源码下载
https://www.cnblogs.com/klchang/p/13207884.html
C++编译器的安装位置(Your C++ compiler installation location)
Windows
Visual Studio — X:\Microsoft Visual Studio 9.0\VC\crt\src; X:\Program files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio 14.0\VC\include\; X:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2017\Enterprise\VC\Tools\MSVC\14.16.27023\crt\src
Note,
1) You even don’t have to install Visual Studio to explore Microsoft implementation. Online compilers can help: rextester.com/NRP17506
2) In Visual Studio if you interesting in concrete(specific) STL-element implementation (for example, any function), right click on its mention in your code and chose “Go to Definition” in context menu. (Or place cursor on this mention and push “F12”)
Linux/Unix
gcc — /usr/include/c++/; /usr/lib/gcc/CTARGET/VERSION/include/g++-v4/
Note, locate iostream is a good solution to find the installation location.
网上开源代码(Online open source codes)
libc++
libc++ — the C++ standard library of LLVM project.
libc++ is an implementation of the C++ standard library, targeting C++11, C++14 and above.
http://libcxx.llvm.org/
https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project/tree/master/libcxx/
gcc
GCC, the GNU Compiler Collection
The GNU project is Free and Open Source software, and contains an implementation of the C++ standard library.
https://github.com/gcc-mirror/gcc/tree/master/libstdc%2B%2B-v3
https://github.com/gcc-mirror/gcc
MSVC STL
Microsoft’s C++ Standard Library
MSVC’s implementation of the C++ Standard Library. https://github.com/microsoft/STL
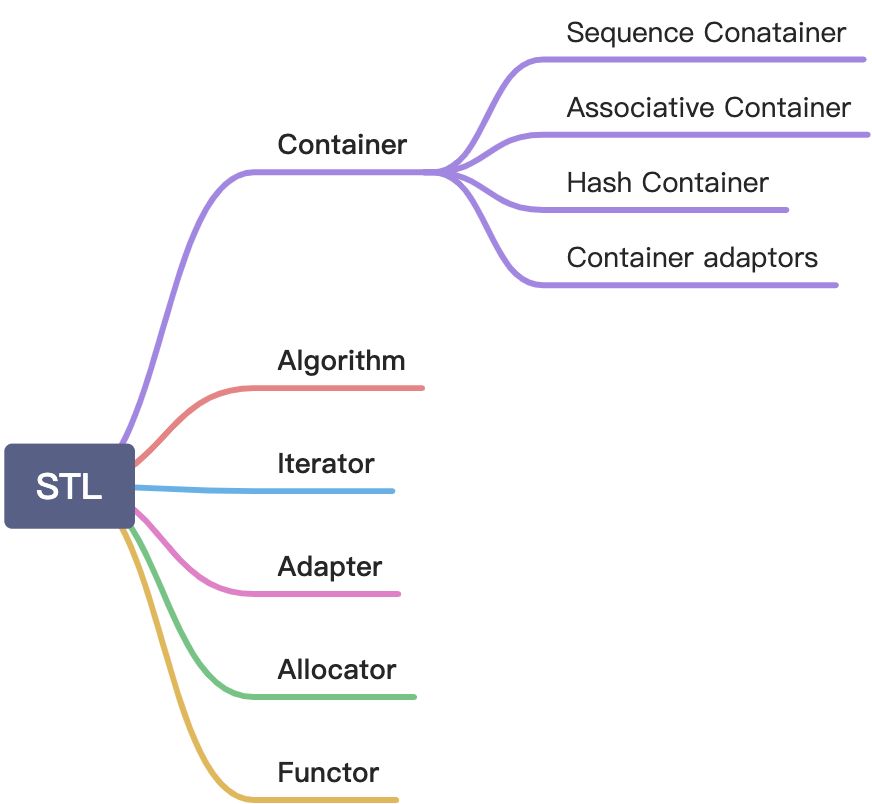
容器结构
https://blog.csdn.net/shenaisi/article/details/81545418
Sequence Conatainer
array
vector
顺序存放,STL内部实现时,首先分配较小的内存空间预备进行存储,即capacity()函数返回的大小,当超过此分配的空间时再整体重新放分配一块内存存储。
增加变量
每次增大容量时,vector.capacity()每次变为原来的两倍。
插入变量
insert
emplace
移动变量
ForwardIt rotate( ForwardIt first, ForwardIt n_first, ForwardIt last )
旋转对[first, last)中的元素,使n_first变成第一个元素。
返回:Iterator to the new location of the element pointed by first. Equal to first + (last - n_first)
// 将it指向的元素移动到vector开头auto rit = make_reverse_iterator(it);rotate(rit - 1, rit, vec.rend());// 将下标为x的元素移动到vector开头auto rit = make_reverse_iterator(next(vec.begin(), x));rotate(rit - 1, rit, vec.rend());
删除变量
vector的pop_back()和erase(), remove(), clear()函数均不会改变capacity,不释放内存。
