双指针
21:删除倒数第k个节点
:::info 题目:如果给定一个链表,请问如何删除链表中的倒数第k个节点?假设链表中节点的总数为n,那么1≤k≤n。要求只能遍历链表一次。例如,输入图4.1(a)中的链表,删除倒数第2个节点之后的链表如图4.1(b)所示。 :::
public class Node {public Node next;public int val;public Node(int val) {this.val = val;}}public class DeleteKNodeFromEnd() {public void deleteKNodeFromEnd(Node head, int k) {// 哨兵节点Node dummy = new Node(0);dummy.next = head;// 定义前后指针Node front = dummy;Node back = dummy;// 先走前指针k步for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) {front = frone.next;}// 再同时走前后指针,直到后指针走到最后一个节点while(front.next != null) {front = front.next;back = back.next;}// 删除back的下一个节点back.next = back.next.next;}}
22:链表中环的入口节点
:::info 题目:如果一个链表中包含环,那么应该如何找出环的入口节点?从链表的头节点开始顺着next指针方向进入环的第1个节点为环的入口节点。例如,在如图4.3所示的链表中,环的入口节点是节点3。 :::
/** Ant Group* Copyright (c) 2004-2024 All Rights Reserved.*/package algorithm.list;/*** @author jiaming* @version DetectCycle22.java, v 0.1 2024年02月07日 11:44 jiaming*/public class DetectCycle22 {// 1. 先写一个辅助函数去找到链表中的环// 如果有环,则返回环中的一个node,否则返回nullprivate static Node findLoopNode(Node head) {if(head == null) {return null;}Node fast = head;Node slow = head;int countSlowStep = 0;while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {// 移动快慢指针fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;countSlowStep++;// 如果有环,快慢指针终究会相遇(本质上是套圈了)if (fast == slow) {return fast;}}// 如果最终退出循环了,且快慢指针没有相遇,那就是没有环,返回nullreturn null;}// 2. 找到环之后,可以确定环的长度k// 3. 再利用快慢指针,快指针先走环的长度k;然后快慢指针同时开始走,直到两者相遇,就是入口节点public static Node detectCycle(Node head) {// 找到环中的一个节点Node loopNode = findLoopNode(head);// 如果没有环直接退出if (loopNode == null) {return null;}// 计算环的长度Node p = loopNode.next;int loopLength = 1;while(p != loopNode) {loopLength++;p = p.next;}// 快慢指针找环的入口Node fast = head;Node slow = head;// 快指针先走loopLength// 这里解释一下,我们的目标是希望快慢指针在环的入口处相遇,那就是希望慢指针走到环的入口时,快指针刚好已经走完一圈了,那么两者就会相遇// 这样的情况下,快指针要比慢指针先多走一圈的长度// 其实这里的trick在于,环以外的长度两个指针都是要走的,所以步数差值的0,所以可以不考虑,甚至我们可以假设head就是环的起点for (int i = 0; i < loopLength; i++) {fast = fast.next;}// 快慢指针同时走,直到相遇,while(fast != slow) {fast = fast.next;slow = slow.next;}return fast;}public static Node detectCycleWithOutLength(Node head) {// loopNode为两个快慢指针相遇的节点// 此时,慢指针走了k步,快指针走了2k步,两者相差了k步// 这 k 步一定是环的长度的整数倍(本质是套圈的逻辑)// PS:其实不用考虑环之外的那一截,因为快慢指针都走过,所以不在差值之内// 所以2k也是环的长度的整数倍Node loopNode = findLoopNode(head);if (loopNode == null) {return null;}// 那接下来的思路就是再搞俩快慢指针// 快指针就在前面找到的环的一个节点上,慢指针从head开始// 此时的关键是,fast比slow多走的k步,k =慢指针走的步数(是环的周长的倍数)// 所以当slow走到入口的时候,fast一定也在入口节点Node fast = loopNode;Node slow = head;while (fast != slow) {fast = fast.next;slow = slow.next;}return fast;}public static void main(String[] args) {Node one = new Node(1);Node two = new Node(2);Node three = new Node(3);Node four = new Node(4);Node five = new Node(5);Node six = new Node(6);one.next = two;two.next = three;three.next = four;four.next = five;five.next = six;six.next = three;System.out.println("Node=" + detectCycle(one));System.out.println("Node=" + detectCycleWithOutLength(one));// six.next = one;// // System.out.println(detectCycle(one));// System.out.println("Node=" + detectCycleWithOutLength(one));// six.next = four;// // System.out.println(detectCycle(one));// System.out.println("Node=" + detectCycleWithOutLength(one));}}
23:两个链表的第1个重合节点‘
:::info 题目:输入两个单向链表,请问如何找出它们的第1个重合节点。例如,图4.5中的两个链表的第1个重合节点的值是4。 :::
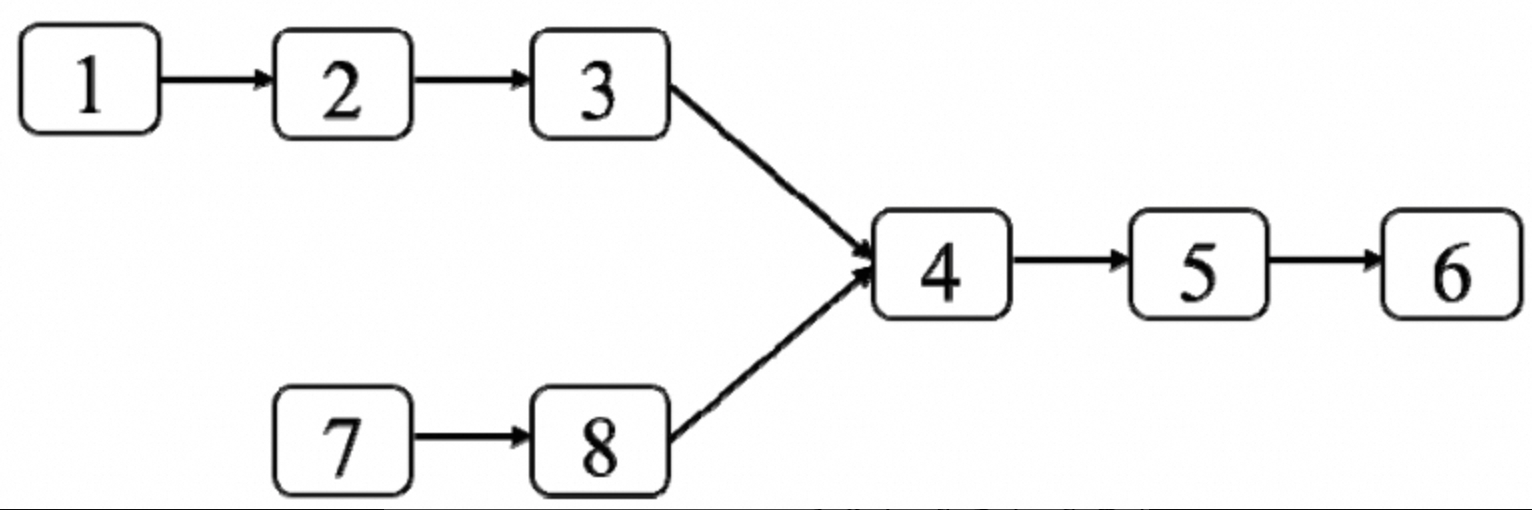
public class IntersectNode{public static Node getIntersectNode(Node headA, Node headB) {if(headA == null || headB == null) {return null;}int lengthA = getListLength(headA);int lengthB = getListLength(headB);Head long = lengthA > lengthB ? headA : headB;Head short = long == headA ? headB : headA;int diff = Math.abd(lengthA - lengthB);for(int i = 0; i < diff; i++) {long = long.next;}while(long != short) {long = long.next;short = short.next;}return short;}private static int getListLength(Node head) {Node p = head;int length = 0;while(p != null) {length++;p = p.next;}return length;}}
反转链表
24:反转链表
:::info 题目:定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头节点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头节点。例如,把图4.8(a)中的链表反转之后得到的链表如图4.8(b)所示。 :::
public class ReverseList {public static Node reverseList(Node head) {Node pre = null;Node cur = head;while(cur != null) {// 保存下一个节点Node next = cur.next;// 反转当前节点cur.next = pre;// 更新cur 和 prepre = cur;cur = next;}// cur 是 null, pre是最后一个节点return pre;}}
25:链表中的数字相加
:::info 题目:给定两个表示非负整数的单向链表,请问如何实现这两个整数的相加并且把它们的和仍然用单向链表表示?链表中的每个节点表示整数十进制的一位,并且头节点对应整数的最高位数而尾节点对应整数的个位数。例如,在图4.10(a)和图4.10(b)中,两个链表分别表示整数123和531,它们的和为654,对应的链表如图4.10(c)所示。 :::
public class AddTwoNumbers {public static Node addTwoNumbers(Node headA, Node headB) {// 反转两个链表Node x = reverseList(headA);Node y = reverseList(headB);// 记录新链表的Node dummy = new Node(0);Node cur = dummy;// 从个位数相加int carry = 0;while(x!=null || y!=null) {Node node = new Node;int sum = 0;if(x != null) {sum += x.val;}if(y != null) {sum += y.val;}sum += carry;// 计算新的carrycarry = sum / 10;// 计算当前位的值node.val = sum%10;cur.next = node;cur = node;}if(carry != 0) {cur.next = new Node(carry);}Node newHead = dummy.next;return reverseList(newHead);}}
26:重排链表
:::info 问题:给定一个链表,链表中节点的顺序是L0→L1→L2→…→Ln-1→Ln,请问如何重排链表使节点的顺序变成L0→Ln→L1→Ln-1→L2→Ln-2→…?例如,输入图4.12(a)中的链表,重排之后的链表如图4.12(b)所示。 :::
public class reorderList {private static Node reorderList(Node head) {if(head == null || head.next == null) {return head;}// 找到链表中间节点;Node middle = findMiddleNode(head);// 将链表分成前后两半,并反转后一半的链表;Node secondHalf = middle.next;middle.next = null;secondHalf = reverseList(secondHalf);// 拼接链表Node x = head;Node y = secondHalf;while(x != null && y != null) {Node xNext = x.next;Node yNext = y.next;x.next = y;y.next = xNext;x = xNext;y = yNext;}return head;}private static Node reverseList(Node head) {if (head == null) {return null;}Node pre = null;Node cur = head;while(cur != null) {// 保存下一个节点Node next = cur.next;// 反转链表cur.next = pre;// 更新指针pre = cur;cur = next;}return pre;}private static Node findMiddleNode(Node head) {if(head == null) {return null;}Node dummy = new Node(0);dummy.next = head;Node fast = dummy;Node slow = dummy;while(fast != null && fast.next !