包含自定义任务、定时任务等方法,当异步任务较多时需要添加将任务到线程池,通常有添加到Handler和Context两种方式
自定义任务:
当客户端的Channel与EventLoopGroup绑定后,在通道没有关闭之前,对应通道都会一直使用当初绑定的线程进行业务操作
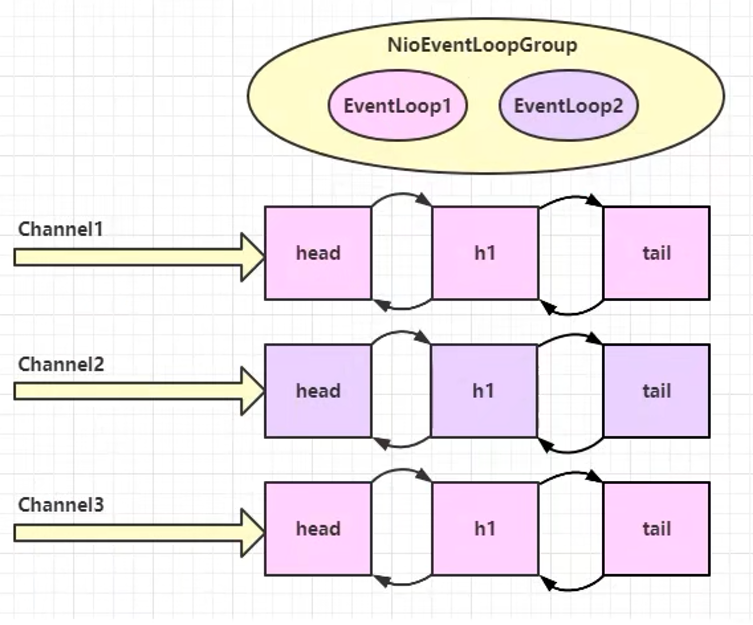
Channel和EventLoop线程绑定关系
自定义普通任务:
在服务端读取客户端通道数据时往往需要做业务操作,当操作较为耗时时需要使用异步方式进行处理(异步任务执行的线程依旧是使用服务端ServerBootstrap定义的workGroup,只是操作是异步的),在添加多个异步任务时需要等待
对服务端自定义Handler的channelRead方法进行修改即可
代码:
package simple;import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/** 自定义管道 Handler* 1、自定义一个 Handler,需要继承 Netty 规定好的某个 HandlerAddapter* 2、这时我们自定义一个 Handler,才能称为一个 Handler*/public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {/*当有读取事件时该方法将被触发* 参数一: ChannelHandlerContext 上下文对象,含有管道 PipeLine、通道* 参数二: Object 客户端发送的数据,默认是Object需要转换*/@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {/* 用户自定义普通任务 : 使用异步处理 > 找到客户端 Channel 对应的 NioEventLoop 的 TaskQueue 中* 用于处理耗时非常长的业务处理方式*/ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(()->{try {System.out.println("ExecuteThread1 is: "+Thread.currentThread().getName());TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("3秒的异步任务已完成!",StandardCharsets.UTF_8));} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(()->{try {System.out.println("ExecuteThread2 is: "+Thread.currentThread().getName());TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("10秒的异步任务已完成!",StandardCharsets.UTF_8));} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});System.out.println("异步任务开始处理!"+LocalDateTime.now()+" 当前线程是: "+Thread.currentThread().getName());}/* 数据读取完毕后触发* 参数一: ChannelHandlerContext 上下文对象,含有管道 PipeLine、通道*/@Overridepublic void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {//对发送数据进行编码后写入到缓存并刷新ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("服务端连接成功,欢迎!",StandardCharsets.UTF_8));}/* 处理异常,一般为关闭通道 */@Overridepublic void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {ctx.close(); //和 ctx.channel().close() 是一个意思}}