remove函数已删除remove函数不仅不改变capacity,甚至还不改变size,其原理为:在遍历容器中的元素时,一旦遇到目标元素,就做上标记,然后继续遍历,直到找到一个非目标元素,即用此元素将最先做标记的位置覆盖掉,同时将此非目标元素所在的位置也做上标记,等待找到新的非目标元素将其覆盖。遍历完成后返回最后一个元素的迭代器位置,此迭代器后面都是一些无用的元素,因此一般要结合erase一起使用。
修改内存
resize()既修改capacity大小,也修改size大小,如果增大内存,会需要传入后面变量的初始化参数,否则调用默认构造参数。
reserve()只增加capacity大小,如果传入参数比capacity小,不做任何操作。
shrink_to_fit()函数,主动释放内存使capacity和size匹配,没有参数,。
初始化
std::vector<int> myvector{1,2,3,4,5};
//myvector:[1,2,3,4,5]
std::vector<int> myvector(3,100);
//myvector:[100,100,100]
插入
myvector.insert(myvector.begin(),2,100) //头部插入两个100
deque
双端队列,两端都可以插入/删除
deque是在功能上合并了vector和list,在内存中分段连续。
优点:(1) 随机访问方便,即支持[ ]操作符和vector.at()
(2) 在内部方便的进行插入和删除操作
(3) 可在两端进行push、pop
缺点:(1) 占用内存多
list
forward_list
Container adaptors
stack
queue
内部结构为deque
没有iterator
头文件queue,默认依托于deque,也可以选list。
template<
class T,
class Container = std::deque<T>
> class queue;
heap
STL中没有heap这个容器,堆以make_heap(),pop_heap(),push_heap(),sort_heap()几个函数依托于序列式容器存在,传入的参数为随机访问迭代器。
template< class RandomIt >
constexpr void make_heap( RandomIt first, RandomIt last );
template< class RandomIt, class Compare >
constexpr void make_heap( RandomIt first, RandomIt last,
Compare comp );
priority_queue
其实就是个堆
头文件queue,但queue默认依赖于deque,而priority_queue默认依赖于vector。
默认比较方式为<,默认为大根堆,与sort函数相反。
template<
class T,
class Container = std::vector<T>,
class Compare = std::less<typename Container::value_type>
> class priority_queue;
例子:
priority_queue<int> p;
p.push(1);
p.push(2);
p.push(8);
p.push(5);
p.push(43);
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
cout<<p.top()<<endl;
p.pop();
}
自定义比较。也可以重载element的opetator<。
operator()要包含在结构体内传递给priority_queue。
struct Node{
int x,y;
Node(int a=0, int b=0):
x(a), y(b) {}
};
struct cmp{
bool operator() (Node a, Node b){
if(a.x == b.x) return a.y>b.y;
return a.x>b.x;
}
};
int main(){
priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, cmp>p;
for(int i=0; i<10; ++i)
p.push(Node(rand(), rand()));
while(!p.empty()){
cout<<p.top().x<<' '<<p.top().y<<endl;
p.pop();
}
return 0;
}
Associative Container
map
红黑树(平衡二叉树)
有排序(自动对key排序),有key和value
不可重复
可以直接用[]插入
如果一个key存在, operator[] 对这个key-value进行重写
如果一个key存在, insert 不会对原来的key-value进行重写
set
multiset
multimap
Hash Container
unordered_set
HashSet,在set的基础上用哈希表存放,无排序。元素不可重复。
unordered_map
HashMap,在map的基础上用哈希表存放key,和python中的dict一样。
find和contains
如果不存在find返回容器.end()
判断一个key是否存在,contains返回bool值
[]操作符
如果key不存在,不管是否对value赋值,[]操作符都会创建一个新元素。
hashmap1[9]; // 这里没有赋值,但如果原来没有等于9的key,也会创建一个新元素
insert
insert前记得make_pair()
