Vue
1、MVVM模式
- 基本定义
- MVVM是Model-View-ViewModel的缩写,MVVM是一种设计思想,Model 层代表数据模型,也可以在Model中定义数据修改和操作的业务逻辑;View 代表UI 组件,它负责将数据模型转化成UI 展现出来,ViewModel 是一个同步View 和 Model的对象,在MVVM架构下,View 和 Model 之间并没有直接的联系,而是通过ViewModel进行交互,Model 和ViewModel 之间的交互是双向的, 因此View 数据的变化会同步到Model中,而Model 数据的变化也会立即反应到View 上,ViewModel 通过双向数据绑定把 View 层和 Model 层连接了起来,而View 和 Model 之间的同步工作完全是自动的,无需人为干涉,因此开发者只需关注业务逻辑,不需要手动操作DOM, 不需要关注数据状态的同步问题,复杂的数据状态维护完全由 MVVM 来统一管理
- 图解
2、Vue双向绑定的原理
- 基本定义
- 在Vue2版本中,双向绑定的原理,采用的是,
数据劫持结合发布者,订阅者模式实现的,通过Object.definePropety()来劫持各个属性的setter,和getter,在数据发生变动的时,发布消息给订阅者,触发相应监听回调,把一个普通的javaScript对象传给Vue实例,作为它的data选项,Vue将遍历所有的属性,利用Object.definePropetype把它们转换为getter/setter,用户看到不到getter/setter,但是在内部使用Vue追踪依赖,在属性被访问和修改时,通知发生变化 - Vue将MVVM作为数据绑定的入口,整合Observer,Compile和Watch三者,通过Observer来监听自己的model数据变化,通过Compile来解析编译模板指令,最用它利用Watcher大气observer和Compile之间的通讯桥梁,达到数据变化,->视图更新,视图交互变化->数据Model变更双向绑定的结果
- 在Vue2版本中,双向绑定的原理,采用的是,
- 代码实现
<body> <!-- <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue"></script> --> <div id="app"></div> <input id="txt"></input> <p id="show"></p> <script> var obj= {} // 1- 监听空对象obj,和input输入框 Object.defineProperty(obj,'txt',{ // 2- get属性获取外部obj对象 get:function(){ return obj }, // 3- set改写,并且把文本,和视图,进行关联 set:function(newValue){ document.getElementById('txt').value= newValue document.getElementById('show').innerHTML=newValue } }) // 4- 监听keyup事件,实现数据同时显示和更新 document.addEventListener('keyup',function(e){ obj.txt=e.target.value }) </script> </body>
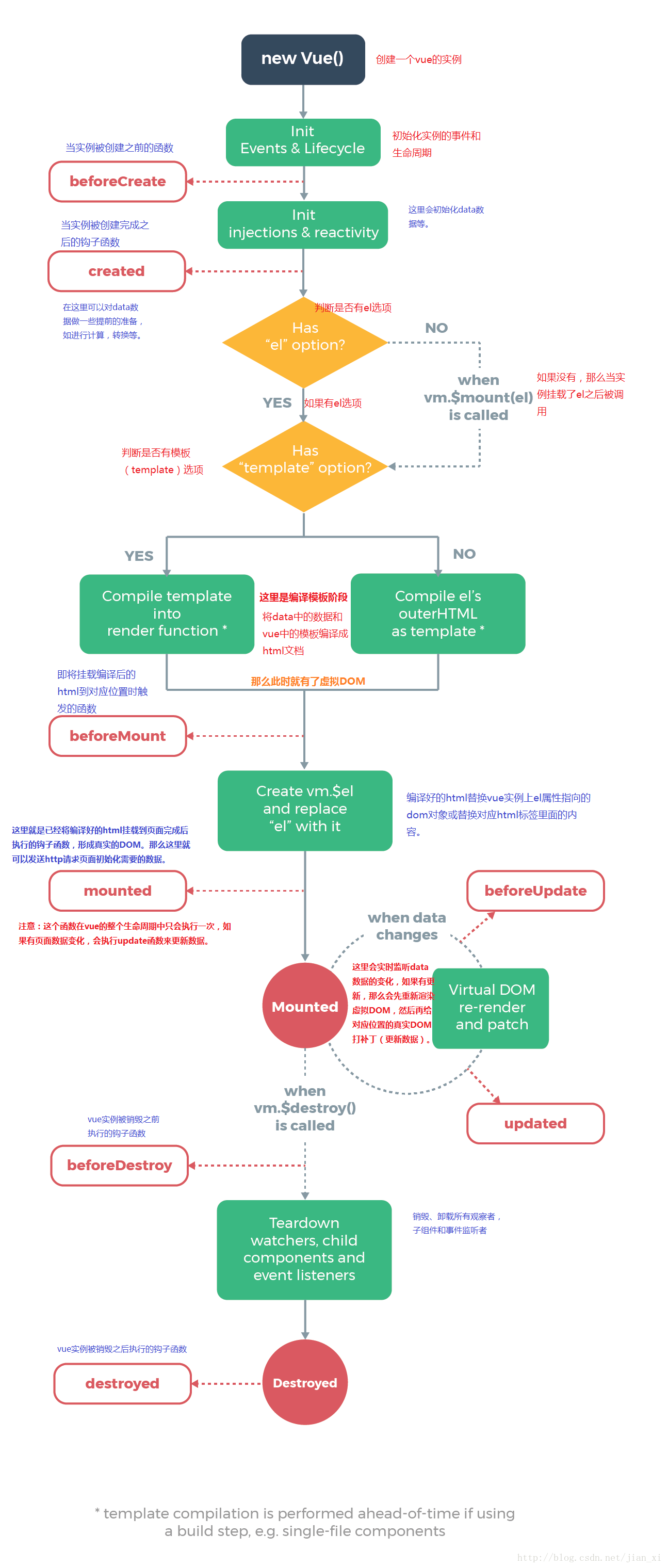
3、生命周期函数
- 基本定义
- 生命周期函数,可以为
创建期间和运行期间以及销毁期间- 创建期间
- beforeCreate,created,beforeMount,mounted
- 运行期间
- beforeUpdate,updated
- 销毁期间
- beforeDestroy,destroyed
- 创建期间
- 生命周期函数,可以为
- 详细说明
1- 创建期间- beforeCreate
- Vue或者组件刚刚实例化,data和methods还没有被创建
- created
- 此时data和methods已经被创建,可以使用,但还没有开始编译,如果首屏的ajax请求,可以放到这个钩子中执行
- beforeMount
- created的下一个阶段,此时模板已经被编译,但是还没有挂载到网页中
- mounted
- 模板代码已经加载到了网页中,但此时创建期间所有的事情都已经准备好了,网页开始运行
- beforeCreate
2- 运行期间- beforeUpdate
- 在网页运行期间,data中的数据可能会更新,在这个阶段,数据只是在data中进行更新了,但是没有在模板中进行更新,因此网页显示的还是之前的
- update
- 数据在data中更新了,此时页面上的数据都是最新的
- beforeUpdate
3-销毁期间- beforeDestroy
- Vue实例或者是组件在销毁之前执行的函数,在这一个函数中Vue或者组件中的所有属性,都是可用的
- destroyed
- Vue实例或者组件被销毁后执行的,此时Vue实例上所有的东西都会解绑,所有的时间都会被移除,所有子元素都会被销毁
- beforeDestroy
4、指令系列
4-1 常见指令
- v-model
- 用于表单元素的绑定,箭筒用户输出事件的以及更新数据
- v-text
- 更新元素的extContent,将数据解析为纯文本
- v-on
- 绑定事件
- 语法
v-on:click="say" or v-on:click="say('参数', $event) - 简写:
@click='say' - 使用逗号分隔绑定多个事件
<div v-on="click:onClick, keyup:onKeyup, keydown:onKeydown"></div>
v-for
- 根据数据多次渲染元素或模板
遍历数组 item 为当前项,index 为索引 <p v-for="(item, index) in list">{{item}} -- {{index}}</p> 遍历对象 item 为值,key 为键,index 为索引 <p v-for="(item, key, index) in obj">{{item}} -- {{key}}</p> 遍历常量 item为从1开始的递增值 <p v-for="item in 10">{{item}}</p>
- 根据数据多次渲染元素或模板
v-bind
- 绑定属性
- 语法:
v-bind:title='msg' - 简写:
:title='msg'
- v-html
- 更新元素的innerHTML,把数据解析为纯文本显示
- v-if/v-else/v-else-if
- 根据表达式值的真假条件,销毁或重建元素v-if,适合条件不大可能的改变的场景,v-if-else和v-else不用脱离v-if单独存在
- v-show
- 根据表达式真假结果,切换元素的diplay css属性,dom元素一直在v-show适合频繁切换
- v-once
- 只渲染元素组件一次,随后重新进行渲染,元素/组件以及其所有子节点,都被视为静态内容跳过,可以优化更新性能
- v-pre
- 主要应用与跳过这个元素和子元素编译过程,可以用来显示原始标签,跳过大量没有指令的节点,加快编译
- v-model
4-2 自定义指令
- 基本定义
- 自定义指令分为: 全局自定义指令/局部自定义指令
- 使用
Vue.directive('focus',{bind(el,binding){},inserted(){} })实现全局自定义指令 - 参数1: 指令的名称