测试:
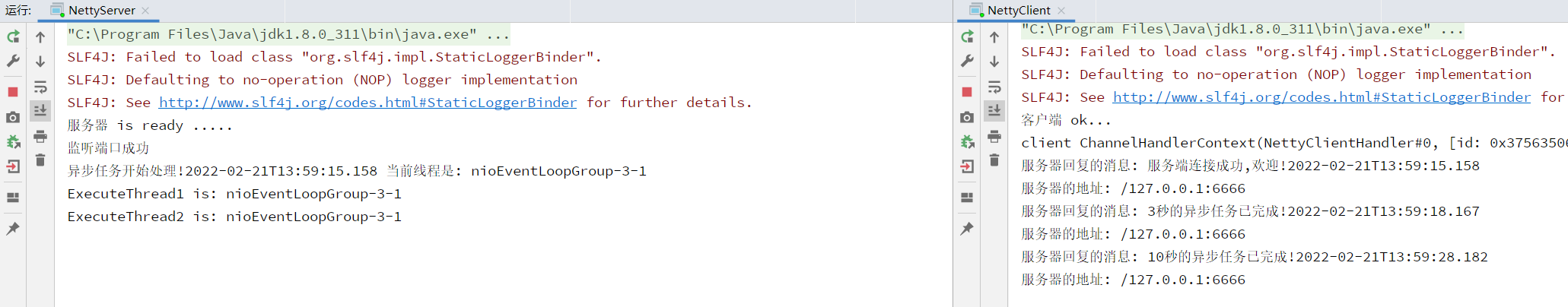
服务端使用异步方法轮流处理任务
自定义定时任务:
指定延时时间运行任务,定时任务被添加到 ScheduledTaskQueue 中,优先级比普通任务的 TaskQueue 低(异步任务执行的线程依旧是使用服务端ServerBootstrap定义的workGroup,只是操作是异步的)
定时时间以添加到队列中为开始,当之前存在普通任务时,存在普通任务执行结束后直接执行定时任务的情况,因此需要设置好定时时间
对服务端自定义Handler的channelRead方法进行修改即可
代码:
package simple;import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;import java.time.LocalDateTime;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/** 自定义管道 Handler* 1、自定义一个 Handler,需要继承 Netty 规定好的某个 HandlerAddapter* 2、这时我们自定义一个 Handler,才能称为一个 Handler*/public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {/*当有读取事件时该方法将被触发* 参数一: ChannelHandlerContext 上下文对象,含有管道 PipeLine、通道* 参数二: Object 客户端发送的数据,默认是Object需要转换*/@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(()->{try {System.out.println("ExecuteThread2 is: "+Thread.currentThread().getName());TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("10秒的异步任务已完成!"+LocalDateTime.now(),StandardCharsets.UTF_8));} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});System.out.println("异步任务开始处理!"+LocalDateTime.now()+" 当前线程是: "+Thread.currentThread().getName());/* 用户自定义定时任务,任务被添加到 NioEventLoop 的 ScheduledTaskQueue 中 */ctx.channel().eventLoop().schedule(()->{System.out.println("ExecuteThread3 is: "+Thread.currentThread().getName());ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("自定义定时任务已完成!"