一、简单介绍
官网地址:https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/integration.html#cache
- Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache 和 org.springframework.cacheCacheManage 接口来统一不同的缓存技术;并使用JCache注解来简化我们的开发。
- Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合;Cache接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现;如RedisCache,concurrentMapCache等;
- 每次调用需要缓存功能的方式时,Spring会检查指定参数的指定目标方法是否已经被调用过;如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法的结果,如果没有就调用方法并缓存结果后返回给用户。下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
- 使用Spring缓存抽象时我们需要关注一下两点;
- 1、确定方法需要被缓存以及他们的缓存策略
- 2、从缓存中读取之前缓存的数据。


CacheManage 缓存管理器可以管理各种各样的缓存,如ConcurrentHashMap、Redis等。Redisson也会继承CacheManage 。
public interface CacheManager {/*** Get the cache associated with the given name.* <p>Note that the cache may be lazily created at runtime if the* native provider supports it.* @param name the cache identifier (must not be {@code null})* @return the associated cache, or {@code null} if such a cache* does not exist or could be not created*/@NullableCache getCache(String name);/*** Get a collection of the cache names known by this manager.* @return the names of all caches known by the cache manager*/Collection<String> getCacheNames();}
二、简单使用
以下所说的是基于Springboot下的cache使用
2.1 依赖和配置
2.1.1 引入依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId><exclusions><exclusion><groupId>io.lettuce</groupId><artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId></exclusion></exclusions></dependency>
2.1.2 引入配置
- Springboot中的CacheAutoConfiguration会导入RedisCacheConfiguration.class,RedisCacheConfiguration.class里面自动配好了缓存管理器。
- 配置使用redis作为缓存
spring.cache.type=redisspring.cache.redis.time-to-live=60000
2.1.3 开启SpringChache
1、直接使用注解 @EnableCaching
@EnableCaching@SpringBootApplicationpublic class SpringBootStarter {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(SpringBootStarter.class, args);}}
2、使用配置类
```java @EnableConfigurationProperties(CacheProperties.class) @Configuration @EnableCaching public class MyCacheConfig {
// @Autowired // private CacheProperties cacheProperties
