介绍
- 什么是代理模式
- 静态代理
- JDK 自带的动态代理
- CGLIB 动态代理
代理模式
意图:为其他对象提供一种代理,以控制对这个对象的访问。
例子:买火车票不一定要在火车站,去网上各个代理商那里也可以
代码思路:实体类 A 实现了接口 IA,而实体类 A 很复杂,那么使用实体类 B 去实现接口 IA,通过实体类 B 调用实体类 A 去满足功能。
注意事项:
1、和适配器模式的区别:适配器模式主要改变所考虑对象的接口,而代理模式不能改变所代理类的接口。
2、和装饰器模式的区别:装饰器模式为了增强功能,而代理模式是为了加以控制。
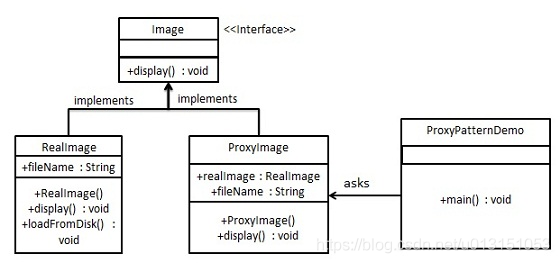
静态代理
静态代理其实就是在程序运行之前,提前写好被代理方法的代理类,编译后运行。
下面代理模式实现需要写很多代码,不建议使用。
// 接口 Apublic interface IServiceA {void sayHello(String str);}// ServiceAImpl 实现接口 Apublic class ServiceAImpl implements IServiceA {@Overridepublic void sayHello(String str) {System.out.println(str);}}// 代理对象 ServiceProxyAImpl 也实现接口 A,并且构造函数必须传入接口 A 的实例public class ServiceProxyAImpl implements IServiceA {private IServiceA iServiceA;public ServiceProxyAImpl(IServiceA iServiceA) {this.iServiceA = iServiceA;}@Overridepublic void sayHello(String str) {iServiceA.sayHello(str+ " is proxy ");}}// 进行测试public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {IServiceA realA = new ServiceAImpl();// 传入真实对象IServiceA proxyA = new ServiceProxyAImpl(realA);realA.sayHello("realA");// 代理对象的调用proxyA.sayHello("proxyA");}}程序输出 :ServiceAImpl sayrealAServiceAImpl sayproxyA is proxy
动态代理
通过反射机制,在运行时生成代理类
JDK 动态代理
被代理的类需要是接口实现,如果被代理的类没有实现接口,就不能使用 JDK 动态代理
- java.lang.reflect.Proxy:生成动态代理类和对象;
- java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler:通过 invoke 方法实现对真实角色的代理访问。
// 接口 Apublic interface IServiceA {void sayHello(String str);}// ServiceAImpl 实现接口 Apublic class ServiceAImpl implements IServiceA {@Overridepublic void sayHello(String str) {System.out.println(str);}}public class ProxyHandler implements InvocationHandler {private IServiceA serviceA;public ProxyHandler(IServiceA serviceA) {this.serviceA = serviceA;}@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {return method.invoke(serviceA, args);}}public class MainProxy {public static void main(String[] args) {// 真实对象IServiceA serviceA = new ServiceAImpl();// 通过 Proxy 得到代理对象IServiceA proxyServiceA = (IServiceA) Proxy.newProxyInstance(serviceA.getClass().getClassLoader(), serviceA.getClass().getInterfaces(),new ProxyHandler(serviceA));serviceA.sayHello("serviceA");proxyServiceA.sayHello("proxy serviceA");}}程序输出:serviceAproxy serviceA
CGLIB 动态代理
通过改变字节码,对需要被代理的类,生成他的子类,子类去覆盖被代理类的方法,其中 private、final 修饰的方法不会被重写。
- 首先实现 MethodInterceptor,方法调用会被转发到该类的 intercept() 方法。
- 通过 Enhancer 来指定要代理的目标对象、实际处理代理逻辑的对象,最终通过调用 create() 方法得到代理对象
// 接口 Apublic interface IServiceA {void sayHello(String str);}// ServiceAImpl 实现接口 Apublic class ServiceAImpl implements IServiceA {@Overridepublic void sayHello(String str) {System.out.println(str);}}public class MyMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {return methodProxy.invokeSuper(o,objects);}}public class CGLIBMain {public static void main(String[] args) {IServiceA serviceA = new ServiceAImpl();serviceA.sayHello("serviceA");Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer(); // 字节码增强enhancer.setSuperclass(ServiceAImpl.class); // 设置父类enhancer.setCallback(new MyMethodInterceptor()); // 设置回调方法IServiceA proxyA = (IServiceA) enhancer.create();proxyA.sayHello("proxyA");}}程序输出:serviceAproxyA

