概述
我们都知道,Java 的 ThreadLocal 用在多线程环境下,提供一种访问某个变量的特殊方式,具体可看Java核心技术之ThreadLocal。由于 ThreadLocal 是在空间和时间之间寻求平衡,较好兼顾时间和性能。但是,Netty 通过理解 ThreadLocal 使用场景,觉得时间至上,最后利用空间换时间的思想重新设置了新的 FastThreadLocal,并配套实现了 FastThreadLocalThread 和 InternalThreadLocalMap 两个重要的类。
我们下面要讲的 FastThreadLocal、FastThreadLocalThread、InternalThreadLocalMap 是和 ThreadLocal、Thread、ThreadLocalMap 是对等的,我们可以按照 ThreadLocal 的逻辑理解它们,区别是底层的实现不同。
下面我们一起探究 Netty 的 FastThreadLocal 是怎么比 ThreadLocal 快 3 倍的。
FastThreadLocalThread
FastThreadLocalThread 是对 Thread 类的一层包装,主要是为 Thread 添加 InternalThreadLocalMap 这个重要的类变量。相关 API 定义如下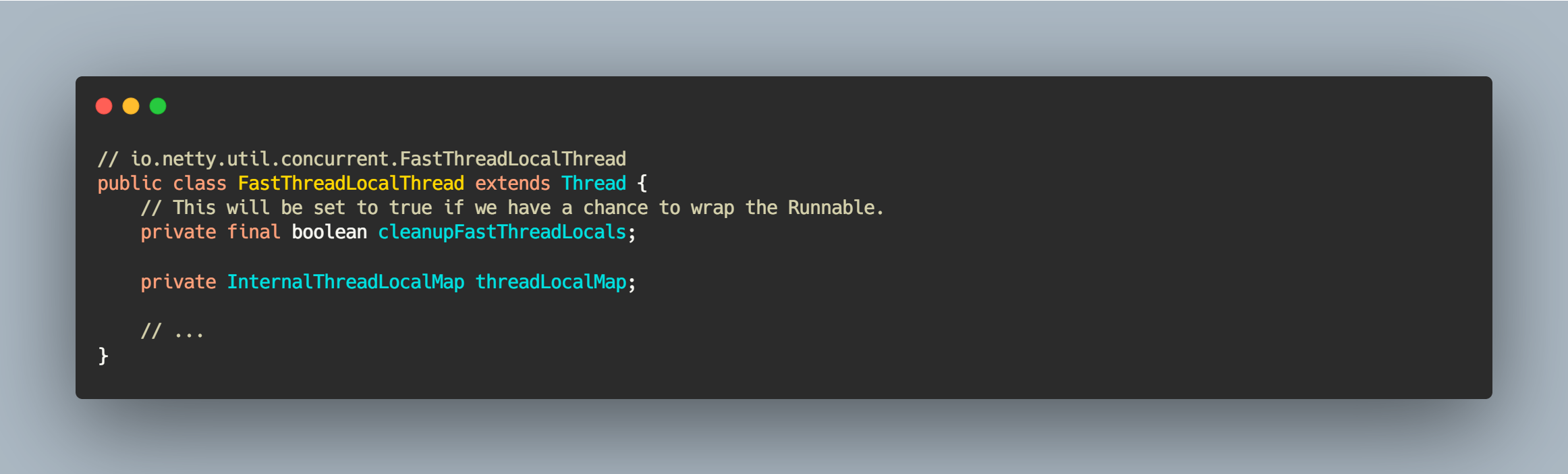
// io.netty.util.concurrent.FastThreadLocalThreadpublic class FastThreadLocalThread extends Thread {// This will be set to true if we have a chance to wrap the Runnable.private final boolean cleanupFastThreadLocals;private InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap;// ...}
FastThreadLocal
是 ThreadLocal 特殊的变体,在内部,FastThreadLocal 使用数组中的索引值查找变量,而非通过哈希表查找。这使它比使用哈希表查找具有轻微的性能优势,而且在频繁访问时非常有用。需要和 FastThreadLocalThread 配合使用才能发挥最高性能,Netty 提供 DefaultThreadFactory 工厂类创建 FastThreadLocalThread 线程。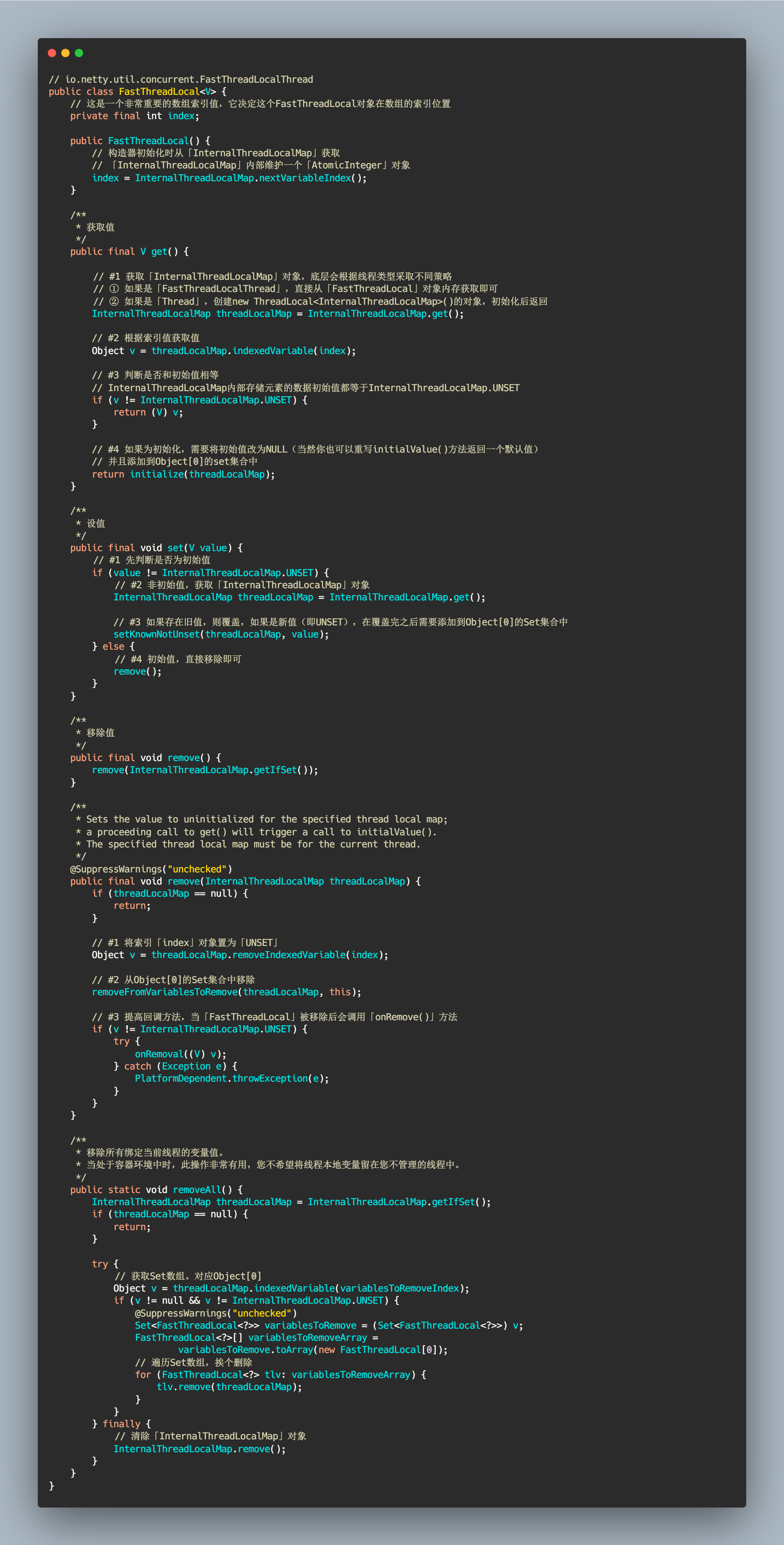
// io.netty.util.concurrent.FastThreadLocalThreadpublic class FastThreadLocal<V> {// 这是一个非常重要的数组索引值,它决定这个FastThreadLocal对象在数组的索引位置private final int index;public FastThreadLocal() {// 构造器初始化时从「InternalThreadLocalMap」获取// 「InternalThreadLocalMap」内部维护一个「AtomicInteger」对象index = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();}/*** 获取值*/public final V get() {// #1 获取「InternalThreadLocalMap」对象,底层会根据线程类型采取不同策略// ① 如果是「FastThreadLocalThread」,直接从「FastThreadLocal」对象内存获取即可// ② 如果是「Thread」,创建new ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap>()的对象,初始化后返回InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get();// #2 根据索引值获取值Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(index);// #3 判断是否和初始值相等// InternalThreadLocalMap内部存储元素的数据初始值都等于InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSETif (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {return (V) v;}// #4 如果为初始化,需要将初始值改为NULL(当然你也可以重写initialValue()方法返回一个默认值)// 并且添加到Object[0]的set集合中return initialize(threadLocalMap);}/*** 设值*/public final void set(V value) {// #1 先判断是否为初始值if (value != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {// #2 非初始值,获取「InternalThreadLocalMap」对象InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get();// #3 如果存在旧值,则覆盖,如果是新值(即UNSET),在覆盖完之后需要添加到Object[0]的Set集合中setKnownNotUnset(threadLocalMap, value);} else {// #4 初始值,直接移除即可remove();}}/*** 移除值*/public final void remove() {remove(InternalThreadLocalMap.getIfSet());}/*** Sets the value to uninitialized for the specified thread local map;* a proceeding call to get() will trigger a call to initialValue().* The specified thread local map must be for the current thread.*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public final void remove(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {if (threadLocalMap == null) {return;}// #1 将索引「index」对象置为「UNSET」Object v = threadLocalMap.removeIndexedVariable(index);// #2 从Object[0]的Set集合中移除removeFromVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);// #3 提高回调方法,当「FastThreadLocal」被移除后会调用「onRemove()」方法if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {try {onRemoval((V) v);} catch (Exception e) {PlatformDependent.throwException(e);}}}/*** 移除所有绑定当前线程的变量值。* 当处于容器环境中时,此操作非常有用,您不希望将线程本地变量留在您不管理的线程中。*/public static void removeAll() {InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.getIfSet();if (threadLocalMap == null) {return;}try {// 获取Set数组。对应Object[0]Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex);if (v != null && v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Set<FastThreadLocal<?>> variablesToRemove = (Set<FastThreadLocal<?>>) v;FastThreadLocal<?>[] variablesToRemoveArray =variablesToRemove.toArray(new FastThreadLocal[0]);// 遍历Set数组,挨个删除for (FastThreadLocal<?> tlv: variablesToRemoveArray) {tlv.remove(threadLocalMap);}}} finally {// 清除「InternalThreadLocalMap」对象InternalThreadLocalMap.remove();}}}
UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap
UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap 是 InternalThreadLocalMap 的父类,可将它看成是一个数据结构,用来存储本地线程变量。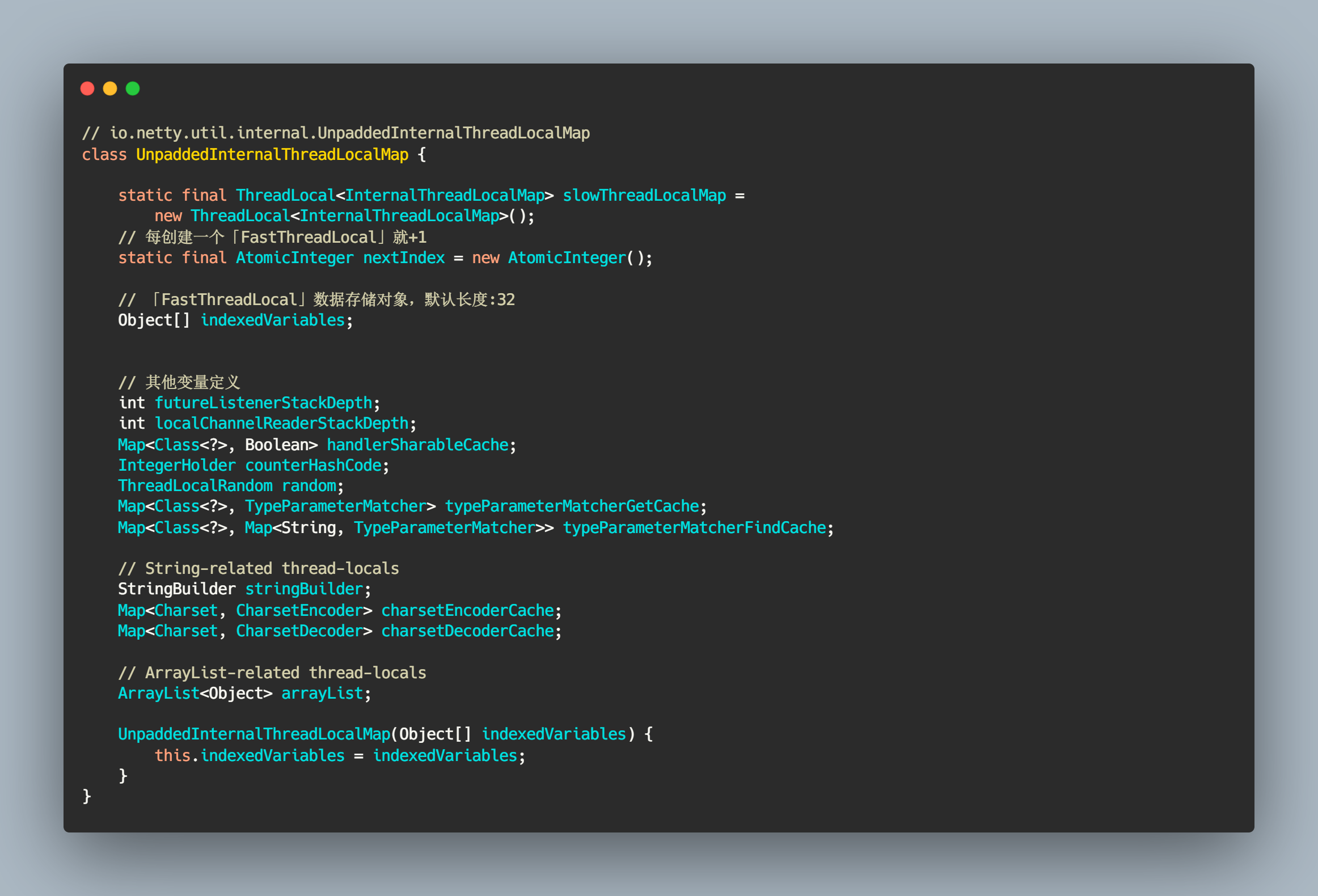
// io.netty.util.internal.UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap
class UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap {
static final ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap> slowThreadLocalMap =
new ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap>();
// 每创建一个「FastThreadLocal」就+1
static final AtomicInteger nextIndex = new AtomicInteger();
// 「FastThreadLocal」数据存储对象,默认长度:32
Object[] indexedVariables;
// 其他变量定义
int futureListenerStackDepth;
int localChannelReaderStackDepth;
Map<Class<?>, Boolean> handlerSharableCache;
IntegerHolder counterHashCode;
ThreadLocalRandom random;
Map<Class<?>, TypeParameterMatcher> typeParameterMatcherGetCache;
Map<Class<?>, Map<String, TypeParameterMatcher>> typeParameterMatcherFindCache;
// String-related thread-locals
StringBuilder stringBuilder;
Map<Charset, CharsetEncoder> charsetEncoderCache;
Map<Charset, CharsetDecoder> charsetDecoderCache;
// ArrayList-related thread-locals
ArrayList<Object> arrayList;
UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap(Object[] indexedVariables) {
this.indexedVariables = indexedVariables;
}
}
UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap 类定义了很多变量,在这里我们只需要关注 nextIndex 和 Object[] 即可。
InternalThreadLocalMap
回顾TheadLocal,它使用 ThreadLocalMap 存储数据,而 ThreadLocalMap 底层采用线性探测法解决 Hash 冲突问题,在空间和时间上寻求平衡。但 Netty 对这样的平衡并不满意,因此重新设计,使用 InternalThreadLocalMap 存储数据。核心思想是以空间换时间。InternalThreadLocalMap 是 UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap 对象的子类,之前也说过,可以把 UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap 当成一个数据结构,这里主要用到 nextIndex 和 Object[] 两个变量存储相应数据。那肯定有人会问不通过Hash算法怎么确定位置呢? 这就是很有意思的一点,这里就体现变量 nextIndex 的作用了: 每创建一个 FastThreadLocal 对象就从 InternalTheadLocalMap#getAndIncrement() (即 nextIndex 对象)方法获取索引值并保存在 FastThreadLocal#index 变量中,这个索引对应 Object[] 下标对应,通过索引值就能获取 FastThreadLocal 对象保存的值,这对于频繁获取值是非常高效的。其中有一个特殊情况, Object[0] 会存储一个 SetremoveAll() 方法中只需要遍历 Object[0] 的 Set 集合找到对应的数据并删除。Object[] 数组结构示意图:![Object[]示意图.png](/uploads/projects/clarencezero@mg9fpu/6a4c3d63171c5054fc78840bb5fa04d1.png)
