笔者碎碎念:Swin-T作为ICCV21的最佳论文,一直没来得及看代码,今天就着假期看看代码学习。本文不涉及任何公式推导,并且要求读者有ViT的基础知识,如知道什么是MHSA等。 并且限于笔者水平,可能会有些错误,还请各位看官怒斥。 2022/4/4
codebase: https://github.com/microsoft/Swin-Transformer/blob/main/models/swin_transformer.py
attention公式镇场子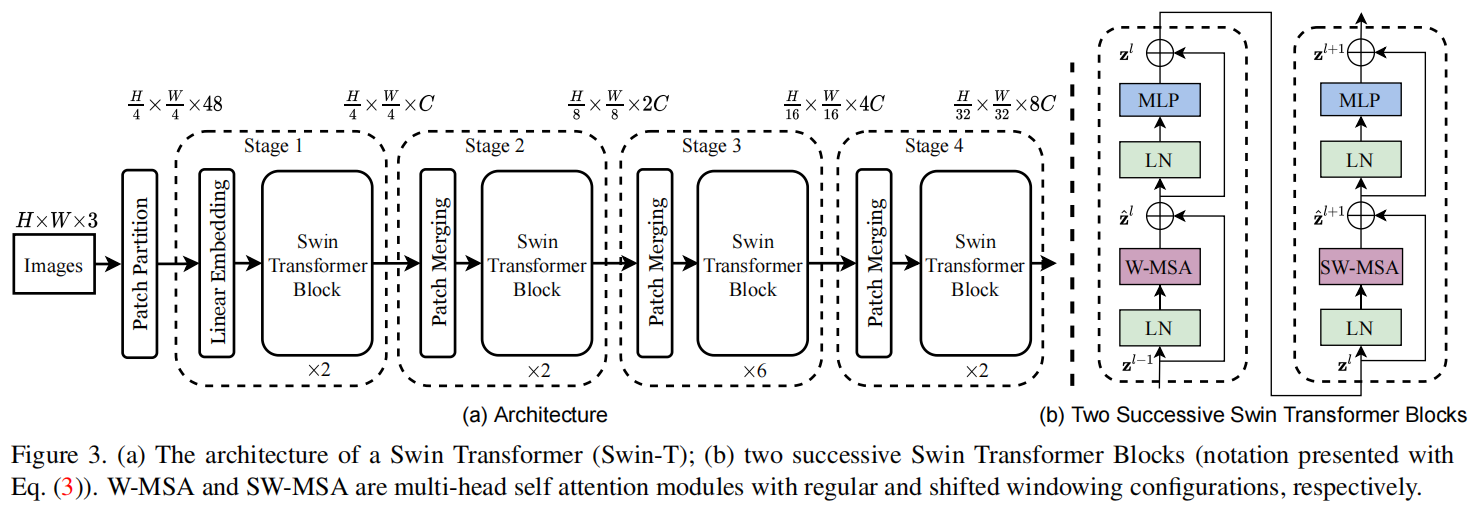
总体架构
Swin-T的结构有下面几个:Patch Patition, Patch Merging, Swin Transformer Block
其中最重要的Swin Transformer Block将ViT的MHSA变成了W-MSA和SW-MSA(一种带shift的,一种不带是shift的)。
总体架构
class SwinTransformer(nn.Module):r""" Swin TransformerA PyTorch impl of : `Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows` -https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.14030Args:img_size (int | tuple(int)): Input image size. Default 224patch_size (int | tuple(int)): Patch size. Default: 4in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3num_classes (int): Number of classes for classification head. Default: 1000embed_dim (int): Patch embedding dimension. Default: 96depths (tuple(int)): Depth of each Swin Transformer layer.num_heads (tuple(int)): Number of attention heads in different layers.window_size (int): Window size. Default: 7mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim. Default: 4qkv_bias (bool): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: Trueqk_scale (float): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set. Default: Nonedrop_rate (float): Dropout rate. Default: 0attn_drop_rate (float): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0drop_path_rate (float): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.1norm_layer (nn.Module): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm.ape (bool): If True, add absolute position embedding to the patch embedding. Default: Falsepatch_norm (bool): If True, add normalization after patch embedding. Default: Trueuse_checkpoint (bool): Whether to use checkpointing to save memory. Default: False"""def __init__(self, img_size=224, patch_size=4, in_chans=3, num_classes=1000,embed_dim=96, depths=[2, 2, 6, 2], num_heads=[3, 6, 12, 24],window_size=7, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None,drop_rate=0., attn_drop_rate=0., drop_path_rate=0.1,norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, ape=False, patch_norm=True,use_checkpoint=False, **kwargs):super().__init__()self.num_classes = num_classesself.num_layers = len(depths)self.embed_dim = embed_dimself.ape = apeself.patch_norm = patch_normself.num_features = int(embed_dim * 2 ** (self.num_layers - 1))self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio# split image into non-overlapping patchesself.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, in_chans=in_chans, embed_dim=embed_dim,norm_layer=norm_layer if self.patch_norm else None)num_patches = self.patch_embed.num_patchespatches_resolution = self.patch_embed.patches_resolutionself.patches_resolution = patches_resolution# absolute position embeddingif self.ape:self.absolute_pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches, embed_dim))trunc_normal_(self.absolute_pos_embed, std=.02)self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate)# stochastic depthdpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))] # stochastic depth decay rule# build layersself.layers = nn.ModuleList()for i_layer in range(self.num_layers):layer = BasicLayer(dim=int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_layer),input_resolution=(patches_resolution[0] // (2 ** i_layer),patches_resolution[1] // (2 ** i_layer)),depth=depths[i_layer],num_heads=num_heads[i_layer],window_size=window_size,mlp_ratio=self.mlp_ratio,qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,drop=drop_rate, attn_drop=attn_drop_rate,drop_path=dpr[sum(depths[:i_layer]):sum(depths[:i_layer + 1])],norm_layer=norm_layer,downsample=PatchMerging if (i_layer < self.num_layers - 1) else None,use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)self.layers.append(layer)self.norm = norm_layer(self.num_features)self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d(1)self.head = nn.Linear(self.num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()self.apply(self._init_weights)def _init_weights(self, m):if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)def forward_features(self, x):x = self.patch_embed(x) # patchifyif self.ape:x = x + self.absolute_pos_embedx = self.pos_drop(x)for layer in self.layers:x = layer(x)x = self.norm(x) # B L Cx = self.avgpool(x.transpose(1, 2)) # B C 1x = torch.flatten(x, 1)return xdef forward(self, x):x = self.forward_features(x)x = self.head(x)return
从forward中看出,图像进去PatchEmbed层先将其划分为一个个token,再加上positional embedding(假设这里默认是绝对位置嵌入),随后是dropout,然后是每个layer层计算注意力,最后将输出展平输出1000类logits(假设是ImageNet图片分类)。
其他层
在看BasicLayer如何定义之前,先给出一些简单的helper layers
Mlp
class Mlp(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=nn.GELU, drop=0.):super().__init__()out_features = out_features or in_featureshidden_features = hidden_features or in_featuresself.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features)self.act = act_layer()self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features)self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop)def forward(self, x):x = self.fc1(x)x = self.act(x)x = self.drop(x)x = self.fc2(x)x = self.drop(x)return x
