【1】mybatis中的缓存
- 什么是缓存?
存在内存中的数据。
将用户经常查询的数据放在缓存(内存)中,用户去查询数据就不用从磁盘(关系型数据库数据文件)上查询,从缓存中查询,从而提高查询效率,解决了高并发系统的性能问题。
- 为什么要使用缓存
减少与数据库的交互次数,减少系统开销,提高系统效率
- 什么样的数据能使用缓存
经常查询且不经常改变的数据
(1)一级缓存和二级缓存
一级缓存:sqlSession级别的缓存,这个缓存默认是存在的,在我们进行数据查询的时候,mybatis会先去数据库中将对应数据查出来,然后将数据封装成对象存到缓存域中,下次再发起查询时,mybatis会从缓存域中读取数据,避免了与数据库的多次交互。
@Testpublic void test07(){UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);//访问数据库List<User> userList1 = mapper.getUserList();//从缓存中获取List<User> userList2 = mapper.getUserList();//输出值为trueSystem.out.println(userList1==userList2);}
- 如何让一级缓存失效?
1、调用清空缓存的方法
2、关闭sqlSession对象
3、第二次查询的数据与第一次查询的数据有偏差(在第一次查询后,执行了添加、删除、修改等操作)
@Testpublic void test07(){UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);//访问数据库List<User> userList1 = mapper.getUserList();//调用清空缓存的方法sqlSession.clearCache();//从缓存中获取List<User> userList2 = mapper.getUserList();//输出值为falseSystem.out.println(userList1==userList2);}
@Testpublic void test07(){UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);//访问数据库List<User> userList1 = mapper.getUserList();sqlSession.close();sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);//从缓存中获取List<User> userList2 = mapper.getUserList();//输出值为falseSystem.out.println(userList1==userList2);}
二级缓存:sqlSessionFactory级别的缓存,这个缓存可以共享所有的sqlSession,将数据通过序列化的方式存到缓存域中,存放的是数据,不是对象!!
配置二级缓存:
1.mybatis-config.xml中
2、在需要查询的UserMapper.xml中开启二级缓存的支持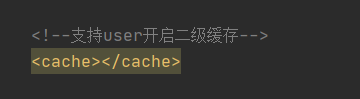
3、UserMapper.xml中方法开启二级缓存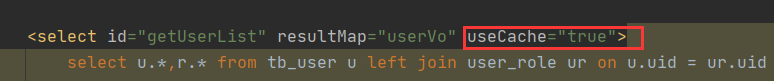
4、实体类实现Serializable接口
如何让二级缓存失效
1、调用清空缓存的方法
2、关闭sqlSession对象
【2】通过注解写sql
1、配置映射器
2、给接口中方法加注解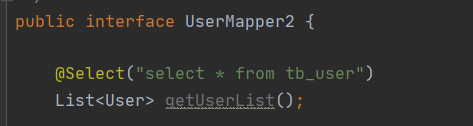
增删改查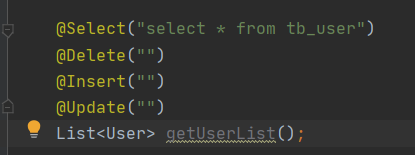
@Results注解
@Results中只有两个属性,id和value,id作为当前@Results注解的唯一标识很好理解;value为@Result数组
@Result中常用的属性是column和property,用于配置数据库中的列名和类中的属性名之间的映射关系。另外one和many用于关联查询。
@Results(id="groupWithUsers",value = {@Result(property = "uid", column = "uid", id = true),@Result(property = "name", column = "name"),@Result(property = "password", column = "password"),@Result(property = "getUserList", javaType=List.class, many =@Many(select="selectUsersByGroupId"), column = "group_id")})

