class 可以理解为构造函数的语法糖。
关于这篇主要掌握相关的语法,最重要的是使用场景。
1、class创建
class ClassSelf {constructor(name,age,lang){this.name = name;this.age = age;this.lang = lang;this.a = 11;this.shot = function(){console.log('constructor',this.lang)}}shout(){console.log(this.lang)}}const cat = new ClassSelf('大咪',2,'喵喵');
cat值:
仅对于class ClassSelf 来说:
- constructor方法不用加function,且直接定义在了类的prototype里。
类的prototype不可枚举的( diff1:但构造函数是可以的)
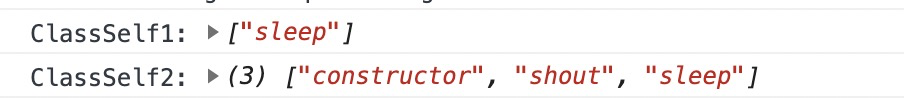
console.log('ClassSelf1:'Object.keys(ClassSelf.prototype))console.log('ClassSelf2:', Object.getOwnPropertyNames(ClassSelf.prototype))
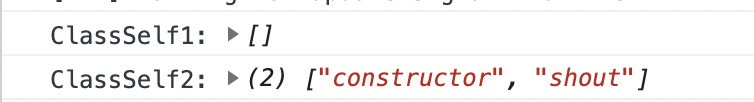
关于可枚举可简单理解为:Object.keys()可枚举构造函数的prototype,不可枚举class里的函数(虽说也是直接添加到了class的prototype里),但可枚举通过prototype、proto添加的属性。Object.getOwnPropertyNames()无论构造函数还是类都可以取出来可直接给类原型添加新方法
Object.assign(ClassSelf.prototype,{sleep(){}})
2、constructor
是类的默认方法,一个类必须有一个constructor()方法。如果没有显示定义,一个空的constructor()方法会被默认添加。
constructor默认返回实例对象(this),也可指定返回其他对象
constructor(name,age,lang){this.name = name;this.age = age;this.lang = lang;this.a = 11;this.shot = function(){console.log('constructor',this.lang)}return {test:1}}
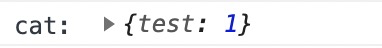
在使用 new生成实例时,会自动调用 constructor函数。
3、类的实例
类必须使用 new 命令生成实例对象,否则报错。( diff2:但构造函数可以不用new,构造函数可以当作普通函数,类不可以)。
- 实例的属性 除非显示定义在本身(即定义在this对象上),否则都是定义在原型上。
❓❎此处存疑:定义在this外的常量也在实例的属性上
解疑:constructor同级的属性 也是实例属性。
class ClassSelf {constructor(name,age,lang){this.name = name;this.age = age;this.lang = lang;this.a = 11;this.shot = function(){console.log('constructor',this.lang)}}b = 2; //!!!!!!!shout(){console.log(this.lang)}}const cat = new ClassSelf('大咪',2,'喵喵');console.log('cat: ',cat)console.log('cat Property: ',Object.getOwnPropertyNames(cat))console.log(cat.hasOwnProperty('b'))

