- 环形链表">环形链表
- 环形链表 II">环形链表 II
- 相交链表">相交链表
- 删除链表的倒数第N个结点">删除链表的倒数第N个结点
- 链表中倒数第k个节点">链表中倒数第k个节点
- 移除链表元素">移除链表元素
- 删除排序链表中的重复元素">删除排序链表中的重复元素
- 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II">删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
- 奇偶链表">奇偶链表
- 回文链表">回文链表
- 合并两个有序链表">合并两个有序链表
- 合并K个升序链表">合并K个升序链表
- 两数相加*">两数相加*
- 反转链表">反转链表
- 反转链表 II">反转链表 II
- 链表向右移动K个位置*">链表向右移动K个位置*
- 重排链表*">重排链表*
- 两两交换链表中的节点">两两交换链表中的节点
- 排序链表*">排序链表*
- K 个一组翻转链表*">K 个一组翻转链表*
环形链表
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
class Solution(object):def hasCycle(self, head):# 快慢指针,一个走一步,一个走两步cur = headpre = headwhile cur and cur.next:pre = pre.nextcur = cur.next.nextif cur is pre:return Truereturn False
环形链表 II
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意,pos 仅仅是用于标识环的情况,并不会作为参数传递到函数中。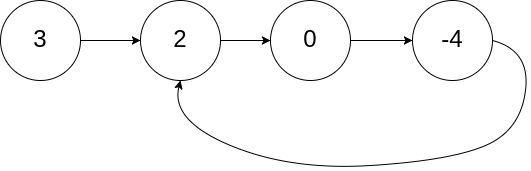
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
class Solution(object):def detectCycle(self, head):cur = headpre = headwhile cur and cur.next:pre = pre.nextcur = cur.next.nextif cur == pre:res = head # 此时res与pre距离环入口相等while pre != res:res = res.nextpre = pre.nextreturn resreturn None
相交链表
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。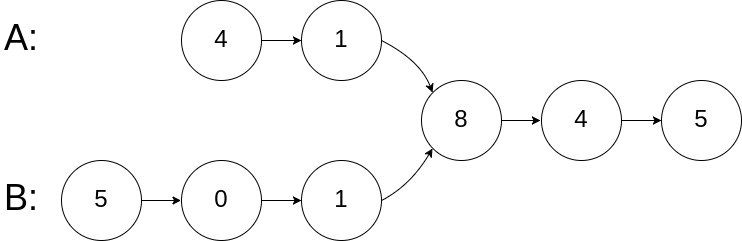
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
class Solution(object):def getIntersectionNode(self, headA, headB):cur = headApre = headBwhile cur != pre:if cur:cur = cur.nextelse:cur = headBif pre:pre = pre.nextelse:pre = headAreturn cur
删除链表的倒数第N个结点
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
输出:[1,2,3,5]
输入:head = [1], n = 1
输出:[]
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1
输出:[1]
class Solution(object):def removeNthFromEnd(self, head, n):# 创建一个头,然后cur先跑n步,然后再一起跑node = ListNode(0, head)cur = nodepre = nodefor _ in range(n):if cur == None:return []cur = cur.nextwhile cur.next is not None:cur = cur.nextpre = pre.nextpre.next = pre.next.nextreturn node.next
链表中倒数第k个节点
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个节点。为了符合大多数人的习惯,本题从1开始计数,即链表的尾节点是倒数第1个节点。例如,一个链表有6个节点,从头节点开始,它们的值依次是1、2、3、4、5、6。这个链表的倒数第3个节点是值为4的节点。
给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 k = 2.
返回链表 4->5.