Window Partition&Reverse
def window_partition(x, window_size):"""Args:x: (B, H, W, C)window_size (int): window sizeReturns:windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)"""B, H, W, C = x.shapex = x.view(B, H // window_size, window_size, W // window_size, window_size, C)windows = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(-1, window_size, window_size, C)return windowsdef window_reverse(windows, window_size, H, W):"""Args:windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)window_size (int): Window sizeH (int): Height of imageW (int): Width of imageReturns:x: (B, H, W, C)"""B = int(windows.shape[0] / (H * W / window_size / window_size))x = windows.view(B, H // window_size, W // window_size, window_size, window_size, -1)x = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(B, H, W, -1)return x
这里的维数有点多,需要大家仔细看。图片进来,直接将其划分为一个个window_size大小的patch。或者,token进来变成图片。
PatchEmbed&PatchMerge
PatchEmbed
class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):r""" Image to Patch EmbeddingArgs:img_size (int): Image size. Default: 224.patch_size (int): Patch token size. Default: 4.in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3.embed_dim (int): Number of linear projection output channels. Default: 96.norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: None"""def __init__(self, img_size=224, patch_size=4, in_chans=3, embed_dim=96, norm_layer=None):super().__init__()img_size = to_2tuple(img_size)patch_size = to_2tuple(patch_size)patches_resolution = [img_size[0] // patch_size[0], img_size[1] // patch_size[1]]self.img_size = img_sizeself.patch_size = patch_sizeself.patches_resolution = patches_resolutionself.num_patches = patches_resolution[0] * patches_resolution[1]self.in_chans = in_chansself.embed_dim = embed_dimself.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_chans, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size)if norm_layer is not None:self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim)else:self.norm = Nonedef forward(self, x):B, C, H, W = x.shape# FIXME look at relaxing size constraintsassert H == self.img_size[0] and W == self.img_size[1], \f"Input image size ({H}*{W}) doesn't match model ({self.img_size[0]}*{self.img_size[1]})."x = self.proj(x).flatten(2).transpose(1, 2) # B Ph*Pw Cif self.norm is not None:x = self.norm(x)return x
PatchEmbed层对于进来的图片划分为一个个的patch,具体使用kernel_size和stride相等的卷积操作,输入维度是96,这样就完成了patchify。对于ImageNet的图片,这一层的输出为(B, 56*56, 96),这样就可以和positional_embedding相加了(x = x + self.absolute_pos_embed)
PatchMerging
class PatchMerging(nn.Module):r""" Patch Merging Layer.Args:input_resolution (tuple[int]): Resolution of input feature.dim (int): Number of input channels.norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm"""def __init__(self, input_resolution, dim, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):super().__init__()self.input_resolution = input_resolutionself.dim = dimself.reduction = nn.Linear(4 * dim, 2 * dim, bias=False)self.norm = norm_layer(4 * dim)def forward(self, x):"""x: B, H*W, C"""H, W = self.input_resolutionB, L, C = x.shapeassert L == H * W, "input feature has wrong size"assert H % 2 == 0 and W % 2 == 0, f"x size ({H}*{W}) are not even."x = x.view(B, H, W, C)x0 = x[:, 0::2, 0::2, :] # B H/2 W/2 Cx1 = x[:, 1::2, 0::2, :] # B H/2 W/2 Cx2 = x[:, 0::2, 1::2, :] # B H/2 W/2 Cx3 = x[:, 1::2, 1::2, :] # B H/2 W/2 Cx = torch.cat([x0, x1, x2, x3], -1) # B H/2 W/2 4*Cx = x.view(B, -1, 4 * C) # B H/2*W/2 4*Cx = self.norm(x)x = self.reduction(x)return x
PatchMerging层的作用是将图片的长宽减半,通道数增加2倍。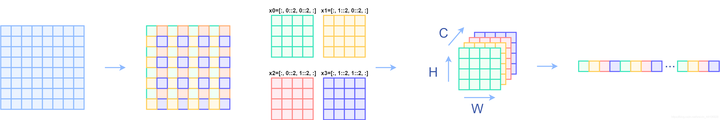
图源自知乎
很像Pixshuffle的反操作
BasicLayer
好啦,一些基础的层到这里就结束了。可以开始重点了。
class BasicLayer(nn.Module):""" A basic Swin Transformer layer for one stage.Args:dim (int): Number of input channels.input_resolution (tuple[int]): Input resolution.depth (int): Number of blocks.num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.window_size (int): Local window size.mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim.qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: Trueqk_scale (float | None, optional): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set.drop (float, optional): Dropout rate. Default: 0.0attn_drop (float, optional): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0.0drop_path (float | tuple[float], optional): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNormdownsample (nn.Module | None, optional): Downsample layer at the end of the layer. Default: Noneuse_checkpoint (bool): Whether to use checkpointing to save memory. Default: False."""def __init__(self, dim, input_resolution, depth, num_heads, window_size,mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, drop=0., attn_drop=0.,drop_path=0., norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, downsample=None, use_checkpoint=False):super().__init__()self.dim = dimself.input_resolution = input_resolutionself.depth = depthself.use_checkpoint = use_checkpoint# build blocksself.blocks = nn.ModuleList([SwinTransformerBlock(dim=dim, input_resolution=input_resolution,num_heads=num_heads, window_size=window_size,shift_size=0 if (i % 2 == 0) else window_size // 2,mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,drop=drop, attn_drop=attn_drop,drop_path=drop_path[i] if isinstance(drop_path, list) else drop_path,norm_layer=norm_layer)for i in range(depth)])# patch merging layerif downsample is not None:self.downsample = downsample(input_resolution, dim=dim, norm_layer=norm_layer)else:self.downsample = Nonedef forward(self, x):for blk in self.blocks:if self.use_checkpoint:x = checkpoint.checkpoint(blk, x)else:x = blk(x)if self.downsample is not None:x = self.downsample(x)return
