Any] = sc.makeRDD(List(List(1, 2), 3, List(4, 5)))val rddMap: RDD[Any] = rdd.flatMap(item => {item match {case list: List[_] => listcase i => List(i) //将不是集合的元素转成集合}})rddMap.collect().foreach(println)
6.groupBy()
函数签名 def groupByK(implicit kt: ClassTag[K]): RDD[(K, Iterable[T])]
作用 遍历集合的元素,将返回值当作key 相同key为一组 最终返回一个元组
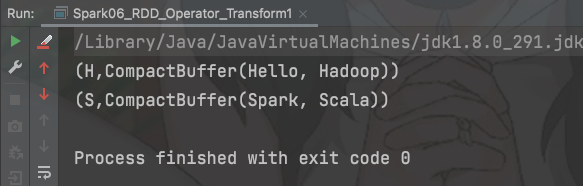
val rdd: RDD[String] = sc.makeRDD(List("Hello", "Spark", "Scala", "Hadoop"))val groupRDD: RDD[(Char, Iterable[String])] = rdd.groupBy(item => item.charAt(0))groupRDD.collect().foreach(println)
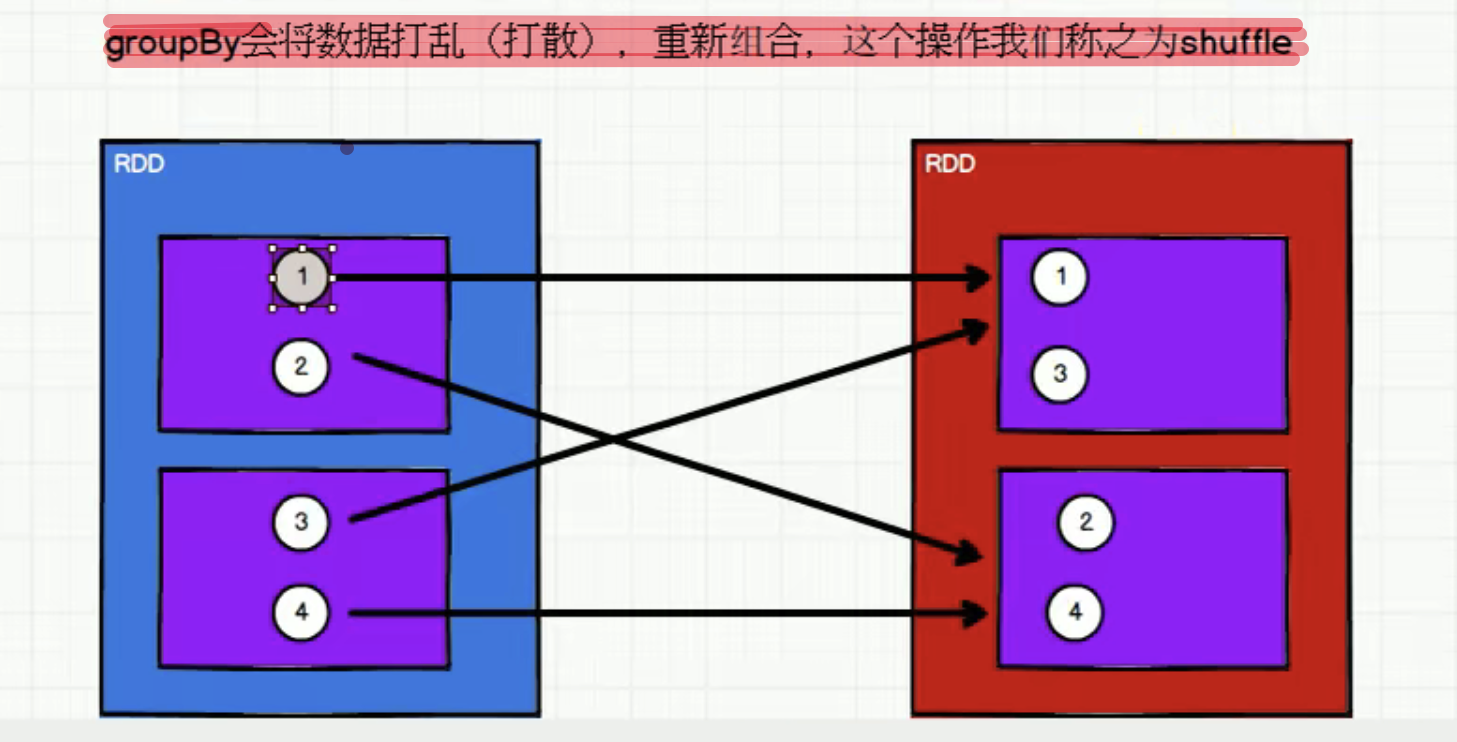
重新分区(shuffle)
val rdd: RDD[Int] = sc.makeRDD(List(1,2,3,567,8))val groupRDD: RDD[(Int, Iterable[Int])] = rdd.groupBy(item => item % 2)
例子
统计每个时间段的访问次数
val sparkConf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("R5")val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(sparkConf)//83.149.9.216 - - 17/05/2015:10:05:03val rdd: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas/apache.log")val mapRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = rdd.map(line => {val datas: Array[String] = line.split(" ")val format: SimpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("dd/MM/yyyy:HH:mm:ss")val date: Date = format.parse(datas(3))val format2: SimpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("HH")val str: String = format2.format(date)(str, 1)})val groupRDD: RDD[(String, Iterable[(String, Int)])] = mapRDD.groupBy(item => item._1)val resRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = groupRDD.map(item => {(item._1, item._2.size)})resRDD.collect().foreach(println)sc.stop()
7.filter()
函数签名 def filter( f : T => Boolean ) : RDD[T]
作用: 过滤集合中元素,false过滤
注意: 此函数可能会出现 数据倾斜,也就是分区间数据量不平衡
例子
筛选出是 2015/05/17 的 访问记录
val filterRDD: RDD[String] = rdd.filter(item => {val line: Array[String] = item.split(" ")line(3).startsWith("17/05/2015")})val value: RDD[(String, String)] = filterRDD.map(item => {val strings: Array[String] = item.split(" ")(strings(3), strings(6))})value.collect().foreach(println)
5.glom()
函数签名 def glom() :RDD[Array[T]
作用: 将一维数据转成二维数组