class Solution:def getKthFromEnd(self, head):# cur先跑n步,然后再一起跑cur = headpre = headfor _ in range(k):if cur == None:return curcur = cur.nextwhile cur != None:cur = cur.nextpre = pre.nextreturn pre
移除链表元素
给你一个链表的头节点head和一个整数val,请你删除链表中所有满足Node.val == val的节点,并返回新的头节点。
输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
输入:head = [], val = 1
输出:[]
class Solution(object):def removeElements(self, head, val):node = ListNode(0, head)cur = headpre = nodewhile cur:if cur.val == val:pre.next = cur.nextelse:pre = pre.nextcur = cur.nextreturn node.next
删除排序链表中的重复元素
存在一个按升序排列的链表,给你这个链表的头节点head,请你删除所有重复的元素,使每个元素只出现一次。
返回同样按升序排列的结果链表。
输入:head = [1,1,2]
输出:[1,2]
输入:head = [1,1,2,3,3]
输出:[1,2,3]
class Solution(object):def deleteDuplicates(self, head):# 方法一:用假头,II题是这种思路if not head:return headnode = ListNode(0)node.next = headcur = nodewhile cur.next and cur.next.next:if cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val:cur.next = cur.next.nextelse:cur = cur.nextreturn node.next# 方法二:不用假头if not head:return headcur = headwhile cur.next:if cur.val == cur.next.val:cur.next = cur.next.nextelse:cur = cur.nextreturn head
删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
存在一个按升序排列的链表,给你这个链表的头节点 head ,请你删除链表中所有存在数字重复情况的节点,只保留原始链表中 没有重复出现 的数字。
返回同样按升序排列的结果链表。
输入:head = [1,2,3,3,4,4,5]
输出:[1,2,5]
输入:head = [1,1,1,2,3]
输出:[2,3]
class Solution(object):def deleteDuplicates(self, head):# 方法一:和I类似,就多了两行代码,需要多次去判断是否相等if not head:return headnode = ListNode(0)node.next = headcur = nodewhile cur.next and cur.next.next:if cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val:tmp = cur.next.valwhile cur.next and cur.next.val == tmp:cur.next = cur.next.nextelse:cur = cur.nextreturn node.next
奇偶链表
给定一个单链表,把所有的奇数节点和偶数节点分别排在一起。请注意,这里的奇数节点和偶数节点指的是节点编号的奇偶性,而不是节点的值的奇偶性。
请尝试使用原地算法完成。你的算法的空间复杂度应为 O(1),时间复杂度应为 O(nodes),nodes 为节点总数。
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 1->3->5->2->4->NULL
输入: 2->1->3->5->6->4->7->NULL
输出: 2->3->6->7->1->5->4->NULL
class Solution(object):def oddEvenList(self, head):if not head:return head# 奇数链cur = head# 偶数链pre = cur.next# 保存偶数链头tmp = prewhile cur.next and cur.next.next:# 分家,拆成奇数链和偶数链cur.next = cur.next.nextpre.next = pre.next.nextcur = cur.nextpre = pre.next# 合并,奇数链指向偶数链cur.next = tmpreturn head
回文链表
请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
输入: 1->2
输出: false
输入: 1->2->2->1
输出: true
class Solution(object):def isPalindrome(self, head):# 这个方法性能太差了lists = []cur = headwhile cur:lists.append(cur.val)cur = cur.nextif lists == lists[::-1]:return Trueelse:return False
合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的升序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
输入:l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]
class Solution(object):def mergeTwoLists(self, l1, l2):# 方法一:递归,下面那个合并k个借鉴这个if l1 is None:return l2if l2 is None:return l1node1 = l1node2 = l2if node1.val < node2.val:node1.next = self.mergeTwoLists(node1.next, node2)return node1else:node2.next = self.mergeTwoLists(node1, node2.next)return node2# 方法二:双指针cur = l1pre = l2node = ListNode(0)mid = nodewhile cur and pre:if cur.val <= pre.val:mid.next = curcur = cur.nextelse:mid.next = prepre = pre.nextmid = mid.nextif pre == None:mid.next = curelse:mid.next = prereturn node.next
合并K个升序链表
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
