1.什么是AOP
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。
AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。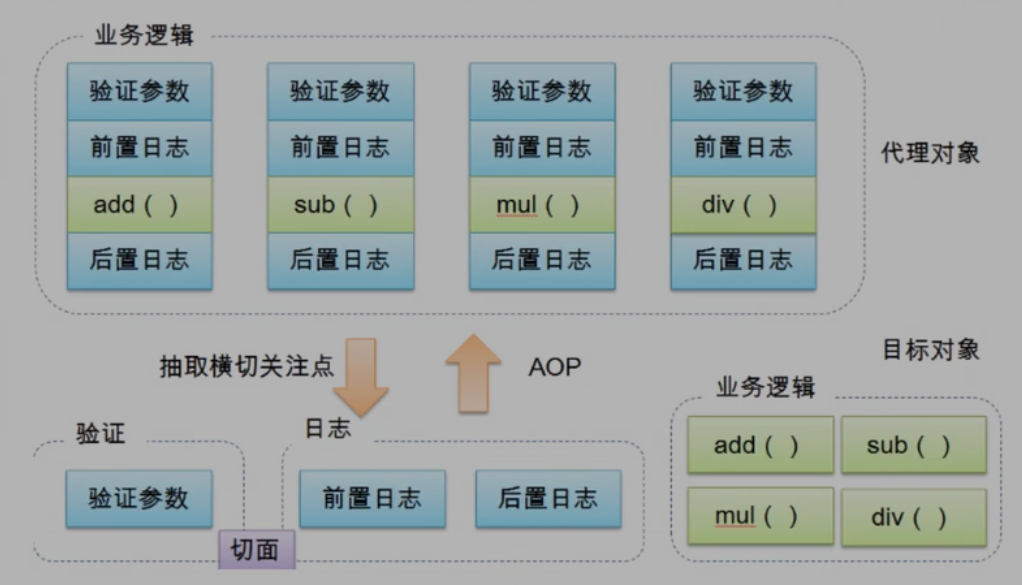
2.Aop在Spring中的作用
提供声明式事务;允许用户自定义切面 以下名词需要了解下:
- 横切关注点:跨越应用程序多个模块的方法或功能。即是,与我们业务逻辑无关的,但是我们需要关注的部分,就是横切关注点。如日志 , 安全 , 缓存 , 事务等等 ….
- 切**面(ASPECT**):横切关注点 被模块化 的特殊对象。即,它是一个类。
- 通知(Advice):切面必须要完成的工作。即,它是类中的一个方法。
- 目标(Target):被通知对象。
- 代理(Proxy):向目标对象应用通知之后创建的对象。
- 切入点(PointCut):切面通知 执行的 “地点”的定义。
- 连接点(JointPoint):与切入点匹配的执行点。
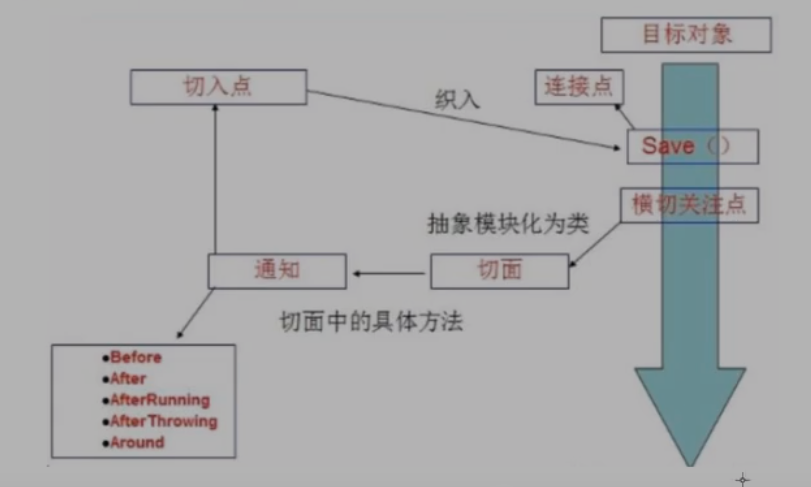
SpringAOP中,通过Advice定义横切逻辑,Spring中支持5种类型的Advice:
| 通知类型 | 连接点 | 实现接口 |
|---|---|---|
| 前置通知 | 方法前 | org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice |
| 后置通知 | 方法后 | org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice |
| 环绕通知 | 方法前后 | org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor |
| 异常抛出通知 | 方法抛出异常 | org.springframework.aop.ThrowsAdvice |
| 引介通知 | 类中增加新的方法属性 | org.springframework.aop.IntroductionInterceptor |
即 Aop 在 不改变原有代码的情况下 , 去增加新的功能 .
