public class CommonFunction {public static void main(String[] args) {//常用Java8内置接口//Consumer 消费类型 接口 demo 对1000进行消费 对这个参数进行操作CommonFunction.shop( 1000, new Consumer <Double>() {@Overridepublic void accept(Double aDouble) {System.out.println( aDouble );}} );//Supiler get方式 Supplier<T>供给型接口 无 T 返回类型为T的对象,方法:T get();可用作工String code = CommonFunction.getCode( 4, () -> {return new Random( 10 ).nextInt();} );System.out.println(code);//Function 函数 操作类型为T的 返回为RInteger length = CommonFunction.functionGet( "张三", (str) -> str.length() );System.out.println(length);//输入参数 然后输入这个参数的判定条件boolean predicate = CommonFunction.predicate( "Lucy", (str) -> str.equals( "Lucy" ) );System.out.println(predicate);}//consumer函数public static void shop(double money, Consumer <Double> consumer) {consumer.accept( money );}//supplier函数public static String getCode(int num, Supplier<Integer>supplier){String str="";for (int i=0;i<num;i++){str+=supplier.get();}return str;}//Function函数public static Integer functionGet(String str,Function<String,Integer> function){return function.apply( str );}//Predicate函数 对某个参数是否符合返回boolean值public static boolean predicate(String str,Predicate<String>predicate){boolean test = predicate.test( str );return test;}}
其他函数
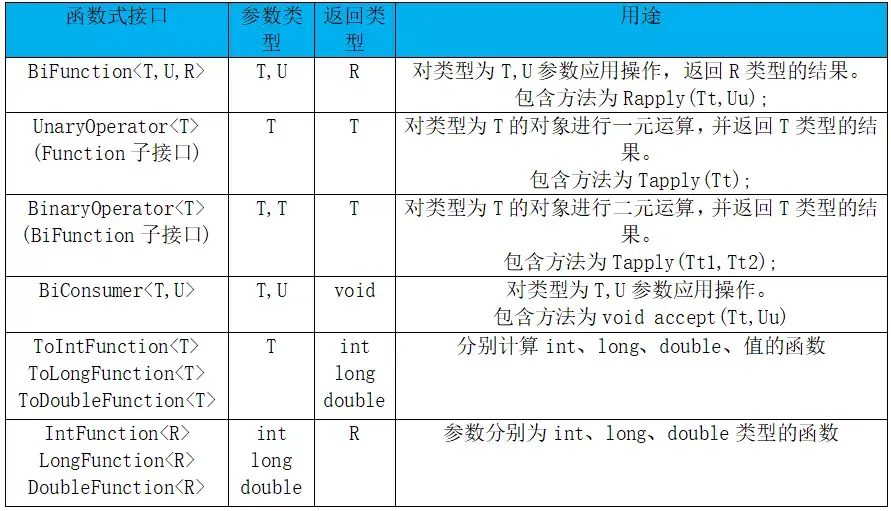
public class OtherFunction {
//接受参数TT 方法 apply 对TT类型参数做二次运算
public static BinaryOperator<Integer>binaryOperator=(x,y)->x+y;
//T U R 对 T 和U 参数操作 返回类型为R
public static BiFunction<String,Integer,String>biFunction=(x,y)->{
return x+y;
};
//接受参数为T 对T类型的参数进行操作 返回类型也为T
public static UnaryOperator<String>unaryOperator=(x)->{
return x.toString();
};
//接受参数为T和U 对T和U的参数进行操作 返回类型为void
public static BiConsumer<String,Integer>biConsumer=(x,y)->{
System.out.println(x+y);
};
//接收参数为Int 类型 对Int类型参数进行计算
public static ToIntFunction<Integer>toIntFunction=(x)->{
return x+1;
};
//参数分别为int long double
public static IntFunction<Integer>integerIntFunction=(x)->{
return x;
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer apply1 = OtherFunction.binaryOperator.apply( 1, 2 );;
System.out.println(apply1);
String sex = OtherFunction.biFunction.apply( "sex", 6 );
System.out.println(sex);
String str = OtherFunction.unaryOperator.apply( "str" );
System.out.println(str);
OtherFunction.biConsumer.accept( "String",1 );
int i = OtherFunction.toIntFunction.applyAsInt( 1 );
System.out.println(i);
Integer apply = OtherFunction.integerIntFunction.apply( 1 );
System.out.println("apply"+apply);
}
}