/*** 1、原来和配置文件绑定的配置类是这样子的** @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.cache")* public class CacheProperties* <p>* 2、要让其生效*/@BeanRedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties) {RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();// 设置序列化器config = config.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()));config = config.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));// 将配置文件中的所有东西让其生效CacheProperties.Redis redisProperties = cacheProperties.getRedis();if (redisProperties.getTimeToLive() != null) {config = config.entryTtl(redisProperties.getTimeToLive());}if (redisProperties.getKeyPrefix() != null) {config = config.prefixKeysWith(redisProperties.getKeyPrefix());}if (!redisProperties.isCacheNullValues()) {config = config.disableCachingNullValues();}if (!redisProperties.isUseKeyPrefix()) {config = config.disableKeyPrefix();}return config;}
}
<a name="W2pcp"></a>## 2.2 基本使用> SpringCache 配置好后主要基于以下几个注解使用> - **@Cacheable:** Triggers cache population. 触发将数据保存到缓存的操作。> - **@CacheEvict: **Triggers cache eviction. 触发将数据从缓存删除的操作。> - **@CachePut:** Updates the cache without interfering with the method execution. 不影响缓存的执行下更新缓存。> - **@Caching: **Regroups multiple cache operations to be applied on a method. 组合以上多个操作。> - **@CacheConfig: **Shares some common cache-related settings at class-level. 在类级别共享缓存的相同配置。<a name="okazK"></a>### 2.2.1 @Cacheable- value:指定Cache的名称,其可以是一个数组表示多个Cache。```java@Cacheable({"cache1", "cache2"})//Cache是发生在cache1和cache2上的public User find(Integer id) {return null;}@Cacheable(value = "category")public String getCache() {System.out.println("没走缓存");return getCategory();}
Key:用来指定Spring缓存方法的返回结果时对应的key,其支持自定义和默认两种。支持SpEL表达式。
@Cacheable(value = "category2", key = "#root.methodName")@GetMapping("test2")public String getCache2() {System.out.println("没走缓存");return getCategory();}
Condition:指定发生的条件,指定需要缓存哪些内容。结果为true,缓存到redis,结果为false,不缓存到redis。
@Cacheable(value={"users"}, key="#user.id", condition="#user.id%2==0")public User find(User user) {System.out.println("find user by user " + user);return user;}
unless:结果为false,缓存到redis。结果为true,不缓存到redis
/*** 测试null,不存null*/@Cacheable(value = "category2", key = "#root.methodName", unless = "#result == null")@GetMapping("queryCache2")public String queryCache2() {System.out.println("queryCache2......");return "11";}
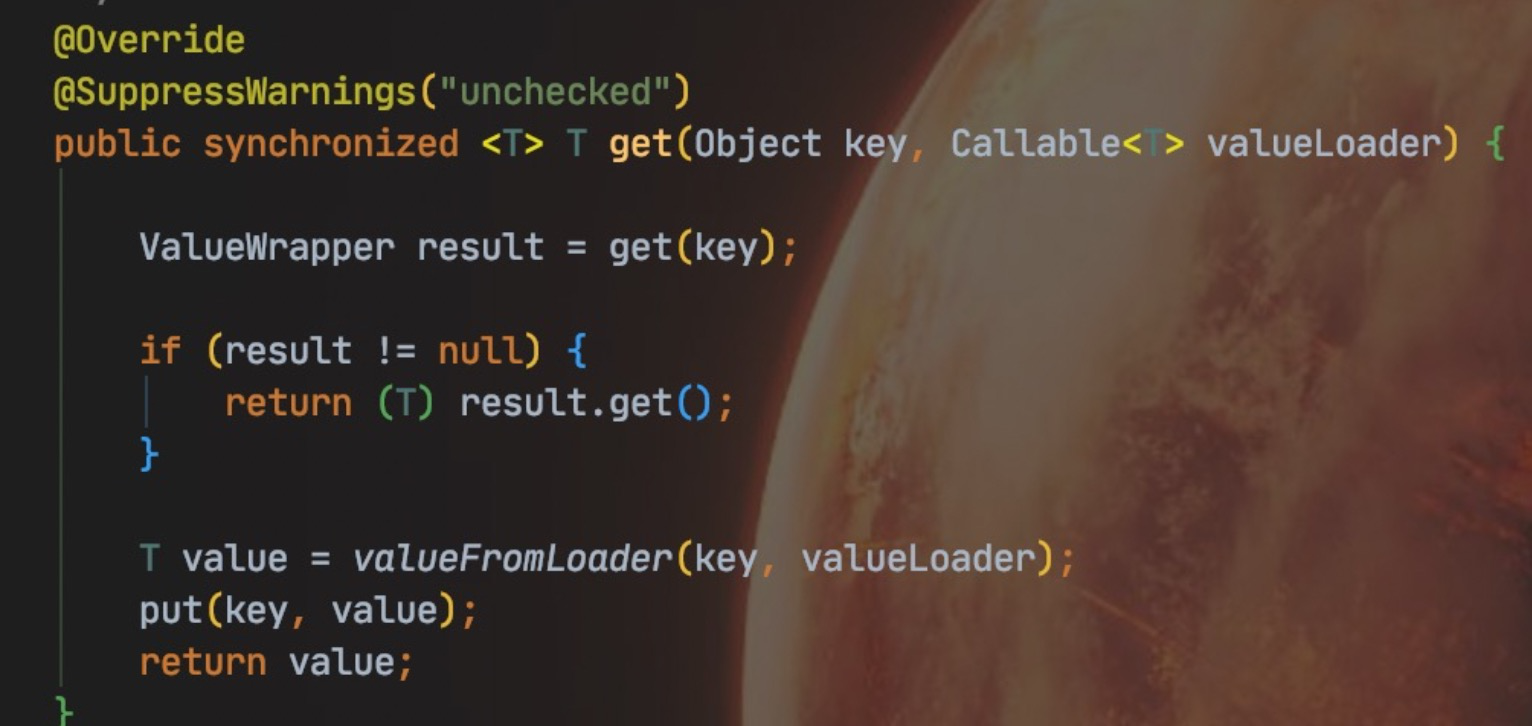
sync :使用缓存的时候需要特别注意,防止缓存并发,并发量较高的情况下,很可能会出现多个请求同时查询1个key的情况,如果我们不加控制,让这些请求全部穿透到数据库,容易造成数据库挂掉。正常的做法是:只放一个请求去数据库查询数据,其他的请求等待 (或者立即返回null) ,查询数据库的那个线程返回结果后再将数据放入缓存。
@Cacheable(value = "category2", key = "#root.methodName", sync = true)public void queryCache() {}
当使用 sync = true 时,会调用加锁的 get方法。
2.2.2 @CacheEvict
value:缓存名,删除指定的名字的缓存
@CacheEvict(value = "menuById")public Boolean deleteById(String id) {return this.removeById(id);}
Key: 删除指定缓存名下的指定key的缓存