- 参数2: 是一个对象,在这个对象上,有对应的钩子函数
- 钩子函数
- 一个指令定义的对象,可以提供以下几个钩子函数(均为可选)
- insterted: 被绑定元素插入父节点时调用(仅保证父节点存在,但不一定被插入文档中)
- bind: 只会调用一次,指令第一个绑定到元素调用时,在这里可以进行一次性的初始化设置
- update: 所有组件的VNode更新时调用,但是可能发生在其子VNode更新之前,指令的值可能发生了变化,也可能没有,但是可以通过比较更新前后的值来忽略不必要的模板更新
- componentUpdated: 指令所在组件的VNode及其子VNode全部更新后调用
- unbind: 只调用一次,指令与元素解绑时调用
- 一个指令定义的对象,可以提供以下几个钩子函数(均为可选)
- 指令钩子的参数
- el: 指令所绑定的元素,可以用来直接操作DOM在每个函数中,第一个参数el,表示被绑定了指令的那个元素,这个el参数,是一个原生的js对象
- binding: 一个对象,包含以下属性
- name: 指令的名字,不包括v-前缀
- value: 指令的绑定值
- oldValue: 指令绑定前的一个值,仅在updata和componentUpdated钩子中可用,无论值是否改变都可以使用
- expression: 字符串形式的指令表达式
- arg: 传给指令的参数,可选
- modiflers: 一个包含修饰符的对象
- vnode: Vue编译时生成的虚拟节点
- oldVnode: 上一个虚拟节点,仅在update和componentUpdate钩子中可用
全局指令
// 2.全局指令,一般在main.js中定义 // 为绑定的元素自动获取焦点: Vue.directive('focus', { inserted: function (el) { // inserted 表示被绑定元素插入父节点时调用 el.focus(); } })局部指令
// 1.创建局部指令 var app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { }, // 创建指令(可以多个) directives: { // 指令名称 dir1: { inserted(el) { // 指令中第一个参数是当前使用指令的DOM console.log(el); console.log(arguments); // 对DOM进行操作 el.style.width = '200px'; el.style.height = '200px'; el.style.background = '#000'; } }, color: { // 为元素设置指定的字体颜色 bind(el, binding) { el.style.color = binding.value; } } })使用方式
//3.指令的使用 <div id="app"> <div v-dir1 v-color="'red'"></div> <input type="text" v-focus /> </div>
- 基本定义
4-3 指令面试题
- 4-4 过滤器
5、组件系列
5-1 组件的基本定义
命名方式
横线分隔
Vue.component('my-component-name',{})驼峰命名
Vue.component('MyComponentName',{})注意事项
- 当使用首字母大写的方式定义组件时,在引用这个自定义元素时,两种方式都可以使用,但是直接在DOM(非字符串的模板)中使用时,只有
my-component的方式才是有效的
- 当使用首字母大写的方式定义组件时,在引用这个自定义元素时,两种方式都可以使用,但是直接在DOM(非字符串的模板)中使用时,只有
注册组件
全局注册
自定义组件 ```
5-2 父子组件传值
- 基本定义
- 父子组件传值,使用是
props实现的,其实就是利用属性读取的方式,在子组件使用props接收父组件传递过来的参数
- 父子组件传值,使用是
使用方式
父组件
<template> <div class="hello"> // 1- 通过绑定在子组件上属性 <Child :parentMessage="parentMessage"></Child> </div> </template> <script> import Child from './Child.vue' export default { components: { Child }, data () { return { // 可以传递给子组件任意类型的数据,但是需要在props中指定接收的类型 parentMessage: "我是来自父组件的消息" } } } </script>子组件
<template> <div> <span>{{parentMessage}}</span> </div> </template> <script> export default { // 使用props用来接收,父组件中传递过来的信息 props: { parentMessage: { // 声明字符的方式 type: String, defalut:'显示默认信息' } } } </script>
- 基本定义
5-3 子父组件传值
- 基本定义
- 子父组件传值的方式使用
$emit的方式,把子组件中的参数,发射出来,通过函数的形式进行传递,this.$emit('arg1',arg2)arg1: 方法名字, arg2: 要传递的值
- 子父组件传值的方式使用
使用方式
子组件
<template><div> <p>{{msg}}</p><button @click="toParent">点击我,向父组件传递数据</button></div></template><script>export default{ data(){ return { msg:'我是子组件中的值' } }, methods:{ toParent(){ this.$emit("toParent",this.msg) } }}</script><style >p{ color:red;}</style>父组件
<template> <div class="hello"> <span>等待接收子组件的值{{parentMessage2}}</span> <hr> // 子组件上,绑定事件 <ChildTwo @toParent="getMsg"/> </div></template><script>import ChildTwo from './ChildTwo.vue'export default { components: { ChildTwo }, data () { return { parentMessage2: "" } }, methods:{ // 声明的事件,形参位置保存的是,子组件中传递进来的数据 getMsg(msg){ // 保存子组件数据的形参,赋值给父组件中声明的parentMessage2 this.parentMessage2=msg } }}</script>
- 基本定义
5-4 兄弟组件传值
- 基本定义
- 兄弟组件之间传值的方式,核心就是利用一个新的Vue实例,作为一个中转,实现传值
使用方式
组件一
<template> <div> <hr> <p>我是第一个子组件,要给Child-Two组件传值</p> <button @click="toBrother">点击给兄弟组件传值</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { data () { return { to: 'Hello Child-Two' } }, methods: { // 这里和子传父采用的方式一样,都是使用$emit,通过触发事件,把当前数据发射出去 toBrother () { this.bus.$emit('toBrother', this.to) } } } </script>组件二
<template> <div> <p>我是第二个子组件</p> <span>我得到的兄弟组件信息是:--->{{get}}</span> </div></template><script>export default { data () { return { get: '' } }, beforeCreate () { // 使用实例对象中的$on方法,获取toBrother,第二个参数,是传递过来的msg,然后赋值给当前的get this.bus.$on('toBrother', msg => { this.get = msg }) }}</script><style >p { color: red;}</style>Event-Bus(vue-cli/main.js中定义)
Vue.prototype.bus=new Vue()5-5 爷孙组件传值
- 基本定义
基本定义
- 使用
provide()和inject()可以实现嵌套组件之间的数据传递,这两个函数只能在setup()函数中使用,父组件中使用provide()函数向下传递,子级组件中使用inject()获取上层传递过来的数据
- 使用
- 使用方式
- 共享普通数据
App.vue根组件```vueApp 根组件
- 共享普通数据
Level One
Level Two
如下代码实现了点按钮切换主题颜色的功能,主要修改了 `App.vue` 组件中的代码,`LevelOne.vue` 和 `LevelTwo.vue` 中的代码不受任何改变: ```vue
App 根组件
按钮被点击了{{ count }}次
 - 当把data选项修改为一个对象(相互之间都会受到影响)
 - **5-7 组件中插槽的作用** - **基本定义** - 插槽`slot`就是子组件中提供给父组件使用的一个占位符,用`
插入组件中的内容----上
插入组件中的内容----下
`Child-子组件`
```vue
<template>
<div class="child">
<span>子组件</span>
<slot name="top">后备内容1</slot>
<hr>
<slot name="bottom">后备内容2</slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
msg: 'Hello Child'
}
}
}
</script>
效果展示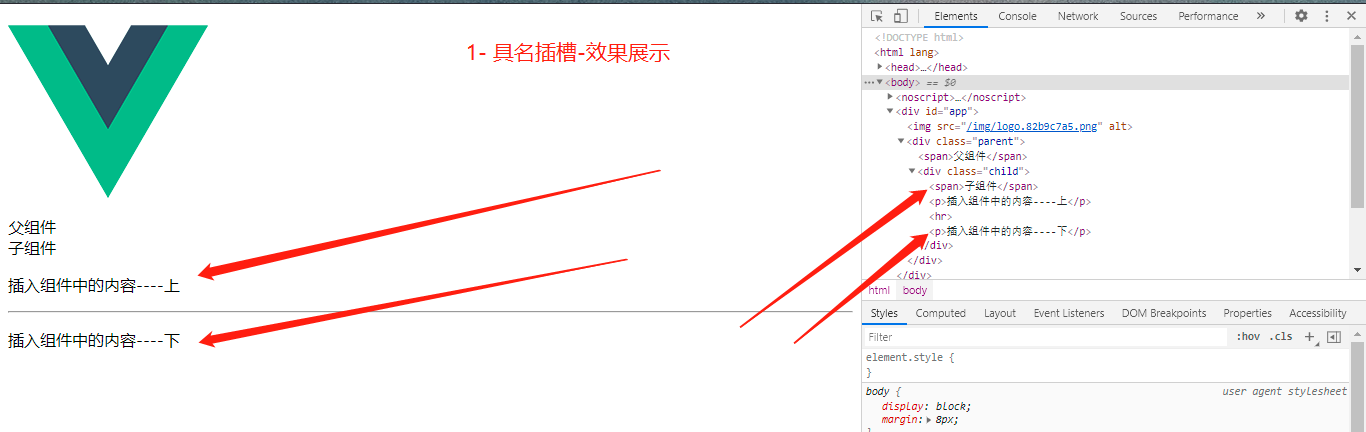
插入多个参数,只需要包裹一个父级标签即可
<template> <div class="parent"> <span>父组件</span> <Child> <div slot="top"> <p>插入组件中内容----上1</p> <p>插入组件中内容----上2</p> <p>插入组件中内容----上3</p> <p>插入组件中内容----上4</p> <p>插入组件中内容----上5</p> </div> <p slot="bottom">插入组件中的内容----下</p> </Child> </div></template>
效果展示
- 作用域插槽(用于子组件向父组件内对应插槽传入数据)
- 首先必须要在对应插槽名字的位置上加入属性
slot-scope=props,props可以随意写,对应处即可,使用{{props.text}}显示子组件插槽传递过来的数据parent-父组件```vue父组件{{props.text}}
插入组件中的内容——下
- 首先必须要在对应插槽名字的位置上加入属性
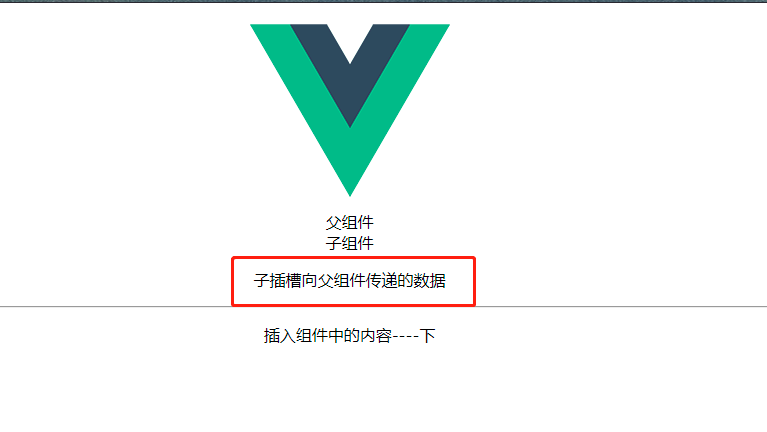 - **匿名插槽** - **5-8 如何实现组件缓存?** - **基本定义** - 使用keep-alive内置组件,可以实现组件缓存,`keep-alive`包裹动态组件的时候,会缓存不活动的组件实例,而不是销毁他们,并且它也是一个抽象的组件,它自身是不会渲染成一个DOM元素的,同时也不会在父组件链中 - **具体使用** - 只有在包含动态组件的时候,才会产生效果,如果不是动态效果组件,则会无效 ```vue
`route/index.js` ```javascript // 1- 在路由配置对象中,path属性值,后面加上参数 { path: '/about/:id', component: About } ``` - `about.vue组件` ```javascript // 2- 在需要跳转的组件中,使用$route.params实现参数的传递
我是关于标题
{{$route.params.id}}
- `效果展示`<br />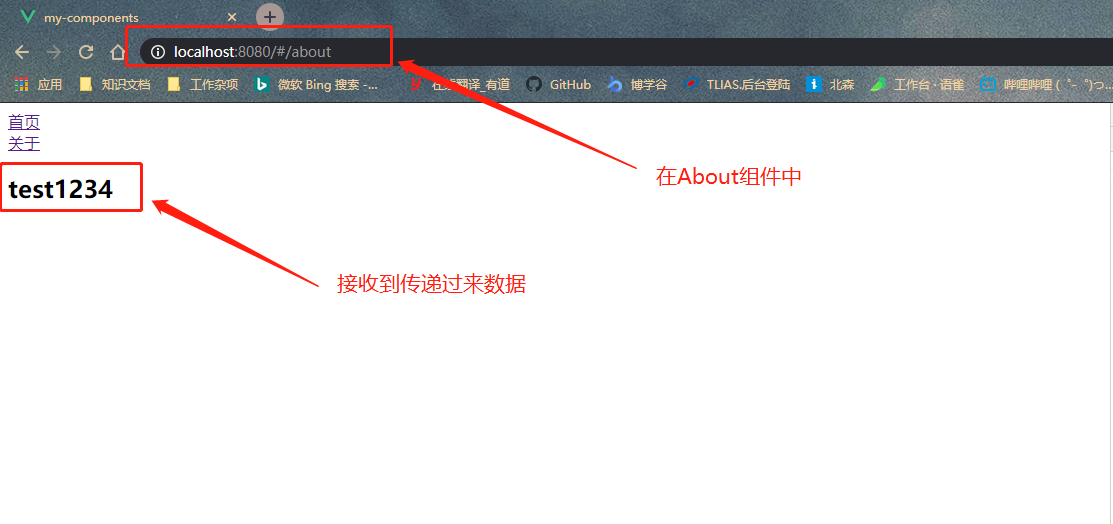
- **7-3 传递参数的方式**
- **通过标签中的to传参**
- 核心定义
- 核心就是采用`router-link`组件中的to属性,分别设置对应的name和params
- 上面的to前边的是带冒号的,后边跟的一个对象形式的字符串
- name: 在路由配置文件中起的name值,叫做命名路由
- params: 要传递的参数,对象的形式,可以在对象中传递多个值
- 具体实现
- 1- 在\src\App.vue组件里面导航中添加以下代码
```vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<router-link to="/home">首页</router-link><br>
// 1- to属性是加上冒号的,设置对象,并且使用params来组建要传递的参数
<router-link :to="{name:'about',params:{userName:'test1234'}}">关于</router-link>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
}
</script>
- 2- 在\src\router\index.js 路由配置文件中添加name字段
{
path: '/about',
// 2- 在路由配置对象中,添加上name属性,要和to中写入的name保持一致
name:'about',
component: About
}
- 3- 在src/components/About.vue 中接收参数
<template>
<div>
// 3- 使用$route呈现传递的参数
<h2>{{$route.params.userName}}</h2>
<p></p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'about'
}
</script>
- 4- 效果展示<br />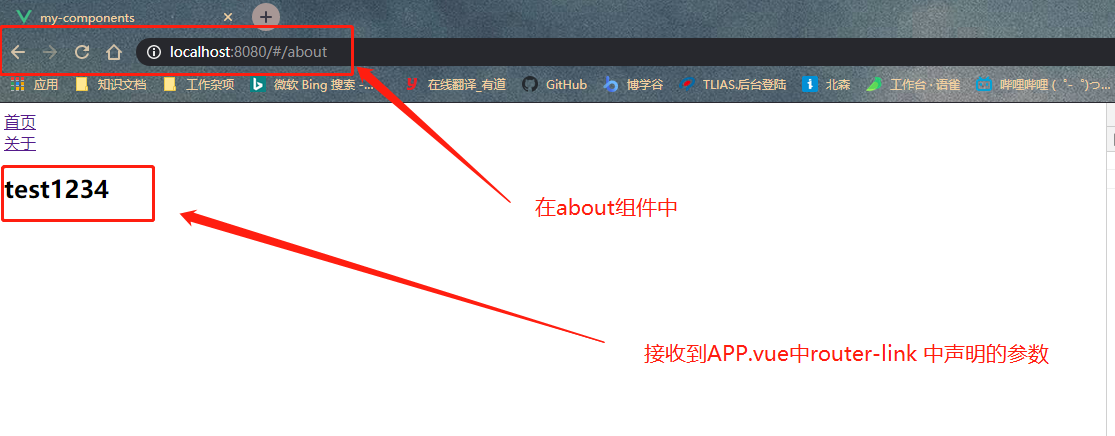
url中传递参数
- 核心定义
- 在需要接收的组件中使用
$route.params来获取传递进来的数据,传递回来的是一个对象,可以通过点语法,实现对值的获取
- 在需要接收的组件中使用
具体实现
1- 在路由中以冒号进行传递,在src/router/index.js中添加
