groupcache
一句话描述
groupcache 是一个分布式缓冲库
简介
groupcache是什么?
- groupcache是一个分布式缓冲库
- 是Server又是 Client
- 与其他peer相连
- 热点缓存副本
Example
git clone git@github.com:colinrs/groupcache-db-example.gitcd groupcache-db-examplemake run
- git@github.com:colinrs/groupcache-db-example.git
- Example的简单架构图
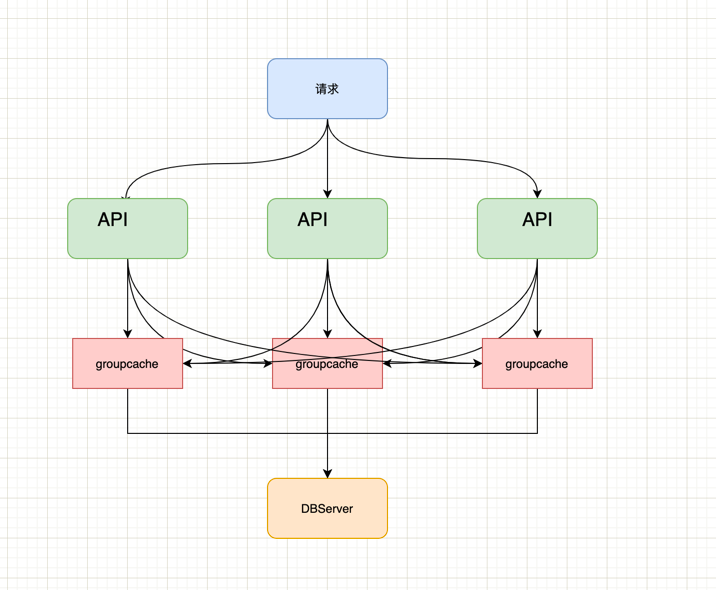
- API服务接收来自用户的请求
- 每一个API服务都有一个groupcache实例
- groupcache 最终的数据源是 DBServer
代码概览
├── byteview.go # 字节操作├── byteview_test.go├── consistenthash #一致性hash实现├── groupcache.go # cache操作├── groupcache_test.go├── groupcachepb # pb文件├── http.go # http 服务├── http_test.go├── lru # LRU 实现├── peers.go # 操作peer├── singleflight├── sinks.go└── testpb
核心的存储结构
Group
type Group struct {name stringgetter Getter // 获取数据接口peersOnce sync.Once // 保证初始化一次peerpeers PeerPicker // peer获取cacheBytes int64 // 对缓存大小的限制接口mainCache cache // mainCache 是分布式中本地分配到的cache部分hotCache cache // hotcache是由于访问频率高而被复制到此节点的缓存,尽管本节点不是它的拥有者。loadGroup flightGroup // 保证key只会获取一次_ int32Stats Stats}
流程分析
初始化
// InitCache ...func InitCache(port string) {// HTTP Server 设置opt := &groupcache.HTTPPoolOptions{Replicas: 1, // 缓存副本BasePath: "/gouache/", // 缓存请求路径}// peers地址cacheGroupHosts := []string{"http://127.0.0.1:8001", "http://127.0.0.1:8002", "http://127.0.0.1:8003"}// peer 初始化peers := groupcache.NewHTTPPoolOpts("http://127.0.0.1:" + cachePort, opt)peerMap := consistenthash.New(opt.Replicas, opt.HashFn)peerMap.Add(cacheGroupHosts...)cacheGroup := groupcache.NewGroup("SlowDBCache", 64<<20, groupcache.GetterFunc(// 源数据获取实现))peers.Set(cacheGroupHosts...) //设置peers地址logger.Info("cachegroup:%s slave starting on:127.0.0.1:%s",cacheGroup.Name(), cachePort)// 开启HTTP服务logger.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(fmt.Sprintf("127.0.0.1:%s",cachePort),http.HandlerFunc(peers.ServeHTTP)))}
- groupcache.NewHTTPPoolOpts 初始化和设置HTTP Server
- groupcache.NewGroup 初始化和设置cache
- consistenthash.New 初始化一致性hash,这里我是为了我们可以找到Key对应的peer才做了这个操作
缓存数据获取
- 使用groupcache.Get 方法获取到数据
func GetData(c *gin.Context) {req := new(Req)err := c.ShouldBind(req)if err!=nil{c.String(http.StatusOK, err.Error())return}var b []byte//Get方法就是groupcache获取数据的方法, b []byte 会存储获取到的值apiCacheGroup.group.Get(c.Request.Context(), req.Key, groupcache.AllocatingByteSliceSink(&b))result := map[string]interface{}{"key": req.Key,"value": string(b),}c.JSON(http.StatusOK, result)}
- Get 方法会尝试从 mainCache 和 hotCache 中获取数据
- 如果本地没有,则用load从数据源或者peer获取数据