BasicLayer层中包含了很多层SwinTransformerBlock,根据你给定的深度,创建depth个Block。需要的话,每个Block后还会有PatchMerging层。(套娃是吧)
SwinTransformerBlock
既然套娃那就接着看。
class SwinTransformerBlock(nn.Module):
r""" Swin Transformer Block.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
input_resolution (tuple[int]): Input resulotion.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
window_size (int): Window size.
shift_size (int): Shift size for SW-MSA.
mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
qk_scale (float | None, optional): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set.
drop (float, optional): Dropout rate. Default: 0.0
attn_drop (float, optional): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0.0
drop_path (float, optional): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0
act_layer (nn.Module, optional): Activation layer. Default: nn.GELU
norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm
"""
def __init__(self, dim, input_resolution, num_heads, window_size=7, shift_size=0,
mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, drop=0., attn_drop=0., drop_path=0.,
act_layer=nn.GELU, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.input_resolution = input_resolution
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.window_size = window_size
self.shift_size = shift_size
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
if min(self.input_resolution) <= self.window_size:
# if window size is larger than input resolution, we don't partition windows
self.shift_size = 0
self.window_size = min(self.input_resolution)
assert 0 <= self.shift_size < self.window_size, "shift_size must in 0-window_size"
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = WindowAttention(
dim, window_size=to_2tuple(self.window_size), num_heads=num_heads,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale, attn_drop=attn_drop, proj_drop=drop)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim, act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)
if self.shift_size > 0:
# calculate attention mask for SW-MSA
H, W = self.input_resolution
img_mask = torch.zeros((1, H, W, 1)) # 1 H W 1
h_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
w_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
cnt = 0
for h in h_slices:
for w in w_slices:
img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cnt
cnt += 1
mask_windows = window_partition(img_mask, self.window_size) # nW, window_size, window_size, 1
mask_windows = mask_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size)
attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2)
attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, float(-100.0)).masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, float(0.0))
else:
attn_mask = None
self.register_buffer("attn_mask", attn_mask)
def forward(self, x):
H, W = self.input_resolution
B, L, C = x.shape
assert L == H * W, "input feature has wrong size"
shortcut = x
x = self.norm1(x)
x = x.view(B, H, W, C)
# cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
shifted_x = torch.roll(x, shifts=(-self.shift_size, -self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
else:
shifted_x = x
# partition windows
x_windows = window_partition(shifted_x, self.window_size) # nW*B, window_size, window_size, C
x_windows = x_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size, C) # nW*B, window_size*window_size, C
# W-MSA/SW-MSA
attn_windows = self.attn(x_windows, mask=self.attn_mask) # nW*B, window_size*window_size, C
# merge windows
attn_windows = attn_windows.view(-1, self.window_size, self.window_size, C)
shifted_x = window_reverse(attn_windows, self.window_size, H, W) # B H' W' C
# reverse cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
x = torch.roll(shifted_x, shifts=(self.shift_size, self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
else:
x = shifted_x
x = x.view(B, H * W, C)
# FFN
x = shortcut + self.drop_path(x)
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
return x
这一层就是W-MSA和SW-MSA层啦,通过shift_size决定是否shift以及shift多少。
先看forward,我们先忽略是否shift的问题,SwinTransformerBlock首先将输入的x划分为很多个window,attention操作就是在这些window里进行,这样可以减少计算量(可以理解为local attention?),输出的维度为(num_window*B, window_size*window_size, C)
接着就做attention操作了,代码里又另起一层专门写这个attention(恼)。
然后将每个window里做好的attention重新reverse成图片的形式(B, H', W', C)
随后过norm和Mlp还有shortcut,这样,完整的Block的流程就走完了。
WindowAttention
接着就是喜闻乐见的Attention环节,熟悉ViT的朋友们看这一节肯定会非常容易。
class WindowAttention(nn.Module):
r""" Window based multi-head self attention (W-MSA) module with relative position bias.