{ // 可以直接设置规则,约定传递的参数特定格式 path: '/about:id(\\d+)/:name', component: About }2- 接受参数,src\views\about.vue
<template> <div> // <h2>{{$route.params.id}}</h2> <h2>{{$route.params.name}}</h2> <p></p> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'about' } </script>3- 路由跳转,在\src\App.vue中添加
<template> <div id="app"> <router-link to="/home">首页</router-link><br> // 2- 设置to属性中的参数 <router-link to="about/1/张三和李四">关于</router-link> <router-view></router-view> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'App', } </script> <style> </style>4- 效果展示

- 核心定义
编程式导航-params传递参数
- 核心定义
- 设置路由配置对象中的信息,添加name字段,然后在接收参数的组件中,使用
$.route.params来进行接收,在要传递参数的组件中,通过创建一个方法,在方法内部使用$.router.push方式组装一个传递参数的对象,这个对象中有两个字段,分别是{name: xxx}目标组件的名称,以及params: {id: xxx ,name: 'xxx'},两者都是放在$router.push()方法中,进行的组装 - 注意事项:
- 动态路由使用params传递参数,在this.$router.push()方法中path不能和params一起使用,否则params将无效,需要name来指定页面
- 以下方式参数不会显示在浏览器的URL地址栏中,如果刷新了一次,就获取不到参数了,改进方式将path:
about/:id/:name按照这种形式改进
- 设置路由配置对象中的信息,添加name字段,然后在接收参数的组件中,使用
具体实现
1- 在src/router/index.js中添加以下代码
{ // 这种方式,刷新页面后,会丢失参数 path: '/about', // 改进为: path: '/about/:id/:name' // 添加上name字段 name:'about', component: About }2- 在src/component/about.vue中,设置接收的参数名称 ```vue
// 2- 通过$route.params来接收参数id:{{$route.params.id}}
name:{{$route.params.name}}
- 3- 在src\App.vue组件中,添加一个事件,通过`$router.push`的方式,传递参数 ```vue <template> <div id="app"> <router-link to="/home">首页</router-link><br> <router-link to="/about">关于</router-link> <router-view></router-view> // 3- 添加一个事件,触发methods中的一个方法 <button @click="toAboutPage">点击我,向About组件传递参数</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'App', methods: { // 4- 实现传参的方法,核心就是通过$router.push方法,组装一个对象,把值进行传递 toAboutPage () { this.$router.push({ name: 'about', params: { id: 1, name: "jack" } }) } } } </script> <style> </style>- 实现效果<br />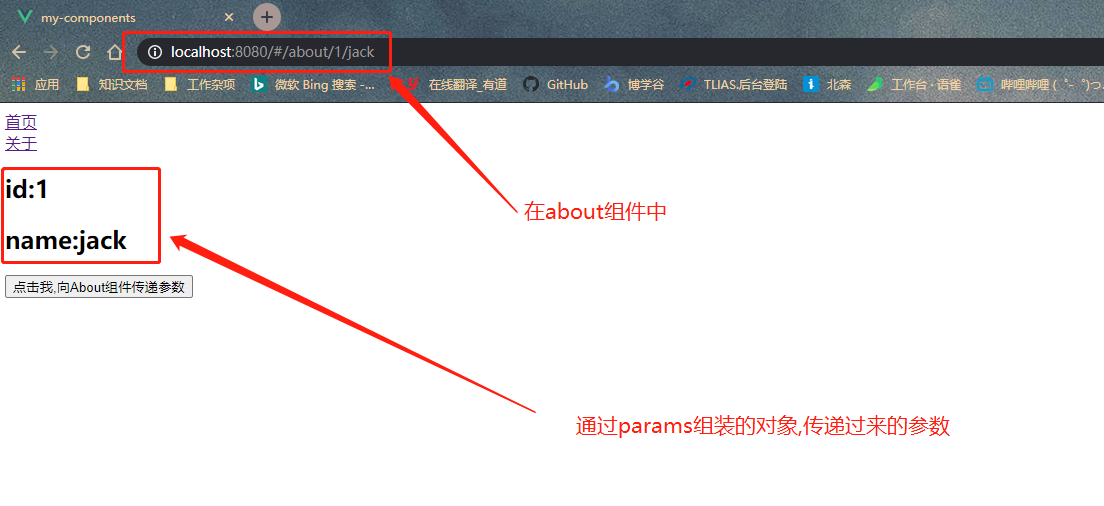编程式导航-query传递参数
- 核心定义
- 和使用params的方式相同,只不过在parmas替换成query即可,两者最大不同的地方在于,使用query方式传递的参数,会直接暴露在URL地址栏上,而使用params方式传递的参数则不会
实现方式
1- 在src\router\index.js中写入需要传参的组件名称
{ // 1- 在这里添加上需要传参组件的名称 path: '/about', name:'about', component: About }2- 在src\views\about.vue中,改为query的方式 ```vue
// 2- 在接收参数的组件内,使用query的方式,接收传递过来的参数id:{{$route.query.id}}
name:{{$route.query.name}}
- 3- 在发送参数的组件内,创建一个方法,使用$router.push()组装一个传递的query对象 ```vue <template> <div id="app"> <router-link to="/home">首页</router-link><br> <router-link to="/about">关于</router-link> <router-view></router-view> <button @click="toAboutPage">点击我,向About组件传递参数</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'App', methods: { toAboutPage () { // 3- 核心是这里,把之前的params该写为query的方式 this.$router.push({ name: 'about', query: { id: 1, name: "jack" } }) } } } </script>- 4- 效果展示<br />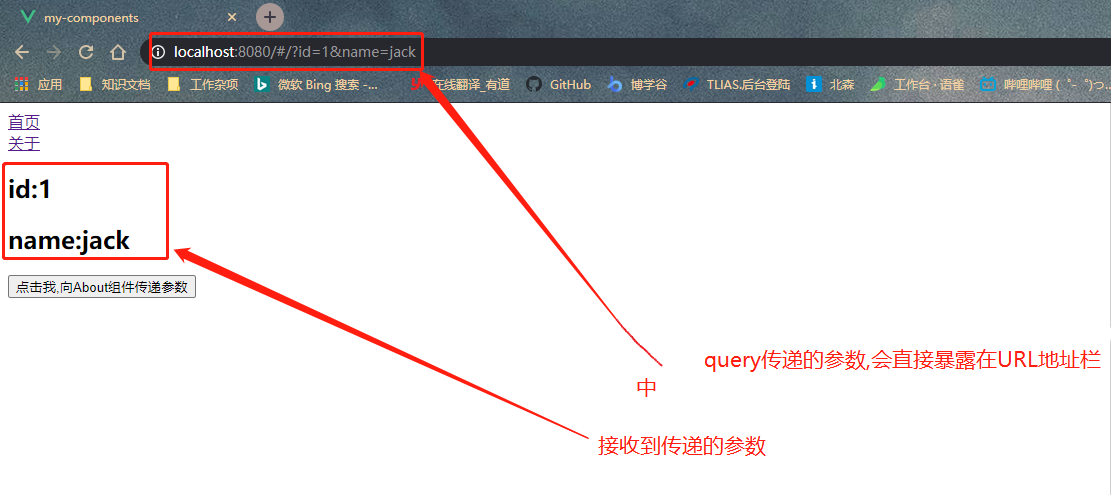- 7-4 Vue-Router中存在哪些钩子函数
- 全局钩子函数
- 具体实现 ```javascript // 定义- 全局导航钩子函数- 进入页面时,实现拦截登录 router.beforeEach((to,from,next)=>{ // 此处可以加入登录逻辑判断 // 放行 next() })
- 全局钩子函数
// 定义- 全局后置钩子函数-常用于结束动画后的操作 router.afterEach(()=>{ // 不接受next() })
- 常用参数 - to:Router 即将要进入的目标[路由对象] - from: Router 当前守卫要离开的路由 - next: Function 继续执行函数 - next() 继续执行 - next(false) 中断当前执行 - next('/')或者next({path: '/'}) 跳转新的页面,常用于登陆失效后跳转登陆 - **路由单独钩子函数** - 基本使用 ```javascript { path:'home', component: Home, // 路由内钩子 beforeEnter: (to,from,next=>{ console.log('进入前执行') next() }) }- 组件内钩子函数
- 基本使用
- beforeRouterEnter: 进入页面时调用
- beforeRouterUpdate: 页面路由改变时调用,一般需要携带参数