class Solution(object):def mergeKLists(self, lists):# 方法一:sort排序,暴力法nodes = []head = point = ListNode(0)# 把所有元素都遍历出来放到列表中排序for cur in lists:while cur:nodes.append(cur.val)cur = cur.nextnodes.sort()for x in nodes:point.next = ListNode(x)point = point.nextreturn head.next# 方法一:不用sort,用堆排序nodes = []head = point = ListNode(0)for cur in lists:while cur:heapq.heappush(nodes, cur.val)cur = cur.nextwhile nodes:point.next = ListNode(heappop(nodes))point = point.nextreturn head.next# 方法二:优先队列堆排序,每次只移动弹出元素所在列表,所以优先队列中不仅储存链表的元素,还要存储链表所在位置,以便弹出时知道该元素属于是哪一个链表。head = ListNode(0)pre = headnodes = []for key in range(len(lists)):if lists[key]:heapq.heappush(nodes, (lists[key].val, key))lists[key] = lists[key].nextwhile nodes:value, key = heapq.heappop(nodes)pre.next = ListNode(value)pre = pre.nextif lists[key]:heapq.heappush(nodes, (lists[key].val, key))lists[key] = lists[key].nextreturn head.next# 方法三:分治法,最优解,每次将链表列表分为两个部分,并分别自底向上合并两部分的链表if len(lists) == 0:return Noneif len(lists) == 1:return lists[0]mid = len(lists) // 2# 递归def mergeTwoLists(node1, node2):if not node1:return node2if not node2:return node1if node1.val < node2.val:node1.next = mergeTwoLists(node1.next, node2)return node1else:node2.next = mergeTwoLists(node1, node2.next)return node2return mergeTwoLists(self.mergeKLists(lists[:mid]), self.mergeKLists(lists[mid:]))
两数相加*
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]输出:[7,0,8]
解释:342 + 465 = 807
输入:l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
class Solution(object):def addTwoNumbers(self, l1, l2):count = 0node = ListNode()cur = nodewhile l1 or l2 or count:num = 0if l1:num += l1.vall1 = l1.nextif l2:num += l2.vall2 = l2.nextif count:num += countcount -= 1count, num = divmod(num, 10)cur.next = ListNode(num)cur = cur.nextreturn node.next
反转链表
反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
class Solution(object):def reverseList(self, head):cur = headpre = Nonewhile cur:# 记录当前节点的下一个节点tmp = cur.next# 然后将当前节点指向precur.next = pre# pre和cur节点都前进一位pre = curcur = tmpreturn pre# Go语言版func reverseList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {var pre *ListNodecur := headfor cur != nil {tmp := cur.Nextcur.Next = prepre = curcur = tmp}return pre}
反转链表 II
给你单链表的头指针 head 和两个整数 left 和 right ,其中 left <= right 。请你反转从位置 left 到位置 right 的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4
输出:[1,4,3,2,5]
输入:head = [5], left = 1, right = 1
输出:[5]
class Solution(object):def reverseBetween(self, head, left, right):# 方法一:比较好理解dummy = ListNode()dummy.next = headpre = dummy# 找到翻转链表部分的前一个节点, 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4 指的是 节点值为1for _ in range(left-1):pre = pre.next# 用双指针,进行链表翻转node = Nonecur = pre.next# cur多走一步到5for _ in range(right-left+1):tmp = cur.nextcur.next = nodenode = curcur = tmp# 将翻转部分 和 原链表拼接pre.next.next = cur # 也就是1.next.next = 5pre.next = node # 1.next = 新反转的链表return dummy.next# 方法二:将节点3插入节点1和节点2之间,变成: 1->3->2->4->5->NULL,再将节点4插入节点1和节点3之间,变成:1->4->3->2->5->NULLnode = ListNode()node.next = headpre = nodefor _ in range(left - 1):pre = pre.next# 用 pre, cur, tmp三指针实现插入操作# tail 是插入pre,与pre.next的节点cur = pre.nexttmp = cur.nextfor _ in range(right - left):cur.next = tmp.nexttmp.next = pre.nextpre.next = tmptmp = cur.nextreturn node.next
链表向右移动K个位置*
给你一个链表的头节点head,旋转链表,将链表每个节点向右移动 k个位置。
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
输出:[4,5,1,2,3]
输入:head = [0,1,2], k = 4
输出:[2,0,1]
class Solution(object):def rotateRight(self, head, k):# 找到原链表的最后一个节点,将其与原链表的头结点相连(成环),并统计链表长度,更新有效 k 值# 从原链表的头节点出发,找到需要断开的点,进行断开if not head or k == 0:return headtmp = 0cur = headwhile cur.next:cur = cur.nexttmp += 1tmp += 1k %= tmpcur.next = headk = tmp - k - 1while k > 0:head = head.nextk -= 1ans = head.nexthead.next = Nonereturn ans
重排链表*
给定一个单链表 L:L0→L1→…→Ln-1→Ln ,将其重新排列后变为: L0→Ln→L1→Ln-1→L2→Ln-2→…
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
给定链表 1->2->3->4, 重新排列为 1->4->2->3.