+LocalDateTime.now(),StandardCharsets.UTF_8));},5,TimeUnit.SECONDS);}/* 数据读取完毕后触发* 参数一: ChannelHandlerContext 上下文对象,含有管道 PipeLine、通道*/@Overridepublic void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {//对发送数据进行编码后写入到缓存并刷新ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("服务端连接成功,欢迎!"+LocalDateTime.now(),StandardCharsets.UTF_8));}/* 处理异常,一般为关闭通道 */@Overridepublic void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {ctx.close(); //和 ctx.channel().close() 是一个意思}}
测试:
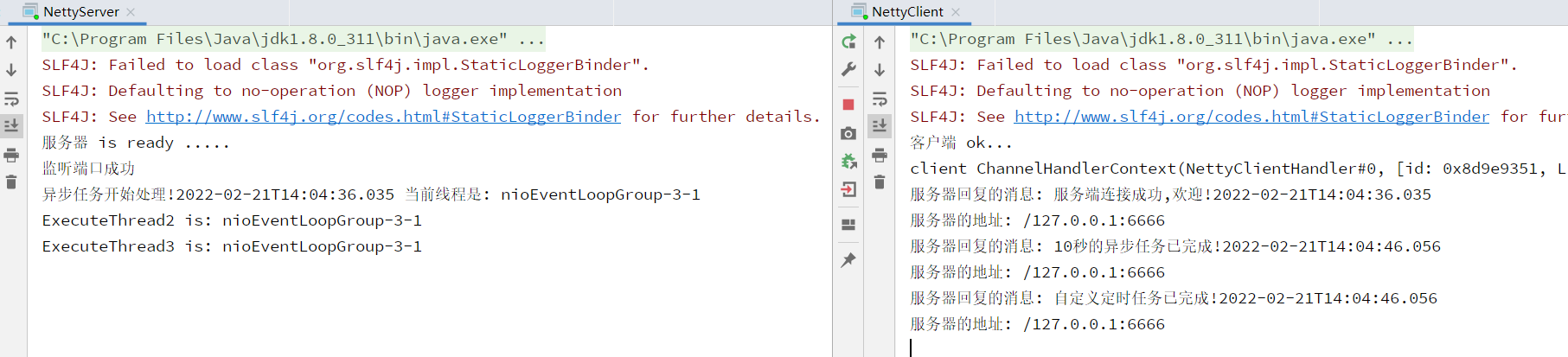
定时任务队列排在普通任务后
线程池处理异步任务:
当客户端的Channel与EventLoopGroup和执行异步任务的DefaultEventLoopGroup绑定后,在通道没有关闭之前都会一直使用当初绑定的线程进行业务操作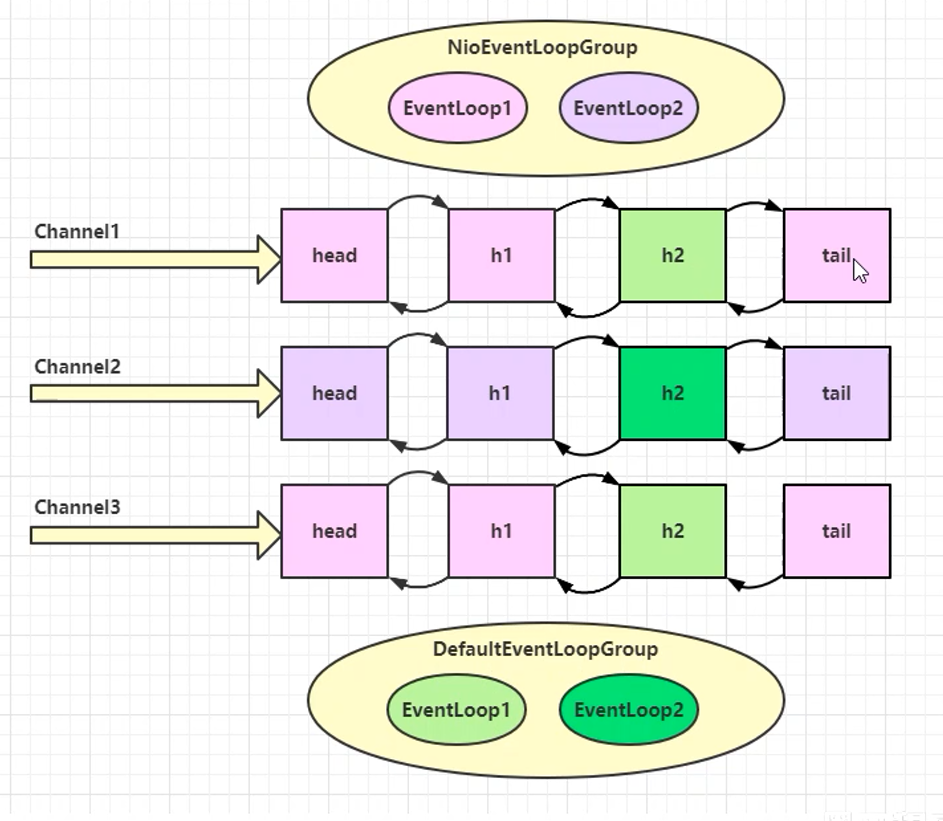
Channel与EventLoop中线程绑定关系
Handler方式:
在handler创建线程组进行异步提交,异步方法使用的是单独创建的EventExecutorGroup内的线程而不是之前服务端中ServerBootstrap定义的workGroup,具体可参考源码中的 execute1
直接执行的方法使用的是workGroup线程,异步提交使用的是线程组线程
源码为 AbstractChannelHandlerContext 中的 write 方法
服务端Handler:
public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {static final EventExecutorGroup group = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(16); //充当业务线程池@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {group.submit(()->{try {System.out.println("ExecuteThread1 is: "+Thread.currentThread().getName());TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);/* 堆内存方式创建ByteBuf*///ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("3秒的异步任务已完成!"+ LocalDateTime.now(),StandardCharsets.UTF_8));/* 直接内存方式创建ButeBuf*/ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer();buffer.writeBytes( ("3秒的异步任务已完成!"+LocalDateTime.now()).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8) );ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});group.submit(()->{try {System.out.println("ExecuteThread2 is: "+Thread.currentThread().getName());TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("10秒的异步任务已完成!"