本文基于 JDK 1.8.0_191
1. 源码对比
- 实现接口类对比
- 扩容机制对比
- 线程安全
1.1 实现接口类对比
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializablepublic class LinkedList<E>extends AbstractSequentialList<E>implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializablepublic class Vector<E>extends AbstractList<E>implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
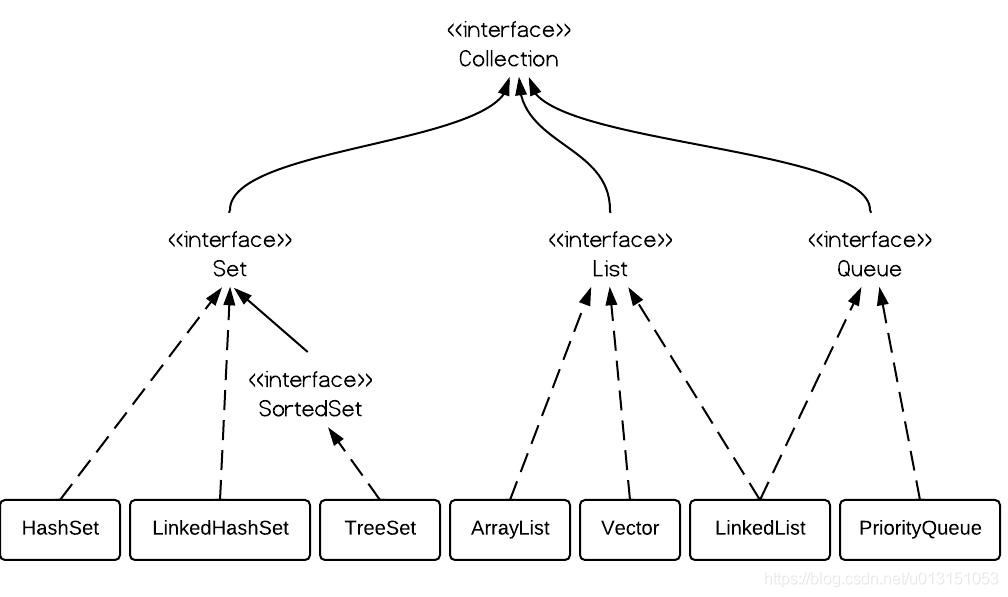
它们都实现 List 接口,说明具备列表的增加、删除、遍历元素等特性。
ArrayList、Vector 额外实现 RandomAccess 接口,说明他们能在常量时间复杂度内快速随机访问元素。
LinkedList 额外实现 Queue 接口,具备队列的入队、出队等特性。
1.2 扩容机制对比
ArrayList
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; // 定义初始大小private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; // 定义列表存储元素数量最大值private void grow(int minCapacity) {// overflow-conscious codeint oldCapacity = elementData.length; // 现有元素数量int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // 增加后元素的数量 = 1 + 0.5if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) // 增加后的元素数量 < 现有的空间,不扩容newCapacity = minCapacity;if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // 增加后的元素数量 > 大于最大值,尝试分配 Integer.MAX_VALUE 个元素,可能会抛出 OutOfMemoryError// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);}
Vector
public Vector() {this(10);}protected int capacityIncrement; // 扩容数量值,Vector 初始化不指定时默认为 0private void grow(int minCapacity) {// overflow-conscious codeint oldCapacity = elementData.length;int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ? capacityIncrement : oldCapacity); // 当扩容数量值小于 0,那么扩容比例为原来的两倍;否则扩容的数量为这个值。if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)newCapacity = minCapacity;if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);}
LinkList
transient int size = 0;
- 初始大小:ArrayList、Vector 默认为 10,LinkList 不指定默认为 0
- 扩容比例:ArrayList 以 1.5 倍进行扩容;Vector 不指定扩容比例时默认为 2 倍进行扩容
1.3 线程安全性
ArrayList
protected transient int modCount = 0;public boolean add(E e) {ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!elementData[size++] = e;return true;}
Vector
protected transient int modCount = 0;public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {modCount++;ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);elementData[elementCount++] = obj;}
Vector add() 方法上增加了 synchronized 关键字,使得 Vector 支持多线程环境下的元素增加删除修改操作。
2. 增删改性能对比
根据数据结构中知识:
顺序表查找元素时间复杂度为 O(1),适用于随机查找元素的场景。
链表增减元素时间复杂度为 O(1),适用于增减元素比较多的场景。
public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();Vector vector = new Vector();long t1, t2;t1 = System.nanoTime();for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {arrayList.add(i);}t2 = System.nanoTime();System.out.println("ArrayList add:" + (t2 - t1));t1 = System.nanoTime();for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {linkedList.add(i);}t2 = System.nanoTime();System.out.println("linkedList add:" + (t2 - t1));t1 = System.nanoTime();for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {vector.add(i);}t2 = System.nanoTime();System.out.println("vector add:" + (t2 - t1));}ArrayList add:6810212linkedList add:3463194vector add:4442985
添加元素,ArrayList 花费时间比 LinkList 时间长。
public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();Vector vector = new Vector();long t1, t2;for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {arrayList.add(i);linkedList.add(i);vector.add(i);}t1 = System.nanoTime();for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {arrayList.get(i);}t2 = System.nanoTime();System.out.println("ArrayList get:" + (t2 - t1));t1 = System.nanoTime();for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {linkedList.get(i);}t2 = System.nanoTime();System.out.println("linkedList get:" + (t2 - t1));t1 = System.nanoTime();for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {vector.get(i);}t2 = System.nanoTime();System.out.println("vector get:" + (t2 - t1));}ArrayList get:72482linkedList get:107975370vector get:242634
查找元素上,ArrayList 最快
3. 总结
将 ArrayList、LinkList 和 Vetor 进行了简单对比,总体来说:
- 在查找元素比较频繁的场合,推荐使用 ArrayList;在修改元素比较频繁的场合,推荐使用 LinkList。
- Vetor 与 ArrayList 类似,区别在于扩容比例、线程安全方面。
- 性能对比测试结果可能存在添加元素 ArrayList 花费时间比 LinkList 多的情况, 这个原因
参考:

