解题步骤
- 新建两个矩阵、分别记录能流到两个大洋的坐标
- 从两个海岸线四个方向同时出发,进行深度优先遍历图,遍历过程中填充对应的两个矩阵
- 遍历矩阵,找出能同时流到两个大洋的坐标
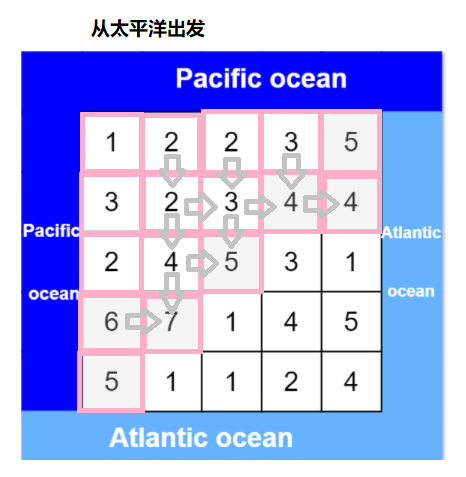
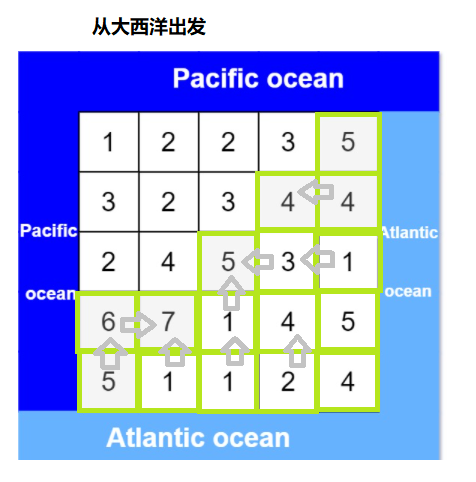
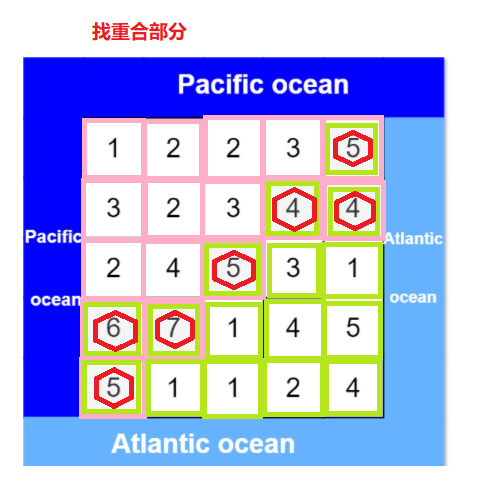
通过图的方式进行实现
- 时间复杂度:O (m * n)
空间复杂度:O (m * n)
function pacificAtlantic(heights) {const rows = heights.length;const cols = heights[0].length;const matrix1 = Array.from({ length: rows }, () => new Array(cols).fill(false));const matrix2 = Array.from({ length: rows }, () => new Array(cols).fill(false));const dfs = (row, col, matrix) => {matrix[row][col] = true;[[row - 1, col],[row + 1, col],[row, col - 1],[row, col + 1],].forEach(([nRow, nCol]) => {const cond1 = nRow >= 0 && nRow < rows && nCol >= 0 && nCol < cols;const cond2 = cond1 ? !matrix[nRow][nCol] : false;const cond3 = cond2 ? heights[row][col] <= heights[nRow][nCol] : false;if (cond1 && cond2 && cond3) {dfs(nRow, nCol, matrix);}});};for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) {dfs(i, 0, matrix1);dfs(i, cols - 1, matrix2);}for (let i = 0; i < cols; i++) {dfs(0, i, matrix1);dfs(rows - 1, i, matrix2);}const res = [];for (let row = 0; row < rows; row++) {for (let col = 0; col < cols; col++) {if (matrix1[row][col] && matrix2[row][col]) {res.push([row, col]);}}}return res;}
上方代码中无论 for 循环写的多么复杂,但是我们实际上只是遍历了矩阵的每一个元素,所以时间复杂度是 O (m n),m 代表是行的长度,n 是代表列的长度。代码中使用了两个矩阵,矩阵的大小是 m n 。所以我们按大的占用空间来算,空间复杂度是 O (m * n)。

