案例代码:
FastThreadLocal 与 ThreadLocal 的使用方法一致
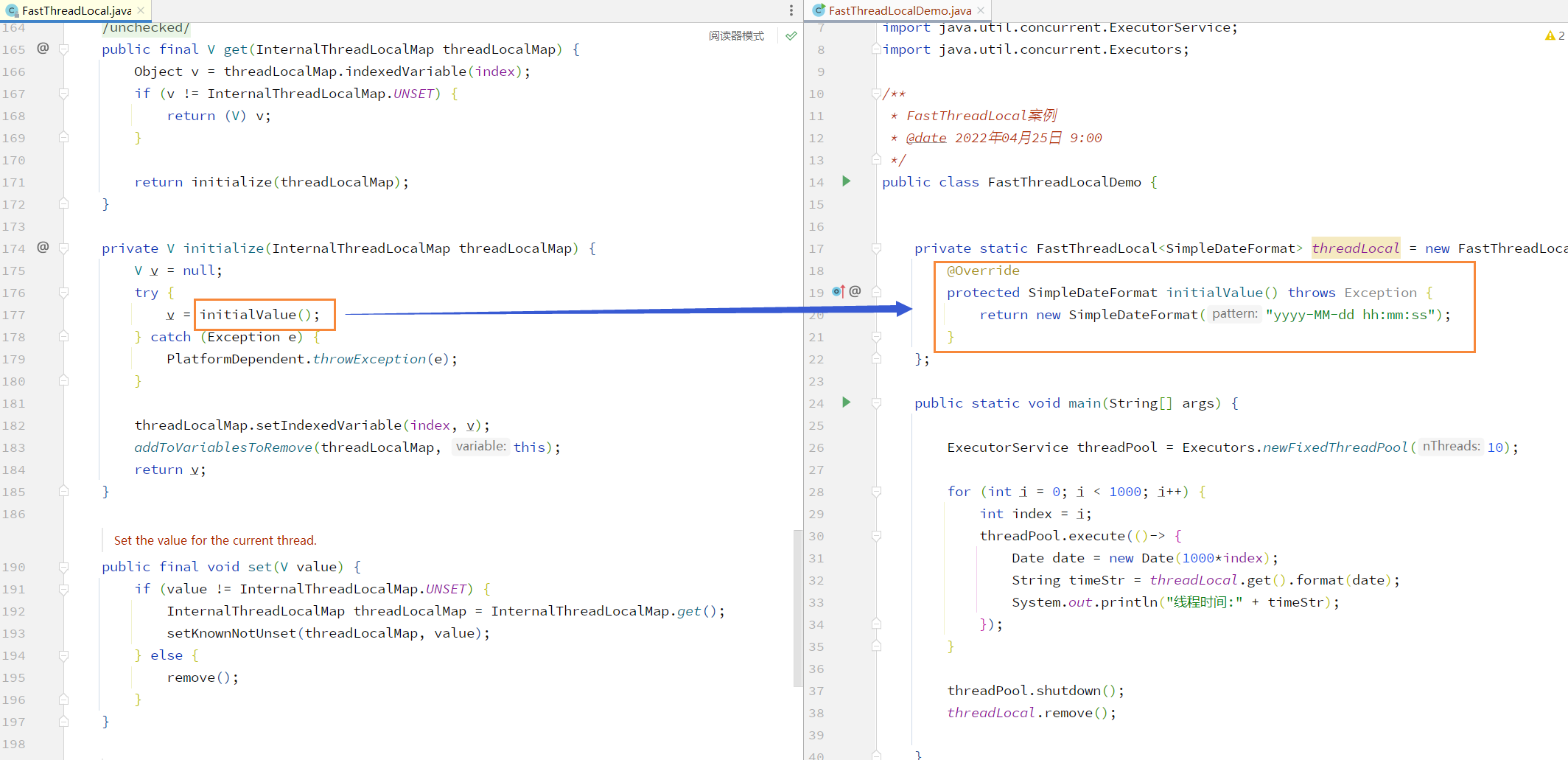
package fastThreadLocal;import io.netty.util.concurrent.FastThreadLocal;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;import java.util.Date;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;import java.util.concurrent.Executors;/*** FastThreadLocal案例* @date 2022年04月25日 9:00*/public class FastThreadLocalDemo {private static FastThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> threadLocal = new FastThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat>(){@Overrideprotected SimpleDateFormat initialValue() throws Exception {return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");}};public static void main(String[] args) {ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {int index = i;threadPool.execute(()-> {Date date = new Date(1000*index);String timeStr = threadLocal.get().format(date);System.out.println("线程时间:" + timeStr);//每次执行完后创建一个新threadLocal.set(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss"));});}threadPool.shutdown();threadLocal.remove();}}
创建过程:
进入 FastThreadLocal 源码查看其构造方法,在每次创建出一个新 FastThreadLocal 对象时会通过原子类自增出专属的 index(索引),当创建出 Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8 个 FastThreadLocal 后将会抛出异常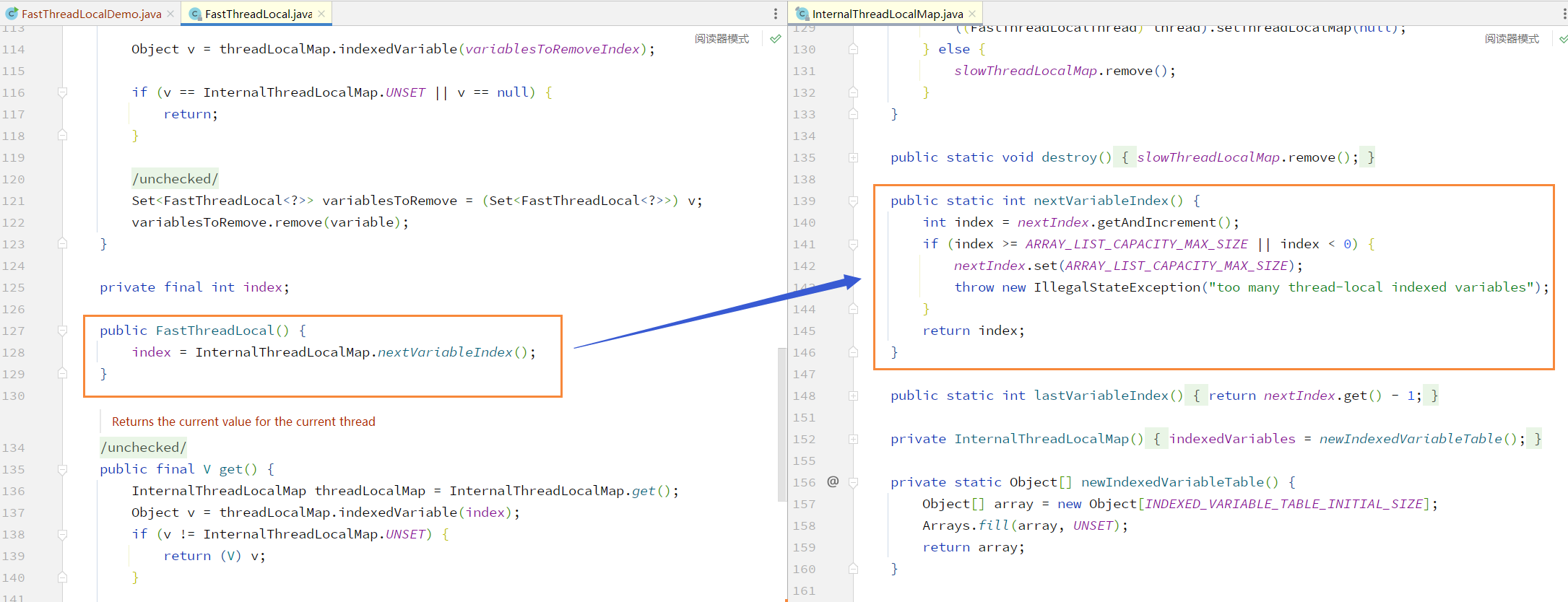
get方法:
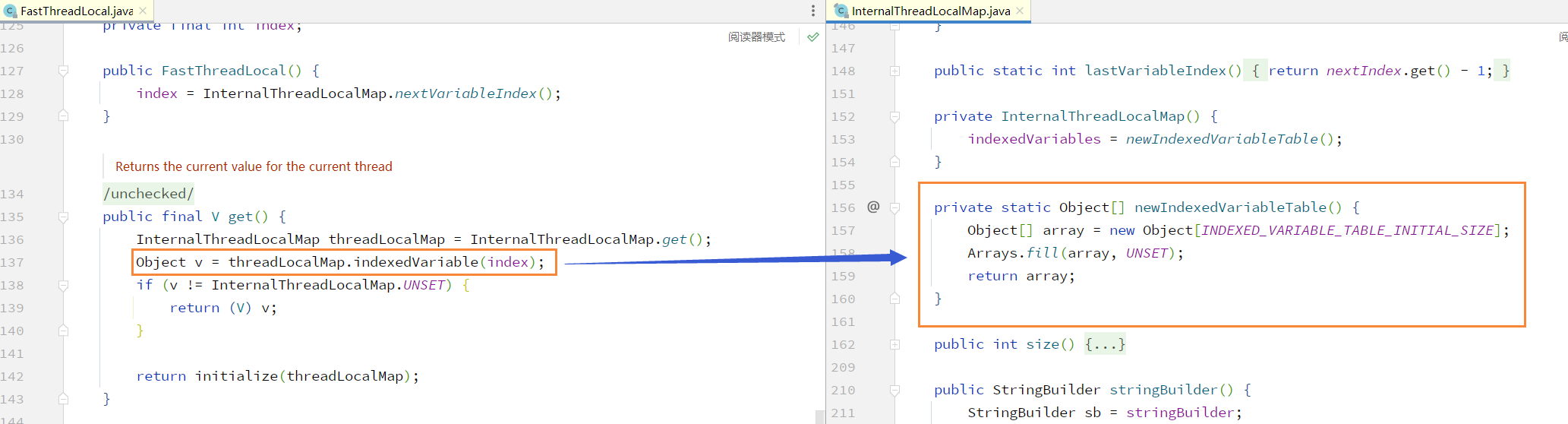
尝试获取当前线程的 InternalThreadLocalMap ,InternalThreadLocalMap 内维护了一个数组,数组内的下标与线程 index 对应,通过 index(索引)即可获取到当前线程保存在 FastThreadLocal 的对象
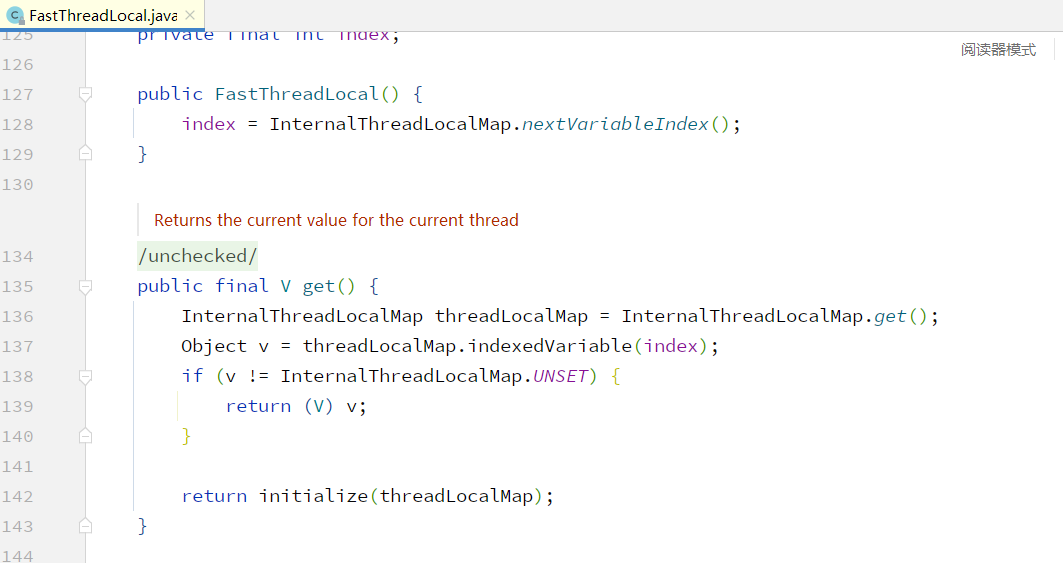
第一次获取对象 v 会返回 unset,因此会执行 initialize 方法,initialize 方法调用重写的 initialize 方法进行数组初始化操作