+ LocalDateTime.now(),StandardCharsets.UTF_8));} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});group.submit(()->{try {System.out.println("ExecuteThread3 is: "+Thread.currentThread().getName());TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(12);ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("12秒的异步任务已完成!"+ LocalDateTime.now(),StandardCharsets.UTF_8));} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});System.out.println("异步任务开始处理!"+LocalDateTime.now()+" 当前线程是: "+Thread.currentThread().getName());ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("服务端开始异步任务开始处理~~~", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));}/* 数据读取完毕后触发* 参数一: ChannelHandlerContext 上下文对象,含有管道 PipeLine、通道*/@Overridepublic void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {//对发送数据进行编码后写入到缓存并刷新ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("服务端连接成功,欢迎!"+LocalDateTime.now(),StandardCharsets.UTF_8));}/* 处理异常,一般为关闭通道 */@Overridepublic void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {ctx.close();}}
测试:
异步任务使用内部线程组调用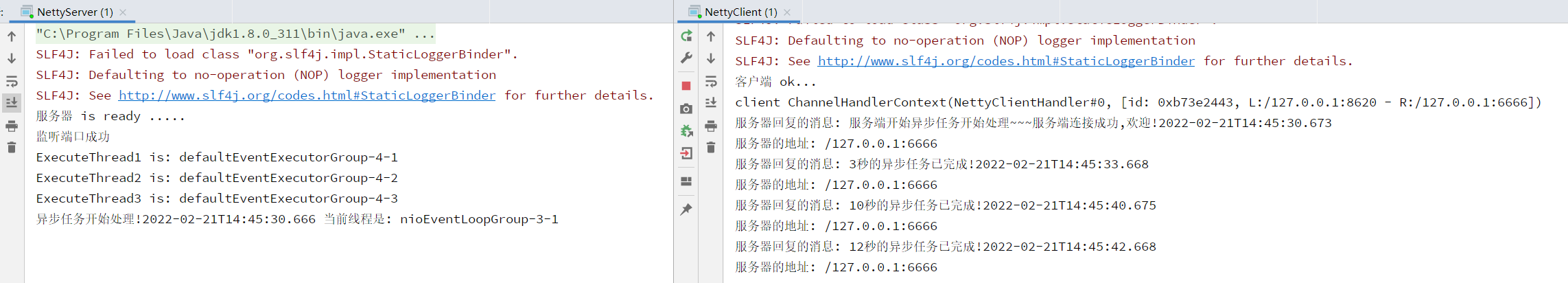
Context方式:
将handler添加到pipeline的时候指定线程组即可,具体可参考源码中的 execute2
使用提交方法用的是workGroup线程执行任务,直接执行的是异步任务
服务端:
package simple.execute2;import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;import io.netty.channel.