3.使用Spring实现Aop
【重点】使用AOP织入,需要导入一个依赖包!
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.aspectj/aspectjweaver --><dependency><groupId>org.aspectj</groupId><artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId><version>1.9.4</version></dependency>
3.1 通过 Spring API 实现
1.首先编写业务接口和实现类
接口类
package com.yuanzi.service;
/**
* @author yuanzi
* @description todo
* @create 2020-09-15 21:15
*/
public interface UserService {
void add();
void delete();
void update();
void select();
}
业务接
package com.yuanzi.service;
/**
* @author yuanzi
* @description todo
* @create 2020-09-15 21:16
*/
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
public void add() {
System.out.println("增加了一个用户");
}
public void delete() {
System.out.println("删除了一个用户");
}
public void update() {
System.out.println("更新了一个用户");
}
public void select() {
System.out.println("查找了一个用户");
}
}
2.编写增强类 , 一个前置增强 一个后置增强
package com.yuanzi.log;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
/**
* @author yuanzi
* @description todo
* @create 2020-09-15 21:19
*/
public class AfterLog implements AfterReturningAdvice {
/**
* @param method 要执行的目标对象的方法
* @param args 参数
* @param target 目标对象
* */
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("执行了" + method.getName() + "方法, 返回结果为: " + returnValue);
}
}
package com.yuanzi.log;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
/**