It supports both of shifted and non-shifted window.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
window_size (tuple[int]): The height and width of the window.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
qk_scale (float | None, optional): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set
attn_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of attention weight. Default: 0.0
proj_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of output. Default: 0.0
"""
def __init__(self, dim, window_size, num_heads, qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.window_size = window_size # Wh, Ww
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim ** -0.5
# define a parameter table of relative position bias
self.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads)) # 2*Wh-1 * 2*Ww-1, nH
# 2*wh-1 is max(relative_position_index)?
# get pair-wise relative position index for each token inside the window
coords_h = torch.arange(self.window_size[0])
coords_w = torch.arange(self.window_size[1])
coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w])) # 2, Wh, Ww
coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1) # 2, Wh*Ww
relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :] # 2, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww, 2
relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # shift to start from 0
relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1) # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
self.register_buffer("relative_position_index", relative_position_index)
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
trunc_normal_(self.relative_position_bias_table, std=.02)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, x, mask=None):
"""
Args:
x: input features with shape of (num_windows*B, N, C)
mask: (0/-inf) mask with shape of (num_windows, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww) or None
"""
B_, N, C = x.shape
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B_, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2] # make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple)
# q size: [B*nw, wh*ww, C//h] N=wh*ww
q = q * self.scale
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) # [B*nw, N, N]
relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[self.relative_position_index.view(-1)].view(
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1) # Wh*Ww,Wh*Ww,nH