*;import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;import io.netty.util.concurrent.DefaultEventExecutorGroup;import io.netty.util.concurrent.EventExecutorGroup;import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;import java.time.LocalDateTime;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/* 异步任务添加到Handler版服务端代码 */public class NettyServer {static final EventExecutorGroup group1 = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(2); //创建业务1线程池static final EventExecutorGroup group2 = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(2); //创建业务2线程池public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {/* 创建 BossGroup 和 WorkerGroup 线程组* BossGroup 只处理连接请求,真正的和客户端业务处理会交给 WorkGrouop 完成* bossGroup 和 workerGroup 含有的子线程的个数默认为 CPU最大线程数 X 2,可以手动指定*/EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); //创建子线程的个数为1的 bossGroupEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(8); //创建子线程的个数为8的 workerGrouptry {//创建服务器端的启动对象,配置参数ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();//使用链式参数配置启动参数bootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup) //设置两个线程组.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) //使用 NioSocketChannel 作为服务器通道实现.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,120) //设置线程队列等待连接的个数.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,true) //保持活动连接状态.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { //创建一个通道初始化对象//给PipeLine设置处理器@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();pipeline.addLast(group1,new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {/* 使用的是workerGroup的线程 */ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(()->{try {System.out.println("ExecuteThread1 is: "+Thread.currentThread().getName());TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("耗时3秒的主要任务已完成!"