* @author yuanzi
* @description todo
* @create 2020-09-15 21:19
*/
public class BeforeLog implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
/**
* @param method 要执行的目标对象的方法
* @param args 参数
* @param target 目标对象
* */
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(target.getClass().getName()+ "的" + method.getName() + "被执行了");
}
}
3, 在spring的文件中注册 , 并实现aop切入实现 , 注意导入约束 .
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--注册bean-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.kuang.service.UserServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="log" class="com.kuang.log.Log"/>
<bean id="afterLog" class="com.kuang.log.AfterLog"/>
<!--aop的配置-->
<aop:config>
<!--切入点 expression:表达式匹配要执行的方法-->
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.kuang.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!--执行环绕; advice-ref执行方法 . pointcut-ref切入点-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="log" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="afterLog" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
4.测试
import com.yuanzi.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//动态代理代理的是接口
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.add();
}
}
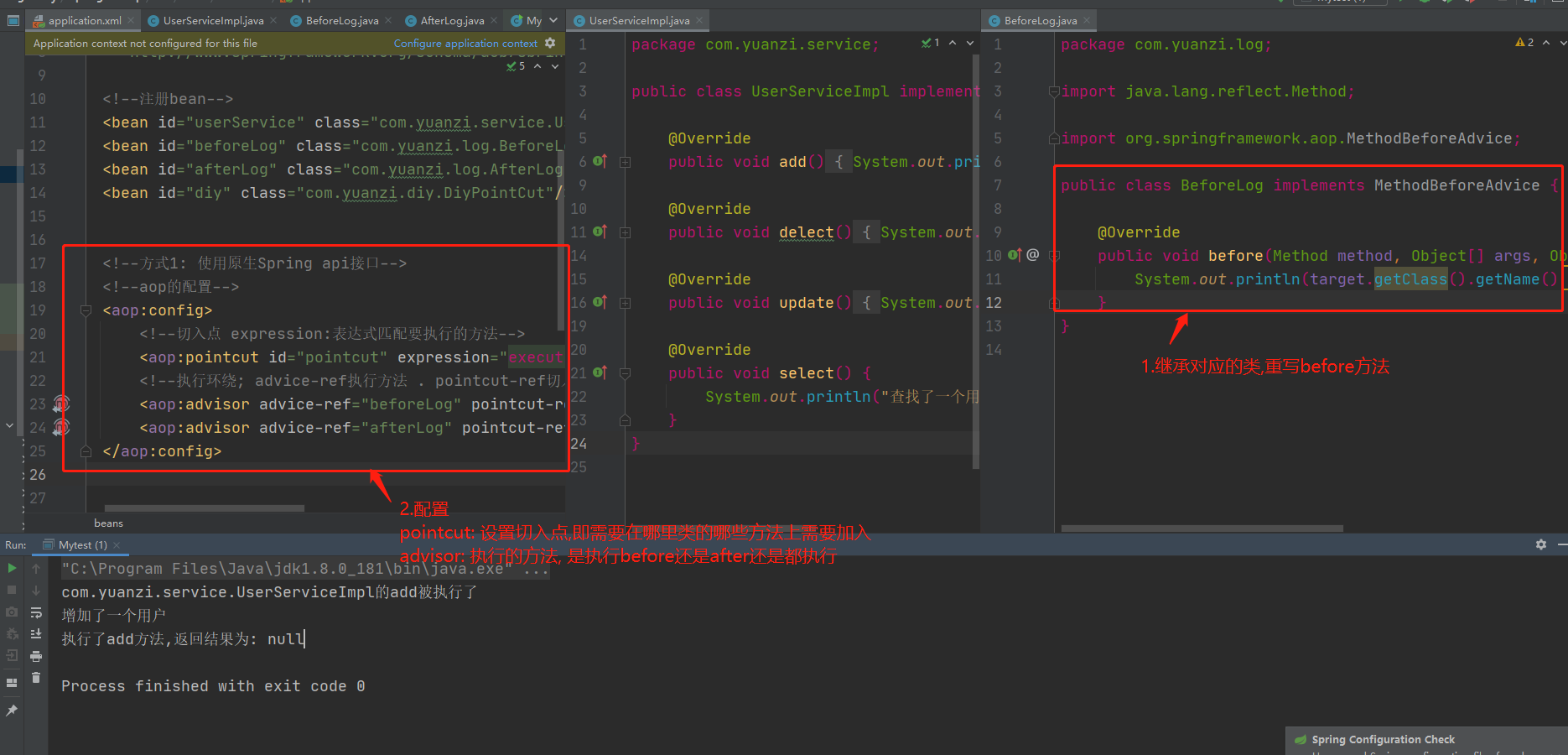
Spring的Aop就是将公共的业务 (日志 , 安全等) 和领域业务结合起来 , 当执行领域业务时 , 将会把公共业务加进来 . 实现公共业务的重复利用 . 领域业务更纯粹 , 程序猿专注领域业务 , 其本质还是动态代理 .