=null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}System.out.println(slow);return slow;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};Node head = AlgorithmUtils.constructNode(nums);AlgorithmUtils.printListNode(reorderList(head));}}
27:回文链表
:::info 问题:如何判断一个链表是不是回文?要求解法的时间复杂度是O(n),并且不得使用超过O(1)的辅助空间。如果一个链表是回文,那么链表的节点序列从前往后看和从后往前看是相同的。例如,图4.13中的链表的节点序列从前往后看和从后往前看都是1、2、3、3、2、1,因此这是一个回文链表。 :::
public class palindromeList(Node head) {public static boolean checkPalindromeList(Node head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return true;}// 将链表分成前后两半Node slow = head;Node fast = head.next;// 这个循环条件,能让前一半比较短while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}// 如果链表总程度是奇数 fast == nullNode secondHalf;// 如果后一半比较长,说明链表长度是奇数,需要丢弃后一半的第一节点,也就是整个链表的最中间的节点if (fast.next != null) {// 把最中间的值丢弃secondHalf = slow.next.next;} else {secondHalf = slow.next;}slow.next = null;// 翻转前一半的链表head = reverseList(head);// 对比两条链表的节点是否一致Node x = head;Node y = secondHalf;while (x != null && y != null) {if (x.val != y.val) {return false;}x = x.next;y = y.next;}return x == null && y == null;}private Node findMiddleNode(Node head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return head;}Node dummy = new Node(0);dummy.next = head;Node fast = dummy;Node slow = dummy;while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}return slow;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 3, 2, 1};Node head = AlgorithmUtils.constructNode(nums);System.out.println(checkPalindromeList(head));int[] nums2 = {1, 2, 3, 2, 1};Node head2 = AlgorithmUtils.constructNode(nums2);System.out.println(checkPalindromeList(head2));int[] nums3 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 1};Node head3 = AlgorithmUtils.constructNode(nums3);System.out.println(checkPalindromeList(head3));}}
双向链表和循环链表
28:展平多级双向链表
:::info 问题:在一个多级双向链表中,节点除了有两个指针分别指向前后两个节点,还有一个指针指向它的子链表,并且子链表也是一个双向链表,它的节点也有指向子链表的指针。请将这样的多级双向链表展平成普通的双向链表,即所有节点都没有子链表。例如,图4.14(a)所示是一个多级双向链表,它展平之后如图4.14(b)所示。 :::
/*** 定义带child的双联表节点*/public class ChildNode {public ChildNode next;public ChildNode pre;public ChildNode child;public int val;public ChildNode(int val) {this.val = val;}public void link(ChildNode pre, ChildNode next, ChildNode child) {this.pre = pre;this.next = next;this.child = child;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return String.valueOf(val);}}