// Get ...func (g *Group) Get(ctx context.Context, key string, dest Sink) error {g.peersOnce.Do(g.initPeers)g.Stats.Gets.Add(1)if dest == nil {return errors.New("groupcache: nil dest Sink")}value, cacheHit := g.lookupCache(key) // 从本地的mainCache 和 hitCache 获取数据if cacheHit {g.Stats.CacheHits.Add(1)return setSinkView(dest, value)}// Optimization to avoid double unmarshalling or copying: keep// track of whether the dest was already populated. One caller// (if local) will set this; the losers will not. The common// case will likely be one caller.destPopulated := falsevalue, destPopulated, err := g.load(ctx, key, dest) // 从数据源或者peer获取数据if err != nil {return err}if destPopulated {return nil}return setSinkView(dest, value)}
- load 依然会从本地获取一次,因为在并发的情况下,有可能有一个协程已经将值获取到了并设置到本地缓存中
- 然后PickPeer 获取到Key对应的Peer
- 如果从Peer获取失败了,则用getLocally从数据源获取数据
- 最后将数据缓存在本地
// load loads key either by invoking the getter locally or by sending it to another machine.func (g *Group) load(ctx context.Context, key string, dest Sink) (value ByteView, destPopulated bool, err error) {g.Stats.Loads.Add(1)viewi, err := g.loadGroup.Do(key, func() (interface{}, error) {// 再一次从本地缓存获取, 因为在并发的情况下,有可能有一个协程已经将值获取到了并设置到本地缓存中if value, cacheHit := g.lookupCache(key); cacheHit {g.Stats.CacheHits.Add(1)return value, nil}g.Stats.LoadsDeduped.Add(1)var value ByteViewvar err error// 获取到peerif peer, ok := g.peers.PickPeer(key); ok {// 从peer获取到数据value, err = g.getFromPeer(ctx, peer, key)if err == nil {g.Stats.PeerLoads.Add(1)return value, nil}g.Stats.PeerErrors.Add(1)// TODO(bradfitz): log the peer's error? keep// log of the past few for /groupcachez? It's// probably boring (normal task movement), so not// worth logging I imagine.}// 从数据源获取到值,也就是我们在初始化的注册的 Getter 接口value, err = g.getLocally(ctx, key, dest)if err != nil {g.Stats.LocalLoadErrs.Add(1)return nil, err}g.Stats.LocalLoads.Add(1)destPopulated = true // only one caller of load gets this return valueg.populateCache(key, value, &g.mainCache) // 从数据源获取到的数据缓存在mainCache中,同时也会根据缓存大小清除hotCache中较少使用的return value, nil})if err == nil {value = viewi.(ByteView)}return}func (g *Group) getFromPeer(ctx context.Context, peer ProtoGetter, key string) (ByteView, error) {req := &pb.GetRequest{Group: &g.name,Key: &key,}res := &pb.GetResponse{}err := peer.Get(ctx, req, res) // 从perr获取,这里的peer是 httpGetter 的实例,最终是通过HTTP请求去请求peerif err != nil {return ByteView{}, err}value := ByteView{b: res.Value}// TODO(bradfitz): use res.MinuteQps or something smart to// conditionally populate hotCache. For now just do it some// percentage of the time.if rand.Intn(10) == 0 {g.populateCache(key, value, &g.hotCache) // 从peer获取到的数据是设置到hotCache中}return value, nil}
流程图如下
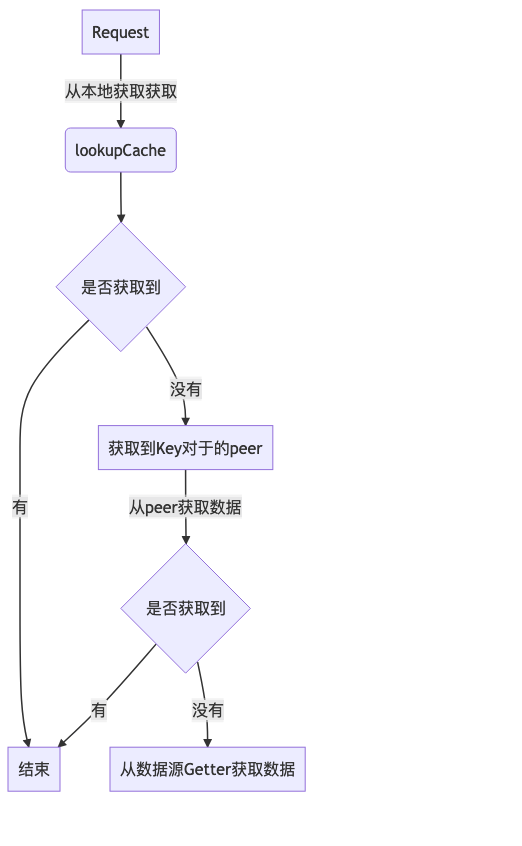
写入缓存流程
- 将从数据源内容更新到mainCache缓存中
- 将从peer获取到的数据更新到hotCache缓存中
几个有趣的点
peer的查询
- 给定一个key,groupcache会在本地找不到缓存的情况下,查询该key应该存在的peer。
- 为了在新增或删除peer的时候尽量少的缓存失效,groupcache使用一致性hash的方案,并提供了一个consistenthash的实现,就在consistenthash/consistenthash.go中。
我们再来看下peer的设置
- peer的设置