3.2 自定义类来实现Aop
1.编写自定义的类, 添加两个方法
package com.yuanzi.diy;
public class DiyPointCut {
public void before(){
System.out.println("------------方法执行前");
}
public void after(){
System.out.println("方法执行后------------");
}
}
2.添加配置
<!--方式2: 使用自定义类-->
<aop:config>
<!--自定义切面, ref 要引用的类-->
<aop:aspect ref="diy">
<!--切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="point" expression="execution(* com.yuanzi.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!--通知-->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="point"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="point"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
3.测试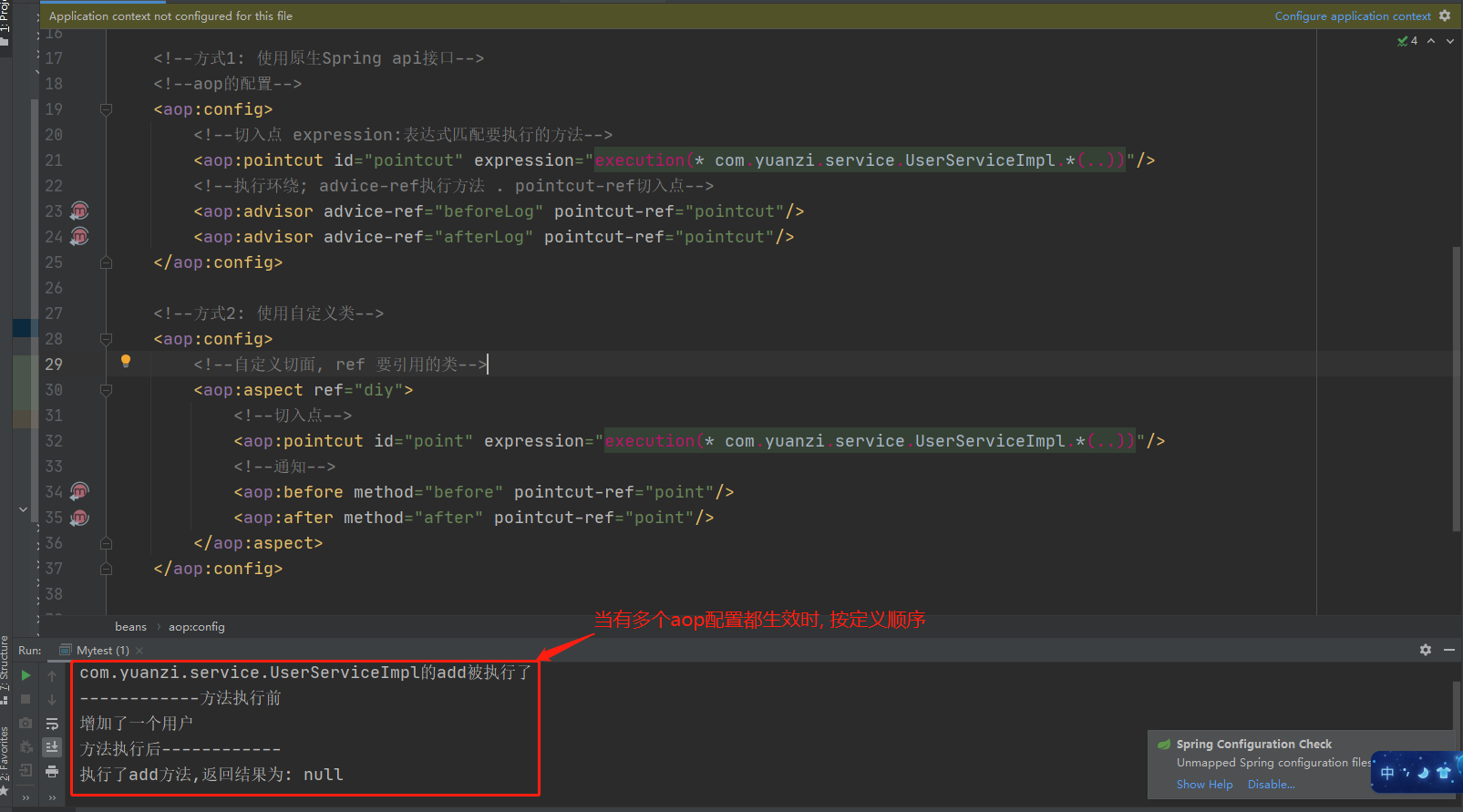
和python的装饰器有点像
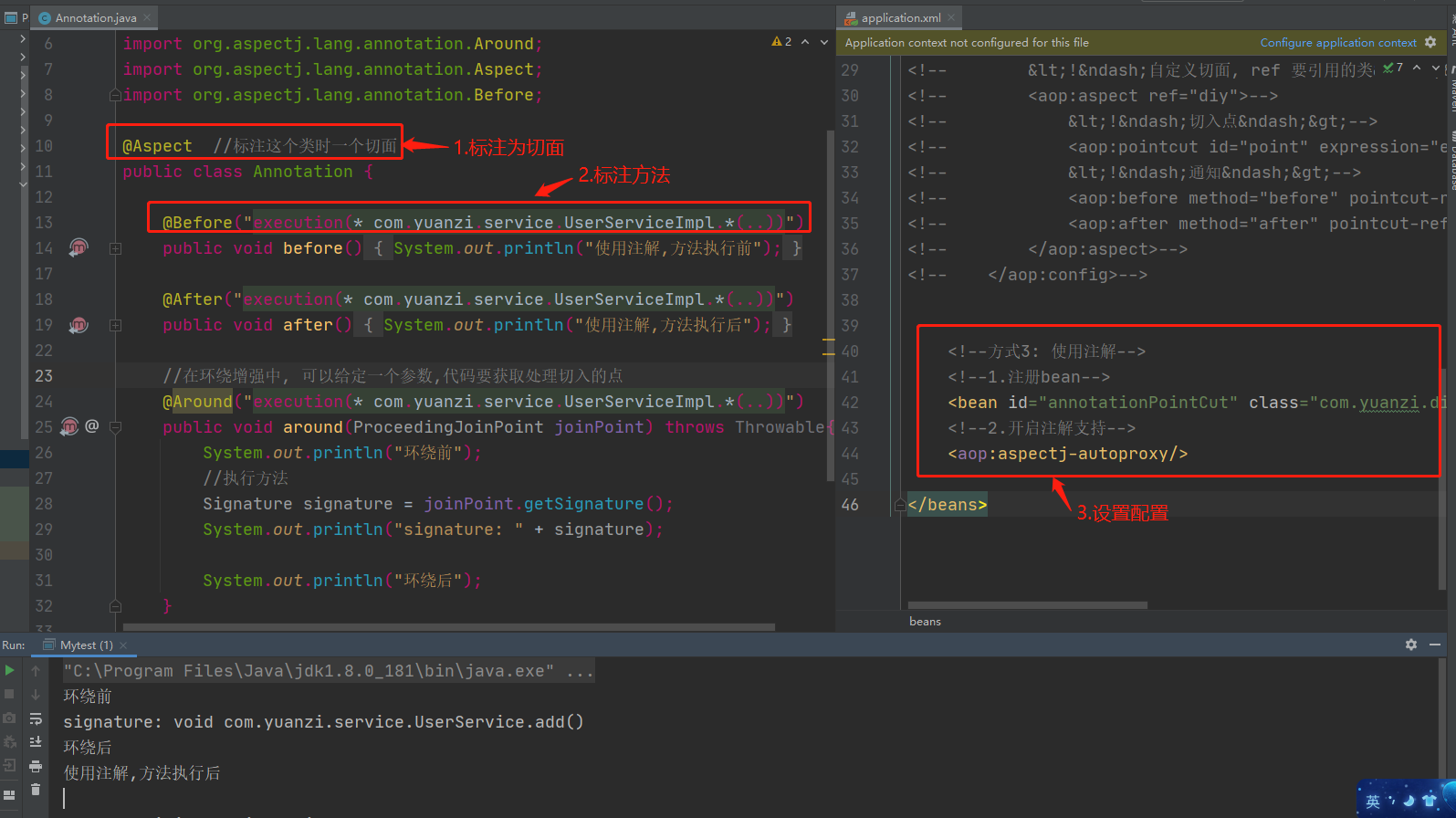
3.3 使用注解实现
1.用注解标注类为一个切面
package com.yuanzi.diy;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
@Aspect //标注这个类时一个切面
public class Annotation {
@Before("execution(* com.yuanzi.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before(){
System.out.println("使用注解,方法执行前");
}
@After("execution(* com.yuanzi.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after(){
System.out.println("使用注解,方法执行后");
}
//在环绕增强中, 可以给定一个参数,代码要获取处理切入的点
@Around("execution(* com.yuanzi.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("环绕前");
//执行方法
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("signature: " + signature);
System.out.println("环绕后");
}
}
2.开启配置
<!--方式3: 使用注解-->
<!--1.注册bean-->
<bean id="annotationPointCut" class="com.yuanzi.diy.Annotation"/>
<!--2.开启注解支持-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
3.测试