InternalThreadLocalMap 源码并不复杂,稍微 DEBUG 就能理清思路了。下面只摘录部分源码。
// io.netty.util.internal.InternalThreadLocalMap
public final class InternalThreadLocalMap extends UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap {
public static final Object UNSET = new Object();
static final ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap> slowThreadLocalMap =
new ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap>();
/**
* 从「ThreadLocal(包含FastThreadLocal,下面统一使用 ThreadLocal 说明)」对象中获取值
*/
public static InternalThreadLocalMap get() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
// #1 判断是否为 FastThreadLocalThread,只有它才有index索引值
if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {
return fastGet((FastThreadLocalThread) thread);
} else {
// 如果非 FastThreadLocalThread,Netty的做法是通过ThreadLocal对象保存一个
// InternalThreadLocalMap 对象,间接实现。
return slowGet();
}
}
/**
* 因为线程FastThreadLocalThread内部持有一个InternalThreadLocalMap变量,因此,可以直接获取
*/
private static InternalThreadLocalMap fastGet(FastThreadLocalThread thread) {
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = thread.threadLocalMap();
if (threadLocalMap == null) {
thread.setThreadLocalMap(threadLocalMap = new InternalThreadLocalMap());
}
return threadLocalMap;
}
/**
* 非FastThreadLocalThread线程类型获取比较曲折。首先,Thread内存没有InternalThreadLocalMap变量
* 因此需要通过ThreadLocal变相保存InternalThreadLocalMap。
* 因此慢获取一个值会经历两个步骤:
* ① 首先通过slowGet()方法获取InternalThreadLocalMap对象
* ② 从InternalThreadLocalMap对象获取值
* 所以还不如直接使用ThreadLocal保存对象值来得更快些。
* 因此,如果FastThreadLocal没有配合FastThread使用的话,可能性能会变得更慢
*/
private static InternalThreadLocalMap slowGet() {
// #1 获取一个ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap>()对象
ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap> slowThreadLocalMap =
UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap.slowThreadLocalMap;
// #2 从「ThreadLocal」中获取InternalThreadLocalMap对象,里面保存用户数据
InternalThreadLocalMap ret = slowThreadLocalMap.get();
if (ret == null) {
// 没有则初始化InternalThreadLocalMap
ret = new InternalThreadLocalMap();
// 添加到ThreadLocal对象中
slowThreadLocalMap.set(ret);
}
return ret;
}
/**
* 在「index」添加值
*/
public boolean setIndexedVariable(int index, Object value) {
Object[] lookup = indexedVariables;
if (index < lookup.length) {
Object oldValue = lookup[index];
lookup[index] = value;
return oldValue == UNSET;
} else {
// 长度不够,扩容来凑
expandIndexedVariableTableAndSet(index, value);
return true;
}
}
/**
* 移除
*/
public static void remove() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {
// 直接将InternalThreadLocalMap置为null
((FastThreadLocalThread) thread).setThreadLocalMap(null);
} else {
// 需要清除ThreadLocal变量
slowThreadLocalMap.remove();
}
}
/**
* 数组扩容。扩容值为当前容量最接近且大于当前容量的2的次幂
*/
private void expandIndexedVariableTableAndSet(int index, Object value) {
Object[] oldArray = indexedVariables;
final int oldCapacity = oldArray.length;
// 这段位运算代码似曾相识,为什么没有减-操作呢?因为数据index就已经帮我们-1了
int newCapacity = index;
newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 1;
newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 2;
newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 4;
newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 8;
newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 16;
newCapacity ++;
Object[] newArray = Arrays.copyOf(oldArray, newCapacity);
Arrays.fill(newArray, oldCapacity, newArray.length, UNSET);
newArray[index] = value;
indexedVariables = newArray;
}
}
小结
FastThreadLocal 是 Netty 内部使用的、根据实际情况重构的本地线程缓存,与 ThreadLocal 采用线程探测法解决Hash冲突不同,FastThreadLocal 可以说根本没有冲突,内部有一个变量 index 确定存储地址,每创建一个 FastThreadLocal 都会导致全局的 nextIndex++,只有这会导致线程竞争,但弊端是如果大量使用 FastThreadLocal 的话,会导致空间以 2的次幂膨胀,但是一般情况下 FastThreadLocal 都会维持比较小的值 ,使用数组存储值,查询效率极高。但是需要和 FastThreadLocalThread 配合使用才能达到最强性能(因为 FastThreadLocalThread 内部可以持有 InernalThreadLocalMap 变量,直接获取即可)。
我的公众号


