一、导读
@Autowired 属于依赖注入中 字段注入 ,主要使用相关注解注入想要的依赖。 字段注入 包含如下注解:
- @Autowired
- @Resource(由CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor解析)
- @Inject(需要引入单独的Jar包)
这里解析 @Autowired ,其它两个注解解析步骤类型,只不过由不同的类完成该解析动作。下面解析Spring如何完成 @Autowired 自动注入的。大致分为三个步骤,分别是
- 元信息解析
- 依赖查找
- 依赖注入(字段、方法)
二、元信息解析
如果对 Spring 了解的同学,应该知道 Spring 容器扫描路径是发生在方法 AbstractApplicationContext#registerBeanPostProcessors 中,调用 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner#doScan 方法对指定的路径进行扫描,并得到 BeanDefinition (ScannedGenericBeanDefinition,针对普通对象而言),相关代码:
// ConfigurationClassParser#doProcessConfigurationClassSet<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {// △3-1 解析@ComponentScan指定的基本包路径,通过扫描获取Bean元信息数据并注册到工厂的beanDefinitionMap中Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());// 3-2 检查扫描的定义集是否有其他配置类,并在需要时递归解析for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();if (bdCand == null) {bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();}// 3-3 如果一个类包含注解(@Component、@ComponentScan、@Import、@ImportResource、@Bean),则判断为配置类,递归解析// 也就是说再走一次配置类解析流程if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());}}}}
BeanDefinition 就像一道菜谱,里面记录了如何从原材料加工为一道极其美味的佳肴。于是,在真正厨师做菜的环节,需要对照菜谱一步一步来做。第一步:找原材料,即 解析注入点 :
// AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessMergedBeanDefinition
@Override
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
// △: 对被注入对象中获取注入点元信息(InjectionMetadata)。
// InjectionMetadata保存Collection<InjectedElement>注入点详情集合,member是存储已完成解析后的注入点详情,包含注入对象的名称、类型、声明的注解详情
// 该方法只会解析@Autowired以及@Value注解,不会解析@Resource(由另一个后置处理器解析)
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, beanType, null);
metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
}
// AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#findAutowiringMetadata
/**
* 查的可自动装配元数据(先从缓存获取、再判断是否需要刷新缓存数据)
*/
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// 回退类名称作为缓存键,以实现与自定义调用程序的向后兼容性
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// 首先以最小的锁定快速检查并发映射
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
// 缓存刷新
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
// △:若缓存不存在,则构建注入点详情
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
// AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#buildAutowiringMetadata
/**
* 完成注入点构建
* @param clazz
* @return
*/
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
// 保存完成注解解析的元素
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();
// #1 解析被注解的字段详情
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
// 静态字段被忽略
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
// 判断@Autowired中的require是否为true,spring默认为true
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
// #2 解析被注解的方法详情
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
method);
}
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
// 2-1 获取方法参数的属性描述符
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
}
简单理解,通过反射分别从类信息中获取带注解的 字段 和带注解的 方法 ,并判断其是否包含 @Autowired 和@Value ,若包含,则构建 AutowiredFieldElement 类以保存注入点信息。这一步获取原材料清单。
三、依赖查找
有了原材料清单,我们就可以从菜市场(BeanFactory,一般为 DefaultListableBeanFactory )买菜了,即通过 依赖查找 想要的对象。
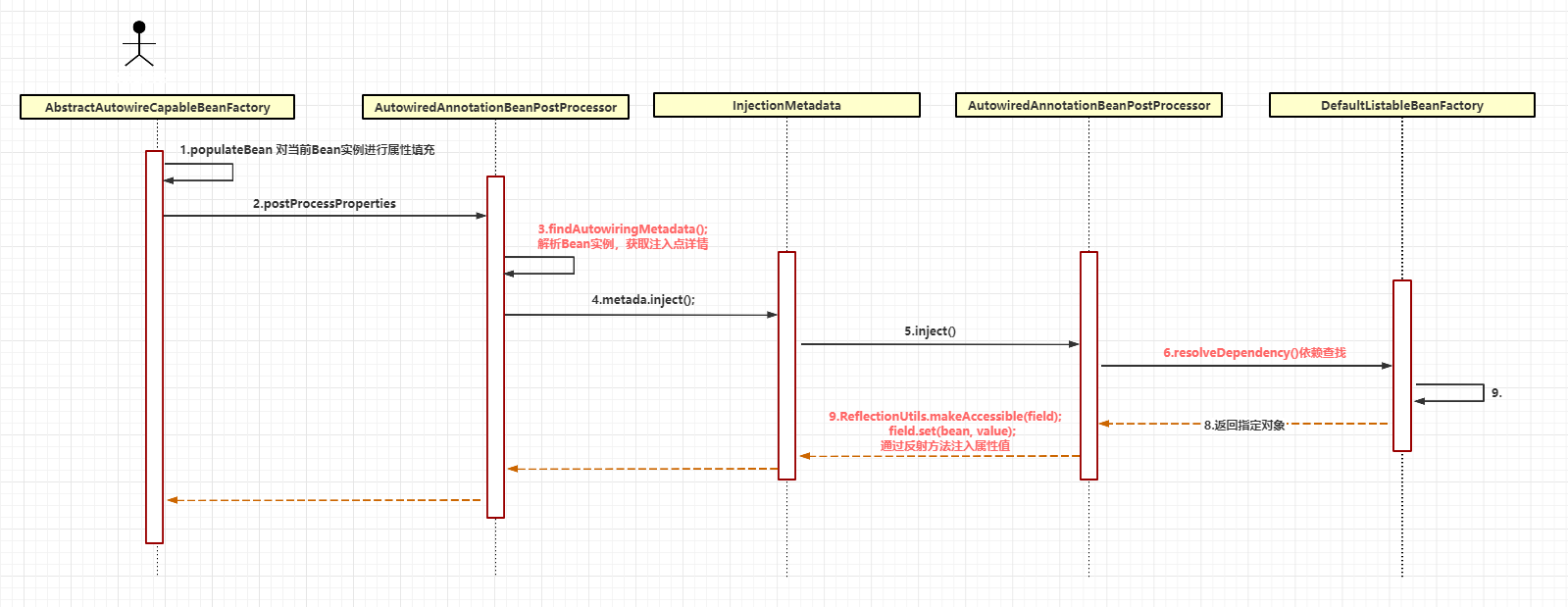
在#2通过后置处理器 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 完成依赖查找动作。
// AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean
// 填充当前Bean的属性
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#populateBean
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
// 2-1 执行相应的后置处理器
// 回调InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties方法,完成属性查找及属性注入操作
PropertyValues pvsToUse = bp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
pvsToUse = bp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
// AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
// #1 解析Bean实例获取注入点信息
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
// #2 完成对象属性注入
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
private class AutowiredFieldElement extends InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement {
private final boolean required;
private volatile boolean cached;
@Nullable
private volatile Object cachedFieldValue;
public AutowiredFieldElement(Field field, boolean required) {
super(field, null);
this.required = required;
}
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
if (this.cached) {
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
else {
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(1);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
// #1 从BeanFacotry获取类型转换器
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
try {
// #2 依赖查找解析的对象
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(field), ex);
}
// #3 写入相关依赖信息(dependentBeanMap)
synchronized (this) {
if (!this.cached) {
if (value != null || this.required) {
this.cachedFieldValue = desc;
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);
if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {
String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) {
this.cachedFieldValue = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
desc, autowiredBeanName, field.getType());
}
}
}
else {
this.cachedFieldValue = null;
}
this.cached = true;
}
}
}
if (value != null) {
// #4 通过反射方法写入字段属性
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);
}
}
}
简单来说,我们从缓存中获取已解析好的注入点对象 InjectedElement ,然后调用AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 内置对象 AutowiredFieldElement 的 inject 方法。
在此方法中通过 beanFactory.resolveDependency 方法完成依赖查找(如果单例池不存在此对象,则实例化),通过反射方式将属性填充对应字段。
四、依赖注入(字段、方法)
对于字段注入,Spring将其信息封装为 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 内部对象 AutowiredFieldElement ,而对于方法注入,则将其信息封装为 AutowiredMethodElement 内部对象,两者处理流程大致相同,都会在各自的 inject 方法中完成 依赖查找 以及通过 反射 完成注入。
@Component
public class A {
private B b;
private A a;
// 成功注入
@Autowired
public void setBbbb(B b, A a) {
this.b = b;
this.a = a;
}
}
// 反射注入方法字段
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
method.invoke(bean, arguments);
五、总结
注解
@Resource是JSR-250规范,@Inject是JSR-330规范。两者都可以替换@Autowired注解。注解@Resource已经由Spring内置的CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor后置处理器实现此注解解析,而@Inject注解需要导入如下maven依赖才能正常解析。@Resource提供更多注入方式,可根据指定名称、类型自动装配。而@Autowired只能通过类型自动装配。<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.inject/javax.inject --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.inject</groupId> <artifactId>javax.inject</artifactId> <version>1</version> </dependency>三个注解解析流程与
@Autowired大同小异,所以不需要过分追究其实现细节。