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous() # nH, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0)
if mask is not None:
nW = mask.shape[0]
attn = attn.view(B_ // nW, nW, self.num_heads, N, N) + mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(0)
attn = attn.view(-1, self.num_heads, N, N)
attn = self.softmax(attn)
else:
attn = self.softmax(attn)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B_, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
对于forward的前几行,就是常规的attention操作(计算出q, k, v,然后按照公式去做就完事了)。
然后后面就多了个relative_position_bias与计算出的attention相加,这个东西叫相对位置编码,实验证明有助于提升模型性能。
这里的代码有点复杂,我们一点点来捋。
我们这里以(2,2)的window_size为例,首先是coords:
coords_h = torch.arange(self.window_size[0])
coords_w = torch.arange(self.window_size[1])
coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w])) # 2, Wh, Ww
coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1) # 2, Wh*Ww
输出为
tensor([[[0, 0],
[1, 1]],
[[0, 1],
[0, 1]]]))
flatten展平得到coords_flatten
tensor([[0, 0, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 1]])
利用广播机制相减得到relative_coords,再将其平移至0,再对其中的某一维做乘法区分
relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :] # 2, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww, 2
relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # shift to start from 0
relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1
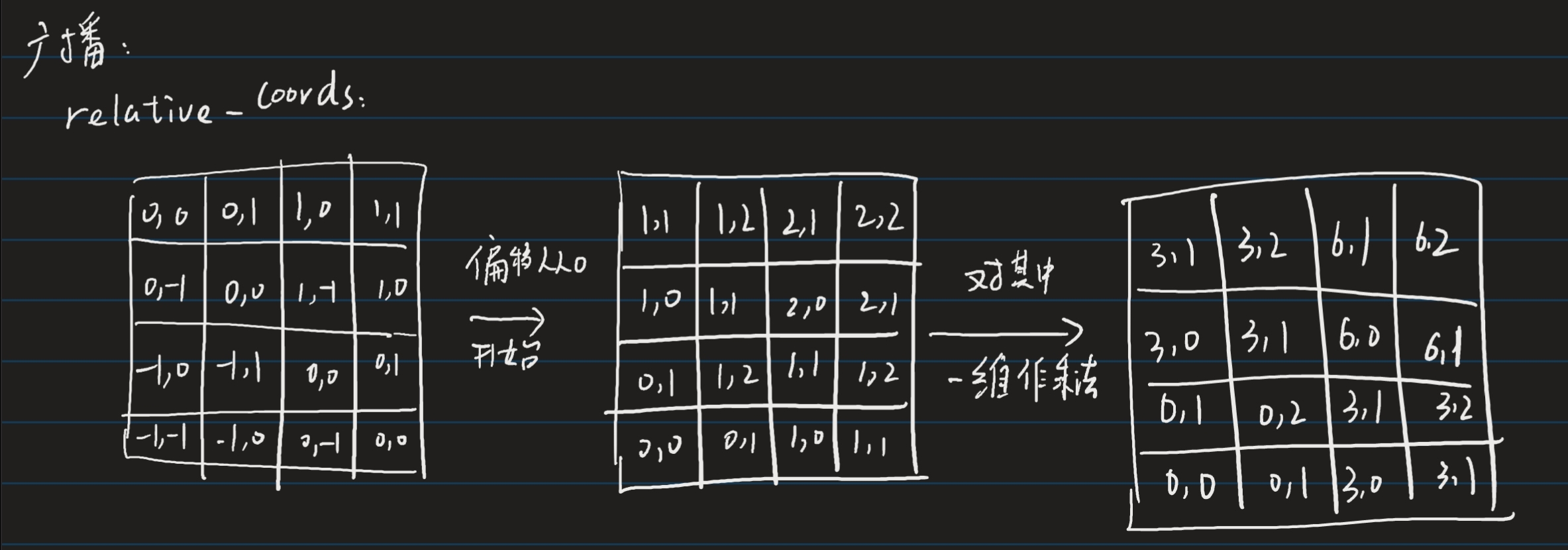
最后再对最后一维相加得到relative_position_index
relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1) # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
将其注册为buffer等待使用。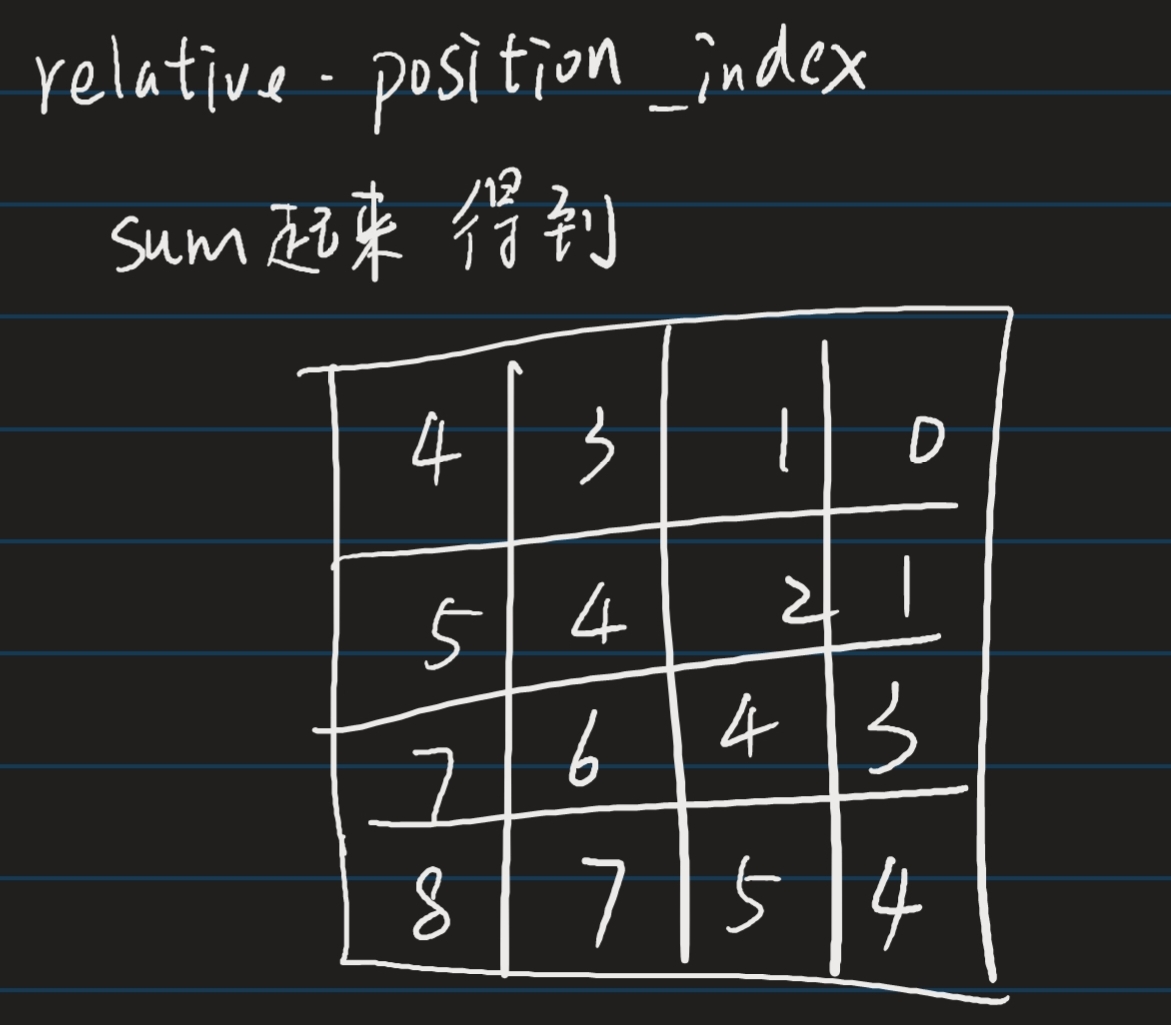
具体是作为索引,将relative_position_bias_table索引出来与attn相加。
shift window
不得不说,我在这里看了至少两个小时才弄懂这里的attn_mask究竟要干什么事
使用torch.roll对特征图进行位移。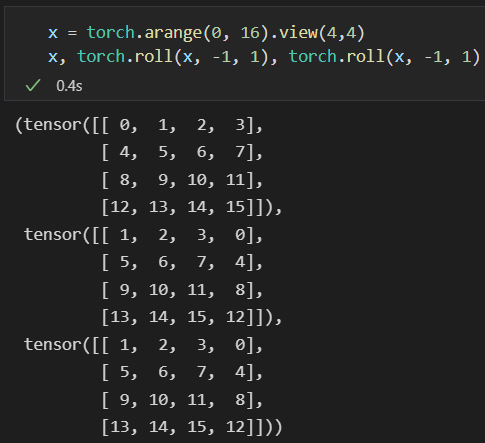
Intuition: 因为要在windows之间传递信息,swin-T使用的是平移特征图,那么就会出现一个问题。假设是向左上方移(实际也是),原来图像上最左上方的像素会被循环平移到右下方,因此在右下方的window计算attention的时候,与距离过远的像素相互的attention不应该被考虑(应该被mask掉)
还记得在计算attention的时候传入的mask吗,它的作用是让具有相同index QK进行计算,而忽略不同index QK计算结果。
因此就有了下面这个我看了两个小时的代码:
这种广播机制我是真服气,太巧妙了
window_size = 2
input_resolution=(4,4)
shift_size = 1
if shift_size > 0:
# calculate attention mask for SW-MSA
H, W = input_resolution
img_mask = torch.zeros((1, H, W, 1)) # 1 H W 1
h_slices = (slice(0, -window_size),
slice(-window_size, -shift_size),
slice(-shift_size, None))
w_slices = (slice(0, -window_size),
slice(-window_size, -shift_size),
