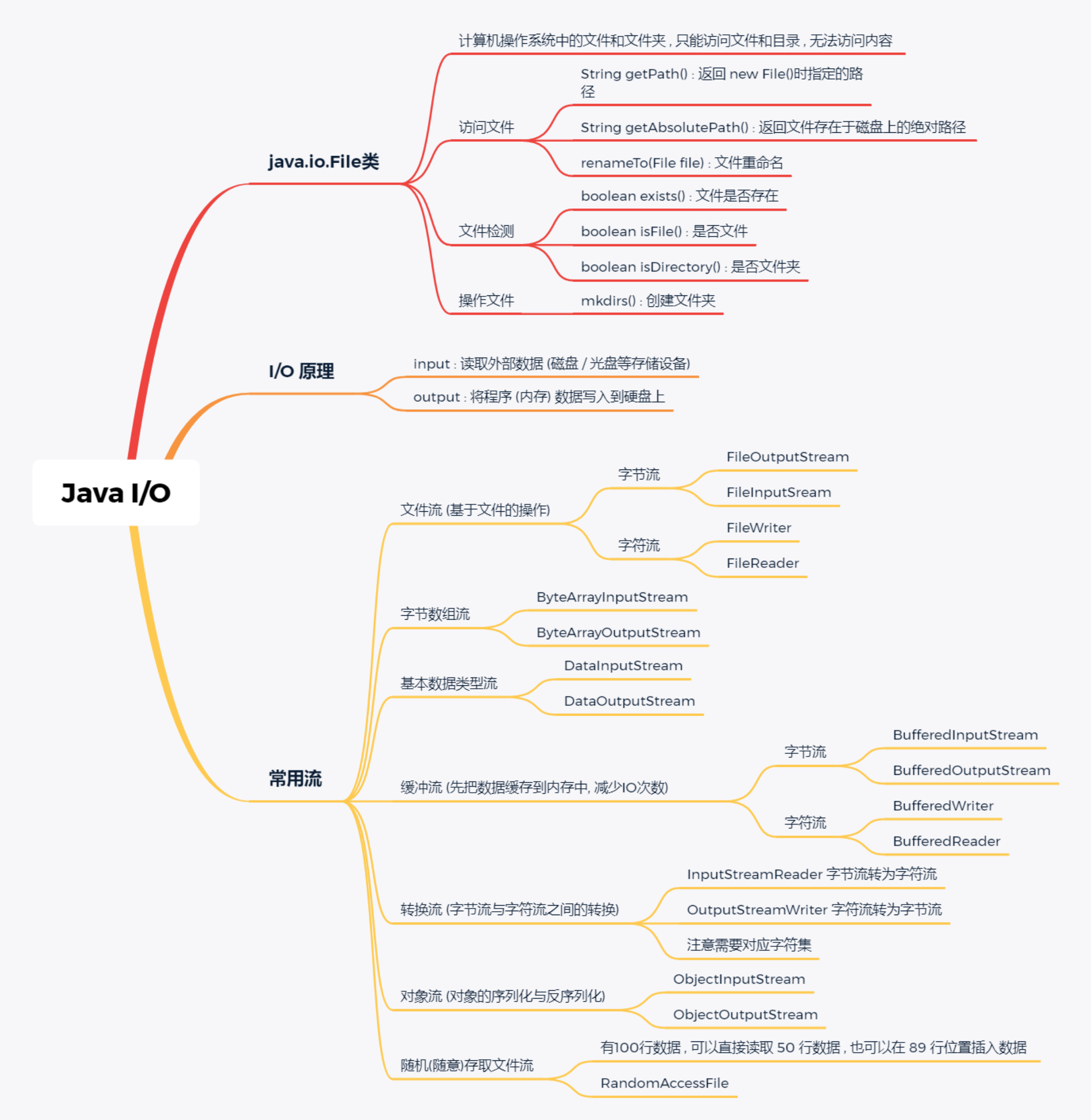
1. File 类
java.io.File 类:文件和目录路径名的抽象表示形式。通过File对象可以访问文件的属性、访问空文件或目录。
分隔符:
- 路径分割符:File.pathSeparator(
:) - 名称分割符:File.separator(
/)
路径的表示方式:
path = “E:\test\2.jpg”; path = “E:” + File.separator + “test” + File.separator + “2.jpg”; path = “E:/test/2.jpg”;
第二种可以跨平台,推荐第三种
相对路径和绝对路径构造File对象:
- 相对路径:
绝对路径:File file = new File(parentPath,name);File file = new FIle(new File(parentPath),name);System.out.println(file.getName);System.out.println(file.getPath);
File file = new FIle(E:/02.jpg);
注意:没有盘符时,以user.dir构建
File的相关方法
1. 文件名
getName() 文件名、路径名getPath() 路径名getAbsoluteFile() 绝对路径所对应的File对象getAbsolutePath() 绝对路径名getParent() 父目录,相对路径的父目录,可能为nullrenameTo(File newName) 重命名
2. 判断信息
exists()canWrite()canReader()isFile()isDirectory() 是否是文件夹(不是真实存在的默认为文件夹)isAbsolute() 是否为绝对路径。消除平台差异,ie以盘符开头,其他的以/开头
3. 长度length():返回字节数。
4. 创建、删除
createNewFile() 不存在创建新文件delete() 删除文件static createTempFile(前缀3个字节长,后缀默认.temp) 默认临时空间static createTempFile(前缀3个字节长,后缀默认.temp,目录)deleteOnExit() 退出虚拟机时删除,常用于删除临时文件
5. 操作目录
mkdir() 必须确保父目录存在,不存在则创建失败mkdirs() 如果目录链不存在,一同创建list() 文件|目录的名称listFiles() 文件|目录的Flile对象static listRoots() 根路径
2. IO 流
2.1 流的概念
流:流动流向。从一段到另一端,源头与目的地。
程序 与 文件|数组|网络连接|数据库。以程序为中心(即输出还是输出都是相对于程序来说的)。
2.2 IO 流分类
- 1、流向:
- 输入流
- 输出流
- 2、数据:
- 字节流:二进制,可以是一切文件,包括纯文本、doc、音频、视频、图片
- 字符流:纯文本文件
- 3、功能
- 节点流:包裹源头
- 处理流:增强功能,提供性能
2.3 字节流与字符流(重点)与文件
2.3.1 字节流
- 输入流
- inputStream
- read(byte[] b)
- read(byte[] b, int off, int len)
- close()
- 实现类:FIleInputStream()
- inputStream
- 输出流
- outPutStream
- write(byte[] b)
- wirte(byte[] b, int off, int len)
- flush()
- close()
- 实现类:FileOutputStream()
- outPutStream
2.3.2 字符流
- 输入流
- reader
- read(char[] cbuf)
- read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
- close()
- 实现类:FileReader()
- reader
- 输出流
- writer
- write(char[] cbuf)
- write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
- flush()
- close()
- 实现类:FileWritre()
- writer
四、操作
1、举例 —-> 读取文件
(1)关联房子 —-> 建立与文件联系
(2)选择搬家公司 —-> 选择对应的流
(3)搬家 —-> 读取|写出
- 卡车大小 —-> 数组大小
- 运输 —-> 读取、写出
(4)打发走over —-> 释放资源
2、操作
- 建立联系
- 选择流
- 操作
- 数组大小
- read、write
- 释放资源
2.4 实例代码
2.4.1 字节流
输入文件
public class Demo03_inputStream {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 建立联系File file = new File("D:/test/a.txt");// 2. 选择流InputStream is = null;try {is = new FileInputStream(file);byte[] car = new byte[1024];int len = 0; // 接收实际读取大小// 循环读取try {// 3. 操作while (-1 != (len = is.read(car))) {// 输出 字节数组转化成字符串String info = new String(car, 0, len);System.out.println(info);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("读取文件失败");}} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("文件不存在");} finally {if (null != is) {try {// 4. 释放资源is.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("关闭输入流失败");}}}}}
写出文件
public class Demo04_outputStream {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 建立联系File file = new File("D:/test/a.txt");// 2. 选择流OutputStream os = null;try {// 为true时,以追加形式写出文件;为false时,覆盖os = new FileOutputStream(file, true);String str = "this is a str \r\n";// 字符串转字节数组byte[] data = str.getBytes();os.write(data, 0, data.length);os.flush(); // 强制刷新数据} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("文件没有找到");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("文件写出失败");} finally {if (null != os) {try {os.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("关闭输出流失败");}}}}}