std::pair
访问时
如果key不存在,at会抛出异常std::out_of_range
如果key不存在,operator[]会创建新元素,并调用默认构造函数初始化value
插入时
如果一个key存在, operator[] 对这个key-value进行重写
如果一个key存在, insert 不会对原来的key-value进行重写,返回值中包含是否插入成功的信息(有重复元素会插入失败)。
其他
通用的容器基础操作
emplace_back和push_back,emplace和insert
push_back接受临时对象时,需要先构造,再移动 / 复制(移动优先于复制,当没有移动构造函数时使用复制构造函数)
emplace_back直接在目标地址构造,其参数为构造函数的参数。
insert() 函数的功能是在 vector 容器的指定位置插入一个或多个元素。
emplace() 是 C++ 11 标准新增加的成员函数,用于在 vector 容器指定位置插入一个新的元素。其参数第一位是迭代器指示插入位置,后面的参数就是构造函数的参数。
与前面两个函数类似,接受临时对象时emplace也是直接在目标地址构造,insert需要先构造再移动或拷贝。
迭代器操作
在gdb中直接p xxx.begin()显示的是*xxx.begin()的值
如果要查看迭代器的地址需要p it._M_current
distance, advance, next
std::distance返回迭代器或指针之间的距离。
distance(A.begin(), A.end())
advance修改迭代器it让它前进n个单位,没有返回值。如果是随机访问容器,只用执行一次迭代器加法;顺序访问容器需要执行n次it++或it—。
advance(it, n)
next(it, n)返回让迭代器it前进n个单位后的迭代器
swap_iter
交换迭代器指向地址的值,swap_iter(it1, it2)相当于swap(it1, it2)
std::make_reverse_iterator
将一个正向迭代器变成反向迭代器,注意转换之后指向的元素变成了前面一个元素
equal, mismatch
输入两个序列,如果两个序列的内容完全相同或匹配返回true。
输入两个序列,返回第一个不匹配的位置两个序列的元素的迭代器组成的pair。第二个序列可以比第一个序列长。
begin, end
对容器使用返回迭代器;也可以对数组使用,返回指针。
int arr1[] = {1, 2, 3}
end(arr1) - begin(arr1); // 3
vector<int> arr2{1, 2, 3};
arr2.end() - arr2.begin(); //3


三种反向迭代的方法
// use reverse_iterator by for loop
for(vector<int>::reverse_iterator r_iter = ivec.rbegin(); r_iter != ivec.rend(); ++r_iter)
cout << *r_iter << " ";
// use ordinary iterator to print reversely
for(vector<int>::const_iterator iter = (--ivec.end()); iter >= ivec.begin();iter--) {
cout << *iter << " ";
}
// use reverse_iterator with copy() algorithm
copy(ivec.rbegin(), ivec.rend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
pair
tuple
需要#include
使用get<常量表达式>(tuple_name)来访问或修改tuple的元素(返回引用)
tuple<int,double,string> t3 = {1, 2.0, "3"};
get<0>(t3) = 4;
cout << get<1>(t3) << endl;
//output: 2
tie
需要#include
std::tie会将变量的引用整合成一个tuple,从而实现批量赋值。
tuple<int,double,string> t3 = {1, 2.0, "3"};
int i; double d; string s;
tie(i, d, s) = t3;
cout << i << " " << d << " " << s << endl;
还可以使用std::ignore忽略某些tuple中的某些返回值,如
tie(i, ignore, s) = t3;
与tie等效的语法:
const auto [i, d, s] = t3;
copy函数
int myints[]={10,20,30,40,50,60,70};
std::vector<int> myvector (7);
std::copy ( myints, myints+7, myvector.begin() );
//myvector:10 20 30 40 50 60 70
不同容器相互转换
从向量建立集合,再用集合给向量赋值
vector<int> vec = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 9, 3, 2, 1, 0, 4, 8 };
set<int> st(vec.begin(), vec.end());
vec.assign(st.begin(), st.end());
