第五章 共享模型之内存
本章内容
上一章讲解的 Monitor 主要关注的是访问共享变量时,保证临界区代码的原子性
这一章我们进一步深入学习共享变量在多线程间的【可见性】问题与多条指令执行时的【有序性】问题
5.1 Java内存模型
JMM 即 Java Memory Model,它定义了主存、工作内存抽象概念,底层对应着 CPU 寄存器、缓存、硬件内存、CPU 指令优化等。
JMM 体现在以下几个方面
- 原子性 - 保证指令不会受到线程上下文切换的影响
- 可见性 - 保证指令不会受 cpu 缓存的影响
-
5.2 可见性
退不出的循环
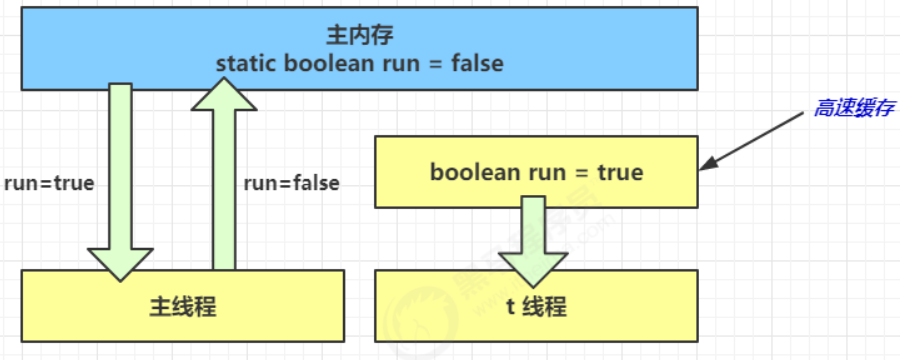
先来看一个现象,main 线程对 run 变量的修改对于 t 线程不可见,导致了 t 线程无法停止:
static boolean run = true;public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t = new Thread(()->{while(run){// ....}});t.start();sleep(1);run = false; // 线程t不会如预想的停下来}
为什么呢?分析一下:
- 初始状态, t 线程刚开始从主内存读取了 run 的值到工作内存。
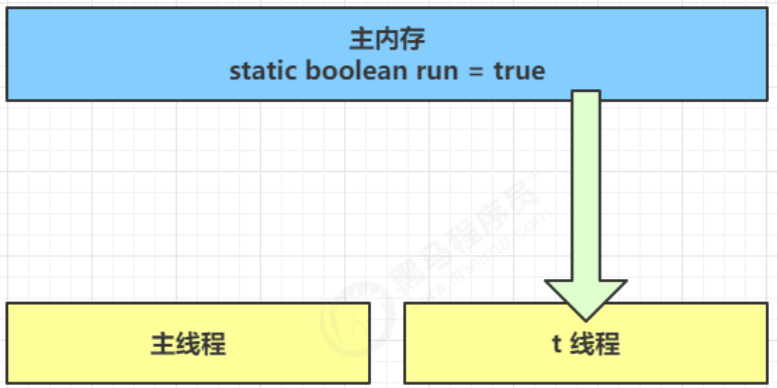
2. 因为 t 线程要频繁从主内存中读取 run 的值,JIT 编译器会将 run 的值缓存至自己工作内存中的高速缓存中,
减少对主存中 run 的访问,提高效率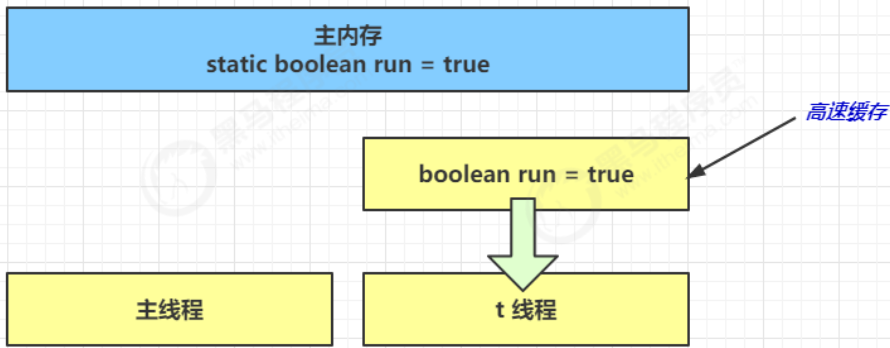
- 1 秒之后,main 线程修改了 run 的值,并同步至主存,而 t 是从自己工作内存中的高速缓存中读取这个变量
的值,结果永远是旧值
解决方法
volatile(易变关键字)
它可以用来修饰成员变量和静态成员变量,他可以避免线程从自己的工作缓存中查找变量的值,必须到主存中获取它的值,线程操作 volatile 变量都是直接操作主存
可见性 vs 原子性
前面例子体现的实际就是可见性,它保证的是在多个线程之间,一个线程对 volatile 变量的修改对另一个线程可见, 不能保证原子性,仅用在一个写线程,多个读线程的情况: 上例从字节码理解是这样的:(volatile可保证可见性,因此这种一个线程写,多个线程读非常适合,但是和synchronized比还是有很多不足,synchronized不仅可以保证可见性,还能保证原子性,我们看下面的例子)
getstatic run // 线程 t 获取 run truegetstatic run // 线程 t 获取 run truegetstatic run // 线程 t 获取 run truegetstatic run // 线程 t 获取 run trueputstatic run // 线程 main 修改 run 为 false, 仅此一次getstatic run // 线程 t 获取 run false
比较一下之前我们将线程安全时举的例子:两个线程一个 i++ 一个 i— ,只能保证看到最新值,不能解决指令交错
其中1和6,7,8是一个线程,2,3,4,5是另外一个线程。我们看到指令1读到0,指令2读到0,然后线程2一顿操作。在指令5时,此时是线程1,其还是在指令1的基础上操作的,即还是在0的基础上操作的,纵使你加了volatile,但是呢?你已经读过了。因此这里用synchronized更好,用volatile无法保证原子性
// 假设i的初始值为0getstatic i // 线程2-获取静态变量i的值 线程内i=0getstatic i // 线程1-获取静态变量i的值 线程内i=0iconst_1 // 线程1-准备常量1iadd // 线程1-自增 线程内i=1putstatic i // 线程1-将修改后的值存入静态变量i 静态变量i=1iconst_1 // 线程2-准备常量1isub // 线程2-自减 线程内i=-1putstatic i // 线程2-将修改后的值存入静态变量i 静态变量i=-1
注意 synchronized 语句块既可以保证代码块的原子性,也同时保证代码块内变量的可见性。但缺点是synchronized 是属于重量级操作,性能相对更低 如果在前面示例的死循环中加入 System.out.println() 会发现即使不加 volatile 修饰符,线程 t 也能正确看到对 run 变量的修改了,想一想为什么? 因为 printIn() 方法使用了 synchronized 同步代码块,可以保证原子性与可见性,它是 PrintStream 类的方法。
原理之CPU缓存架构
模式之两阶段终止
模式之Balking
5.3 有序性
JVM 会在不影响正确性的前提下,可以调整语句的执行顺序,思考下面一段代码
static int i;static int j;// 在某个线程内执行如下赋值操作i = ...;j = ...;
可以看到,至于是先执行 i 还是 先执行 j ,对最终的结果不会产生影响。所以,上面代码真正执行时,既可以是
i = ...;j = ...;
也可以是
j = ...;i = ...;
这种特性称之为『指令重排』,多线程下『指令重排』会影响正确性。为什么要有重排指令这项优化呢?从 CPU
执行指令的原理来理解一下吧
原理之指令级并行
诡异的结果
int num = 0;boolean ready = false;// 线程1 执行此方法public void actor1(I_Result r) {if(ready) {r.r1 = num + num;} else {r.r1 = 1;}}// 线程2 执行此方法public void actor2(I_Result r) {num = 2;ready = true;}
I_Result 是一个对象,有一个属性 r1 用来保存结果,问,可能的结果有几种?
有同学这么分析
情况1:线程1 先执行,这时 ready = false,所以进入 else 分支结果为 1
情况2:线程2 先执行 num = 2,但没来得及执行 ready = true,线程1 执行,还是进入 else 分支,结果为1
情况3:线程2 执行到 ready = true,线程1 执行,这回进入 if 分支,结果为 4(因为 num 已经执行过了)
但我告诉你,结果还有可能是 0 😁😁😁,信不信吧!
这种情况下是:线程2 执行 ready = true,切换到线程1,进入 if 分支,相加为 0,再切回线程2 执行 num = 2
相信很多人已经晕了 😵😵😵
我这里有一个疑问,就是可见性,线程2修改了ready,线程1可以看到吗?我个人认为是可以看到,为什么?因为线程1只会取1次ready值,如果线程2没改前取,那就是false,之后就是true,都是从主内存取的,因为只是一次,没有进入工作内存取的可能。
这种现象叫做指令重排,是 JIT 编译器在运行时的一些优化,这个现象需要通过大量测试才能复现:
借助 java 并发压测工具 jcstress https://wiki.openjdk.java.net/display/CodeTools/jcstress
mvn archetype:generate -DinteractiveMode=false -DarchetypeGroupId=org.openjdk.jcstress -DarchetypeArtifactId=jcstress-java-test-archetype -DarchetypeVersion=0.5 -DgroupId=cn.itcast -DartifactId=ordering -Dversion=1.0
创建 maven 项目,提供如下测试类
@JCStressTest@Outcome(id = {"1", "4"}, expect = Expect.ACCEPTABLE, desc = "ok")@Outcome(id = "0", expect = Expect.ACCEPTABLE_INTERESTING, desc = "!!!!")@Statepublic class ConcurrencyTest {int num = 0;boolean ready = false;@Actorpublic void actor1(I_Result r) {if(ready) {r.r1 = num + num;} else {r.r1 = 1;}}@Actorpublic void actor2(I_Result r) {num = 2;ready = true;}}
执行
mvn clean installjava -jar target/jcstress.jar
会输出我们感兴趣的结果,摘录其中一次结果:
*** INTERESTING testsSome interesting behaviors observed. This is for the plain curiosity.2 matching test results.[OK] test.ConcurrencyTest(JVM args: [-XX:-TieredCompilation])Observed state Occurrences Expectation Interpretation0 1,729 ACCEPTABLE_INTERESTING !!!!1 42,617,915 ACCEPTABLE ok4 5,146,627 ACCEPTABLE ok[OK] test.ConcurrencyTest(JVM args: [])Observed state Occurrences Expectation Interpretation0 1,652 ACCEPTABLE_INTERESTING !!!!1 46,460,657 ACCEPTABLE ok4 4,571,072 ACCEPTABLE ok
可以看到,出现结果为 0 的情况有 638 次,虽然次数相对很少,但毕竟是出现了。
解决方法
volatile 修饰的变量,可以禁用指令重排
@JCStressTest@Outcome(id = {"1", "4"}, expect = Expect.ACCEPTABLE, desc = "ok")@Outcome(id = "0", expect = Expect.ACCEPTABLE_INTERESTING, desc = "!!!!")@Statepublic class ConcurrencyTest {int num = 0;volatile boolean ready = false;@Actorpublic void actor1(I_Result r) {if(ready) {r.r1 = num + num;} else {r.r1 = 1;}}@Actorpublic void actor2(I_Result r) {num = 2;ready = true;}}
结果为:
*** INTERESTING testsSome interesting behaviors observed. This is for the plain curiosity.0 matching test results.
原理之volatile
happens-before
happens-before 规定了对共享变量的写操作对其它线程的读操作可见,它是可见性与有序性的一套规则总结,抛开以下 happens-before 规则,JMM 并不能保证一个线程对共享变量的写,对于其它线程对该共享变量的读可见
- 线程解锁 m 之前对变量的写,对于接下来对 m 加锁的其它线程对该变量的读可见 ```java static int x; static Object m = new Object();
new Thread(()->{ synchronized(m) { x = 10; } },”t1”).start();
new Thread(()->{ synchronized(m) { System.out.println(x); } },”t2”).start();
- 线程对 volatile 变量的写,对接下来其它线程对该变量的读可见```javavolatile static int x;new Thread(()->{x = 10;},"t1").start();new Thread(()->{System.out.println(x);},"t2").start();
线程 start 前对变量的写,对该线程开始后对该变量的读可见
static int x;x = 10;new Thread(()->{System.out.println(x);},"t2").start();
- 线程结束前对变量的写,对其它线程得知它结束后的读可见(比如其它线程调用 t1.isAlive() 或 t1.join()等待
它结束) ```java static int x;
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{ x = 10; },”t1”); t1.start();
t1.join(); System.out.println(x);
- 线程 t1 打断 t2(interrupt)前对变量的写,对于其他线程得知 t2 被打断后对变量的读可见(通过<br />t2.interrupted 或 t2.isInterrupted)```javastatic int x;public static void main(String[] args) {Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{while(true) {if(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {System.out.println(x);break;}}},"t2");t2.start();new Thread(()->{sleep(1);x = 10;t2.interrupt();},"t1").start();while(!t2.isInterrupted()) {Thread.yield();}System.out.println(x);}
- 对变量默认值(0,false,null)的写,对其它线程对该变量的读可见
- 具有传递性,如果 x hb-> y 并且 y hb-> z 那么有 x hb-> z ,配合 volatile 的防指令重排,有下面的例子 ```java volatile static int x; static int y;
new Thread(()->{ y = 10; x = 20; },”t1”).start();
new Thread(()->{ // x=20 对 t2 可见, 同时 y=10 也对 t2 可见 System.out.println(x); },”t2”).start();
> 变量都是指成员变量或静态成员变量> 参考: 第17页<a name="GvwpV"></a>### 习题<a name="RZBBi"></a>### balking模拟习题希望 doInit() 方法仅被调用一次,下面的实现是否有问题,为什么?```javapublic class TestVolatile {volatile boolean initialized = false;void init() {if (initialized) {return;}doInit();initialized = true;}private void doInit() {}}
volatile修只能保证共享变的可见性,但是有多行代码设计共享变量,不能保证这多行代码的原子性。
线程安全单例习题
单例模式有很多实现方法,饿汉、懒汉、静态内部类、枚举类,试分析每种实现下获取单例对象(即调用
getInstance)时的线程安全,并思考注释中的问题
饿汉式:类加载就会导致该单实例对象被创建 懒汉式:类加载不会导致该单实例对象被创建,而是首次使用该对象时才会创建
实现1:
// 问题1:为什么加 final 怕子类破坏父类的单例// 问题2:如果实现了序列化接口, 还要做什么来防止反序列化破坏单例public final class Singleton implements Serializable {// 问题3:为什么设置为私有? 是否能防止反射创建新的实例? 但是是不能,我们知道反射很强大,就是私有构造也可以创建对象private Singleton() {}// 问题4:这样初始化是否能保证单例对象创建时的线程安全? 静态成员变量的赋值是在类加载阶段完成的,我们可以相信JVM保证了线程安全private static final Singleton INSTANCE = new Singleton();// 问题5:为什么提供静态方法而不是直接将 INSTANCE 设置为 public, 说出你知道的理由 原有很多:更好的封装性;用方法可以有泛型的支持,静态成员变量没有;可以在方法中提供附加功能;等等public static Singleton getInstance() {return INSTANCE;}public Object readResolve() {return INSTANCE;}}
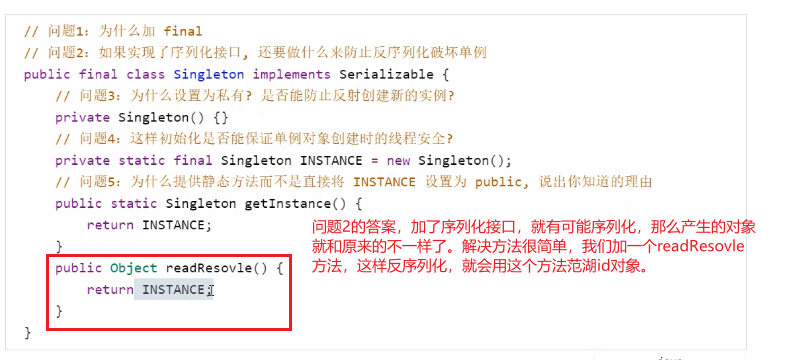
实现2:
// 问题1:枚举单例是如何限制实例个数的 里面定义几个,就有几个实例// 问题2:枚举单例在创建时是否有并发问题 没有,因为其也是静成员变量,也是在类加载阶段完成的// 问题3:枚举单例能否被反射破坏单例 不能// 问题4:枚举单例能否被反序列化破坏单例 强调一下,枚举类都是默认实现序列化接口的,但是枚举类设计考虑到了这个破坏单例,因此不可以破话// 问题5:枚举单例属于懒汉式还是饿汉式 饿汉式// 问题6:枚举单例如果希望加入一些单例创建时的初始化逻辑该如何做 很简单,加入构造方法就可以了,枚举类也可以加构造方法enum Singleton {INSTANCE;}
实现3:
public final class Singleton {private Singleton() { }private static Singleton INSTANCE = null;// 分析这里的线程安全, 并说明有什么缺点 缺点,锁的范围大,第二次,第三次都需要锁public static synchronized Singleton getInstance() {if( INSTANCE != null ){return INSTANCE;}INSTANCE = new Singleton();return INSTANCE;}}
实现4:DCL 其实就是double-check
public final class Singleton {private Singleton() { }// 问题1:解释为什么要加 volatile ?private static volatile Singleton INSTANCE = null;// 问题2:对比实现3, 说出这样做的意义public static Singleton getInstance() {if (INSTANCE != null) {return INSTANCE;}synchronized (Singleton.class) {// 问题3:为什么还要在这里加为空判断, 之前不是判断过了吗 防止首次创建,多个线程的并发问题if (INSTANCE != null) { // t2return INSTANCE;}INSTANCE = new Singleton();return INSTANCE;}}}
实现5 静态内部类
public final class Singleton {private Singleton() { }// 问题1:属于懒汉式还是饿汉式 懒汉式private static class LazyHolder {static final Singleton INSTANCE = new Singleton();}// 问题2:在创建时是否有并发问题 没有,因为是JVM操作public static Singleton getInstance() {return LazyHolder.INSTANCE;}}
本章小结
本章重点讲解了 JMM 中的
- 可见性 - 由 JVM 缓存优化引起
- 有序性 - 由 JVM 指令重排序优化引起
- happens-before 规则
- 原理方面
- CPU 指令并行
- volatile
- 模式方面
6.1 问题提出
有如下需求,保证 account.withdraw 取款方法的线程安全
package cn.itcast;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;interface Account {// 获取余额Integer getBalance();// 取款void withdraw(Integer amount);/*** 方法内会启动 1000 个线程,每个线程做 -10 元 的操作* 如果初始余额为 10000 那么正确的结果应当是 0*/static void demo(Account account) {List<Thread> ts = new ArrayList<>();long start = System.nanoTime();for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {ts.add(new Thread(() -> {account.withdraw(10);}));}ts.forEach(Thread::start);ts.forEach(t -> {try {t.join();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});long end = System.nanoTime();System.out.println(account.getBalance()+ " cost: " + (end-start)/1000_000 + " ms");}}
原有实现并不是线程安全的
class AccountUnsafe implements Account {private Integer balance;public AccountUnsafe(Integer balance) {this.balance = balance;}@Overridepublic Integer getBalance() {return balance;}@Overridepublic void withdraw(Integer amount) {balance -= amount;}}
执行测试代码
public static void main(String[] args) {Account.demo(new AccountUnsafe(10000));}
某次的执行结果
330 cost: 306 ms
为什么不安全
withdraw 方法
public void withdraw(Integer amount) {balance -= amount;}
对应的字节码
ALOAD 0 // <- thisALOAD 0GETFIELD cn/itcast/AccountUnsafe.balance : Ljava/lang/Integer; // <- this.balanceINVOKEVIRTUAL java/lang/Integer.intValue ()I // 拆箱ALOAD 1 // <- amountINVOKEVIRTUAL java/lang/Integer.intValue ()I // 拆箱ISUB // 减法INVOKESTATIC java/lang/Integer.valueOf (I)Ljava/lang/Integer; // 结果装箱PUTFIELD cn/itcast/AccountUnsafe.balance : Ljava/lang/Integer; // -> this.balance
多线程执行流程
ALOAD 0 // thread-0 <- thisALOAD 0GETFIELD cn/itcast/AccountUnsafe.balance // thread-0 <- this.balanceINVOKEVIRTUAL java/lang/Integer.intValue // thread-0 拆箱ALOAD 1 // thread-0 <- amountINVOKEVIRTUAL java/lang/Integer.intValue // thread-0 拆箱ISUB // thread-0 减法INVOKESTATIC java/lang/Integer.valueOf // thread-0 结果装箱PUTFIELD cn/itcast/AccountUnsafe.balance // thread-0 -> this.balanceALOAD 0 // thread-1 <- thisALOAD 0GETFIELD cn/itcast/AccountUnsafe.balance // thread-1 <- this.balanceINVOKEVIRTUAL java/lang/Integer.intValue // thread-1 拆箱ALOAD 1 // thread-1 <- amountINVOKEVIRTUAL java/lang/Integer.intValue // thread-1 拆箱ISUB // thread-1 减法INVOKESTATIC java/lang/Integer.valueOf // thread-1 结果装箱PUTFIELD cn/itcast/AccountUnsafe.balance // thread-1 -> this.balance
- 单核的指令交错
-
解决思路-锁
首先想到的是给 Account 对象加锁
class AccountUnsafe implements Account {private Integer balance;public AccountUnsafe(Integer balance) {this.balance = balance;}@Overridepublic synchronized Integer getBalance() {return balance;}@Overridepublic synchronized void withdraw(Integer amount) {balance -= amount;}}
结果:
0 cost: 399 ms
解决思路-无锁()原理看后面
class AccountSafe implements Account {private AtomicInteger balance;public AccountSafe(Integer balance) {this.balance = new AtomicInteger(balance);}@Overridepublic Integer getBalance() {return balance.get();}@Overridepublic void withdraw(Integer amount) {while (true) {// 获取余额的最新值 前两个值都是在栈中,线程私有int prev = balance.get();// 要修改的余额 前两个值都是在栈中,线程私有int next = prev - amount;// 真正的修改if (balance.compareAndSet(prev, next)) {break;}}// 可以简化为下面的方法// balance.addAndGet(-1 * amount);}}
执行测试代码
public static void main(String[] args) {Account.demo(new AccountSafe(10000));}
某次的执行结果
0 cost: 302 ms
6.2 CAS 与 volatile
前面看到的 AtomicInteger 的解决方法,内部并没有用锁来保护共享变量的线程安全。那么它是如何实现的呢?
