IoU(Intersection over Union),又称重叠度/交并比。
1 NMS:当在图像中预测多个proposals、pred bboxes时,由于预测的结果间可能存在高冗余(即同一个目标可能被预测多个矩形框),因此可以过滤掉一些彼此间高重合度的结果;具体操作就是根据各个bbox的score降序排序,剔除与高score bbox有较高重合度的低score bbox,那么重合度的度量指标就是IoU;
2 mAP:得到检测算法的预测结果后,需要对pred bbox与gt bbox一起评估检测算法的性能,涉及到的评估指标为mAP,那么当一个pred bbox与gt bbox的重合度较高(如IoU score > 0.5),且分类结果也正确时,就可以认为是该pred bbox预测正确,这里也同样涉及到IoU的概念;
提到IoU,大家都知道怎么回事,讲起来也都头头是道,我拿两个图示意下(以下两张图都不是本人绘制):
IOU = gt bbox、pred bbox交集的面积 / 二者并集的面积
候选框为pre,真实框为gt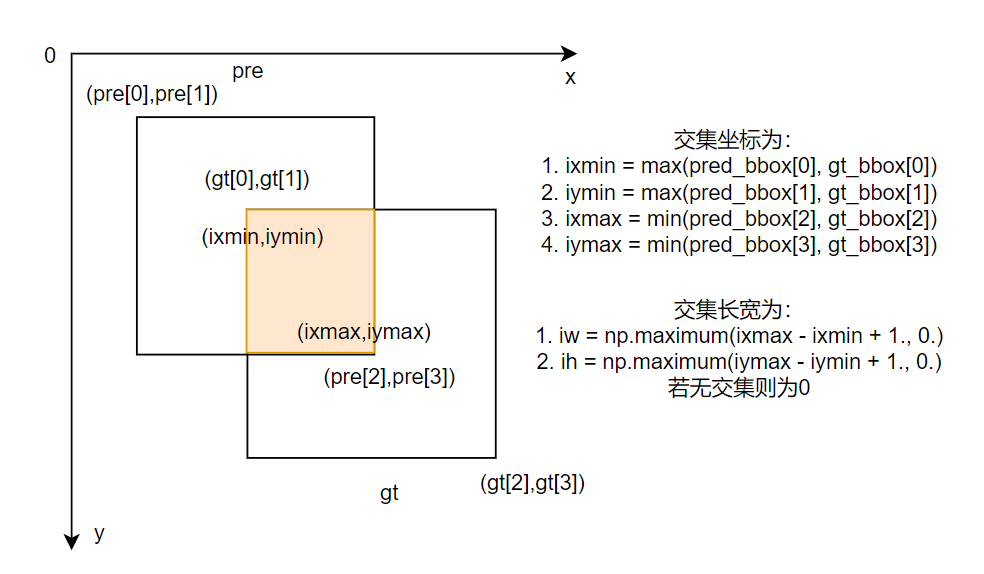
代码实现:
from __future__ import print_function, absolute_importimport numpy as npdef get_IoU(pred_bbox, gt_bbox):# bbox should be valid, actually we should add more judgements, just ignore here...# assert ((abs(pred_bbox[2] - pred_bbox[0]) > 0) and# (abs(pred_bbox[3] - pred_bbox[1]) > 0))# assert ((abs(gt_bbox[2] - gt_bbox[0]) > 0) and# (abs(gt_bbox[3] - gt_bbox[1]) > 0))# -----0---- get coordinates of intersixmin = max(pred_bbox[0], gt_bbox[0])iymin = max(pred_bbox[1], gt_bbox[1])ixmax = min(pred_bbox[2], gt_bbox[2])iymax = min(pred_bbox[3], gt_bbox[3])iw = np.maximum(ixmax - ixmin + 1., 0.)ih = np.maximum(iymax - iymin + 1., 0.)# -----1----- intersectioninters = iw * ih# -----2----- union, uni = S1 + S2 - intersuni = ((pred_bbox[2] - pred_bbox[0] + 1.) * (pred_bbox[3] - pred_bbox[1] + 1.) +(gt_bbox[2] - gt_bbox[0] + 1.) * (gt_bbox[3] - gt_bbox[1] + 1.) -inters)# -----3----- iouoverlaps = inters / unireturn overlapsdef get_max_IoU(pred_bboxes, gt_bbox):"""given 1 gt bbox, >1 pred bboxes, return max iou score for the given gt bbox and pred_bboxes:param pred_bbox: predict bboxes coordinates, we need to find the max iou score with gt bbox for these pred bboxes:param gt_bbox: ground truth bbox coordinate:return: max iou score"""# bbox should be valid, actually we should add more judgements, just ignore here...# assert ((abs(gt_bbox[2] - gt_bbox[0]) > 0) and# (abs(gt_bbox[3] - gt_bbox[1]) > 0))if pred_bboxes.shape[0] > 0:# -----0---- get coordinates of inters, but with multiple predict bboxesixmin = np.maximum(pred_bboxes[:, 0], gt_bbox[0])iymin = np.maximum(pred_bboxes[:, 1], gt_bbox[1])ixmax = np.minimum(pred_bboxes[:, 2], gt_bbox[2])iymax = np.minimum(pred_bboxes[:, 3], gt_bbox[3])iw = np.maximum(ixmax - ixmin + 1., 0.)ih = np.maximum(iymax - iymin + 1., 0.)# -----1----- intersectioninters = iw * ih# -----2----- union, uni = S1 + S2 - intersuni = ((gt_bbox[2] - gt_bbox[0] + 1.) * (gt_bbox[3] - gt_bbox[1] + 1.) +(pred_bboxes[:, 2] - pred_bboxes[:, 0] + 1.) * (pred_bboxes[:, 3] - pred_bboxes[:, 1] + 1.) -inters)# -----3----- iou, get max score and max iou indexoverlaps = inters / uniovmax = np.max(overlaps)jmax = np.argmax(overlaps)return overlaps, ovmax, jmaxif __name__ == "__main__":# test1pred_bbox = np.array([50, 50, 90, 100]) # top-left: <50, 50>, bottom-down: <90, 100>, <x-axis, y-axis>gt_bbox = np.array([70, 80, 120, 150])print (get_IoU(pred_bbox, gt_bbox))# test2pred_bboxes = np.array([[15, 18, 47, 60],[50, 50, 90, 100],[70, 80, 120, 145],[130, 160, 250, 280],[25.6, 66.1, 113.3, 147.8]])gt_bbox = np.array([70, 80, 120, 150])print (get_max_IoU(pred_bboxes, gt_bbox))