// vec = {0 1 2 3 4 8 9}
遍历容器的同时删除元素
erase和for循环一起使用时一定要注意,erase本身就相当于一次操作,而for循环在执行循环条件判断前也会执行increment操作。尽量和while一起用,并且用if来判断如果执行erase操作就不要对循环变量执行操作。
https://blog.csdn.net/zymill/article/details/79836586
对于节点式容器(map, list, set)元素的删除,插入操作会导致指向该元素的迭代器失效,其他元素迭代器不受影响
std::map<int, struct> mapInfo; ... std::map<int, struct>::iterator it = mapInfo.begin(); while (it != mapInfo.end()) { if (...) { // 删除节点的同时,对迭代器进行后移的操作,因为其他元素不会失效 mapInfo.erase(it++); } else { it++; } }对于顺序式容器(vector,string,deque)元素的删除、插入操作会导致指向该元素以及后面的元素的迭代器失效
std::vector<int> arrayInt; ... std::vector<int>::iterator it = arrayInt.begin(); while (it != arrayInt.end()) { if (...) { // 需要注意的是,因为顺序式容器会使本身和后面的元素迭代器都失效,所以不能简单的++操作 // 顺序式容器的erase()会返回紧随被删除元素的下一个元素的有效迭代器(节点式容器的erase()的返回值是void) it = arrayInt.erase(it); } else { it++; }Algorithm
排序 / partition / 查找 / 统计
sort, stable_sort
vector重载了比较符”<”, “>”, “=”。两个vector的大小比较类似于左对齐的数字大小比较,首位大的vector更大,前几位相同的话,长的vector大,两个vector完全相同时才相等。
partition
使前面的元素全是true,后边的元素全部是false,可用于快排
template <class ForwardIt> void quicksort(ForwardIt first, ForwardIt last) { if(first == last) return; auto pivot = *std::next(first, std::distance(first,last)/2); ForwardIt middle1 = std::partition(first, last, [pivot](const auto& em){ return em < pivot; }); ForwardIt middle2 = std::partition(middle1, last, [pivot](const auto& em){ return !(pivot < em); }); quicksort(first, middle1); quicksort(middle2, last); }is_partitioned
前面的元素全是true,后边的元素全部是false时返回true,否则返回false
The behavior of this function template is equivalent to:template <class InputIterator, class UnaryPredicate> bool is_partitioned (InputIterator first, InputIterator last, UnaryPredicate pred) { while (first!=last && pred(*first)) { ++first; } while (first!=last) { if (pred(*first)) return false; ++first; } return true; }nth_element
执行partition操作,第二个参数指定一个位置,patition之后这个位置上的数为第k大的数,之前的数大于它,之后的数小于它
int main() { std::vector<int> v{5, 6, 4, 3, 2, 6, 7, 9, 3}; std::nth_element(v.begin(), v.begin() + v.size()/2, v.end()); std::cout << "The median is " << v[v.size()/2] << '\n'; std::nth_element(v.begin(), v.begin()+1, v.end(), std::greater<int>()); std::cout << "The second largest element is " << v[1] << '\n'; }lower_bound, upper_bound, binary_search
传入的容器需要已经用与传入比较函数相同的标准排好序,或者至少要根据key的值分成两半。
时间复杂度:对于随机访问容器时间复杂度为o(logn),对非随机访问容器时间复杂度为o(n)
lower_bound:返回不小于key的最左值(大于等于key的最小值)的指针/迭代器。如果没有返回end()。