CAS虽然没有用锁,但是是在CPU指令级别保证了原子性。下面的compareAndSet还有后面的compareAndSweep被称为CAS。public void withdraw(Integer amount) {while(true) {// 需要不断尝试,直到成功为止while (true) {// 比如拿到了旧值 1000int prev = balance.get();// 在这个基础上 1000-10 = 990int next = prev - amount;/*compareAndSet 正是做这个检查,在 set 前,先比较 prev 与当前值- 不一致了,next 作废,返回 false 表示失败比如,别的线程已经做了减法,当前值已经被减成了 990那么本线程的这次 990 就作废了,进入 while 下次循环重试- 一致,以 next 设置为新值,返回 true 表示成功*/if (balance.compareAndSet(prev, next)) {break;}}}}
其中的关键是 compareAndSet,它的简称就是 CAS (也有 Compare And Swap 的说法),它必须是原子操作(cpu指令层面保证原子性)。
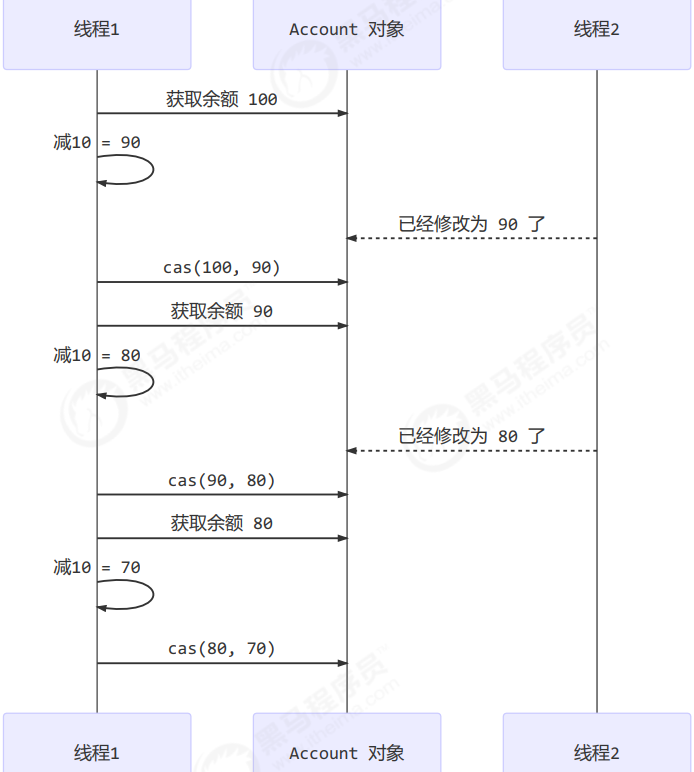
注意
其实 CAS 的底层是 lock cmpxchg 指令(X86 架构),在单核 CPU 和多核 CPU 下都能够保证【比较-交换】的原子性。- 在多核状态下,某个核执行到带 lock 的指令时,CPU 会让总线锁住,当这个核把此指令执行完毕,再开启总线。这个过程中不会被线程的调度机制所打断,保证了多个线程对内存操作的准确性,是原子的。
慢动作分析
@Slf4jpublic class SlowMotion {public static void main(String[] args) {AtomicInteger balance = new AtomicInteger(10000);int mainPrev = balance.get();log.debug("try get {}", mainPrev);new Thread(() -> {sleep(1000);int prev = balance.get();balance.compareAndSet(prev, 9000);log.debug(balance.toString());}, "t1").start();sleep(2000);log.debug("try set 8000...");boolean isSuccess = balance.compareAndSet(mainPrev, 8000);log.debug("is success ? {}", isSuccess);if(!isSuccess){mainPrev = balance.get();log.debug("try set 8000...");isSuccess = balance.compareAndSet(mainPrev, 8000);log.debug("is success ? {}", isSuccess);}}private static void sleep(int millis) {try {Thread.sleep(millis);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
输出结果
2019-10-13 11:28:37.134 [main] try get 100002019-10-13 11:28:38.154 [t1] 90002019-10-13 11:28:39.154 [main] try set 8000...2019-10-13 11:28:39.154 [main] is success ? false2019-10-13 11:28:39.154 [main] try set 8000...2019-10-13 11:28:39.154 [main] is success ? true
volatile
获取共享变量时,为了保证该变量的可见性,需要使用 volatile 修饰。
它可以用来修饰成员变量和静态成员变量,他可以避免线程从自己的工作缓存中查找变量的值,必须到主存中获取它的值,线程操作 volatile 变量都是直接操作主存。即一个线程对 volatile 变量的修改,对另一个线程可见。
注意 volatile 仅仅保证了共享变量的可见性,让其它线程能够看到最新值,但不能解决指令交错问题(不能保证原子性)
CAS 必须借助 volatile 才能读取到共享变量的最新值来实现【比较并交换】的效果
为什么无锁效率高
- 无锁情况下,即使重试失败,线程始终在高速运行,没有停歇,而 synchronized 会让线程在没有获得锁的时候,发生上下文切换,进入阻塞。打个比喻
- 线程就好像高速跑道上的赛车,高速运行时,速度超快,一旦发生上下文切换,就好比赛车要减速、熄火,等被唤醒又得重新打火、启动、加速… 恢复到高速运行,代价比较大
- 但无锁情况下,因为线程要保持运行,需要额外 CPU 的支持,CPU 在这里就好比高速跑道,没有额外的跑道,线程想高速运行也无从谈起,虽然不会进入阻塞,但由于没有分到时间片,仍然会进入可运行状态,还是会导致上下文切换。
CAS的特点
结合 CAS 和 volatile 可以实现无锁并发,适用于线程数少、多核 CPU 的场景下(前面我们分析过,CAS和volatile实现的并发,线程数不要多余核心数)。
- CAS 是基于乐观锁的思想:最乐观的估计,不怕别的线程来修改共享变量,就算改了也没关系,我吃亏点再
重试呗。 - synchronized 是基于悲观锁的思想:最悲观的估计,得防着其它线程来修改共享变量,我上了锁你们都别想改,我改完了解开锁,你们才有机会。
CAS 体现的是无锁并发、无阻塞并发,请仔细体会这两句话的意思
AtomicBoolean
- AtomicInteger
- AtomicLong
以 AtomicInteger 为例
前面我们用过compareAndSet,但是其要配合while使用才行,这是很不方便的。 因此这里提供了几个加减法不需要配合while使用。 其中有之前的i++,++i,i—和—i。 还有getAndAdd和addAndGet,当然这个可以替换上面的例子中的compareAndSet。
上面这些只是加和减。都很简单的,那么更复杂的呢乘和除?? 那么就是getAndUpdate和updateAndGet,我们发现其要传入的是一个函数式接口,如下 AtomicInteger i = new AtomicInteger(5); i.getAndUpdate(value -> value * 2); 那么这个就i.get() 就是10了。就乘以10了。当然这个也可用于加和减。
如果只是这么看API,我们有点不知所以,假设我们要自己模仿一下updateAndGet方法,如果让我们自己做一个线程安全的计算,我们该怎么实现?我就用最基的compareAndSet实现!
AtomicInteger i = new AtomicInteger(0);// 获取并自增(i = 0, 结果 i = 1, 返回 0),类似于 i++System.out.println(i.getAndIncrement());// 自增并获取(i = 1, 结果 i = 2, 返回 2),类似于 ++iSystem.out.println(i.incrementAndGet());// 自减并获取(i = 2, 结果 i = 1, 返回 1),类似于 --iSystem.out.println(i.decrementAndGet());// 获取并自减(i = 1, 结果 i = 0, 返回 1),类似于 i--System.out.println(i.getAndDecrement());// 获取并加值(i = 0, 结果 i = 5, 返回 0)System.out.println(i.getAndAdd(5));// 加值并获取(i = 5, 结果 i = 0, 返回 0)System.out.println(i.addAndGet(-5));// 获取并更新(i = 0, p 为 i 的当前值, 结果 i = -2, 返回 0)// 其中函数中的操作能保证原子,但函数需要无副作用System.out.println(i.getAndUpdate(p -> p - 2));// 更新并获取(i = -2, p 为 i 的当前值, 结果 i = 0, 返回 0)// 其中函数中的操作能保证原子,但函数需要无副作用System.out.println(i.updateAndGet(p -> p + 2));// 获取并计算(i = 0, p 为 i 的当前值, x 为参数1, 结果 i = 10, 返回 0)// 其中函数中的操作能保证原子,但函数需要无副作用// getAndUpdate 如果在 lambda 中引用了外部的局部变量,要保证该局部变量是 final 的// getAndAccumulate 可以通过 参数1 来引用外部的局部变量,但因为其不在 lambda 中因此不必是 finalSystem.out.println(i.getAndAccumulate(10, (p, x) -> p + x));// 计算并获取(i = 10, p 为 i 的当前值, x 为参数1, 结果 i = 0, 返回 0)// 其中函数中的操作能保证原子,但函数需要无副作用System.out.println(i.accumulateAndGet(-10, (p, x) -> p + x));
6.4 原子引用
为什么需要原子引用类型?
- AtomicReference
- AtomicMarkableReference
- AtomicStampedReference
有如下方法
public interface DecimalAccount {// 获取余额BigDecimal getBalance();// 取款void withdraw(BigDecimal amount);/*** 方法内会启动 1000 个线程,每个线程做 -10 元 的操作* 如果初始余额为 10000 那么正确的结果应当是 0*/static void demo(DecimalAccount account) {List<Thread> ts = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {ts.add(new Thread(() -> {account.withdraw(BigDecimal.TEN);}));}ts.forEach(Thread::start);ts.forEach(t -> {try {t.join();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});System.out.println(account.getBalance());}}
试着提供不同的 DecimalAccount 实现,实现安全的取款操作
不安全实现
class DecimalAccountUnsafe implements DecimalAccount {BigDecimal balance;public DecimalAccountUnsafe(BigDecimal balance) {this.balance = balance;}@Overridepublic BigDecimal getBalance() {return balance;}@Overridepublic void withdraw(BigDecimal amount) {BigDecimal balance = this.getBalance();this.balance = balance.subtract(amount);}}
安全实现-使用锁
class DecimalAccountSafeLock implements DecimalAccount {private final Object lock = new Object();BigDecimal balance;public DecimalAccountSafeLock(BigDecimal balance) {this.balance = balance;}@Overridepublic BigDecimal getBalance() {return balance;}@Overridepublic void withdraw(BigDecimal amount) {synchronized (lock) {BigDecimal balance = this.getBalance();this.balance = balance.subtract(amount);}}}
安全实现-使用CAS
class DecimalAccountSafeCas implements DecimalAccount {AtomicReference<BigDecimal> ref;public DecimalAccountSafeCas(BigDecimal balance) {ref = new AtomicReference<>(balance);}@Overridepublic BigDecimal getBalance() {return ref.get();}@Overridepublic void withdraw(BigDecimal amount) {while (true) {BigDecimal prev = ref.get();BigDecimal next = prev.subtract(amount);if (ref.compareAndSet(prev, next)) {break;}}}}
测试代码
DecimalAccount.demo(new DecimalAccountUnsafe(new BigDecimal("10000")));DecimalAccount.demo(new DecimalAccountSafeLock(new BigDecimal("10000")));DecimalAccount.demo(new DecimalAccountSafeCas(new BigDecimal("10000")));
运行结果
4310 cost: 425 ms0 cost: 285 ms0 cost: 274 ms
ABA问题及解决
ABA问题
static AtomicReference<String> ref = new AtomicReference<>("A");public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {log.debug("main start...");// 获取值 A// 这个共享变量被它线程修改过?String prev = ref.get();other();sleep(1);// 尝试改为 Clog.debug("change A->C {}", ref.compareAndSet(prev, "C"));}private static void other() {new Thread(() -> {log.debug("change A->B {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.get(), "B"));}, "t1").start();sleep(0.5);new Thread(() -> {log.debug("change B->A {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.get(), "A"));}, "t2").start();}
输出
11:29:52.325 c.Test36 [main] - main start...11:29:52.379 c.Test36 [t1] - change A->B true11:29:52.879 c.Test36 [t2] - change B->A true11:29:53.880 c.Test36 [main] - change A->C true
主线程仅能判断出共享变量的值与最初值 A 是否相同,不能感知到这种从 A 改为 B 又 改回 A 的情况,如果主线程希望:
只要有其它线程【动过了】共享变量,那么自己的 cas 就算失败,这时,仅比较值是不够的,需要再加一个版本号
AtomicStampedReference
static AtomicStampedReference<String> ref = new AtomicStampedReference<>("A", 0);public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {log.debug("main start...");// 获取值 AString prev = ref.getReference();// 获取版本号int stamp = ref.getStamp();log.debug("版本 {}", stamp);// 如果中间有其它线程干扰,发生了 ABA 现象other();sleep(1);// 尝试改为 Clog.debug("change A->C {}", ref.compareAndSet(prev, "C", stamp, stamp + 1));}private static void other() {new Thread(() -> {log.debug("change A->B {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.getReference(), "B",ref.getStamp(), ref.getStamp() + 1));log.debug("更新版本为 {}", ref.getStamp());}, "t1").start();sleep(0.5);new Thread(() -> {log.debug("change B->A {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.getReference(), "A",ref.getStamp(), ref.getStamp() + 1));log.debug("更新版本为 {}", ref.getStamp());}, "t2").start();}
输出为
15:41:34.891 c.Test36 [main] - main start...15:41:34.894 c.Test36 [main] - 版本 015:41:34.956 c.Test36 [t1] - change A->B true15:41:34.956 c.Test36 [t1] - 更新版本为 115:41:35.457 c.Test36 [t2] - change B->A true15:41:35.457 c.Test36 [t2] - 更新版本为 215:41:36.457 c.Test36 [main] - change A->C false
AtomicStampedReference 可以给原子引用加上版本号,追踪原子引用整个的变化过程,如: A -> B -> A -> C ,通过AtomicStampedReference,我们可以知道,引用变量中途被更改了几次。
但是有时候,并不关心引用变量更改了几次,只是单纯的关心是否更改过,所以就有了AtomicMarkableReference 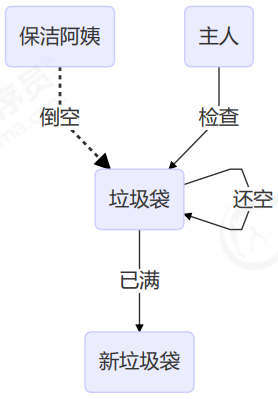
AtomicMarkableReference
class GarbageBag {String desc;public GarbageBag(String desc) {this.desc = desc;}public void setDesc(String desc) {this.desc = desc;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return super.toString() + " " + desc;}}
@Slf4jpublic class TestABAAtomicMarkableReference {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {GarbageBag bag = new GarbageBag("装满了垃圾");// 参数2 mark 可以看作一个标记,表示垃圾袋满了AtomicMarkableReference<GarbageBag> ref = new AtomicMarkableReference<>(bag, true);log.debug("主线程 start...");GarbageBag prev = ref.getReference();log.debug(prev.toString());new Thread(() -> {log.debug("打扫卫生的线程 start...");bag.setDesc("空垃圾袋");while (!ref.compareAndSet(bag, bag, true, false)) {}log.debug(bag.toString());}).start();Thread.sleep(1000);log.debug("主线程想换一只新垃圾袋?");boolean success = ref.compareAndSet(prev, new GarbageBag("空垃圾袋"), true, false);log.debug("换了么?" + success);log.debug(ref.getReference().toString());}}
输出
2019-10-13 15:30:09.264 [main] 主线程 start...2019-10-13 15:30:09.270 [main] cn.itcast.GarbageBag@5f0fd5a0 装满了垃圾2019-10-13 15:30:09.293 [Thread-1] 打扫卫生的线程 start...2019-10-13 15:30:09.294 [Thread-1] cn.itcast.GarbageBag@5f0fd5a0 空垃圾袋2019-10-13 15:30:10.294 [main] 主线程想换一只新垃圾袋?2019-10-13 15:30:10.294 [main] 换了么?false2019-10-13 15:30:10.294 [main] cn.itcast.GarbageBag@5f0fd5a0 空垃圾袋
6.5 原子数组
- AtomicIntegerArray
- AtomicLongArray
- AtomicReferenceArray
有如下方法
/**参数1,提供数组、可以是线程不安全数组或线程安全数组参数2,获取数组长度的方法参数3,自增方法,回传 array, index参数4,打印数组的方法*/// supplier 提供者 无中生有 ()->结果// function 函数 一个参数一个结果 (参数)->结果 , BiFunction (参数1,参数2)->结果// consumer 消费者 一个参数没结果 (参数)->void, BiConsumer (参数1,参数2)->private static <T> void demo(Supplier<T> arraySupplier,Function<T, Integer> lengthFun,BiConsumer<T, Integer> putConsumer,Consumer<T> printConsumer ) {List<Thread> ts = new ArrayList<>();T array = arraySupplier.get();int length = lengthFun.apply(array);for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {// 每个线程对数组作 10000 次操作ts.add(new Thread(() -> {for (int j = 0; j < 10000; j++) {putConsumer.accept(array, j%length);}}));}ts.forEach(t -> t.start()); // 启动所有线程ts.forEach(t -> {try {t.join();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}); // 等所有线程结束printConsumer.accept(array);}
不安全的数组
demo(()->new int[10],(array)->array.length,(array, index) -> array[index]++,array-> System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)));
结果
[9870, 9862, 9774, 9697, 9683, 9678, 9679, 9668, 9680, 9698]
安全的数组
demo(()-> new AtomicIntegerArray(10),(array) -> array.length(),(array, index) -> array.getAndIncrement(index),array -> System.out.println(array));
结果
[10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000]
6.6 字段更新器
- AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater // 域 字段
- AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater
- AtomicLongFieldUpdater
利用字段更新器,可以针对对象的某个域(Field)进行原子操作,只能配合 volatile 修饰的字段使用,否则会出现异常
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Must be volatile type
public class Test5 {private volatile int field;public static void main(String[] args) {AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater fieldUpdater =AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(Test5.class, "field");Test5 test5 = new Test5();fieldUpdater.compareAndSet(test5, 0, 10);// 修改成功 field = 10System.out.println(test5.field);// 修改成功 field = 20fieldUpdater.compareAndSet(test5, 10, 20);System.out.println(test5.field);// 修改失败 field = 20fieldUpdater.compareAndSet(test5, 10, 30);System.out.println(test5.field);}}
输出
102020
6.7 原子累加器
累加器性能比较
private static <T> void demo(Supplier<T> adderSupplier, Consumer<T> action) {T adder = adderSupplier.get();long start = System.nanoTime();List<Thread> ts = new ArrayList<>();// 4 个线程,每人累加 50 万for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {ts.add(new Thread(() -> {for (int j = 0; j < 500000; j++) {action.accept(adder);}}));}ts.forEach(t -> t.start());ts.forEach(t -> {try {t.join();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});long end = System.nanoTime();System.out.println(adder + " cost:" + (end - start)/1000_000);}
比较 AtomicLong 与 LongAdder
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {demo(() -> new LongAdder(), adder -> adder.increment());}for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {demo(() -> new AtomicLong(), adder -> adder.getAndIncrement());}
输出
1000000 cost:431000000 cost:91000000 cost:71000000 cost:71000000 cost:71000000 cost:311000000 cost:271000000 cost:281000000 cost:241000000 cost:22
性能提升的原因很简单,就是在有竞争时,设置多个累加单元,Therad-0 累加 Cell[0],而 Thread-1 累加Cell[1]… 最后将结果汇总。这样它们在累加时操作的不同的 Cell 变量,因此减少了 CAS 重试失败,从而提高性能。
源码之 LongAdder
LongAdder 是并发大师 @author Doug Lea (大哥李)的作品,设计的非常精巧
LongAdder 类有几个关键域
// 累加单元数组, 懒惰初始化transient volatile Cell[] cells;// 基础值, 如果没有竞争, 则用 cas 累加这个域transient volatile long base;// 在 cells 创建或扩容时, 置为 1, 表示加锁transient volatile int cellsBusy;
cas锁
// 不要用于实践!!!public class LockCas {private AtomicInteger state = new AtomicInteger(0);public void lock() {while (true) {if (state.compareAndSet(0, 1)) {break;}}}public void unlock() {log.debug("unlock...");state.set(0);}}
测试
LockCas lock = new LockCas();new Thread(() -> {log.debug("begin...");lock.lock();try {log.debug("lock...");sleep(1);} finally {lock.unlock();}}).start();new Thread(() -> {log.debug("begin...");lock.lock();try {log.debug("lock...");} finally {lock.unlock();}}).start();
输出
18:27:07.198 c.Test42 [Thread-0] - begin...18:27:07.202 c.Test42 [Thread-0] - lock...18:27:07.198 c.Test42 [Thread-1] - begin...18:27:08.204 c.Test42 [Thread-0] - unlock...18:27:08.204 c.Test42 [Thread-1] - lock...18:27:08.204 c.Test42 [Thread-1] - unlock...
