先记点简单的,再慢慢补充
函数声明
一个被函数声明创建的函数是一个Function对象,它具有Function对象的所有属性、方法和行为。
- 有原型的属性和方法,还有部分继承Object对象,可查看Function对象的详细信息
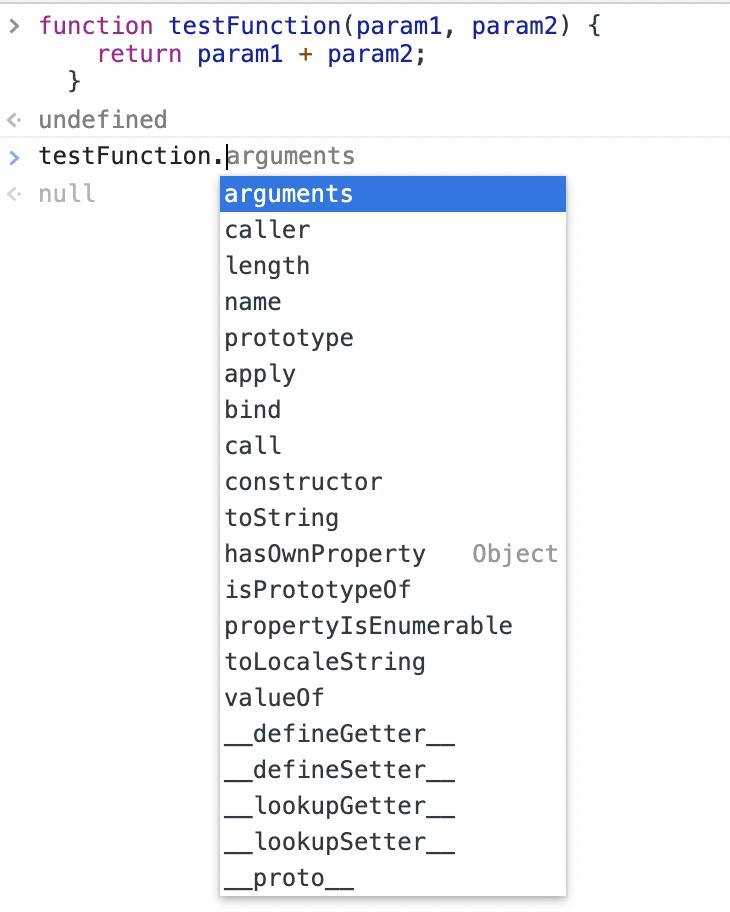
- xx
- 函数声明提升
可以在函数声明前使用函数
console.log('执行:',testFunction(6,7))function testFunction(param1, param2) {return param1 + param2;}
函数表达式
- 函数表达式没有提升,不可提前使用 ```javascript test1() //Uncaught ReferenceError: Cannot access ‘test1’ before initialization const test1 = function (){ return ‘test1’ }
2. **name**函数名称```javascriptlet function_expression = function [name]([param1[, param2[, ..., paramN]]]) {statements};
可省略。省略后就是匿名函数
const test1 = function (){return 'test1'}console.log(test1.name) // ‘test1’const test11 = test1console.log(test11.name) // ‘test1’
不省略
const test2 = function test(){return 1}console.log(test2.name) ‘test’test() //ReferenceError: test is not defined
直接调用名字,报错,没有一点b用。
被函数表达式赋值的变量 会有一个name属性。
如果把这个变量赋值给另一个变量,它的name属性值不会改变。
如果函数是匿名函数,它的name属性值是被赋值变量的名称(隐藏值)。
如果函数不是匿名函数,那么属性值就是这个函数的名称(显性值)。
(就像箭头函数,箭头函数没有名字要给赋予name属性一个隐性名)