文件拷贝
public void copyFile(File src, File dest) throws IOException {if (!src.isFile()) {System.out.println("只能copy文件");throw new IOException("只能copy文件");}if (dest.isDirectory()) {System.out.println("不能建立与文件夹同名的文件");throw new IOException(dest.getAbsolutePath() + "不能建立与文件夹同名的文件");}InputStream is = null;OutputStream os = null;byte[] data = new byte[1024];int len = 0;is = new FileInputStream(src);os = new FileOutputStream(dest);while (-1 != (len = is.read(data))) {os.write(data, 0, len);}os.flush();// 先开的后关闭os.close();is.close();}
文件夹的拷贝
/*** 文件夹的copy 1、文件:复制 copyFile 2、文件夹:创建 mkdirs() 3、递归查找子孙级*/public static void copyDir(String srcPath, String destPath) {File src = new File(srcPath);File dest = new File(destPath);if (src.isDirectory()) {dest = new File(destPath, src.getName());}copyDieDetails(src, dest);}private static void copyDieDetails(File src, File dest) {if (src.isFile()) {try {copyFile(src, dest);// 调用上面文件拷贝的方法} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}} else if (src.isDirectory()) {dest.mkdirs();for (File sub : src.listFiles()) {copyDieDetails(sub, new File(dest, sub.getName()));}}}
2.4.2 字符流
只能处理纯文本,全部为可见字符。.txt、.html
对应的节点流:
- Reader —> FileReader
- Writer —> FileWriter
使用方式和字节流相似:
- 建立联系
- 选择流: FileReadre、FileWriter
- 读取 char[] flush = new char[1024]
- 关闭
2.4.3. 处理流
- 缓冲流
- 字节缓冲流
- BufferedInputStream
- BufferedOutputStream
- 字符缓冲流
- BufferedReader(Reader in) 创建一个使用默认大小输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流。
- BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz) 创建一个使用指定大小输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流。
- readLine() 读取一个文本行。
- BufferedWriter(Writer out)
- BufferedWriter(Writer out, int sz)
- newLine() 写入一个行分隔符
- 字节缓冲流
字符缓冲流 实现文件拷贝
public class Demo07_bufferedChar {public static void main(String[] args) {File src = new File("D:/test/a.txt");File dest = new File("D:/test/b.txt");BufferedReader reader = null;BufferedWriter writer = null;try {reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src));writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dest));// 旧的读取方法/** char[] flush = new char[1024]; int len = 0;* while(-1!=(reader.read(flush))){ writer.write(flush, 0, len); }*/// 新增方法的操作String line = null;while (null != (line = (reader.readLine()))) {writer.write(line);// writer.append("\r\n");writer.newLine();// 换行符号}writer.flush();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
2.4.4 转换流
字节流转为字符流,设计处理乱码问题。
- 编码与解码概念
- 编码: 字符 —-编码字符集—>二进制
- 解码: 二进制 —-解码字符集—>字符
- 乱码
- 编码与解码的字符集不统一
- 字节缺少,长度丢失
转换流
- 输入流 InputStreamReader (解码)
- 输出流 OutputStreamWriter (编码)
2.4.5. 其他流
字节流
- 字节数组 节点流
- 输入流: ByteArrayInputStream read(byte[] b, int off, int len) + close();(close可用可不用
- 输出流: ByteArrayOutputStream write(byte[] b, int off, int len) + toByteArray() (不要使用多态)
处理流
- 数据类型处理流(基本类型+String)
- 输入流:DataInputStream readXxx
- read(byte[] b)
- read(byte[] b, int off, int len)