- beroreRouterLeave: 离开页面时调用
- 实现方式
<script> export default { name: 'Two', data () { return { msg: 'Hi, I am Two Page!' } }, // 进入页面前调用 beforeRouteEnter(to, from, next) { console.log('进入enter路由钩子') next() }, // 离开页面调用 beforeRouteLeave(to,from, next){ console.log('进入leave路由钩子') next() }, // 页面路由改变时调用 beforeRouteUpdate(to, from, next) { console.log('进入update路由钩子') console.log(to.params.id) next() } } </script>
- 基本使用
7-5 嵌套路由的实现
- 基本定义
- 子路由,也叫嵌套路由,采用在
children后跟路由数组实现,数组中和其它配置路由信息基本相同,需要配置path和component,然后在对应的位置添加上<router-view></router-view>来展示子页面信息,相当于嵌套ifname
- 子路由,也叫嵌套路由,采用在
具体实现
1- src\components\Home.vue(父组件)
<template> <div> <h1>{{msg}}</h1> <!-- 添加子路由导航 --> <router-link to="/home">首页</router-link> <br> <hr> <router-link to="/home/ComOne">ComOne组件-展示区域</router-link> <br> <hr> <router-link to="/home/ComTwo">ComTwo组件-展示区域</router-link> <!-- 展示子组件 --> <router-view></router-view> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'Home', data () { return { msg: 'Hello Home' } } } </script>2- src\components\ComOne.vue
<template> <div> <h2>{{msg}}</h2> </div> </template> <script> export default { name:'ComOne', data(){ return { msg:'Hello ComOne' } } } </script>3- src\components\ComTwo.vue
<template> <div> <h2>{{msg}}</h2> </div> </template> <script> export default { name:'ComTwo', data(){ return { msg:"Hello ComTwo" } } } </script>4- src\router\index.js ```javascript import Vue from ‘vue’ import VueRouter from ‘vue-router’ // 配置路由的映射关系 import Home from ‘@/components/Home.vue’ import ComOne from ‘@/components/ComOne.vue’ import ComTwo from ‘@/components/ComTwo.vue’
- 基本定义
// 1- 注入插件 Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 2- 定义路由 const routes = [ // 默认展示组件home { path: ‘/‘, redirect: ‘/home’ }, { path: ‘/home’, // 父级路由 component: Home, children: [ // 定义嵌套路由的关键属性children { path: ‘ComOne’, // 子路由1 component: ComOne }, { path: ‘ComTwo’, // 子路由2 component: ComTwo } ] } ] // 3- 创建Router实例 const router = new VueRouter({ routes }) // 4- 导出实例 export default router
- 效果展示<br /> 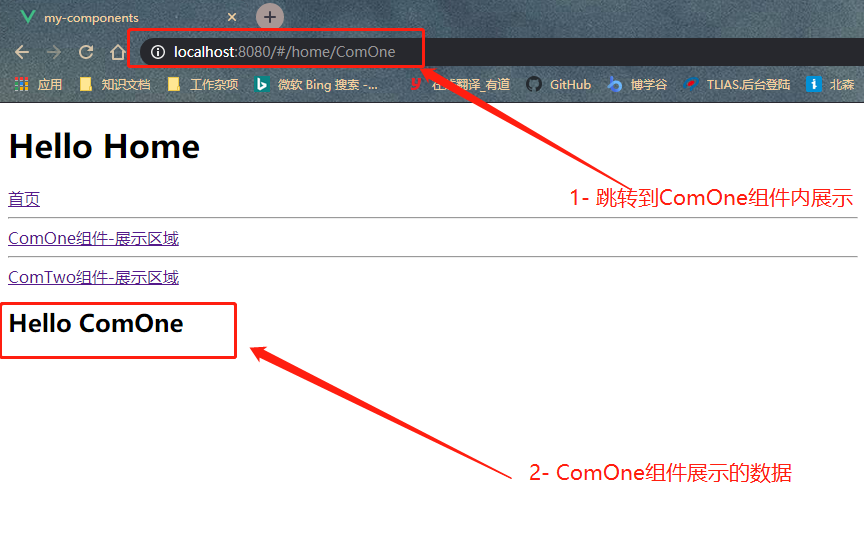 - **7-6 `$route`和`$router`的区别** - **$route** - 基本定义 - $route是路由参数对象,包括了path,params,hash,query,fullPath,matched,name等路由信息参数<br /> - 常用参数 - `$route.path` - 字符串形式,对应当前路由的路径,总是解析为绝对路径,如"/ComOne" - `$route.params` - 一个key/value对象,包含了动态片段和全匹配片段,如果没有路由参数,那么是一个空对象形式 - `$route.query` - 一个key/value对象,表示URL查询参数,例如,对于路径/home?user=1,则有$router.user为1,如果没有查询参数,是一个空对象形式 - `$route.fullPath` - 完整解析后的URL,包含查询的参数和hash的完整路径信息 - `$router.matched` - 数组形式,包含当前的路径中所包含的所有片段和对应的配置参数对象 - `$route.name` - 当前路径的名字 - **$router** - 基本定义 - $router是路由实例对象,即VueRouter创建的实例,包括了路由的跳转方法,钩子函数等<br /> - 常用方法 - `go()` - 跳转到上次浏览的页面 ```javascript showRouter: function () { // 1- 跳转到上次浏览的页面 this.$router.go(-1) }- `replace()` - 跳转到指定地址showRouter: function(){ // 2- 跳转到指定地址 this.$router.replace('/ComTwo') }- 跳转到指定名字地址showRouter: function () { // 3-指定跳转路由的名字下 this.$router.replace({name:'ComTwo'}) } // router/index.js // 需要在router配置文件中,设置对象name字段,才可以实现跳转 { path: 'ComTwo', // 添加上name属性 name:'ComTwo', component: ComTwo }- `push()` - 跳转到指定位置showRouter: function(){ // 4- 通过push跳转 this.$router.push('/ComTwo') }- 跳转到指定名字地址showRouter: function () { // 4- 通过push跳转 this.$router.push({name:"'/ComTwo'"}) } // router/index.js // 需要在router配置文件中,设置对象的name字段,才可以实现跳转 { path: 'ComTwo', // 添加上name属性 name:'ComTwo', component: ComTwo }- `$router.push和$router.repleace`的区别 - 使用`push`方法的跳转会向`history`栈添加一个新的记录,当点击浏览器的back返回按钮时,可以看到之前的页面 - 使用`replace`方法不会向`history`添加新记录,而是替换掉当前的`history`记录,也就是`replace`跳转到页面后,back按钮不能查看到之前的页面7-7 路由懒加载