upper_bound:返回key小于它的最左值(大于key的最小值)的指针/迭代器。如果没有返回end()。
binary_search:找到了key返回True,否则返回False
注意:自定义comp时,对于有两个元素以上元素的容器的大小比较,根据视情况决定要不要把a.first < b.first, a.second == b.second的情况当作a < b写进comp函数,只要有个元素不符合cmp定义的小于key,lower_bound就会停在那个元素上。而对于upper_bound,内部的判断用的是if(!(val<*it)) left=mid+1(只要key不小于mid就会向右移),会停在cmp定义的第一个key小于那个元素的位置。find, find_first_of
O(n)
从左到右搜索返回第一个等于val的值的迭代器,如果找不到返回end。p = std::find (myints, myints+4, 30);find_first_of返回第一个与给定序列中任一值相当或匹配的值的迭代器,如果找不到返回end。
find_if
search, find_end
O(n1n2)
从左到右搜索返回第一个匹配指定序列的子序列的首部迭代器,如果找不到返回end。可以自定义匹配函数。// set some values: haystack: 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 for (int i=1; i<10; i++) haystack.push_back(i*10); int needle1[] = {40,50,60,70}; std::vector<int>::iterator it; it = std::search (haystack.begin(), haystack.end(), needle1, needle1+4);find_end返回最后一个匹配指定序列的子序列首部迭代器,如果找不到返回end。
search_n
std::search_n查找区间内连续n个满足某一条件或者等于某一值的情况,并返回满足条件的第一个元素位置。
std::accumulate
求和、求乘积 ```cpp template< class InputIt, class T > constexpr T accumulate( InputIt first, InputIt last, T init );
template< class InputIt, class T, class BinaryOperation > constexpr T accumulate( InputIt first, InputIt last, T init, BinaryOperation op );
<a name="N0GSl"></a>
### max_element, min_element
得到最大元素<br />*max_element(A.begin(), A.end())<br />得到最大元素的位置:<br />std::min_element, std::max_element在algorithm头文件中,返回的是指向最小/最大元素的迭代器。<br />distance(A, max_element(A, A + N)) //for array<br />distance(A.begin(), max_element(A.begin(), A.end())) //for container
<a name="2GlLl"></a>
### count
```cpp
// counting elements in array:
int myints[] = {10,20,30,30,20,10,10,20}; // 8 elements
int mycount = std::count (myints, myints+8, 10);
std::cout << "10 appears " << mycount << " times.\n";
// counting elements in container:
std::vector<int> myvector (myints, myints+8);
mycount = std::count (myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), 20);
std::cout << "20 appears " << mycount << " times.\n";
排列组合
is_permutation
next_permutation, prev_permutation
原地操作,返回布尔值,代表是否操作成功(是否有下一个/前一个序列)
next_permutation的具体实现参考:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/next-permutation/solution/xia-yi-ge-pai-lie-by-leetcode-solution/
需要两遍扫描找到待交换的元素,交换两个元素,然后reverse后面的序列,得到下一个排列
堆
make_heap(), pop_heap(), push_heap(), sort_heap()
默认为大根堆
可以用array, vector, list, deque, forward_list作为底部容器
sort_heap会破坏堆
vector<int> x{3, 2, 4, 1, 5, 9};
make_heap(x.begin(), x.end(), less<int>);