- readBoolean()
- readByte()
- readByte()
- readDouble()
- readFloat()
- readFully
- 输出流:DataOutputstream WriteXxx
- 。。。同上
- 输入流:DataInputStream readXxx
- 引用类型(对象) 保留数据+类型
- 反序列化 ObjectOutputStream readObject()
- 序列化 ObjectInputStream wirteObject()
- 注意:
- 先序列化后反序列化。反序列化顺序必须和序列化顺序一致
- 不是所有的对象都可以序列化,必须实现
java.io.Serilizable接口。 - 不是所有的属性都序列化,不需要序列化的属性用
transient
注意:
- java.io.EOFException:没有读取到相关的内容
- 读取顺序可能存在数据问题
ByteArrayInputstream 和 ByteArrayOutputStream
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {byte[] data = getBytesFromFile("D:/test/a.txt");toFileFromByteArray(data, "D:/test/c.txt");}/*** 文件 --> 程序--> 字节数组** @throws IOException*/public static byte[] getBytesFromFile(String path) throws IOException {File file = new File(path);byte[] dest = null;InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();byte[] flush = new byte[1024];int len = 0;while (-1 != (len = is.read(flush))) {bos.write(flush, 0, len);}bos.flush();dest = bos.toByteArray();// 先开后关bos.close();is.close();return dest;}/*** 字节数组 --> 程序 --> 文件** @throws IOException*/public static void toFileFromByteArray(byte[] src, String dest) throws IOException {File file = new File(dest);InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(src));OutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));byte[] flush = new byte[1024];int len = 0;while (-1 != (len = is.read(flush))) {os.write(flush, 0, len);}os.flush();os.close();is.close();}
对象通过流实现序列化和反序列化
Object:
/*** 空接口只是一个标识,说明可以序列化* 不需要序列化的属性加 transient*/public class Employee implements java.io.Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;private transient String name;private double salary;...
ObjectInputStream 和 ObjectOutputStream
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {seri("D:/test/seri.txt");read("D:/test/seri.txt");}// 序列化public static void seri(String destPath) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {Employee emp = new Employee("张三", 5000);int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 54 };File dest = new File(destPath);ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest)));oos.writeObject(emp);oos.writeObject(arr);oos.flush();oos.close();}// 反序列化public static void read(String destPath) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {File dest = new File(destPath);ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(dest)));Object obj = ois.readObject();if (obj instanceof Employee) {Employee emp = (Employee) obj;System.out.println(emp.getName());System.out.println(emp.getSalary());}int[] arr = (int[]) ois.readObject();System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));ois.close();}
2.4.6. 关闭流方法
public class Demo11_FileUtil {/*** 关闭流 可变参数 ...: 代表参数随意指定。只能放在形参的最后一个位置,处理方式与数组一致* 使用:Demo11_FileUtil.close(is, os, oos)*/public static void close(Closeable... io) {for (Closeable temp : io) {if (null != temp) {try {temp.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}/*** 使用泛型*/public static <T extends Closeable> void closeAll(Closeable... io) {for (Closeable temp : io) {if (null != temp) {try {temp.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}