- 核心定义
- Vue是单页面应用,如果没有应用懒加载技术,那么通过webpack打包后的文件将会异常的庞大,造成用户进入页面的时候,一次加载的内容过多,时间过长,那么就会造成白屏出现,及时做了loading也是不利于用户体验,使用了懒加载则可以把页面进行划分,在需要的时候加载,可以有效的分担首页所承担的加载压力,减少首页加载用时
具体实现
Vue异步组件
compoent: (resolve)=> require(['@/component/One'],resolve)ES6-import(常用的方式)
component: ()=>import('@/components/Two')webpack提供的require.ensure()
component: r=> require.ensure([], ()=> rrequire('@/component/Three')), 'group-home')
- 核心定义
8、Vuex系列
- 8-1 单向数据流
- 核心定义
- Vuex是一个专门为Vue提供的
状态管理模式,它采用的是集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态,按照以一种可预测的方式发生变化 - 单向数据流
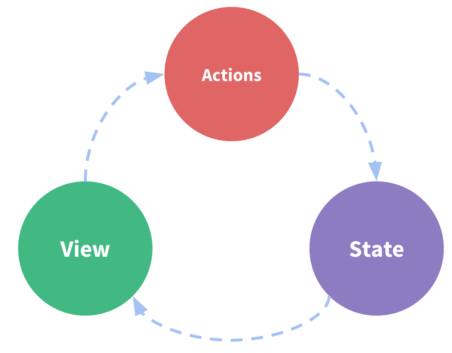
- 示图说明
- State: 驱动应用的数据源(单向数据流)
- View: 以声明方式将State映射到视图(静态显示出来的数据源)
- Actions: 处理用户在view上面操作而导致的状态变化(数据源追踪)
- 示例代码
<template> <div> <!-- view --> <div>{{ count }}</div> <button @click="increment">increment</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { // state data () { return { count: 0 } }, // actions methods: { increment () { this.count++ } } } </script>
- 8-2 Vuex实现流程
- 核心定义
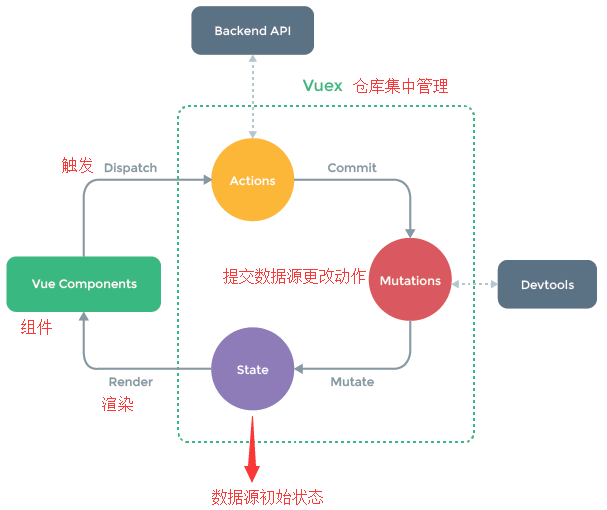
- 示图说明
- 1- Vue Component: Vue组件,HTML页面上,负责接收用户操作等行为,执行dispatch方法触发对应的action进行回应
- 2- Dispatch: 操作行为触发方法,是唯一执行action的方法
- 3- Actions: 操作行为处理模块,负责处理components接收到的所有交互行为,包含同步/异步操作,支持多个同名方法,按照注册的顺序依次触发,向后台API请求的操作就在这个模块中进行,包括触发其它aciton以及提交的mutaion操作,同时该模块提供了对Promise的封装,以支持action的链式触发
- 4- Commit: 状态改变提交操作方法,对mutation进行提交,是唯一能执行mutation的方法
- 5- Mutations: 状态改边的操作方法,是Vuex修改state的唯一推荐方法,其它修改方式在
严格模式下会报错,该方法只能进行同步操作,并且是全局唯一,操作之中会有hook暴露出来,以进行state的监控等 - 6- State: 页面状态管理容器对象,几种存储Vue components中data对象的零散数据,全局唯一,以进行统一的状态管理,页面显示所需的数据从该对象中进行获取,利用Vue的细粒度数据响应机制进行高效的状态更新
- 7- Getters: state对象读取方法,图中没有单独列出该模块,应该被包含在了render中,Vue Components通过该方法读取全局state对象
- 总结描述
- Vue组件的接收行为,
用dispatch方法触发action相关处理,若页面状态需要改变,则调用commit方法提交mutation修改state,通过getters获取到state新值,重新渲Vue Components,界面随之更新
- Vue组件的接收行为,
- 具体实现
- src/vuex/store.js ```javascript // 引入vue import Vue from ‘vue’ // 引入vuex import Vuex from ‘vuex’
- 核心定义
// 使用Vuex Vue.use(Vuex)
// 1- state 创建初始化状态 const state = { // 放置初始状态 count: 1 }
// 2- mutations 创建改变状态的方法 const mutations = { // 状态函数,一般大写 ADD (state, n) { state.count += n } }
// 3- getters 提供外部获取state const getters = { count: function (state) { return state.count } }
// 4- actions 创建驱动方法改变mutations const actions = { // 触发mutations中相应的方法,一般小写 add ({ commit }, data) { commit(‘ADD’, data) } }
// 5- 全部注入到store中 const store = new Vuex.Store({ state, mutations, getters, actions })
// 6- 导出store export default store
- src/main.js ```javascript import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' import router from './router' // 引入store import store from './vuex/index' Vue.config.productionTip = false new Vue({ router, store, // 注入到全局 render: h => h(App), }).$mount('#app')- src/component/Count.vue<template> <div> <h1>{{msg}}</h1> <h2>{{count}}</h2> <button @click="clickAdd">新增</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'Count', data () { return { msg:'Hello Vuex' } }, computed:{ // 1- 获取state的值 count(){ return this.$store.state.count } }, methods:{ clickAdd(){ // 2- 分发action中的add方法 this.$store.dispatch('add',1) } } } </script>- **效果展示**<br />8-3 介绍一下Vuex中的核心属性