原理之伪共享
其中 Cell 即为累加单元
// 防止缓存行伪共享@sun.misc.Contendedstatic final class Cell {volatile long value;Cell(long x) { value = x; }// 最重要的方法, 用来 cas 方式进行累加, prev 表示旧值, next 表示新值final boolean cas(long prev, long next) {return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapLong(this, valueOffset, prev, next);}// 省略不重要代码}
得从缓存说起
缓存与内存的速度比较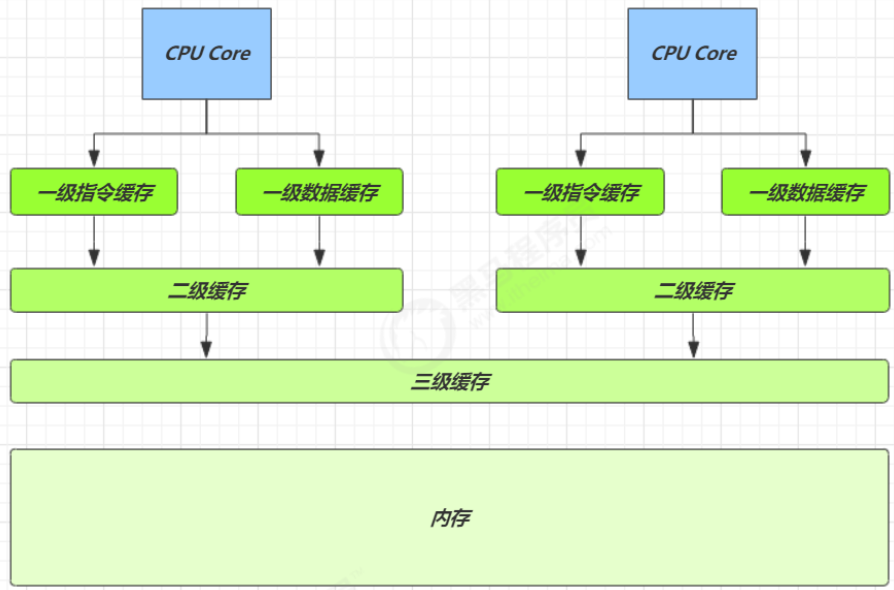
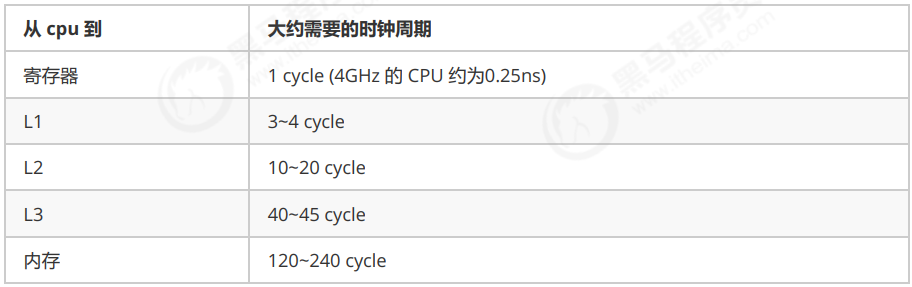
因为 CPU 与 内存的速度差异很大,需要靠预读数据至缓存来提升效率。
而缓存以缓存行为单位,每个缓存行对应着一块内存,一般是 64 byte(8 个 long)
缓存的加入会造成数据副本的产生,即同一份数据会缓存在不同核心的缓存行中
CPU 要保证数据的一致性,如果某个 CPU 核心更改了数据,其它 CPU 核心对应的整个缓存行必须失效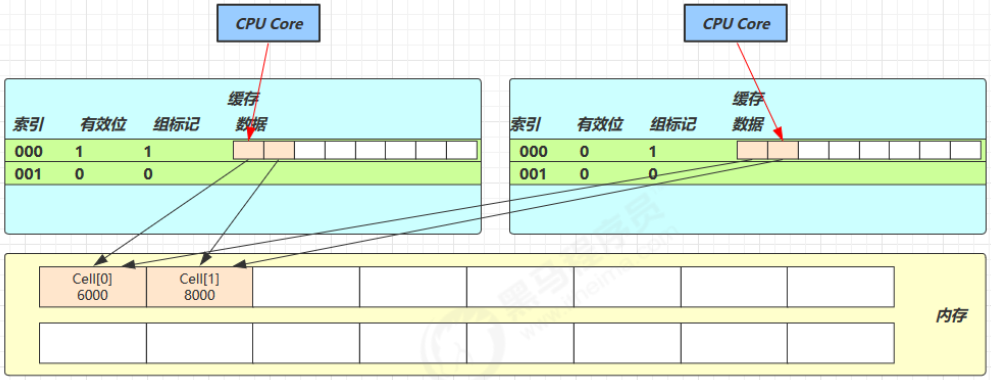
因为 Cell 是数组形式,在内存中是连续存储的,一个 Cell 为 24 字节(16 字节的对象头和 8 字节的 value),因此缓存行可以存下 2 个的 Cell 对象。这样问题来了:
- Core-0 要修改 Cell[0]
- Core-1 要修改 Cell[1]
无论谁修改成功,都会导致对方 Core 的缓存行失效,比如 Core-0 中 Cell[0]=6000, Cell[1]=8000 要累加Cell[0]=6001, Cell[1]=8000 ,这时会让 Core-1 的缓存行失效
@sun.misc.Contended 用来解决这个问题,它的原理是在使用此注解的对象或字段的前后各增加 128 字节大小的padding,从而让 CPU 将对象预读至缓存时占用不同的缓存行,这样,不会造成对方缓存行的失效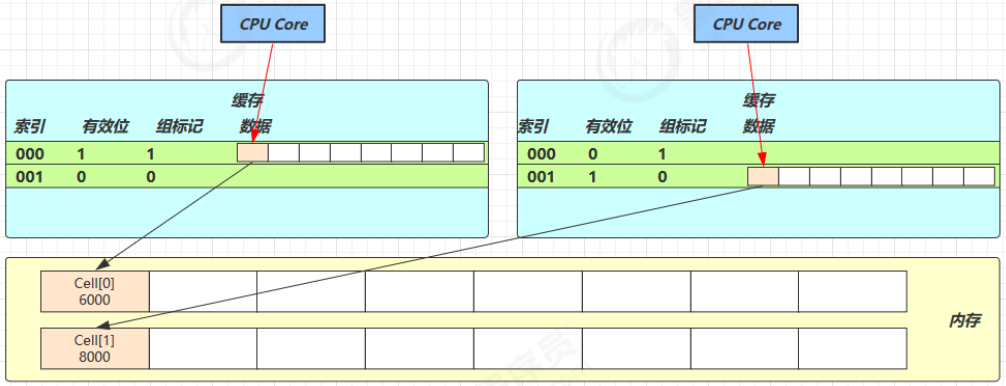
累加主要调用下面的方法
public void add(long x) {// as 为累加单元数组// b 为基础值// x 为累加值Cell[] as; long b, v; int m; Cell a;// 进入 if 的两个条件// 1. as 有值, 表示已经发生过竞争, 进入 if// 2. cas 给 base 累加时失败了, 表示 base 发生了竞争, 进入 ifif ((as = cells) != null || !casBase(b = base, b + x)) {// uncontended 表示 cell 没有竞争boolean uncontended = true;if (// as 还没有创建as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||// 当前线程对应的 cell 还没有(a = as[getProbe() & m]) == null ||// cas 给当前线程的 cell 累加失败 uncontended=false ( a 为当前线程的 cell )!(uncontended = a.cas(v = a.value, v + x))) {// 进入 cell 数组创建、cell 创建的流程longAccumulate(x, null, uncontended);}}}
add 流程图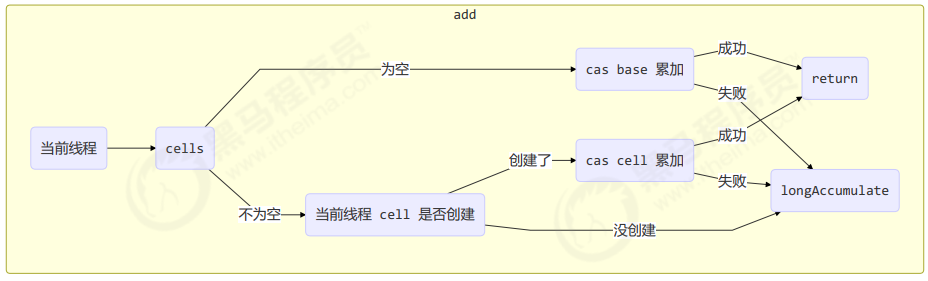
final void longAccumulate(long x, LongBinaryOperator fn,boolean wasUncontended) {int h;// 当前线程还没有对应的 cell, 需要随机生成一个 h 值用来将当前线程绑定到 cellif ((h = getProbe()) == 0) {// 初始化 probeThreadLocalRandom.current();// h 对应新的 probe 值, 用来对应 cellh = getProbe();wasUncontended = true;}// collide 为 true 表示需要扩容boolean collide = false;for (;;) {Cell[] as; Cell a; int n; long v;// 已经有了 cellsif ((as = cells) != null && (n = as.length) > 0) {// 还没有 cellif ((a = as[(n - 1) & h]) == null) {// 为 cellsBusy 加锁, 创建 cell, cell 的初始累加值为 x// 成功则 break, 否则继续 continue 循环}// 有竞争, 改变线程对应的 cell 来重试 caselse if (!wasUncontended)wasUncontended = true;// cas 尝试累加, fn 配合 LongAccumulator 不为 null, 配合 LongAdder 为 nullelse if (a.cas(v = a.value, ((fn == null) ? v + x : fn.applyAsLong(v, x))))break;// 如果 cells 长度已经超过了最大长度, 或者已经扩容, 改变线程对应的 cell 来重试 caselse if (n >= NCPU || cells != as)collide = false;// 确保 collide 为 false 进入此分支, 就不会进入下面的 else if 进行扩容了else if (!collide)collide = true;// 加锁else if (cellsBusy == 0 && casCellsBusy()) {// 加锁成功, 扩容continue;}// 改变线程对应的 cellh = advanceProbe(h);}// 还没有 cells, 尝试给 cellsBusy 加锁else if (cellsBusy == 0 && cells == as && casCellsBusy()) {// 加锁成功, 初始化 cells, 最开始长度为 2, 并填充一个 cell// 成功则 break;}// 上两种情况失败, 尝试给 base 累加else if (casBase(v = base, ((fn == null) ? v + x : fn.applyAsLong(v, x))))break;}}
longAccumulate 流程图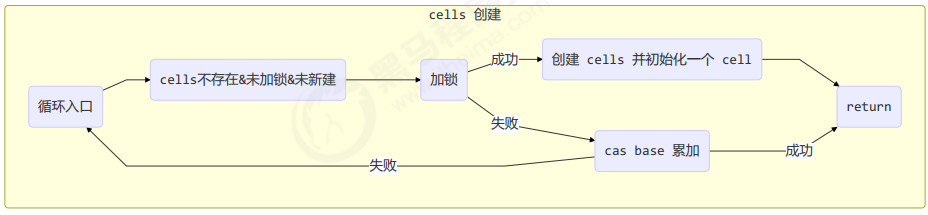
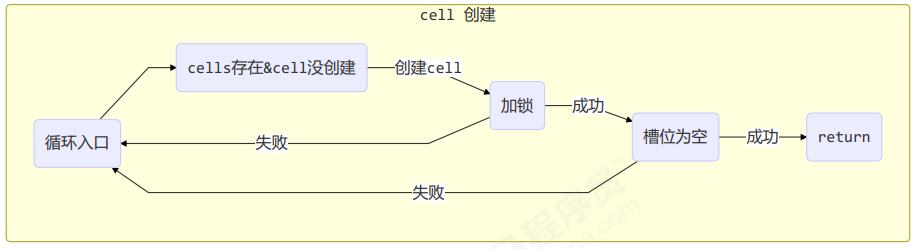
每个线程刚进入 longAccumulate 时,会尝试对应一个 cell 对象(找到一个坑位)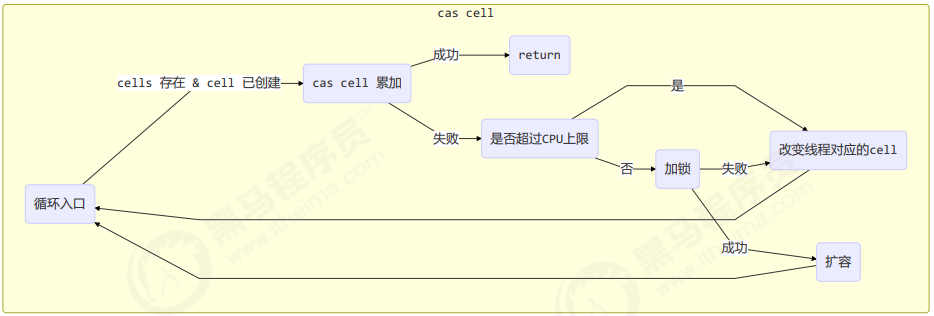
获取最终结果通过 sum 方法
public long sum() {Cell[] as = cells; Cell a;long sum = base;if (as != null) {for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {if ((a = as[i]) != null)sum += a.value;}}return sum;}
6.8 Unsafe
概述
Unsafe 对象提供了非常底层的,操作内存、线程的方法,Unsafe 对象不能直接调用,只能通过反射获得
public class UnsafeAccessor {static Unsafe unsafe;static {try {Field theUnsafe = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");theUnsafe.setAccessible(true);unsafe = (Unsafe) theUnsafe.get(null);} catch (NoSuchFieldException | IllegalAccessException e) {throw new Error(e);}}static Unsafe getUnsafe() {return unsafe;}}
Unsafe CAS操作
@Dataclass Student {volatile int id;volatile String name;}
Unsafe unsafe = UnsafeAccessor.getUnsafe();Field id = Student.class.getDeclaredField("id");Field name = Student.class.getDeclaredField("name");// 获得成员变量的偏移量long idOffset = UnsafeAccessor.unsafe.objectFieldOffset(id);long nameOffset = UnsafeAccessor.unsafe.objectFieldOffset(name);Student student = new Student();// 使用 cas 方法替换成员变量的值UnsafeAccessor.unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(student, idOffset, 0, 20); // 返回 trueUnsafeAccessor.unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(student, nameOffset, null, "张三"); // 返回 trueSystem.out.println(student);
输出
Student(id=20, name=张三)
使用自定义的 AtomicData 实现之前线程安全的原子整数 Account 实现
class AtomicData {private volatile int data;static final Unsafe unsafe;static final long DATA_OFFSET;static {unsafe = UnsafeAccessor.getUnsafe();try {// data 属性在 DataContainer 对象中的偏移量,用于 Unsafe 直接访问该属性DATA_OFFSET = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(AtomicData.class.getDeclaredField("data"));} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {throw new Error(e);}}public AtomicData(int data) {this.data = data;}public void decrease(int amount) {int oldValue;while(true) {// 获取共享变量旧值,可以在这一行加入断点,修改 data 调试来加深理解oldValue = data;// cas 尝试修改 data 为 旧值 + amount,如果期间旧值被别的线程改了,返回 falseif (unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, DATA_OFFSET, oldValue, oldValue - amount)) {return;}}}public int getData() {return data;}}
Account 实现
Account.demo(new Account() {AtomicData atomicData = new AtomicData(10000);@Overridepublic Integer getBalance() {return atomicData.getData();}@Overridepublic void withdraw(Integer amount) {atomicData.decrease(amount);}});
本章小结
- CAS 与 volatile
- API
- 原子整数
- 原子引用
- 原子数组
- 字段更新器
- 原子累加器
- Unsafe
- * 原理方面
7.1 日期转换的问题
问题的提出
下面的代码在运行时,由于 SimpleDateFormat 不是线程安全的
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {new Thread(() -> {try {log.debug("{}", sdf.parse("1951-04-21"));} catch (Exception e) {log.error("{}", e);}}).start();}
有很大几率出现 java.lang.NumberFormatException 或者出现不正确的日期解析结果,例如:
19:10:40.859 [Thread-2] c.TestDateParse - {}java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: ""at java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:65)at java.lang.Long.parseLong(Long.java:601)at java.lang.Long.parseLong(Long.java:631)at java.text.DigitList.getLong(DigitList.java:195)at java.text.DecimalFormat.parse(DecimalFormat.java:2084)at java.text.SimpleDateFormat.subParse(SimpleDateFormat.java:2162)at java.text.SimpleDateFormat.parse(SimpleDateFormat.java:1514)at java.text.DateFormat.parse(DateFormat.java:364)at cn.itcast.n7.TestDateParse.lambda$test1$0(TestDateParse.java:18)at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)19:10:40.859 [Thread-1] c.TestDateParse - {}java.lang.NumberFormatException: empty Stringat sun.misc.FloatingDecimal.readJavaFormatString(FloatingDecimal.java:1842)at sun.misc.FloatingDecimal.parseDouble(FloatingDecimal.java:110)at java.lang.Double.parseDouble(Double.java:538)at java.text.DigitList.getDouble(DigitList.java:169)at java.text.DecimalFormat.parse(DecimalFormat.java:2089)at java.text.SimpleDateFormat.subParse(SimpleDateFormat.java:2162)at java.text.SimpleDateFormat.parse(SimpleDateFormat.java:1514)at java.text.DateFormat.parse(DateFormat.java:364)at cn.itcast.n7.TestDateParse.lambda$test1$0(TestDateParse.java:18)at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)19:10:40.857 [Thread-8] c.TestDateParse - Sat Apr 21 00:00:00 CST 195119:10:40.857 [Thread-9] c.TestDateParse - Sat Apr 21 00:00:00 CST 195119:10:40.857 [Thread-6] c.TestDateParse - Sat Apr 21 00:00:00 CST 195119:10:40.857 [Thread-4] c.TestDateParse - Sat Apr 21 00:00:00 CST 195119:10:40.857 [Thread-5] c.TestDateParse - Mon Apr 21 00:00:00 CST 17896064519:10:40.857 [Thread-0] c.TestDateParse - Sat Apr 21 00:00:00 CST 195119:10:40.857 [Thread-7] c.TestDateParse - Sat Apr 21 00:00:00 CST 195119:10:40.857 [Thread-3] c.TestDateParse - Sat Apr 21 00:00:00 CST 1951
思路-同步锁
这样虽能解决问题,但带来的是性能上的损失,并不算很好:
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {new Thread(() -> {synchronized (sdf) {try {log.debug("{}", sdf.parse("1951-04-21"));} catch (Exception e) {log.error("{}", e);}}}).start();}
思路-不可变
如果一个对象在不能够修改其内部状态(属性),那么它就是线程安全的,因为不存在并发修改啊!这样的对象在Java 中有很多,例如在 Java 8 后,提供了一个新的日期格式化类:
DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd");for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {new Thread(() -> {LocalDate date = dtf.parse("2018-10-01", LocalDate::from);log.debug("{}", date);}).start();}
可以看 DateTimeFormatter 的文档:
@implSpecThis class is immutable and thread-safe.
7.2 不可变设计
另一个大家更为熟悉的 String 类也是不可变的,以它为例,说明一下不可变设计的要素
public final class Stringimplements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence {/** The value is used for character storage. */private final char value[];/** Cache the hash code for the string */private int hash; // Default to 0// ...}
final 的使用
发现该类、类中所有属性都是 final 的
- 属性用 final 修饰保证了该属性是只读的,不能修改
- 类用 final 修饰保证了该类中的方法不能被覆盖,防止子类无意间破坏不可变性
保护性拷贝
但有同学会说,使用字符串时,也有一些跟修改相关的方法啊,比如 substring 等,那么下面就看一看这些方法是如何实现的,就以 substring 为例:
发现其内部是调用 String 的构造方法创建了一个新字符串,再进入这个构造看看,是否对 final char[] value 做出public String substring(int beginIndex) {if (beginIndex < 0) {throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);}int subLen = value.length - beginIndex;if (subLen < 0) {throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen);}return (beginIndex == 0) ? this : new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);}
了修改:
结果发现也没有,构造新字符串对象时,会生成新的 char[] value,对内容进行复制 。这种通过创建副本对象来避免共享的手段称之为【保护性拷贝(defensive copy)】public String(char value[], int offset, int count) {if (offset < 0) {throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);}if (count <= 0) {if (count < 0) {throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);}if (offset <= value.length) {this.value = "".value;return;}}if (offset > value.length - count) {throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);}this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count);}
模式之亨元
原理之final
7.3 无状态
在 web 阶段学习时,设计 Servlet 时为了保证其线程安全,都会有这样的建议,不要为 Servlet 设置成员变量,这种没有任何成员变量的类是线程安全的
因为成员变量保存的数据也可以称为状态信息,因此没有成员变量就称之为【无状态】
本章小结
- 不可变类使用
- 不可变类设计
- 原理方面
- final
- 原理方面
模式方面
-
8. 共享模型之工具
8.1 线程池
1. 自定义线程池
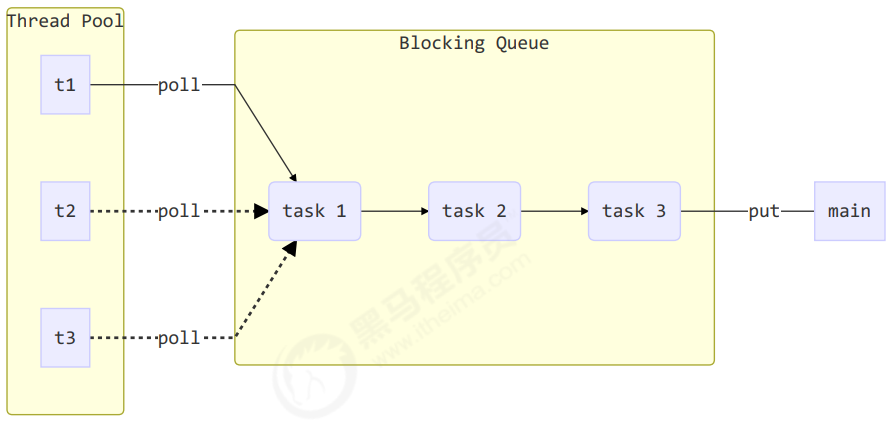
步骤1:自定义拒绝策略接口@FunctionalInterface // 拒绝策略interface RejectPolicy<T> {void reject(BlockingQueue<T> queue, T task);}
步骤2:自定义任务队列
class BlockingQueue<T> {// 1. 任务队列private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();// 2. 锁private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();// 3. 生产者条件变量private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition();// 4. 消费者条件变量private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition();// 5. 容量private int capcity;public BlockingQueue(int capcity) {this.capcity = capcity;}// 带超时阻塞获取public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {lock.lock();try {// 将 timeout 统一转换为 纳秒long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);while (queue.isEmpty()) {try {// 返回值是剩余时间if (nanos <= 0) {return null;}nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}T t = queue.removeFirst();fullWaitSet.signal();return t;} finally {lock.unlock();}}// 阻塞获取public T take() {lock.lock();try {while (queue.isEmpty()) {try {emptyWaitSet.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}T t = queue.removeFirst();fullWaitSet.signal();return t;} finally {lock.unlock();}}// 阻塞添加public void put(T task) {lock.lock();try {while (queue.size() == capcity) {try {log.debug("等待加入任务队列 {} ...", task);fullWaitSet.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}log.debug("加入任务队列 {}", task);queue.addLast(task);emptyWaitSet.signal();} finally {lock.unlock();}}// 带超时时间阻塞添加public boolean offer(T task, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit) {lock.lock();try {long nanos = timeUnit.toNanos(timeout);while (queue.size() == capcity) {try {if(nanos <= 0) {return false;}log.debug("等待加入任务队列 {} ...", task);nanos = fullWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}log.debug("加入任务队列 {}", task);queue.addLast(task);emptyWaitSet.signal();return true;} finally {lock.unlock();}}public int size() {lock.lock();try {return queue.size();} finally {lock.unlock();}}public void tryPut(RejectPolicy<T> rejectPolicy, T task) {lock.lock();try {// 判断队列是否满if(queue.size() == capcity) {rejectPolicy.reject(this, task);} else { // 有空闲log.debug("加入任务队列 {}", task);queue.addLast(task);emptyWaitSet.signal();}} finally {lock.unlock();}}}