print("after make_heap, x", x);
pop_heap:交换第一个元素和最后一个元素,调整前n-1个元素作为新的堆
push_heap:将最后一个元素插入堆
sort_heap:反复调用pop_heap,使大根堆变成从小到大排序的序列
遍历、生成序列
all_of, any_of
功能类似于Python的any()和all()
从first迭代到last,对每个对象执行函数fn,要求fn是个一元布尔函数
返回true或者false
for_each
从first迭代到last,对每个对象执行函数fn,要求fn是个一元函数,可以传引用。
template<class InputIterator, class Function>
Function for_each(InputIterator first, InputIterator last, Function fn)
{
while (first!=last) {
fn (*first);
++first;
}
return fn; // or, since C++11: return move(fn);
}
generate, generate_n
// function generator:
int RandomNumber () { return (std::rand()%100); }
std::generate (myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), RandomNumber);
std::generate_n (myarray, 9, RandomNumber);
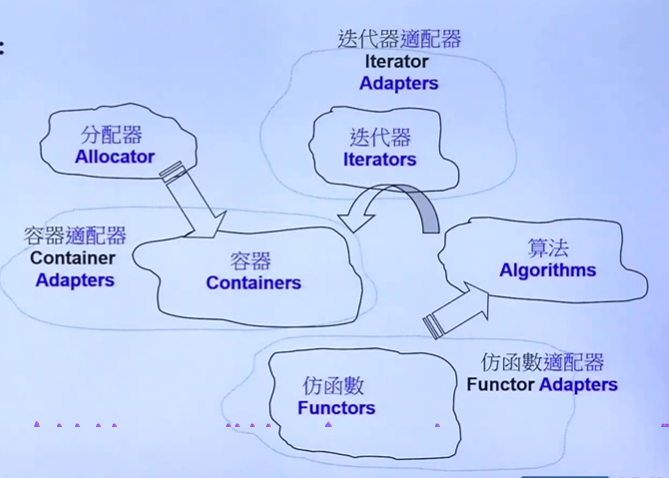
Allocator 分配器
Funtors仿函数 (Function Object)
调用时记得加()创建实例
less()
less_equal()
greater()
greater_equal()
Adapter适配器
Function Adapter函数适配器
std::function
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/heartchord/p/5017071.html
可包装普通函数、函数指针、仿函数、类成员函数、模板函数、模板类成员函数、lambda函数。
尖括号里表明返回值类型和参数类型。
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
T g_Minus(T i, T j)
{
return i - j;
}
int main()
{
function<int(int, int)> f = g_Minus<int>;
cout << f(1, 2) << endl; // -1
return 1;
}
std::bind
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
void f(int& n1, int& n2, const int& n3)
{
std::cout << "In function: " << n1 << ' ' << n2 << ' ' << n3 << '\n';
++n1; // increments the copy of n1 stored in the function object
++n2; // increments the main()'s n2
// ++n3; // compile error
}
int main()
{
int n1 = 1, n2 = 2, n3 = 3;
std::function<void()> bound_f = std::bind(f, n1, std::ref(n2), std::cref(n3));
n1 = 10;
n2 = 11;
n3 = 12;
std::cout << "Before function: " << n1 << ' ' << n2 << ' ' << n3 << '\n';
bound_f();
std::cout << "After function: " << n1 << ' ' << n2 << ' ' << n3 << '\n';
}
如果不用std::ref会按值绑定,记录声明时变量的值。
std::ref是T&,std::cref是const T&。
std::bind2nd
将adaptable binary funtion转换为unary function
#include <functional>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int numbers[] = {10,-20,-30,40,-50};
int cx;
cx = count_if ( numbers, numbers+5, bind2nd(less<int>(),0) );
平时碰不到的STL底层代码
迭代器
谓的 traits 编程技法无非就是利用模板参数推导机制,增加一层中间的模板 class,以解决获取迭代器的型别中的原生指针问题。利用一个中间层 iterator_traits 固定了 func 的形式,使得重复的代码大量减少,唯一要做的就是稍稍特化一下iterator_tartis 使其支持 pointer 和 const pointer 。
标准库中其他常用的头文件
std::accumulate
std::toupper
转换一个char字符变成大写