State(唯一数据源,所有数据都要放到state中存储)
- 全局中的唯一容器,用于存储components中data对象的零散数据,今天统一的状态管理,页面中显示的数据从该对象中进行获取
1- 定义state
export default new Vuex.Store({ state:{ count:0 } })2- 组件访问state中数据的第一种方式($store.state的方式) ```javascript
// 第一种访问的方式, 直接通过 $store.state访问,在template中,可以省略this当前最新的count的值为:{{$store.state.count}}
- 3- 组件访问state中数据的第二种方式(mapState的方式) ```javascript <template> <div> <h1>当前最新的count的值为:{{count}}</h1> <button>+1</button> </div> </template> <script> // 1- 按需导入mapSate import {mapState} from 'vuex' export default { name:"Addition", data(){ return{} }, computed:{ // 2- 将全局函数,映射为当前组件的计算属性 ...mapState(['count']) } } </script>
Mutation(用于变更state中的数据)
- 只能通过mutation变更store中的数据,不可以直接操作state中的数据,并且可以集中管理store中的数据
Mutation本质上也是一个函数,只能通过Mutation修改state中的数据,并且保证必须是同步的操作,否则将无法追踪
1- 定义Mutations
export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0 }, mutations: { // 两个参数: 参数1是当前的state 参数2是要传递进来的值 addN (state, step) { // 变更state的状态 state.count += step }, sub(state){ state.count-- } }, })2- 触发mutations的第一种方式(commit()传递参数)
<template> <div> <h1>当前最新的count的值为:{{count}}</h1> <button @click="addCount">+1</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { name:"Addition", data(){ return{ } } methods:{ addCount(){ // 两个参数, 参数1是 mutation创建的方法名称,参数2是addN方法的第二个形参 // commit的作用就是为了触发一个mutation return this.$store.commit('addN',1) } } } </script>3- 触发mutions的第二种方式(mapMutations函数) ```javascript
当前最新的count的值为:{{$store.state.count}}
```
- Action(用于处理异步任务-本质上是一个函数)
- 如果需要操作异步任务,只能通过Action,不能使用Mutation,但是在Action中触发Mutation的方式间接变更数据
- 为了执行异步操作,VueX在组件和Mutation之间增加了Action这个
中间媒介 - Action中通过
异步的方式获取数据,并且把数据转交给MutIon,最终由Mutation负责变更State中的数据 - 1- 定义Action ```javascript // 引入vue import Vue from ‘vue’ // 引入vuex import Vuex from ‘vuex’
// 使用Vuex Vue.use(Vuex) export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0 }, mutations: { // 两个参数: 参数1是当前的state 参数2是要传递进来的值 addN (state, step) { // 变更state的状态 state.count += step }, sub (state) { state.count— } }, actions: { // 使用actions来处理所有的异步操作 addAsync(context){ setTimeout(()=>{ // 在Action中不能直接修改state中的数据,要想修改,只能触发一个mutation才可以 context.commit(‘addN’,3) },1000) }, subAsync(context){ setTimeout(()=>{ // 在Action中不能直接修改state中的数据,要想修改,只能触发一个mutation才可以 context.commit(‘sub’,) },1000) } } })
- 2- 触发action的第一种方式(dispatch) ```vue <template> <div> <h1>当前最新的count的值为:{{count}}</h1> <button @click="AddHandle">+1--Async</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { name:"Addition", data(){ return{ } } methods:{ AddHandle(){ // 触发Action的第一种方式 this.$store.dispatch('addAsync') } } } </script>- 3- 触发action的第二种方式(导入napActions)<template> <div> <h1>当前最新的count的值为:{{$store.state.count}}</h1> <button @click="subAsync">-1 Async</button> </div> </template> <script> // 1- 按需导入mapActions import { mapActions } from 'vuex' export default { name:"Subtraction", data(){ return{ } }, methods:{ // 2- 展开mapAction函数,并且传入参数 ...mapActions(['subAsync']) } } </script>- Getter(Vuex中的计算属性-本质也是一个函数)
- 定义Getter
- Getter本质上是一个函数,是VueX中的计算属性,Getter可以依赖于Store中原始数据的变化,并返回计算后的新数据
- Getter的返回值会被缓存起来,只有依赖项发生变化的时候,Getter的值才会被从新计算 ```javascript // 引入vue import Vue from ‘vue’ // 引入vuex import Vuex from ‘vuex’
- 定义Getter