// 设置peer集群cacheGroupHosts := []string{"http://127.0.0.1:8001", "http://127.0.0.1:8002", "http://127.0.0.1:8003"}// 初始化本地peerpeers := groupcache.NewHTTPPoolOpts("http://127.0.0.1:" + cachePort, opt)// 设置peer集群peers.Set(cacheGroupHosts...)// peer 提供HTTP 服务供其他的peer来查询数据logger.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(fmt.Sprintf("127.0.0.1:%s",cachePort),http.HandlerFunc(peers.ServeHTTP)))
- 初始化一致性hash
- 初始化本地peer的Getter接口,是httpGetter实例
- Map.Add 方法将peer地址算出一个hash值,根据设置的副本数量将peer放在hash环中对应的位置
func (p *HTTPPool) Set(peers ...string) {p.mu.Lock()defer p.mu.Unlock()p.peers = consistenthash.New(p.opts.Replicas, p.opts.HashFn)p.peers.Add(peers...)p.httpGetters = make(map[string]*httpGetter, len(peers))for _, peer := range peers {p.httpGetters[peer] = &httpGetter{transport: p.Transport, baseURL: peer + p.opts.BasePath}}}// Add adds some keys to the hash.func (m *Map) Add(keys ...string) {for _, key := range keys {for i := 0; i < m.replicas; i++ {hash := int(m.hash([]byte(strconv.Itoa(i) + key)))m.keys = append(m.keys, hash)m.hashMap[hash] = key}}sort.Ints(m.keys)}
peer的获取
- peer的获取主要看 consistenthash 中Map 方法
- 首先会使用相同的hash函数算出hash值
- 然后将hash值排序之后找出peer在hash环中位置 index
- 最后再从hashMap中根据hash值获取到hash值对应的peer地址
// Get gets the closest item in the hash to the provided key.func (m *Map) Get(key string) string {if m.IsEmpty() {return ""}hash := int(m.hash([]byte(key)))// Binary search for appropriate replica.idx := sort.Search(len(m.keys), func(i int) bool { return m.keys[i] >= hash })// Means we have cycled back to the first replica.if idx == len(m.keys) {idx = 0}return m.hashMap[m.keys[idx]]}
缓存从数据源或者peer获取数据方式
- 从数据源或者peer获取数据方式会保证对同一个Key只会有一个请求在请求数据源或者peer
- 主要看 flightGroup的Do方法
// load loads key either by invoking the getter locally or by sending it to another machine.func (g *Group) load(ctx context.Context, key string, dest Sink) (value ByteView, destPopulated bool, err error) {g.Stats.Loads.Add(1)viewi, err := g.loadGroup.Do(key, func() (interface{}, error) {// 从数据源或者peer获取数据})return}// flightGroup的Do方法// 使用 mux 保证只会有一个协程在设置 g.m// g.m 用来判断是否有key存在// 使用 call (实际上就是 WaitGroup 包了一次)保证第二个请求同一个Key时需要等到前一个请求完成,直接使用前一个请求的结果就可以func (g *Group) Do(key string, fn func() (interface{}, error)) (interface{}, error) {g.mu.Lock()if g.m == nil {g.m = make(map[string]*call)}if c, ok := g.m[key]; ok { //如果已经有一个key初始化了,那么只需要等到请求完成就可以了,不需要再请求g.mu.Unlock()c.wg.Wait()return c.val, c.err // 使用前一个请求的结果就可以}c := new(call) // 如果没有,则西药初始化callc.wg.Add(1)g.m[key] = c // 设置key对应的callg.mu.Unlock()c.val, c.err = fn() // 实际的业务函数c.wg.Done()g.mu.Lock()delete(g.m, key) // 删除key对应的callg.mu.Unlock()return c.val, c.err}
为何缓存没有过期时间设置
- 根据使用场景来设计,我的理解上groupcache的设计目标是给文件做缓存,因为文件没有那么频繁更新,所以不需要设计过期时间的支持
- https://github.com/golang/groupcache/issues/3