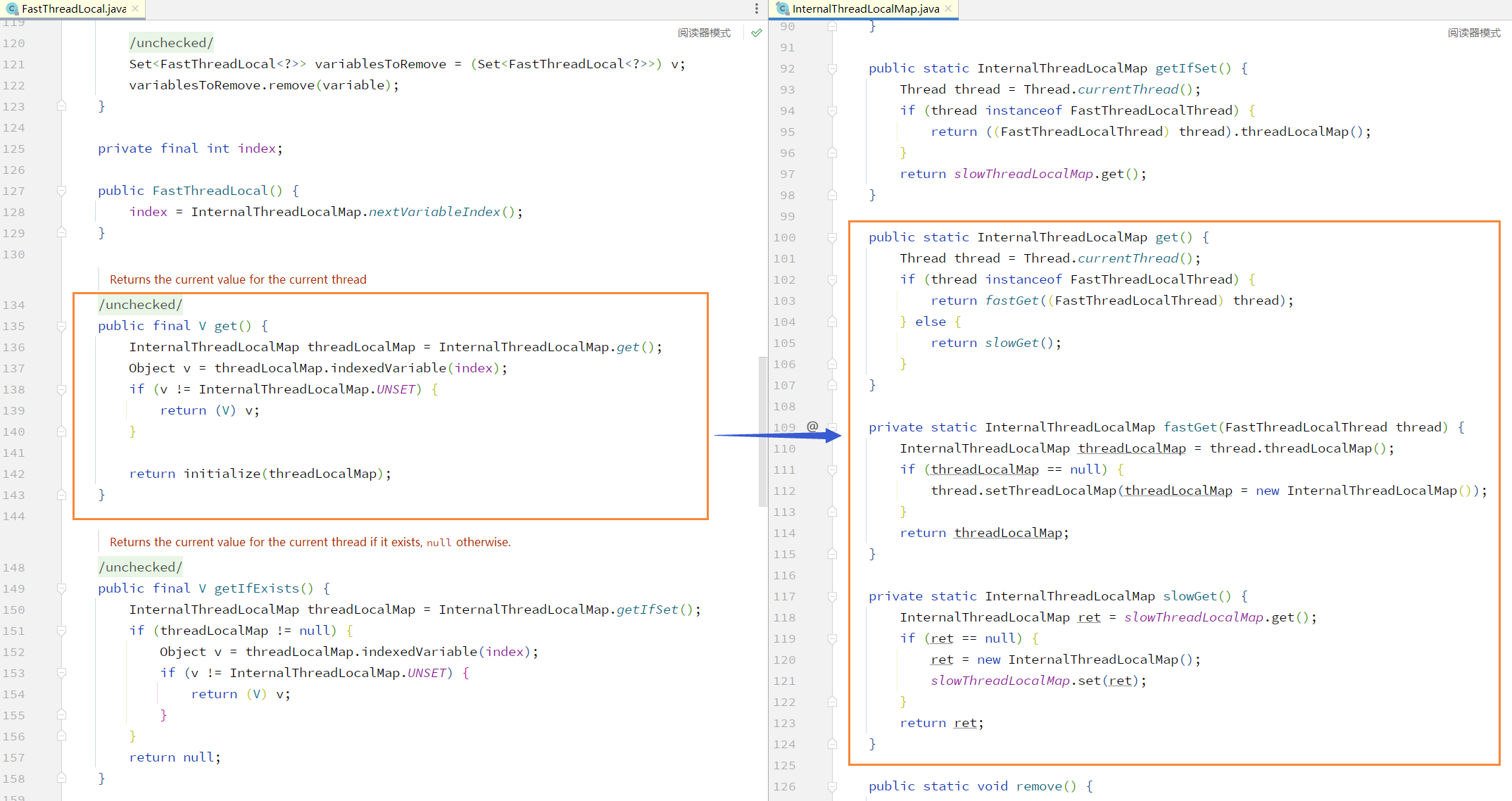
进入 InternalThreadLocalMap.get(); 方法,首先会判断当前线程是否属于 FastThreadLocalThread,如果不属于 FastThreadLocalThread 线程,执行 slowGet() 方法(通过JDK的ThreadLocal实现),如果属于,执行 fastGet() 方法
slowGet方法执行逻辑:
1、使用 ThreadLocal 创建出没有初始化的全局 InternalThreadLocalMap
2、如果创建出的 InternalThreadLocalMap 获取为 null,创建新 InternalThreadLocalMap 放入 ThreadLocal 中·
3、返回该线程的 InternalThreadLocalMap
fastGet 方法执行逻辑:
1、获取当前线程的 threadLocalMap
2、如果获取为空,创建出新的 threadLocalMap
set 方法:
主要分为三步:
1、获取ThreadLocalMap (参考 get 方法讲解 )
2、直接通过索引set对象
3、移除对象