// 使用Vuex Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0 } getters: { // getter本质上就是一个函数,第一个形参永远都是state countPlus (state) { return state.count * 2 } } })
- 使用Getter的第一种方式 ```vue <template> <div> <p>当前cuount最新的值为:{{this.$store.getters.countPlus}}</p> <!-- 1- 在template模板中,可以省略掉this,直接写成以下方式 --> <p>当前cuount最新的值为:{{$store.getters.countPlus}}</p> </div> </template> <script> import {mapState} from 'vuex' export default { name:"Addition", data(){ return{ } } } </script>- 使用Getter的第二种方式<template> <div> <p>当前cuount最新的值为:{{countPlus}}</p> </div> </template> <script> import {mapState,mapGetters} from 'vuex' export default { name:"Addition", data(){ return{ } }, computed:{ // mapGetters辅助函数,仅仅是将state中的getter映射为当前组件的计算属性 ...mapGetters(['countPlus']) } } </script>Module(命名空间,为了防止命名冲突)
声明用户模块
export default { state: () => ({ userInfo: { name: 'jack', age: 20 } }), mutations: { updateUserInfo (state) { console.log(state); // 更新用户信息 state.userInfo = { name: 'rows', age: 30 } } } }注册用户模块 ```javascript // 引入vue import Vue from ‘vue’
// 引入vuex import Vuex from ‘vuex’
// 导入用户模块 import moduleUser from ‘./ModuleUser’
// 使用Vuex Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({ modules: { // user就是用户模块的注册名称 user: moduleUser } })
- 使用模块数据中的第一种方式 ```vue <template> <div class='container'> <!-- 在template中可以使用this的方式,同时也可以使用$store的方式来访问数据--> <p>{{$store.state.user.userInfo.name}}</p> <p>{{this.$store.state.user.userInfo.age}}</p> </div> </template> <script> export default { data () { return {} } </script> <style scoped lang='less'> </style>- 使用模块数据中的第二种方式<template> <div class='container'> </div> </template> <script> import {mapState } from 'vuex' export default { data () { return {} }, computed:{ // 把User模块中的数据,映射为当前组件的计算属性 ...mapState({ userinfo: state=> state.user.userinfo }) } } </script> <style scoped lang='less'> </style>- 调用模块中Mutation方法的第一种方式<template> <div class='container'> <button @click="onBtnClick">点击我,查看updateUserInfo方法</button> </div> </template> <script> import { mapMutations } from 'vuex' export default { data () { return {} } methods: { // 访问命名空间下的state数据 // 参数1: 命名空间的名字 // 参数2: 要映射的方法名字列表(数组或对象) ...mapMutations('user', ['updateUserInfo']), // 按钮的点击事件处理函数 onBtnClick () { console.log(this.updateUserInfo()) } } } </script> <style scoped lang='less'> </style>- 访问命名空间下的action和getter<template> <div class='container'> </div> </template> <script> import { mapGetters, mapActions} from 'vuex' export default { data () { return {} }, computed: { // 把User模块中的数据,映射为当前组件的计算属性 ...mapActions('user',['userinfo']) }, methods: { // 访问命名空间下的state数据 // 参数1: 命名空间的名字 // 参数2: 要映射的方法名字列表(数组或对象) ...mapGetters('user',['userinfo']), } } </script> <style scoped lang='less'> </style>10、webpack系列
10-1 webpack概述
webpakc是一个模块化JavaScript的工具,在webpakc里一切文件皆都是模块,通过
Loader转换文件,通过Plugin注入钩子,最后输出由多个模块组合成的文件,Webpack专注于构建模块化项目,
一切文件: JavaScrip,CSS、SCSS、图片、模板,在 Webpack 眼中都是一个个模块,这样的好处是能清晰的描述出各个模块之间的依赖关系,以方便 Webpack 对模块进行组合和打包。 经过 Webpack 的处理,最终会输出浏览器能使用的静态资源
Webpack具有很大的灵活性,,能配置如何处理文件,大致使用如下module.exports={ // 所有的模块如快快快,webpakc从入口开始递归解析出所有依赖的模块 entry: './app.js' output: { // 把入口所依赖的所有模块,打包成一个文件bundle.js文件 filename: 'bundle.js' } }webpakc的优点是
- 专注于处理模块化的项目,能做到开箱即用,一步到位
- 通过Plugin扩展,完整好用又不失灵活
- 使用场景不仅限于web
- 庞大的社区,并且活跃度很高,经常引入紧跟时代的的新特新,能为大多数场景找到已有的开源拓展
- 良好的开发体验
- webpack的缺点是
- 只能采用模块化开发的项目
- 7-4 Vue-Router中存在哪些钩子函数
- 核心定义
- 核心定义