给定链表 1->2->3->4->5, 重新排列为 1->5->2->4->3.
class Solution(object):def reorderList(self, head):if not head:return head# 1 2 3 4 5fast = headpre_mid = head# 找到中点, 偶数个找到时上界那个while fast.next and fast.next.next:pre_mid = pre_mid.nextfast = fast.next.next# 翻转中点之后的链表,采用是pre, cur双指针方法pre = Nonecur = pre_mid.next# 1 2 3 5 4while cur:tmp = cur.nextcur.next = prepre = curcur = tmp# 翻转链表和前面链表拼接pre_mid.next = pre# 1 5 2 4 3# 链表头p1 = head# 翻转头p2 = pre_mid.nextwhile p1 != pre_mid:# 建议这部分画图, 很容易理解pre_mid.next = p2.nextp2.next = p1.nextp1.next = p2p1 = p2.nextp2 = pre_mid.nextreturn head
两两交换链表中的节点
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[2,1,4,3]
输入:head = []
输出:[]
class Solution(object):def swapPairs(self, head):# 方法一:双指针node = ListNode(0)node.next = headtmp = nodewhile tmp.next and tmp.next.next:cur = tmp.next.nextpre = tmp.nexttmp.next = curpre.next = cur.nextcur.next = pretmp = prereturn node.next# 方法二:递归if head == None or head.next == None:return headtmp = head.nexthead.next = self.swapPairs(head.next.next)tmp.next = headreturn tmp
排序链表*
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按升序排列并返回排序后的链表。
输入:head = [4,2,1,3]
输出:[1,2,3,4]
输入:head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
输出:[-1,0,3,4,5]
class Solution(object):def sortList(self, head):# 方法一:自顶向下归并排序if not head or not head.next:return headpre = headcur = head# 用快慢指针分成两部分while cur.next and cur.next.next:pre = pre.nextcur = cur.next.next# 找到左右部分, 把右边置空mid = pre.nextpre.next = None# 递归下去# 此时head已经变为原来的一般,左半边left = self.sortList(head)# mid为右半边right = self.sortList(mid)# 合并return self.merge(left, right)def merge(self, left, right):node = ListNode(0)cur = nodewhile left and right:if left.val < right.val:cur.next = leftleft = left.nextcur = cur.nextelse:cur.next = rightright = right.nextcur = cur.nextif left:cur.next = leftif right:cur.next = rightreturn node.next# 方法二:自下向上归并排序,最优解,但是过程复杂intv = 1length = 0high = head# 计算链表长度while high:high = high.nextlength += 1node = ListNode(0)node.next = head# merge the list in different intv.while intv < length:mid, high = node, node.nextwhile high:# get the two merge head `h1`, `h2`h1, i = high, intvwhile i and high:high, i = high.next, i - 1if i:break # no need to merge because the `h2` is None.h2, i = high, intvwhile i and high:high, i = high.next, i - 1c1, c2 = intv, intv - i # the `c2`: length of `h2` can be small than the `intv`.# merge the `h1` and `h2`.while c1 and c2:if h1.val < h2.val:mid.next, h1, c1 = h1, h1.next, c1 - 1else:mid.next, h2, c2 = h2, h2.next, c2 - 1mid = mid.nextmid.next = h1 if c1 else h2while c1 > 0 or c2 > 0:mid, c1, c2 = mid.next, c1 - 1, c2 - 1mid.next = highintv *= 2return node.next# 方法三:都取出来排序再重新生成链表if head is None or head.next is None:return headnums = []cur = headwhile cur:nums.append(p.val)cur = cur.nextnums.sort()cur = headwhile cur:cur.val = nums.pop(0)cur = cur.nextreturn head
K 个一组翻转链表*
给你一个链表,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。
如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
输出:[3,2,1,4,5]
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 1
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
class Solution(object):def reverseKGroup(self, head, k):# 我们把 k 个数压入栈中,然后弹出来的顺序就是翻转的!# 这里要注意几个问题:# 第一,剩下的链表个数够不够 k 个(因为不够 k 个不用翻转)# 第二,已经翻转的部分要与剩下链表连接起来。# 方法一:栈dummy = ListNode(0)cur = dummywhile True:count = kstack = []tmp = headwhile count and tmp:stack.append(tmp)tmp = tmp.nextcount -= 1# 注意,目前tmp所在k+1位置# 说明剩下的链表不够k个,跳出循环if count :cur.next = headbreak# 翻转操作while stack:cur.next = stack.pop()cur = cur.next#与剩下链表连接起来cur.next = tmphead = tmpreturn dummy.next# 方法二:最优解,尾插法dummy = ListNode(0)dummy.next = headpre = dummytail = dummywhile True:count = kwhile count and tail:count -= 1tail = tail.nextif not tail: breakhead = pre.nextwhile pre.next != tail:cur = pre.next # 获取下一个元素# pre与cur.next连接起来,此时cur(孤单)掉了出来pre.next = cur.nextcur.next = tail.next # 和剩余的链表连接起来tail.next = cur #插在tail后面# 改变 pre tail 的值pre = headtail = headreturn dummy.next