- 所有的实例共享一个原型。使用proto可改写原型 ```javascript const cat = new ClassSelf(‘大咪’,2,’喵喵’); const cat1 = new ClassSelf(‘小咪’,22,’喵喵喵喵’)
cat.proto.say = function(){ console.log(‘say:’,this.name) } cat1.say()
<a name="p6kTo"></a>### 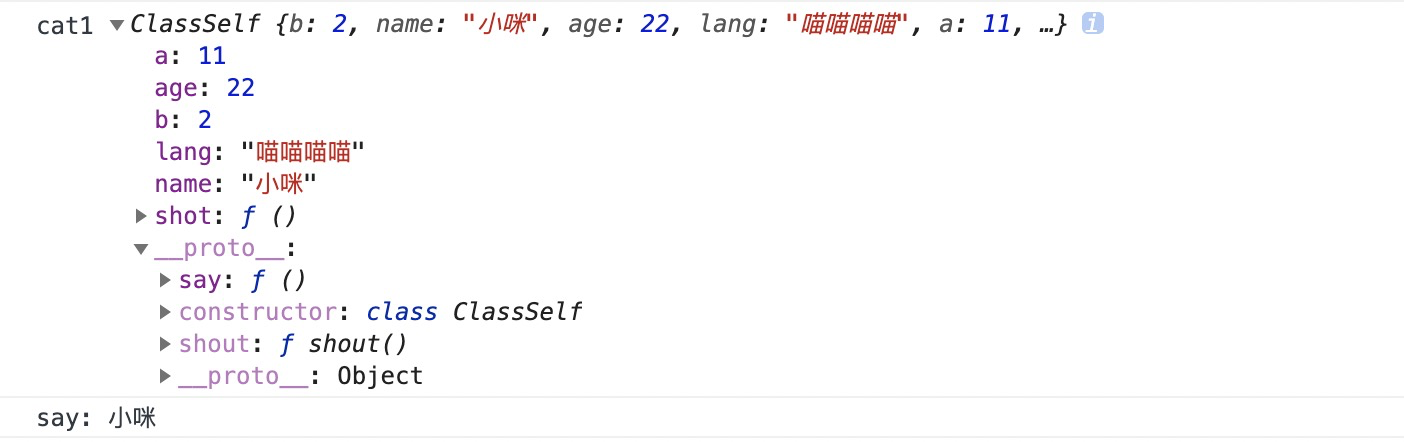<a name="dCcKe"></a>### 4 、get set对某个属性设置存值函数和取值函数,拦截该属性的存取行为。<br />官方解释如上,个人觉得是有点坑的,因为不小心就会会错意。<br />怎么滴个用法呢,如下。```javascriptclass ClassSelf {constructor(name,age,lang){this.age = age;}get _age(){return this.age + 'get'}set _age(value){this.age = value+"set"// this._age = value+"set" 报错 Uncaught RangeError: Maximum call stack size exceeded}}const cat = new ClassSelf('大咪',2,'喵喵');
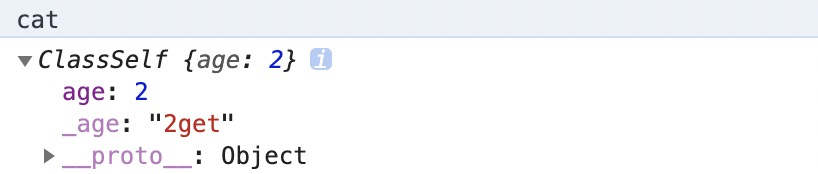
cat._age = 888

- 间接改变改变值,可以实现数据绑定。
- 通过get定义的属性,只要用户访问该属性就会触发这个get。通过set定义的属性,只要用户修改该属性的值,就会触发set。
❌下述写法会报错
class ClassSelf {constructor(name,age,lang){this.age = age;}get age(){return this.age + 'get'}set age(value){this.age = value + 'set'// return value + 'set' 或者这样}}
5、this
实例属性
- 定义在constructor()方法里面的this上面;
- 定义在类的最顶层
好处:看上去比较整洁
class ClassSelf {constructor(name,age,lang){//this上的都是实例属性this.name = name;this.age = age;this.lang = lang;this.a = 11;this.shot = function(){console.log('constructor',this.lang)}}b = 2; //实例属性}
静态方法
如果在一个方法前,加上static关键字,就表示该方法不会被实例继承,而是直接通过类来调用,这就称为“静态方法”。
class ClassSelf {constructor(name,age,lang){this.age = age;this.name = name;this.a = 11;}static see(){// console.log('a:',this.a)// console.log('name:',this.name)console.log('what do you look!')}}ClassSelf.see() //'what do you look!'cat.see() //报错:Uncaught TypeError: cat.see is not a function
- 关于静态方法里的this:指的是类,而不是实例。

- 静态方法和非静态方法可以重名。
-
静态属性
静态属性指的是 Class 本身的属性,即class.propName,而不是定义在实例对象(this)上的属性。 ```javascript class ClassSelf {
static s = ‘see’ //es6后的提案写法 }
ClassSelf.s = ‘see’;
<a name="Fa1Mq"></a>### 私有方法、私有属性私有方法和私有属性,是只能在类的内部访问的方法和属性,外部不能访问。<br />(ES6 不提供,只能通过变通方法模拟实现)<br />变通方法:```javascript//方法3:利用Symbol值的唯一性,将私有方法的名字命名为一个Symbol值const bar = Symbol('bar');const snaf = Symbol('snaf');class ClassSelf {// 公有方法foo (baz) {this._bar(baz);}// 私有方法//方法1:在命名上加以区别,不保险,在类的外部也可以调用_bar(baz) {return this.snaf = baz;}//方法2:私有方法移出类foo (baz) {bar.call(this, baz);}foo(baz) {//方法3:this[bar](baz);}[bar](baz) {// 私有方法return this[snaf] = baz;}//提案:方法是在属性名之前,使用#表示#count = 0;}//方法2:function bar(baz) {return this.snaf = baz;}