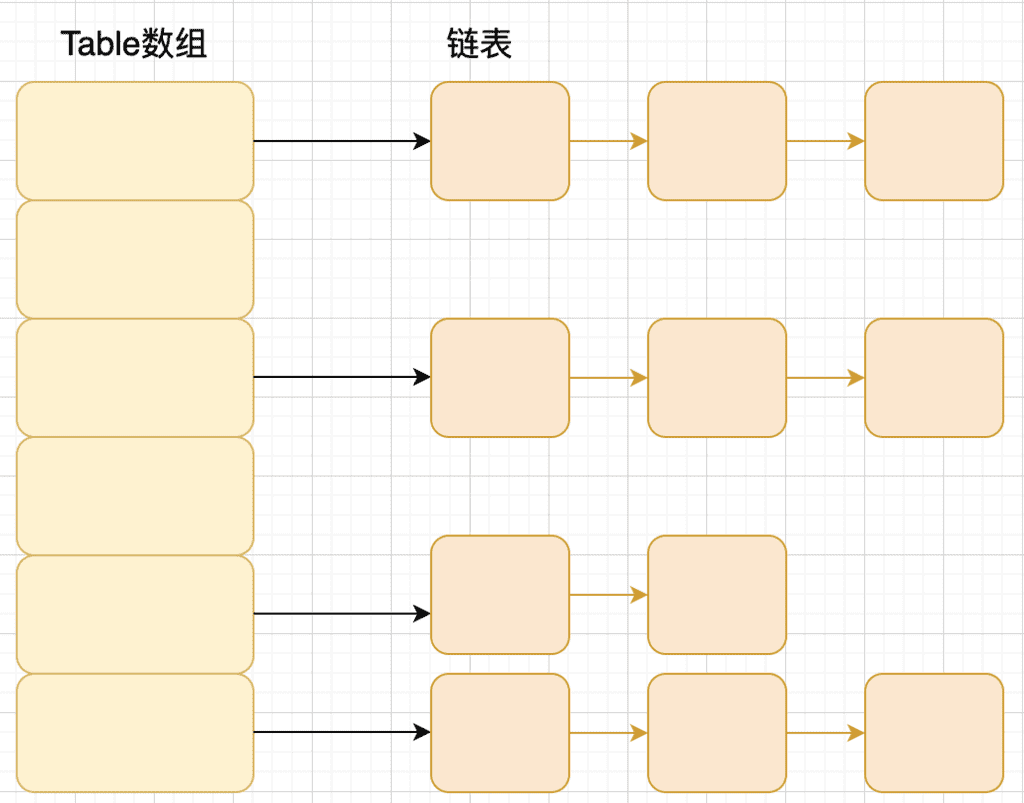
HashMap
hash 哈希表
元素hashCode值通过hash算法,计算出一个值,这个值重复概率很低,对它进行处理得到元素在哈希表中的位置。
关于hash冲突的扩展:解决hash碰撞的四种方法
- 开放定址法(线性探测)
开放定址法就是一旦发生了冲突,就去寻找下一个空的散列地址,只要散列表足够大,空的散列地址总能找到,并将记录存入 - 链地址法(拉链法)
就是hashmap采用的方法
- 二次hash法
发生hash冲突后,再次hash - 建立公共溢出区
将hash表分为基本表和溢出表,将冲突的元素放入溢出表。。
hashmap是如何来解决hash冲突的?(基于jdk1.8)
- 使用链地址法(散列表,数组+链表/红黑树)来链接所有相同hash值的数据。
- hash()函数中,使用两次扰动来降低哈希冲突的概率,使数据分布更均匀(jdk1.7中4次位运算、5次异或,一共9次扰动)
static final int hash(Object key) {int h;/** (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);* hashCode值与自己右移16位进行异或运算(高低位异或)* 使得hashCode的高位也能参与运算*/return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);}
- 引入红黑树,进一步提高遍历的时间复杂度。当散列表中链表长度超过8时,会转化为红黑树
底层结构
1.7 数组+链表
1.8 数组+链表/红黑树
链表长度> 8 且 数组长度达到64时,链表会转化为红黑树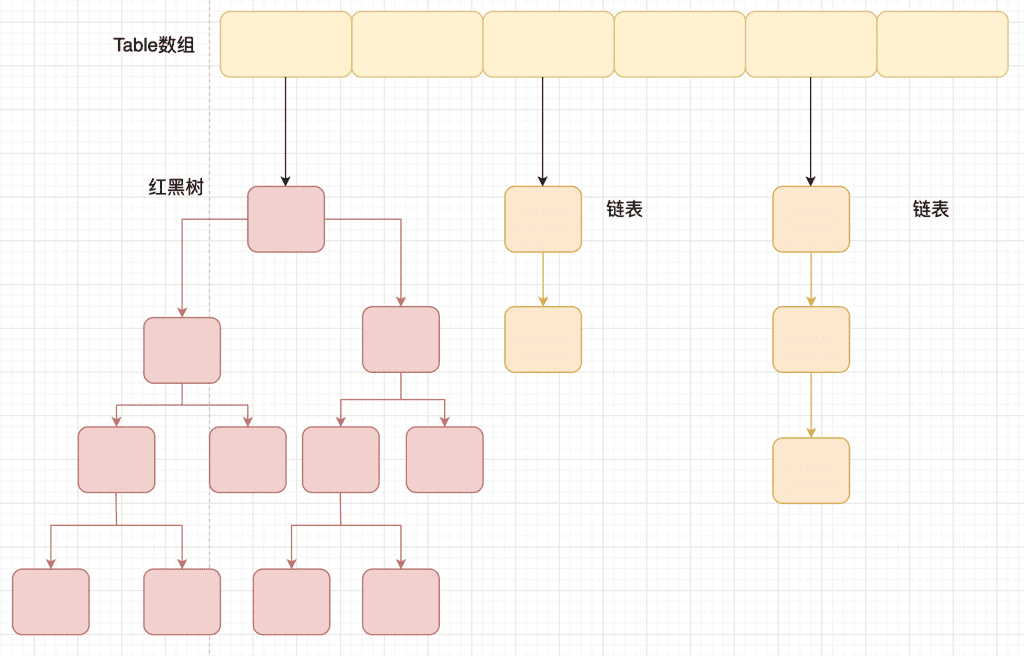
获取数组下标
hash函数
