作者是一个Java开发工作者,在通常,项目上线的时候, 我们都会去选择服务器配置,比如8核16G、等等配置,在这边做一个选择服务器的配置基础认知。 从CPU开始讲解.
1.CPU
CPU是指看得见的 芯片个数、也就是指主板上插CPU的插槽个数
2.核数 cpu cores
在每一个cpu上面,都可能有多个核(core),每一个核中都有独立的 一套ALU、FPU、Cache 组件。所以这个概念也被称之为物理核。
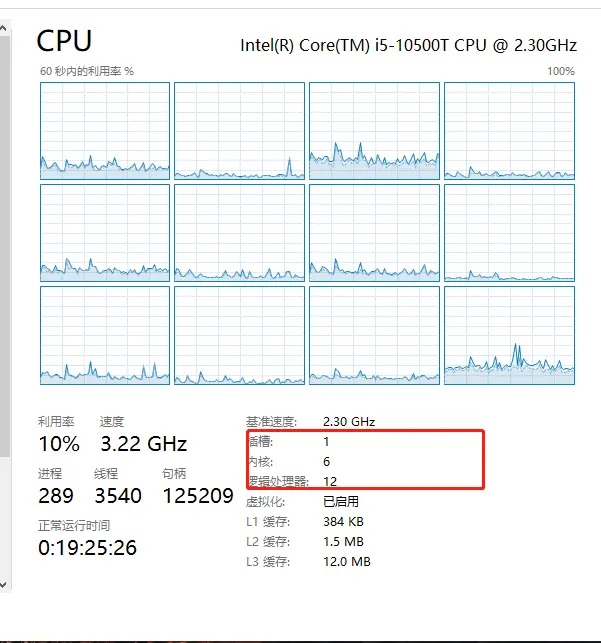
总的CPU物理内核数=物理CPU数*每颗CPU的内核数3.线程数 processor
这个主要得益于现在的超线程技术,可以让一个物理核模拟处多个逻辑核,processor。起作用也就是当我们有多个计算任务、或者处理逻辑的时候,可以让一个计算任务使用ALU的时候,另一个则取使用FPU。这样可以充分利用物理核的各个组件。使得同一个物理核当中也可以执行多个计算任务。
总的逻辑CPU数=物理CPU个数*每颗物理CPU的核数*超线程数 总的逻辑CPU数=总的CPU物理内核书*超线程数几核几线程
我们常说的核指的是内核个数。像下面这张图表示6核12线程。基于上面的逻辑核公式可以推算出每个内核可以运行2个线程数量。
多核的作用主要用于多任务进行计算。 那么是不是在 多线程的情况下,就会使用到多核呢?测试如下
public class ThreadTest {private static final int num = 1000 * 1000;public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {System.out.println(i);}}, "thread1").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {System.out.println(i);}}, "thread2").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {System.out.println(i);}}, "thread3").start();}}
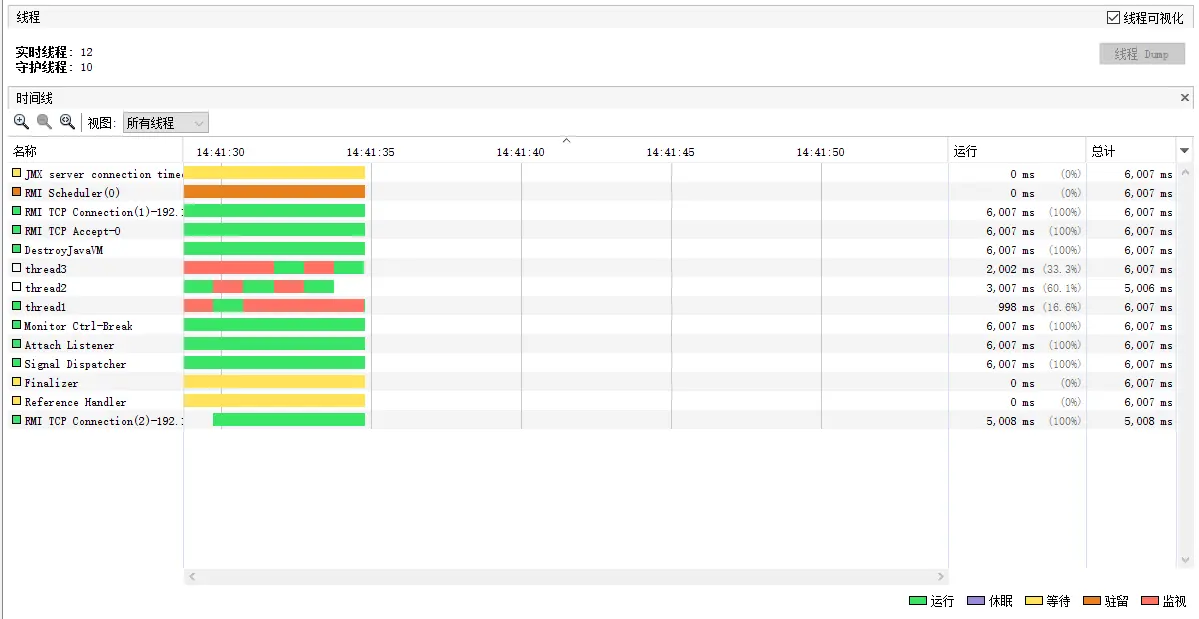
采用VisualVm 进行观察结果如下
创建了3条线程,但是这3条线程并不是一起执行的,所以 对于我们的猜测可能并不是一致, 因为在我们的想法当中这3条线程应该是一起执行的。
Java 多线程如何实现在多 CPU 上分布?线程的调度是由CPU分配的。如果线程运算量不算大,CPU调度县城不一定会被平均分配给每个内核,而是采用切换的方式去运行。
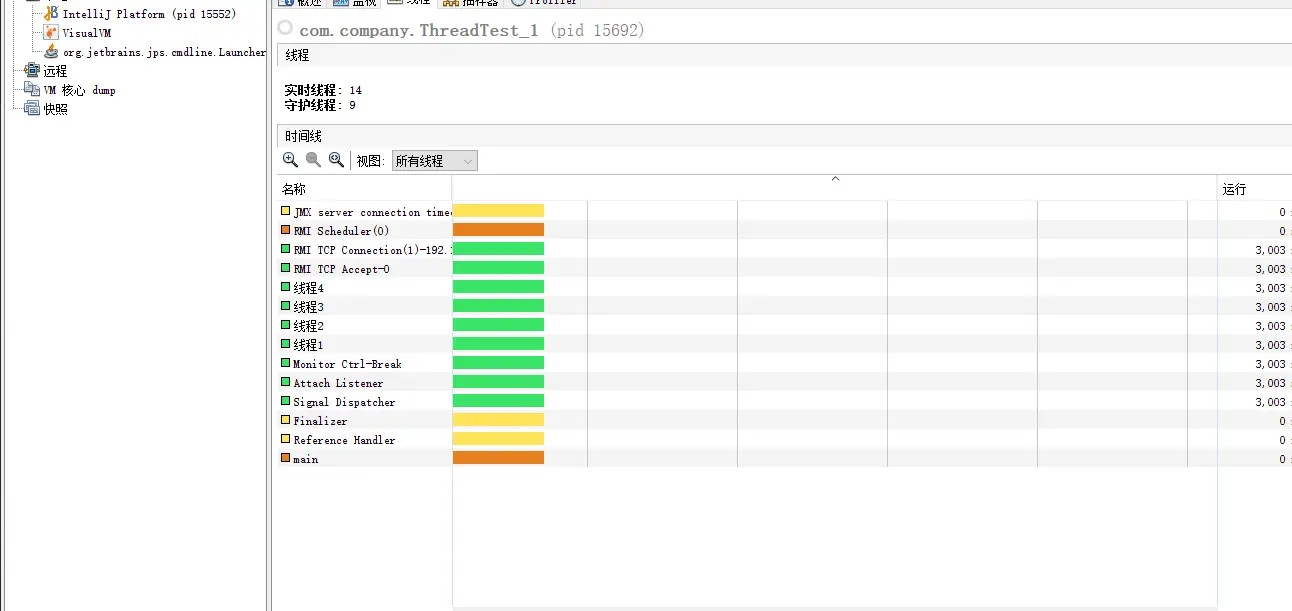
增加线程当中的运算量。
public class ThreadTest_1 {// 数据量private static final int num = 2000 * 1000;// 设置栅栏是为了防止子线程还没结束就执行main线程输出耗时时间private static final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(4);private static ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);private static final String filePath1 = "/Users/hao/IdeaProjects/Sample/src/test1.txt";private static final String filePath2 = "/Users/hao/IdeaProjects/Sample/src/test2.txt";private static final String filePath3 = "/Users/hao/IdeaProjects/Sample/src/test3.txt";private static final String filePath4 = "/Users/hao/IdeaProjects/Sample/src/test4.txt";private static File file1 = new File(filePath1);private static File file2 = new File(filePath2);private static File file3 = new File(filePath3);private static File file4 = new File(filePath4);public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, IOException {// 开始时间long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();new Thread(new WriteFileThread(file1), "线程1").start();new Thread(new WriteFileThread(file2), "线程2").start();new Thread(new WriteFileThread(file3), "线程3").start();new Thread(new WriteFileThread(file4), "线程4").start();try {countDownLatch.await();} finally {service.shutdown();}// 结束时间long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println();System.out.println("总耗时间为:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000.0 + "s");}static class WriteFileThread implements Runnable {private File file;public WriteFileThread(File file) {this.file = file;}@Overridepublic void run() {writeFile(file);}}static void writeFile(File file) {// 判断是否有该文件if (!file.getParentFile().exists()) {file.getParentFile().mkdirs();}if (!file.exists()) {try {file.createNewFile();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();//创建输出缓冲流对象BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = null;try {bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {try {bufferedWriter.write(i);bufferedWriter.newLine();bufferedWriter.flush();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行完成,耗时 : " + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "s");countDownLatch.countDown();try {bufferedWriter.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}