@CacheEvict(value = "menuById", key = "#id")public Boolean deleteById(String id) {return this.removeById(id);}
allEntries:用来指定是否删除整个缓存(value 指定的),默认是false
/*** 清除分区category2内所有数据*/@CacheEvict(value = "category2", allEntries = true)@GetMapping("/deleteCache3")public void deleteCache3() {}
beforeInvocation:清除操作默认是在对应方法成功执行之后触发的,即方法如果因为抛出异常而未能成功返回时也不会触发清除操作。使用beforeInvocation可以改变触发清除操作的时间,当我们指定该属性值为true时,Spring会在调用该方法之前清除缓存中的指定元素。
@CacheEvict(value="users", beforeInvocation=true)public void delete(Integer id) {System.out.println("delete user by id: " + id);}
2.2.3 @CachePut
当需要在不影响方法执行的情况下更新缓存时,可以使用 @CachePut,也就是说,被 @CachePut 注解的缓存方法总是会执行,而且会尝试将结果放入缓存(当然,是否真的会缓存还跟一些注解参数有关,比如:unless 参数)。@CachePut 跟 @Cacheable 有相同的参数属性(但是没有 sync 属性)。@CachePut 更加适合于缓存填充,而不是方法执行流的优化。
其参数和@Cacheable基本相同,只是没有sync属性,以下阐述下它们的区别。@Cacheable 的逻辑是:查找缓存 -有就返回,没有就执行方法体 - 将结果缓存起来;@CachePut 的逻辑是:执行方法体 - 将结果缓存起来。所以 @Cacheable 适用于查询数据的方法,@CachePut 适用于更新数据的方法。@Override@CachePut(value = "menuById", key = "#menu.id")public Menu ReviseById(Menu menu) {this.updateById(menu);return menu;}
2.2.4 @Caching
可以使用多个注解
/*** 组合注解*/@Caching(cacheable = {@Cacheable(value = "emp", key = "#lastName")},put = {//Put一定是在执行方法之后调用,只要一个方法标了@CachePut,那么每次执行查询都会直接去查数据库,然后再将结果插入到缓存中,但是下次在用id查询的时候就不需要查询数据库了,直接从缓存中lookup->get(key)@CachePut(value = "emp", key = "#result.id"),@CachePut(value = "emp", key = "#result.email")})public Employee getByLastName(String lastName) {Employee byLastName = employeeMapper.getByLastName(lastName);System.out.println("查询员工: "+lastName);return byLastName;}
2.2.5 @CacheConfig
有时候一个类中可能会有多个缓存操作,这些操作可能是重复的,这个时候可以使用@CacheConfig ```java // 这里都是使用相同的value,所以可以统一命名 cacheNames = “emp”
@Service @CacheConfig(cacheNames = “emp”) public class EmployeeService {
@Caching( cacheable = { @Cacheable(/value = “emp”,/ key = “#lastName”) }, put = { //Put一定是在执行方法之后调用,只要一个方法标了@CachePut,那么每次执行查 询都会直接去查数据库,然后再将结果插入到缓存中,但是下次在用id查询的时候就不需要查询数据库了,直接从缓存中lookup->get(key) @CachePut(/value = “emp”,/ key = “#result.id”), @CachePut(/value = “emp”,/ key = “#result.email”) } ) public Employee getByLastName(String lastName) { Employee byLastName = employeeMapper.getByLastName(lastName); System.out.println(“查询员工: “+lastName); return byLastName; } ```
2.3 原理
CacheAutoConfiguration -> RedisCacheConfiguration -> 自动配置了RedisCacheManage ->初始化所有缓存->每个缓存决定使用什么配置-> 如果redisCacheConfiguration 有就自己用,没有就用默认配置 -> 想改缓存的配置,只需要给容器中放一个RedisCacheConfiguration即可-> 就会应用到当前RedisCacheManager管理的所有缓存分区中。