slice(-shift_size, None))
cnt = 0
for h in h_slices:
for w in w_slices:
img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cnt
cnt += 1
mask_windows = window_partition(img_mask, window_size) # nW, window_size, window_size, 1
mask_windows = mask_windows.view(-1, window_size * window_size) # nW, window_size*window_size
print('this is mask_windows')
print(mask_windows)
attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2)
print('-'*20)
print('this is attn_mask')
print(attn_mask)
attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, float(-100.0)).masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, float(0.0))
else:
attn_mask = None
输出: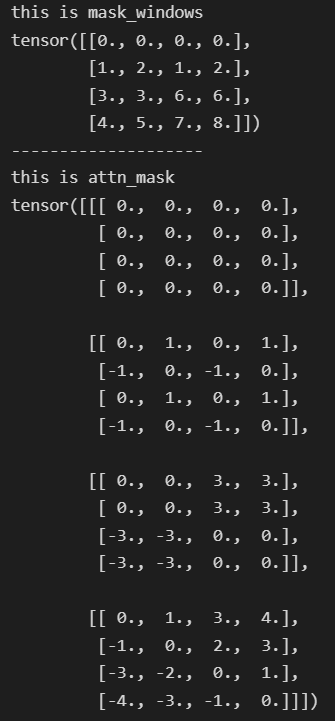
一张图简述根据上述代码生成mask的方法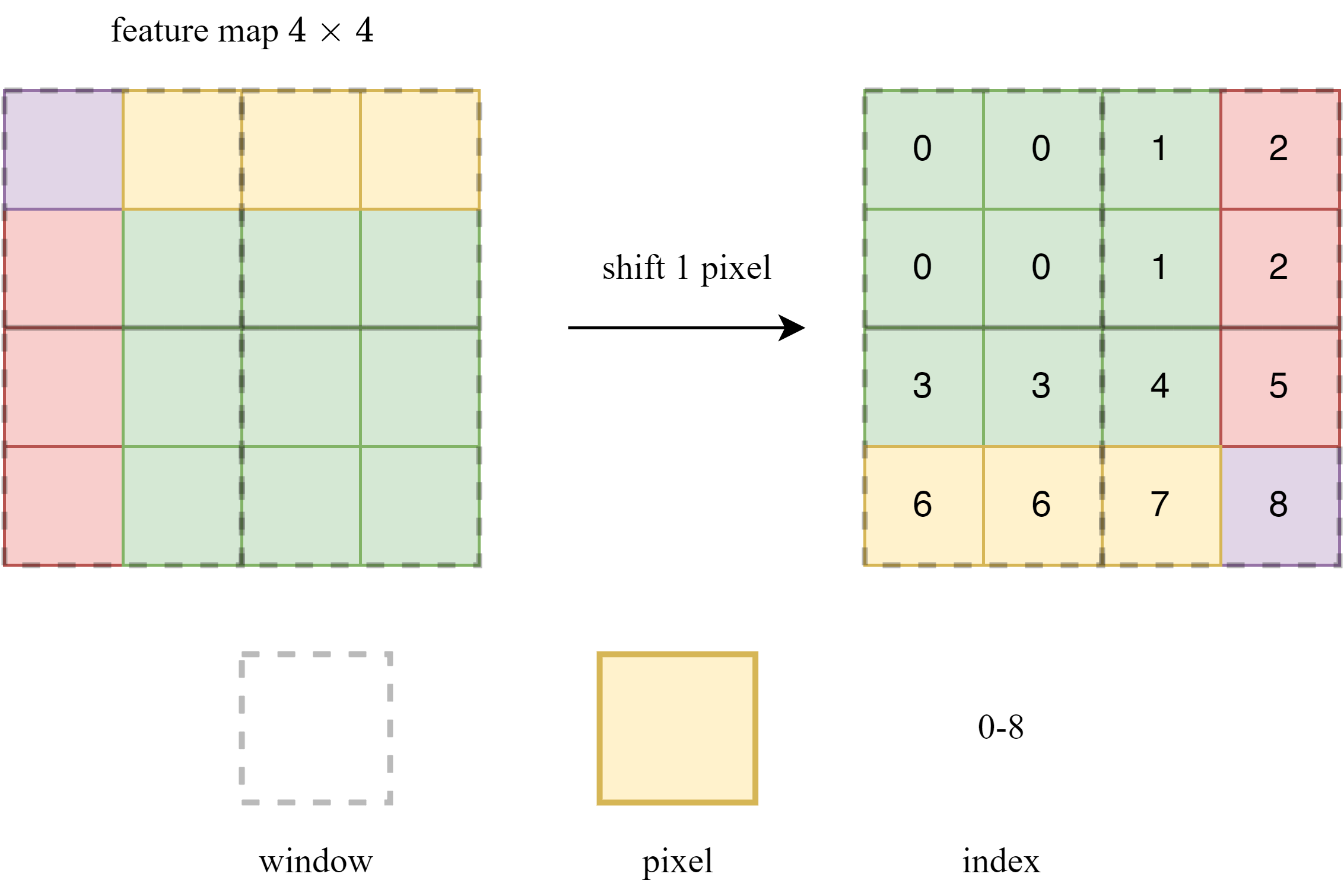
从上到下,从左到右,我们将window分别命名为w1, w2, w3, w4。在window中,由于每个像素都要与这个window中所有的像素计算attention,因此的窗中的attention是
。
对于w1来说,所有的像素在平移之前是相邻的,因此不需要mask;对于w2而言,index为1和2的像素在原图中并不相邻,因此需要在attention中相应的地方进行mask;w3和w4以此类推。
而最核心的一点就是计算在attention中需要被mask掉的地方。
这里还请读者回忆如何计算attention,实际上就是q和k做矩阵乘法。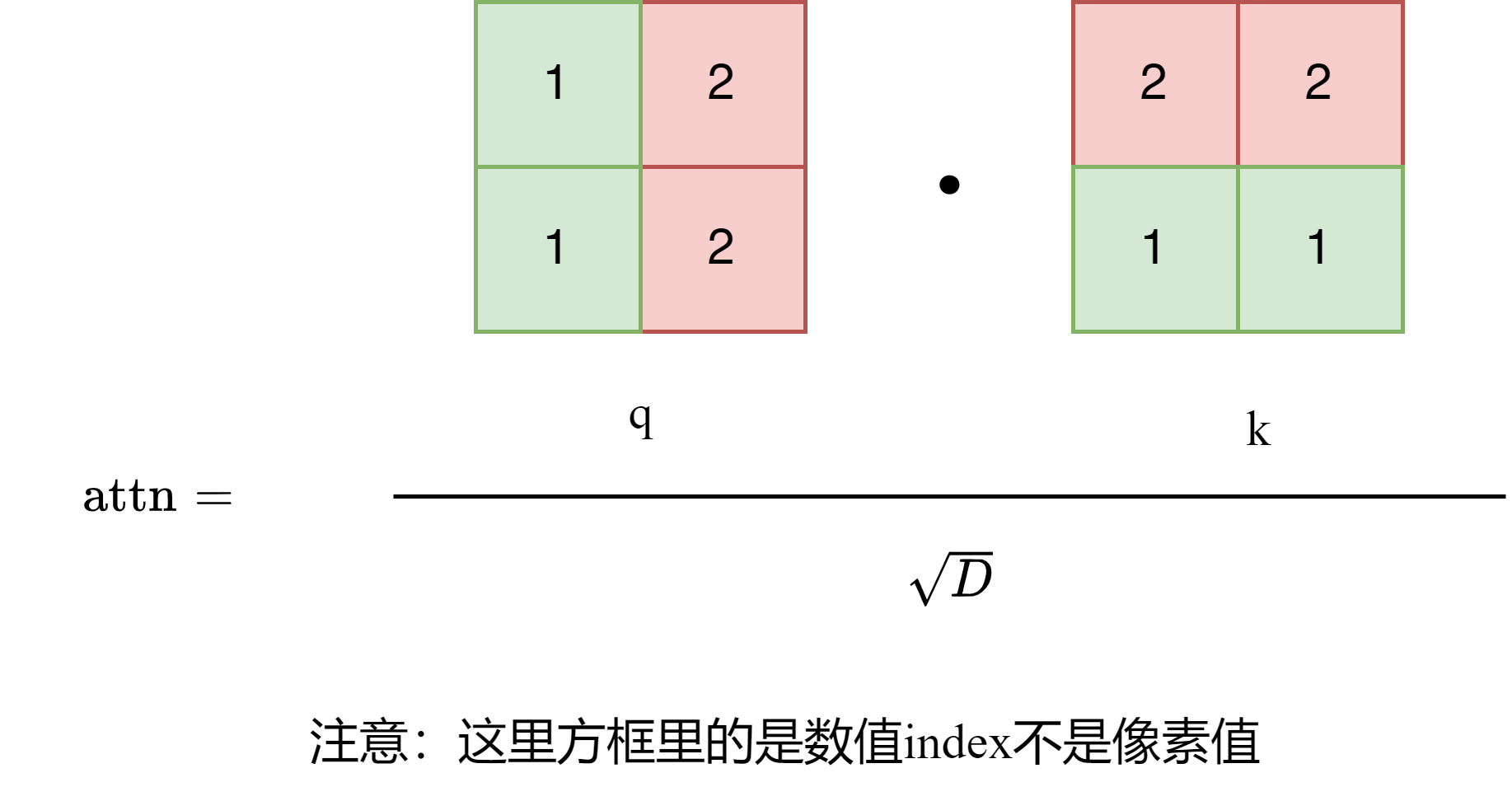
以w2为例
实际上这个顺序就是广播机制的顺序!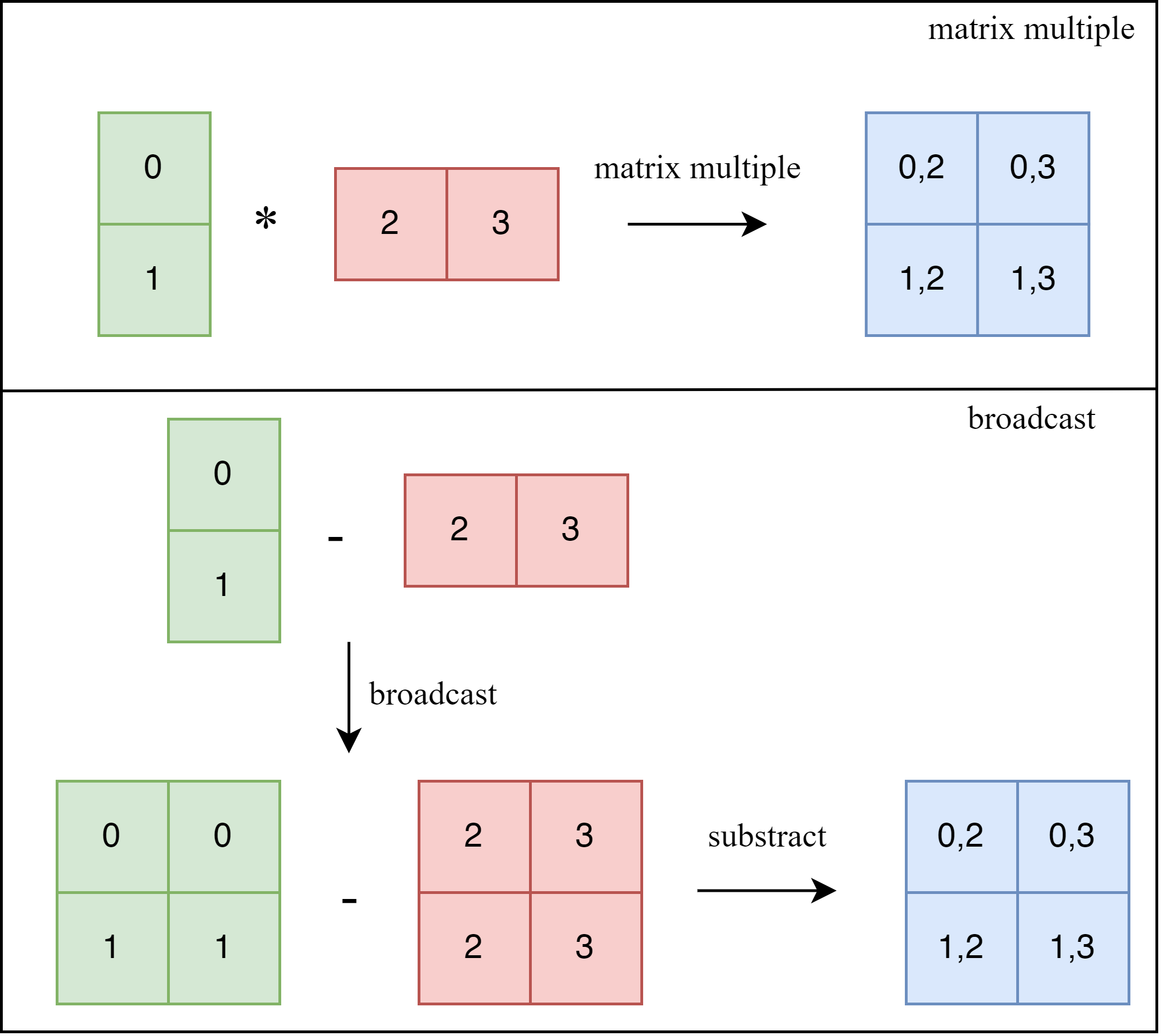
结语
至此,我们的Swin-T的所有代码都阅读完成啦。
之后我会继续和大家分享关于DL的论文和代码阅读。