步骤3:自定义线程池
class ThreadPool {// 任务队列private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;// 线程集合private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();// 核心线程数private int coreSize;// 获取任务时的超时时间private long timeout;private TimeUnit timeUnit;private RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy;// 执行任务public void execute(Runnable task) {// 当任务数没有超过 coreSize 时,直接交给 worker 对象执行// 如果任务数超过 coreSize 时,加入任务队列暂存synchronized (workers) {if(workers.size() < coreSize) {Worker worker = new Worker(task);log.debug("新增 worker{}, {}", worker, task);workers.add(worker);worker.start();} else {// taskQueue.put(task);// 1) 死等// 2) 带超时等待// 3) 让调用者放弃任务执行// 4) 让调用者抛出异常// 5) 让调用者自己执行任务taskQueue.tryPut(rejectPolicy, task);}}}public ThreadPool(int coreSize, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit, int queueCapcity,RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy) {this.coreSize = coreSize;this.timeout = timeout;this.timeUnit = timeUnit;this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(queueCapcity);this.rejectPolicy = rejectPolicy;}class Worker extends Thread{private Runnable task;public Worker(Runnable task) {this.task = task;}@Overridepublic void run() {// 执行任务// 1) 当 task 不为空,执行任务// 2) 当 task 执行完毕,再接着从任务队列获取任务并执行// while(task != null || (task = taskQueue.take()) != null) {while(task != null || (task = taskQueue.poll(timeout, timeUnit)) != null) {try {log.debug("正在执行...{}", task);task.run();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {task = null;}}synchronized (workers) {log.debug("worker 被移除{}", this);workers.remove(this);}}}}
步骤4:测试
public static void main(String[] args) {ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(1,1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 1, (queue, task)->{// 1. 死等// queue.put(task);// 2) 带超时等待// queue.offer(task, 1500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);// 3) 让调用者放弃任务执行// log.debug("放弃{}", task);// 4) 让调用者抛出异常// throw new RuntimeException("任务执行失败 " + task);// 5) 让调用者自己执行任务task.run();});for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int j = i;threadPool.execute(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(1000L);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}log.debug("{}", j);});}}
2. ThreadPpoolExecutor
1)线程池状态
ThreadPoolExecutor 使用 int 的高 3 位来表示线程池状态,低 29 位表示线程数量
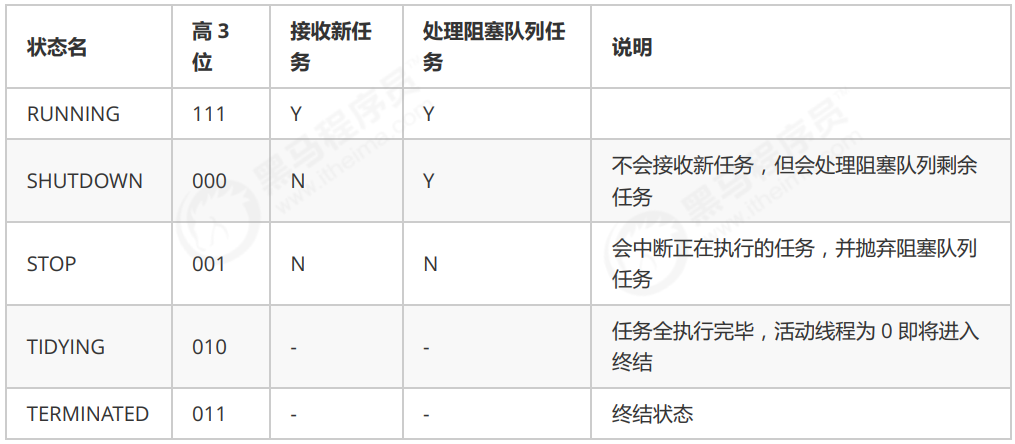
从数字上比较,TERMINATED > TIDYING > STOP > SHUTDOWN > RUNNING
这些信息存储在一个原子变量 ctl 中,目的是将线程池状态与线程个数合二为一,这样就可以用一次 cas 原子操作进行赋值 ```java // c 为旧值, ctlOf 返回结果为新值 ctl.compareAndSet(c, ctlOf(targetState, workerCountOf(c))));
-
// rs 为高 3 位代表线程池状态, wc 为低 29 位代表线程个数,ctl 是合并它们 private static int ctlOf(int rs, int wc) { return rs | wc; }
<a name="nWNYt"></a>#### 2)构造方法```javapublic ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,int maximumPoolSize,long keepAliveTime,TimeUnit unit,BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,ThreadFactory threadFactory,RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
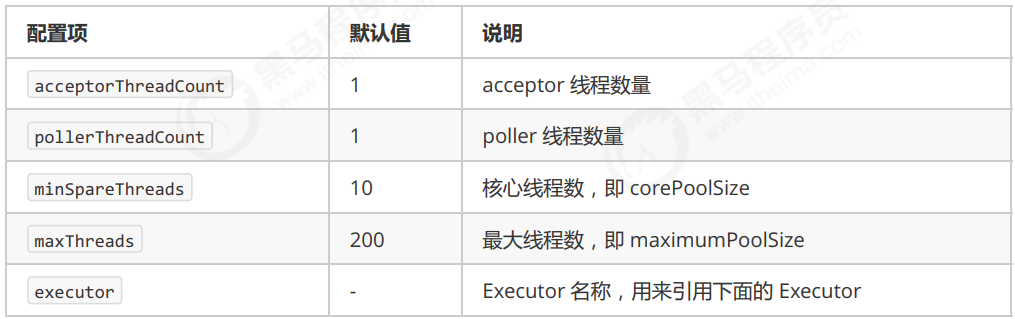
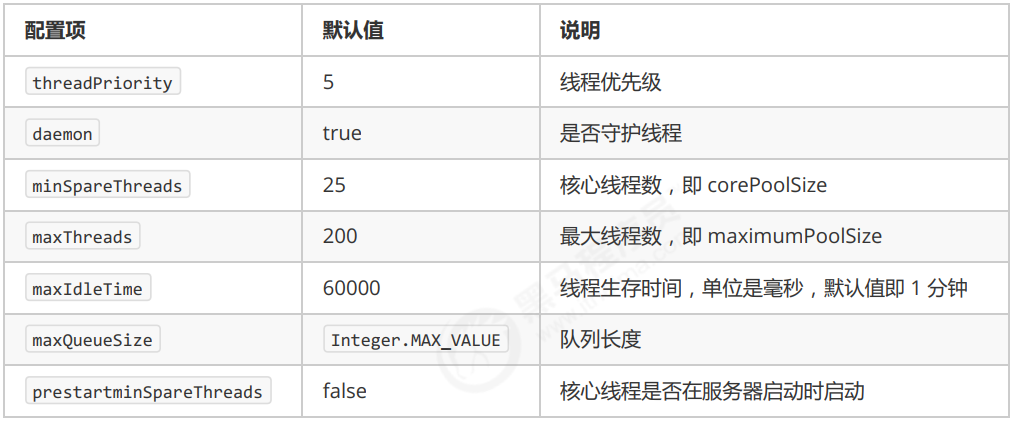
- corePoolSize 核心线程数目 (最多保留的线程数)
- maximumPoolSize 最大线程数目
- keepAliveTime 生存时间 - 针对救急线程
- unit 时间单位 - 针对救急线程
- workQueue 阻塞队列
- threadFactory 线程工厂 - 可以为线程创建时起个好名字
- handler 拒绝策略
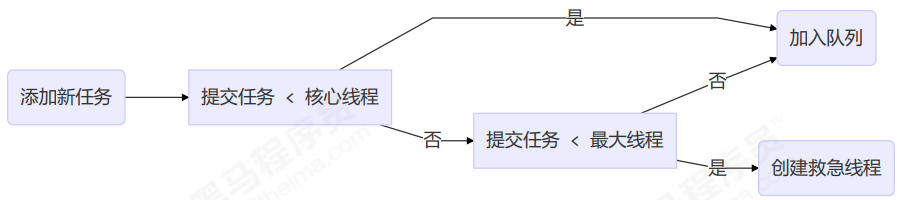
工作方式: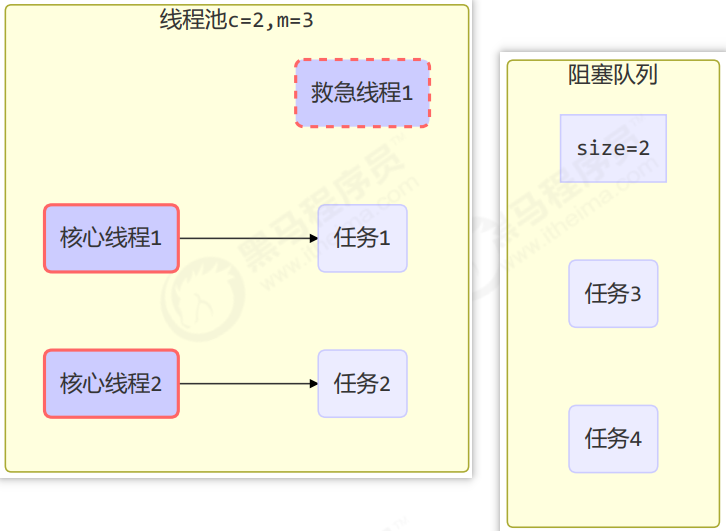
- 线程池中刚开始没有线程,当一个任务提交给线程池后,线程池会创建一个新线程来执行任务。
- 当线程数达到 corePoolSize 并没有线程空闲,这时再加入任务,新加的任务会被加入workQueue 队列排
队,直到有空闲的线程。 - 如果队列选择了有界队列,那么任务超过了队列大小时,会创建 maximumPoolSize - corePoolSize 数目的线
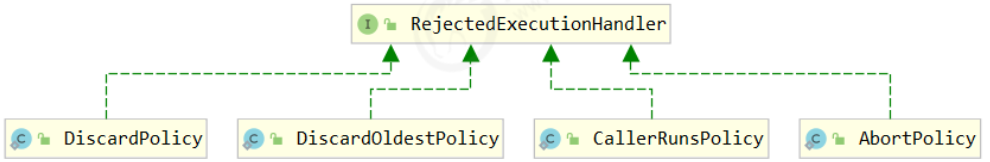
程来救急。 - 如果线程到达 maximumPoolSize 仍然有新任务这时会执行拒绝策略。拒绝策略 jdk 提供了 4 种实现,其它
著名框架也提供了实现- AbortPolicy 让调用者抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常,这是默认策略
- CallerRunsPolicy 让调用者运行任务
- DiscardPolicy 放弃本次任务
- DiscardOldestPolicy 放弃队列中最早的任务,本任务取而代之
- Dubbo 的实现,在抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常之前会记录日志,并 dump 线程栈信息,方
便定位问题 - Netty 的实现,是创建一个新线程来执行任务
- ActiveMQ 的实现,带超时等待(60s)尝试放入队列,类似我们之前自定义的拒绝策略
- PinPoint 的实现,它使用了一个拒绝策略链,会逐一尝试策略链中每种拒绝策略
- 当高峰过去后,超过corePoolSize 的救急线程如果一段时间没有任务做,需要结束节省资源,这个时间由
keepAliveTime 和 unit 来控制。
根据这个构造方法,JDK Executors 类中提供了众多工厂方法来创建各种用途的线程池
3)newFixedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());}
特点
- 核心线程数 == 最大线程数(没有救急线程被创建),因此也无需超时时间
- 阻塞队列是无界的,可以放任意数量的任务
评价 适用于任务量已知,相对耗时的任务
4)newCachedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());}
特点
- 核心线程数是 0, 最大线程数是 Integer.MAX_VALUE,救急线程的空闲生存时间是 60s,意味着
- 全部都是救急线程(60s 后可以回收)
- 救急线程可以无限创建
队列采用了 SynchronousQueue 实现特点是,它没有容量,没有线程来取是放不进去的(一手交钱、一手交货) ```java SynchronousQueue
integers = new SynchronousQueue<>(); new Thread(() -> { try { log.debug("putting {} ", 1);integers.put(1);log.debug("{} putted...", 1);log.debug("putting...{} ", 2);integers.put(2);log.debug("{} putted...", 2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} },”t1”).start();
sleep(1);
new Thread(() -> { try { log.debug(“taking {}”, 1); integers.take(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },”t2”).start();
sleep(1);
new Thread(() -> { try { log.debug(“taking {}”, 2); integers.take(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },”t3”).start();
输出```java11:48:15.500 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t1] - putting 111:48:16.500 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t2] - taking 111:48:16.500 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t1] - 1 putted...11:48:16.500 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t1] - putting...211:48:17.502 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t3] - taking 211:48:17.503 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t1] - 2 putted...