hash函数,在这里也叫扰动函数,防止有些hashCode()方法实现比较差,增加扰动函数,降低hash碰撞概率
1.7中的hash方法
static int hash(int h) {// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);}
1.8中的hash方法
^ 异或 相同为0,不同为1>>> 无符号右移/*** Computes key.hashCode() and spreads (XORs) higher bits of hash* to lower. Because the table uses power-of-two masking, sets of* hashes that vary only in bits above the current mask will* always collide. (Among known examples are sets of Float keys* holding consecutive whole numbers in small tables.) So we* apply a transform that spreads the impact of higher bits* downward. There is a tradeoff between speed, utility, and* quality of bit-spreading. Because many common sets of hashes* are already reasonably distributed (so don't benefit from* spreading), and because we use trees to handle large sets of* collisions in bins, we just XOR some shifted bits in the* cheapest possible way to reduce systematic lossage, as well as* to incorporate impact of the highest bits that would otherwise* never be used in index calculations because of table bounds.*/static final int hash(Object key) {int h;return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);}
hash()函数中,使用两次扰动来降低哈希冲突的概率,使数据分布更均匀
(jdk1.7中4次位运算、5次异或,一共9次扰动)
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
其中 i = (n - 1) & hash ,i的值就是数组下标,n为数组长度
完整过程:
- h = key.hashCode() 取hashCode值
- h ^ (h >>> 16) 取高16位参与运算
即使数组长度较小,也能保证考虑到高低Bit都参与到Hash的计算中,同时不会有太大的开销。
- (n-1) & hash , n 为数组长度,对hash取模
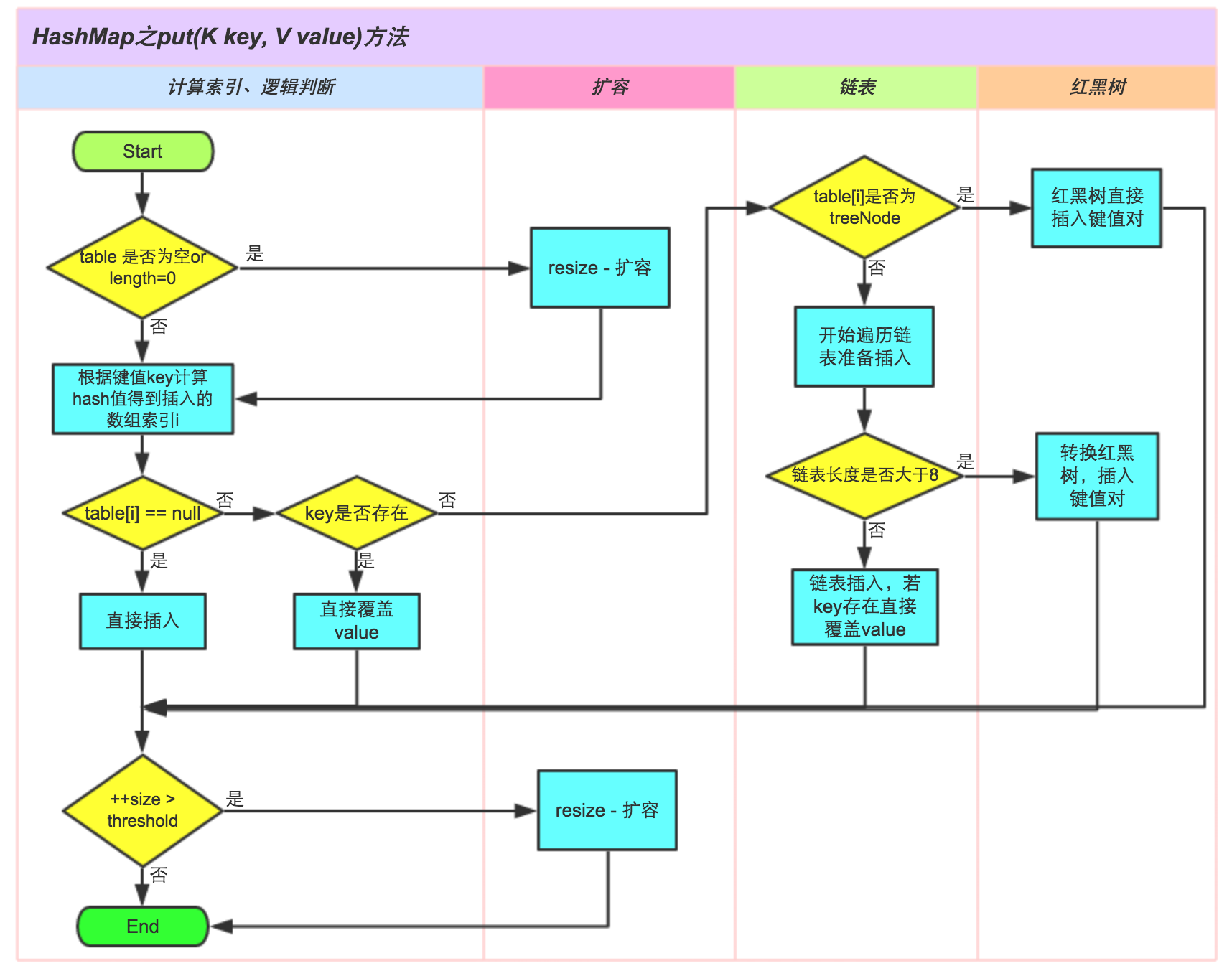
put方法
关键步骤
1.8
- 判断数组是否需要初始化
- 确定坐标,判断此坐标是否有元素
- 如果有元素,判断是插入树还是插入链表
- 如果是链表,则插入到链表尾部
- 最后判断是否需要扩容
拉链法;
如果对应位置有元素,则插入到对应的链表即可。
java8 之前是头插法,就是新来的值会取代原有的值,原有的值就顺推到链表中去。设计这个方法时认为,最新被插入的数据,也最有可能被访问。
java8 开始,改为尾插法
为什么改为尾插法?
