包装类
对应关系
基本数据类型与包装类的对应关系:
| 基本数据类型 | 包装类(引用数据类型) |
|---|---|
| byte | Byte |
| boolean | Boolean |
| short | Short |
| char | Character |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
基本数据类型 变量有默认值,而包装类对象的默认值为 null;
包装类的使用示例
由于包装类的常用方法类似,此处拿Integer举例;
数字相关的包装类都继承了Number类;Byte, Short, Integer, Long, Float, Double等。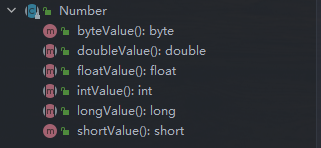 【Number 基本方法】
【Number 基本方法】
Number 类属于抽象类,定义了子类之间相互转换的方法;
包装类常用方法示例:
public class TestInteger {public static void main(String[] args) {//1.基本数据类型转成包装类对象Integer a = new Integer(1);Integer b = Integer.valueOf(2);//2.包装类对象转成基本数据类型int c = b.intValue();double d = b.doubleValue();//3.字符串转成包装类对象Integer e = new Integer("8888");//4.包装类对象转成字符串String f = e.toString();//5.包装类中的常量System.out.println("Integer中最大值:"+Integer.MAX_VALUE);System.out.println("Size:"+Integer.SIZE);}}
自动装箱和拆箱
自动装箱:可以直接把基本数据类型的值或者变量赋值给包装类。
自动拆箱:可以把包装类的变量直接赋值给基本数据类型。
// 自动装箱Integer a = 2;//相当于 Integer a = Integer.valueOf(2);// 自动拆箱int b = a; //编译器自动转为:int b = a.intValue();
整数缓存问题
缓存问题:缓存[-128,127]之间的整数,系统初始化时会创建一个缓存数组;
Integer a = 124;Integer b = 124;System.out.println(a==b); // trueSystem.out.println(a.equals(b)); // trueInteger c = 128;Integer d = 128;System.out.println(c==d); // falseSystem.out.println(c.equals(d)); // true