评价 整个线程池表现为线程数会根据任务量不断增长,没有上限,当任务执行完毕,空闲 1分钟后释放线程。 适合任务数比较密集,但每个任务执行时间较短的情况
5)newSingleTthreadPool
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));}
使用场景:
希望多个任务排队执行。线程数固定为 1,任务数多于 1 时,会放入无界队列排队。任务执行完毕,这唯一的线程也不会被释放。
区别:
- 自己创建一个单线程串行执行任务,如果任务执行失败而终止那么没有任何补救措施,而线程池还会新建一
个线程,保证池的正常工作 - Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor() 线程个数始终为1,不能修改
- FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService 应用的是装饰器模式,只对外暴露了 ExecutorService 接口,因
此不能调用 ThreadPoolExecutor 中特有的方法
- FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService 应用的是装饰器模式,只对外暴露了 ExecutorService 接口,因
- Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1) 初始时为1,以后还可以修改
// 提交任务 task,用返回值 Future 获得任务执行结果
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,带超时时间
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,哪个任务先成功执行完毕,返回此任务执行结果,其它任务取消
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,哪个任务先成功执行完毕,返回此任务执行结果,其它任务取消,带超时时间
<a name="K31f4"></a>#### 7)关闭线程池**shutdown**```java/*线程池状态变为 SHUTDOWN- 不会接收新任务- 但已提交任务会执行完- 此方法不会阻塞调用线程的执行*/void shutdown();
public void shutdown() {final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;mainLock.lock();try {checkShutdownAccess();// 修改线程池状态advanceRunState(SHUTDOWN);// 仅会打断空闲线程interruptIdleWorkers();onShutdown(); // 扩展点 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor} finally {mainLock.unlock();}// 尝试终结(没有运行的线程可以立刻终结,如果还有运行的线程也不会等)tryTerminate();}
shutdownNow
/*线程池状态变为 STOP- 不会接收新任务- 会将队列中的任务返回- 并用 interrupt 的方式中断正在执行的任务*/List<Runnable> shutdownNow();
public List<Runnable> shutdownNow() {List<Runnable> tasks;final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;mainLock.lock();try {checkShutdownAccess();// 修改线程池状态advanceRunState(STOP);// 打断所有线程interruptWorkers();// 获取队列中剩余任务tasks = drainQueue();} finally {mainLock.unlock();}// 尝试终结tryTerminate();return tasks;}
其它方法
// 不在 RUNNING 状态的线程池,此方法就返回 trueboolean isShutdown();// 线程池状态是否是 TERMINATEDboolean isTerminated();// 调用 shutdown 后,由于调用线程并不会等待所有任务运行结束,因此如果它想在线程池 TERMINATED 后做些事情,可以利用此方法等待boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
模式之Worker Thread
8)任务调度线程池
在『任务调度线程池』功能加入之前,可以使用 java.util.Timer 来实现定时功能,Timer 的优点在于简单易用,但由于所有任务都是由同一个线程来调度,因此所有任务都是串行执行的,同一时间只能有一个任务在执行,前一个任务的延迟或异常都将会影响到之后的任务。
public static void main(String[] args) {Timer timer = new Timer();TimerTask task1 = new TimerTask() {@Overridepublic void run() {log.debug("task 1");sleep(2);}};TimerTask task2 = new TimerTask() {@Overridepublic void run() {log.debug("task 2");}};// 使用 timer 添加两个任务,希望它们都在 1s 后执行// 但由于 timer 内只有一个线程来顺序执行队列中的任务,因此『任务1』的延时,影响了『任务2』的执行timer.schedule(task1, 1000);timer.schedule(task2, 1000);}
输出
20:46:09.444 c.TestTimer [main] - start...20:46:10.447 c.TestTimer [Timer-0] - task 120:46:12.448 c.TestTimer [Timer-0] - task 2
使用 ScheduledExecutorService 改写:
ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);// 添加两个任务,希望它们都在 1s 后执行executor.schedule(() -> {System.out.println("任务1,执行时间:" + new Date());try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { }}, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);executor.schedule(() -> {System.out.println("任务2,执行时间:" + new Date());}, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
输出
任务1,执行时间:Thu Jan 03 12:45:17 CST 2019任务2,执行时间:Thu Jan 03 12:45:17 CST 2019
scheduleAtFixedRate 例子:
ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);log.debug("start...");pool.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {log.debug("running...");}, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
输出
21:45:43.167 c.TestTimer [main] - start...21:45:44.215 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...21:45:45.215 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...21:45:46.215 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...21:45:47.215 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...
scheduleAtFixedRate 例子(任务执行时间超过了间隔时间):
ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);log.debug("start...");pool.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {log.debug("running...");sleep(2);}, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
输出分析:一开始,延时 1s,接下来,由于任务执行时间 > 间隔时间,间隔被『撑』到了 2s
21:44:30.311 c.TestTimer [main] - start...21:44:31.360 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...21:44:33.361 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...21:44:35.362 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...21:44:37.362 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...
scheduleWithFixedDelay 例子:
ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);log.debug("start...");pool.scheduleWithFixedDelay(()-> {log.debug("running...");sleep(2);}, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
输出分析:一开始,延时 1s,scheduleWithFixedDelay 的间隔是 上一个任务结束 <-> 延时 <-> 下一个任务开始 所以间隔都是 3s
21:40:55.078 c.TestTimer [main] - start...21:40:56.140 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...21:40:59.143 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...21:41:02.145 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...21:41:05.147 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...
评价 整个线程池表现为:线程数固定,任务数多于线程数时,会放入无界队列排队。任务执行完毕,这些线
程也不会被释放。用来执行延迟或反复执行的任务
9)正确处理执行任务异常
方法1:主动捉异常
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);pool.submit(() -> {try {log.debug("task1");int i = 1 / 0;} catch (Exception e) {log.error("error:", e);}});
输出
21:59:04.558 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - task121:59:04.562 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - error:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zeroat cn.itcast.n8.TestTimer.lambda$main$0(TestTimer.java:28)at java.util.concurrent.Executors$RunnableAdapter.call(Executors.java:511)at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:266)at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149)at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624)at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
方法2:使用 Future
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);Future<Boolean> f = pool.submit(() -> {log.debug("task1");int i = 1 / 0;return true;});log.debug("result:{}", f.get());
输出
21:54:58.208 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - task1Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zeroat java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.report(FutureTask.java:122)at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.get(FutureTask.java:192)at cn.itcast.n8.TestTimer.main(TestTimer.java:31)Caused by: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zeroat cn.itcast.n8.TestTimer.lambda$main$0(TestTimer.java:28)at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:266)at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149)at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624)at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
应用之定时任务
10)Tomcat线程池
Tomcat 在哪里用到了线程池呢
- LimitLatch 用来限流,可以控制最大连接个数,类似 J.U.C 中的 Semaphore 后面再讲
- Acceptor 只负责【接收新的 socket 连接】
- Poller 只负责监听 socket channel 是否有【可读的 I/O 事件】
- 一旦可读,封装一个任务对象(socketProcessor),提交给 Executor 线程池处理
- Executor 线程池中的工作线程最终负责【处理请求】
Tomcat 线程池扩展了 ThreadPoolExecutor,行为稍有不同
- 如果总线程数达到 maximumPoolSize
- 这时不会立刻抛 RejectedExecutionException 异常
- 而是再次尝试将任务放入队列,如果还失败,才抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常
源码 tomcat-7.0.42
public void execute(Runnable command, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {submittedCount.incrementAndGet();try {super.execute(command);} catch (RejectedExecutionException rx) {if (super.getQueue() instanceof TaskQueue) {final TaskQueue queue = (TaskQueue)super.getQueue();try {if (!queue.force(command, timeout, unit)) {submittedCount.decrementAndGet();throw new RejectedExecutionException("Queue capacity is full.");}} catch (InterruptedException x) {submittedCount.decrementAndGet();Thread.interrupted();throw new RejectedExecutionException(x);}} else {submittedCount.decrementAndGet();throw rx;}}}
TaskQueue.java
public boolean force(Runnable o, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {if ( parent.isShutdown() )throw new RejectedExecutionException("Executor not running, can't force a command into the queue");return super.offer(o,timeout,unit); //forces the item onto the queue, to be used if the taskis rejected}
3. Fork/Join
1)概念
Fork/Join 是 JDK 1.7 加入的新的线程池实现,它体现的是一种分治思想,适用于能够进行任务拆分的 cpu 密集型运算
所谓的任务拆分,是将一个大任务拆分为算法上相同的小任务,直至不能拆分可以直接求解。跟递归相关的一些计算,如归并排序、斐波那契数列、都可以用分治思想进行求解
Fork/Join 在分治的基础上加入了多线程,可以把每个任务的分解和合并交给不同的线程来完成,进一步提升了运算效率
Fork/Join 默认会创建与 cpu 核心数大小相同的线程池
2)使用
提交给 Fork/Join 线程池的任务需要继承 RecursiveTask(有返回值)或 RecursiveAction(没有返回值),例如下面定义了一个对 1~n 之间的整数求和的任务
@Slf4j(topic = "c.AddTask")class AddTask1 extends RecursiveTask<Integer> {int n;public AddTask1(int n) {this.n = n;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "{" + n + '}';}@Overrideprotected Integer compute() {// 如果 n 已经为 1,可以求得结果了if (n == 1) {log.debug("join() {}", n);return n;}// 将任务进行拆分(fork)AddTask1 t1 = new AddTask1(n - 1);t1.fork();log.debug("fork() {} + {}", n, t1);// 合并(join)结果int result = n + t1.join();log.debug("join() {} + {} = {}", n, t1, result);return result;}}
然后提交给 ForkJoinPool 来执行
public static void main(String[] args) {ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(4);System.out.println(pool.invoke(new AddTask1(5)));}
结果
[ForkJoinPool-1-worker-0] - fork() 2 + {1}[ForkJoinPool-1-worker-1] - fork() 5 + {4}[ForkJoinPool-1-worker-0] - join() 1[ForkJoinPool-1-worker-0] - join() 2 + {1} = 3[ForkJoinPool-1-worker-2] - fork() 4 + {3}[ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3] - fork() 3 + {2}[ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3] - join() 3 + {2} = 6[ForkJoinPool-1-worker-2] - join() 4 + {3} = 10[ForkJoinPool-1-worker-1] - join() 5 + {4} = 1515
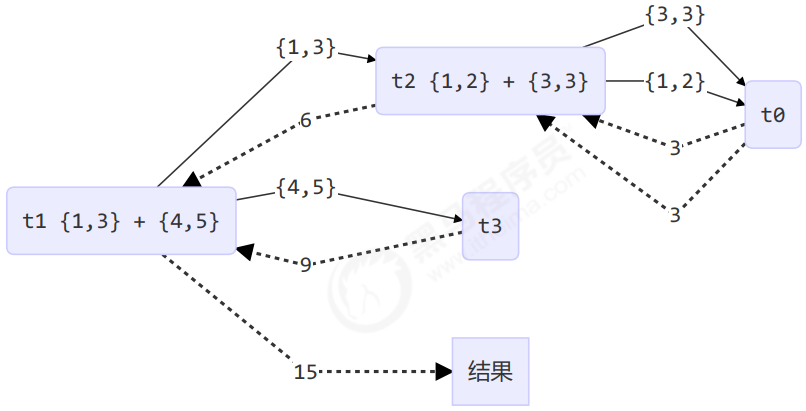
用图来表示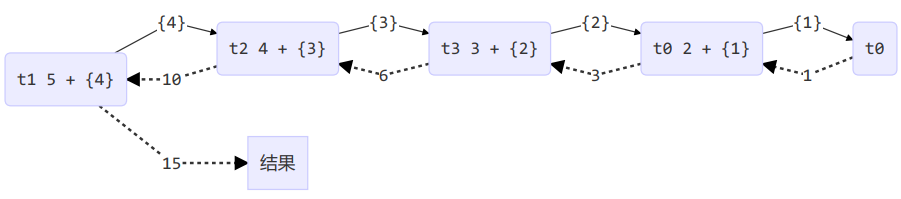
改进
class AddTask3 extends RecursiveTask<Integer> {int begin;int end;public AddTask3(int begin, int end) {this.begin = begin;this.end = end;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "{" + begin + "," + end + '}';}@Overrideprotected Integer compute() {// 5, 5if (begin == end) {log.debug("join() {}", begin);return begin;}// 4, 5if (end - begin == 1) {log.debug("join() {} + {} = {}", begin, end, end + begin);return end + begin;}// 1 5int mid = (end + begin) / 2; // 3AddTask3 t1 = new AddTask3(begin, mid); // 1,3t1.fork();AddTask3 t2 = new AddTask3(mid + 1, end); // 4,5t2.fork();log.debug("fork() {} + {} = ?", t1, t2);int result = t1.join() + t2.join();log.debug("join() {} + {} = {}", t1, t2, result);return result;}}
然后提交给 ForkJoinPool 来执行
public static void main(String[] args) {ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(4);System.out.println(pool.invoke(new AddTask3(1, 10)));}
结果
[ForkJoinPool-1-worker-0] - join() 1 + 2 = 3[ForkJoinPool-1-worker-3] - join() 4 + 5 = 9[ForkJoinPool-1-worker-0] - join() 3[ForkJoinPool-1-worker-1] - fork() {1,3} + {4,5} = ?[ForkJoinPool-1-worker-2] - fork() {1,2} + {3,3} = ?[ForkJoinPool-1-worker-2] - join() {1,2} + {3,3} = 6[ForkJoinPool-1-worker-1] - join() {1,3} + {4,5} = 1515