public Flatten {public static ChildNode flatten(ChildNode head) {flattenGetTail(head);return head;}/*** flatten子链表,并返回子链表的尾结点,用于接上当前节点的next*/private static ChildNode flattenGetTail(ChildNode head) {if (head == null) {return null;}ChildNode node = head;ChildNode tail = null;while (node != null) {ChildNode next = node.next;// 找子节点的tailif (node.child != null) {ChildNode child = node.child;// 递归获取子链表的尾结点ChildNode childTail = flattenGetTail(child);// 处理当前节点node.next = node.child;node.child = null;// 处理child节点child.pre = node;// 处理子链表的tail节点childTail.next = next;// 处理next节点if (next != null) {next.pre = childTail;}// 返回子链表的tailtail = childTail;} else {// 如果没有子链表,tail就是自己tail = node;}// 继续处理下一个节点node = next;}return tail;}public static void main(String[] args) {ChildNode one = new ChildNode(1);ChildNode two = new ChildNode(2);ChildNode three = new ChildNode(3);ChildNode four = new ChildNode(4);ChildNode five = new ChildNode(5);ChildNode six = new ChildNode(6);ChildNode seven = new ChildNode(7);ChildNode eight = new ChildNode(8);ChildNode nine = new ChildNode(9);one.link(null, two, null);two.link(one, three, five);three.link(two, four, null);four.link(three, null, null);five.link(null, six, null);six.link(five, seven, eight);seven.link(six, null, null);eight.link(null, nine, null);nine.link(eight, null, null);AlgorithmUtils.printListChildNode(flatten(one));}}
29:排序的循环链表
:::info 问题:在一个循环链表中节点的值递增排序,请设计一个算法在该循环链表中插入节点,并保证插入节点之后的循环链表仍然是排序的。例如,图4.15(a)所示是一个排序的循环链表,插入一个值为4的节点之后的链表如图4.15(b)所示。 :::
public class insert {public static Node insert(Node head, Node node) {if (head == null) {head = node;head.next = head;} else if (head.next == null) {head.next = node;node.next = head;} else {insertCore(head, node);}return head;}private static void insertCore(Node head, Node node) {Node cur = head;Node biggest = head;// 循环的条件是前后节点的大小不符合,且还未走一圈回到headwhile (!(cur.val <= node.val && cur.next.val >= node.val) && cur.next != head) {cur = cur.next;if (cur.val > biggest.val) {biggest = cur;}}if (cur.val <= node.val && cur.next.val >= node.val) {Node next = cur.next;cur.next = node;node.next = next;} else {node.next = biggest.next;biggest.next = node;}}public static void main(String[] args) {// int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};// Node head = AlgorithmUtils.constructNode(nums);//// Node tail = head;// while(tail.next != null) {// tail = tail.next;// }// tail.next = head;//// insert(head, new Node(3));// AlgorithmUtils.printListCycleNode(head);Node head = null;AlgorithmUtils.printListCycleNode(insert(head, new Node(3)));// Node head = new Node(4);// AlgorithmUtils.printListCycleNode(insert(head, new Node(3)));// int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};// Node head = AlgorithmUtils.constructNode(nums);//// Node tail = head;// while(tail.next != null) {// tail = tail.next;// }// tail.next = head;//// insert(head, new Node(8));// AlgorithmUtils.printListCycleNode(head);}}