+ LocalDateTime.now(),StandardCharsets.UTF_8));} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});/* 非execute执行的使用的是自定义的group线程组线程 */System.out.println("异步任务开始处理!"+LocalDateTime.now()+" 当前线程是: "+Thread.currentThread().getName());TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("10秒的异步任务已完成!"+ LocalDateTime.now(),StandardCharsets.UTF_8));}});pipeline.addLast(group2,new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){@Overridepublic void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {//对发送数据进行编码后写入到缓存并刷新ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("服务端连接成功,欢迎!"+ LocalDateTime.now()+"当前线程是: "+Thread.currentThread().getName(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8));}});}});System.out.println("服务器 is ready .....");//启动服务器绑定一个端口并且同步,生成一个 ChannelFuture 对象ChannelFuture cf = bootstrap.bind(8889).sync();//给CF注册监听器,监控关心的事件cf.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {@Overridepublic void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception {if(cf.isSuccess()){System.out.println("监听端口成功");}else{System.out.println("监听端口失败");}}});//对关闭通道进行监听(当有关闭通道的消息时才进行监听)cf.channel().closeFuture().sync();} finally {bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); //关闭资源workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); //关闭}}}
测试:
异步任务执行成功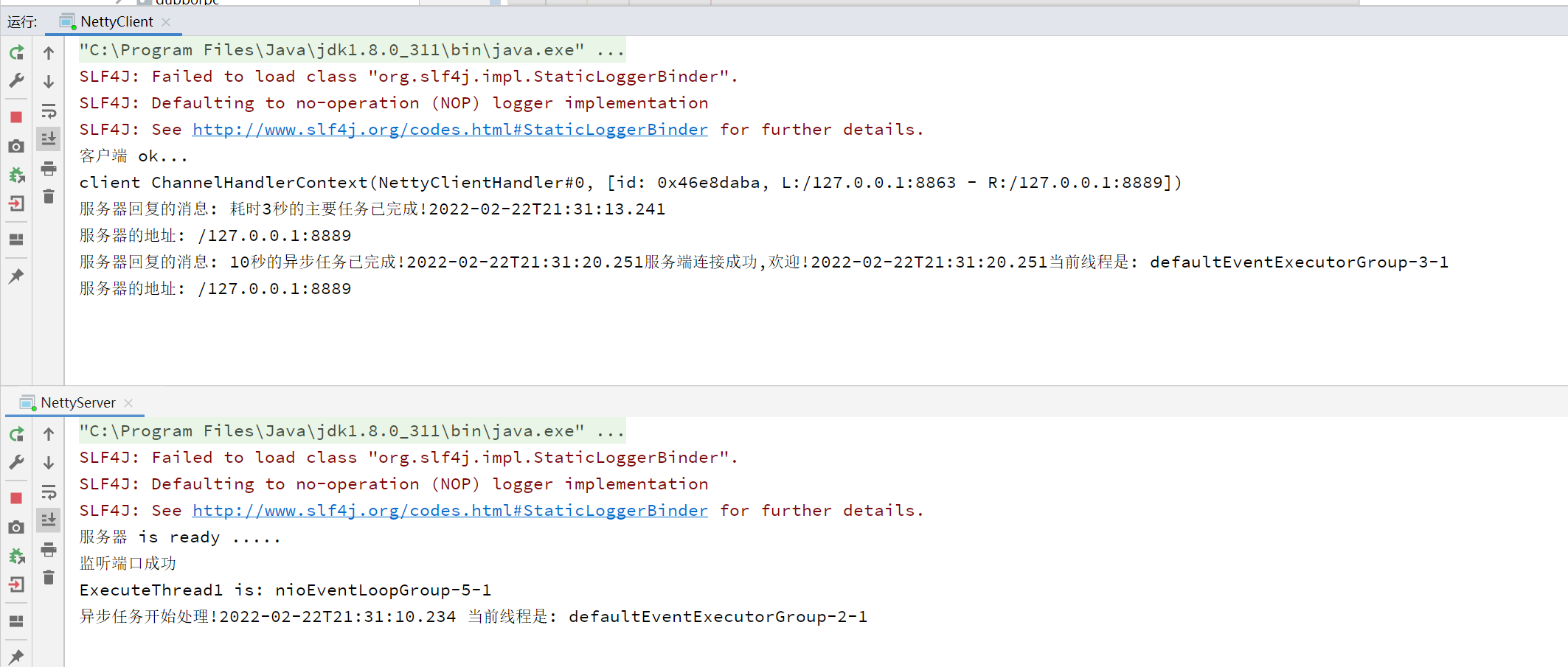
优缺点对比:
第一种方式在handler中添加异步,可能更加的自由,比如如果需要访问数据库,那就异步,如果不需要,就不异步,异步会拖长接口啊应时间。因为需要将任务放进mpscTask 中。如果I0时间很短,Task 很多,可能一个循环下来,都没时间执行整个task,导致响应时间达不到指标
第二种方式是Netty标准方式(即加入到队列),不同的事件(业务)操作可以指定不同的线程池,但是会将整个handler都交给业务线程池,不论耗时不耗时,都加入到队列里,不够灵活
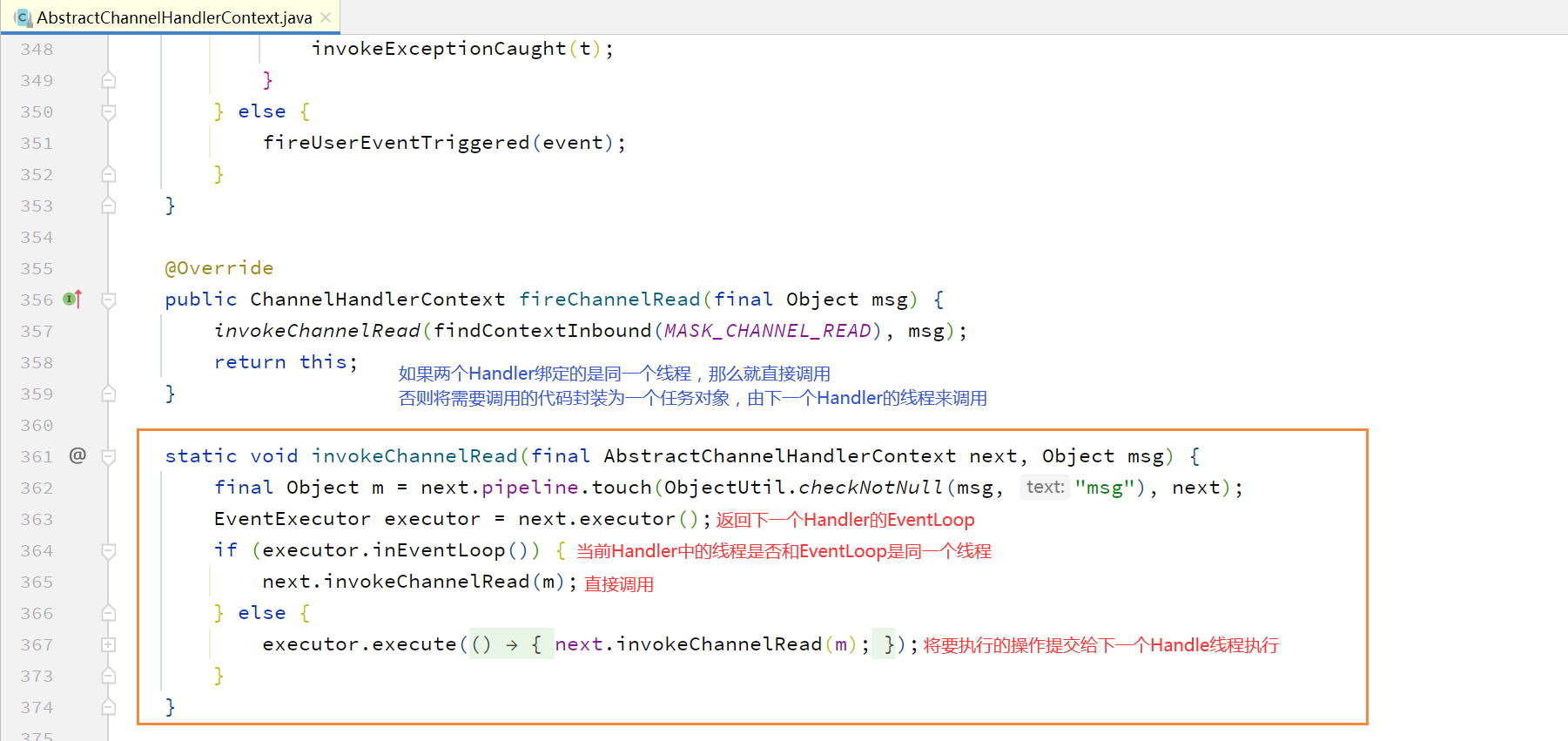
源码实现:
由 AbstractChannelHandlerContext 的 invokeChannelRead 对具体调用的线程进行判断