因为多线程环境下,头插法,可能会产生环形链表。
使用尾插,在扩容时会保持链表元素原本的顺序,就不会出现链表成环的问题了。
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods.
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
扩容
扩容时设计到这几个重要变量,
- capacity 即最大容量,默认16。
- loadFactor 装载,默认是0.75
- threshold 阈值。阈值=容量*加载因子 默认12
当元素数量超过阈值时便会出发扩容。
- 每次扩容的新容量是之前容量的2倍
- 最大容量是有限的,容量达到1<<30,即1073741824,就不会扩容了,且阈值会被设置为Integer.MAX_VALUE( 2^31-1)
- 根据新容量,初始化一个数组
- 将旧数组的数组转移到新数组,需要根据新数组的长度重新计算元素位置
- 修改threshold为新值
jdk1.7中,扩容时,元素数组下标,就是用 hash 对新数组长度取模得到
需要注意的时,就数组中,同一个链表上的元素,在新数组中,可能还在同一链表,也可能不在同一链表;
如果在同一链表的话,由于1.7采用的头插法,同一链表上的元素,扩容后在新数组中的顺序会倒置。(在多线程下,这一特对会导致产生循环链表。1.8采用尾插法优化后已解决此问题)
1.8
1.8中,数组长度必为2的整数次幂,这是为什么? 即,为什么hashmap的长度要定为2的整数次幂?
一个元素的哈希值用hash表示,数组长度用length表示。
确定元素下标的方式是 : index = hash % length
即,hash对length取模,得到的余数就是index值。
令 x = 1<<4,即 x 为 1左移4位,就是2 的 4 次方, x : 00010000 x-1 : 00001111
令 y = 10110010 再令y与 x-1 做与运算,可以去除 y 位级表示的第 4 位以上数: y : 10110010 x-1 : 00001111 y&(x-1) : 00000010
这个性质和 y 对 x 取模效果是一样的: y : 10110010 x : 00010000 y%x : 00000010
综上,如果 length = 2^n,则 hash % length = hash & (length-1)
即如果 length 是2的整数次幂,则hash对length取模得到的值与 hash与(length-1) 的与运算结果相同。所以可以直接用位运算代替取余运算,大大提高运算速度
重要参数
table:一个哈希桶数组,键值对就存放在里面。
size:表示实际存在的键值对数量。
modCount:记录修改次数。
// 表示容器所能容纳的key-value对极限。
int threshold;
// 负载因子
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
final float loadFactor;
初始容量(inital capacity):指table的初始长度length(默认值是16)。
负载因子(load factor):指自动扩容的临界值(默认值是0.75)。
多线程下map的改进
HashMap并发问题,多线程访问不是线程安全的。
HashTable
ConcurrentHashMap
1.7
分段的思想,减小锁的粒度,为每个segement加锁
static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2249069246763182397L;
// 和 HashMap 中的 HashEntry 作用一样,真正存放数据的桶
transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table;
transient int count;
transient int modCount;
transient int threshold;
final float loadFactor;
}
作者:crossoverJie
链接:https://juejin.cn/post/6844903641866846222
来源:稀土掘金
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
1.8
CAS + synchronized
扩展
上面反复提到的hash算法应用很广泛,如数据分片等,在这些场景下的普通hash算法在扩容时有问题,这就需要一致性hash算法
一致性hash算法 普通hash算法存在什么问题? 一致性hash算法如何解决此问题? 一致性hash算法如何解决数据倾斜的问题?(自动缓存重建+虚拟节点)
参考
Java 8系列之重新认识HashMap【美团技术团队】
深入理解HashMap源码【掘金】
hashmap循环链表【coolshell】