分析开始
以官网的例子,来分析vuex的源码,首先从引入开始。
import Vue from 'vue'import Vuex from 'vuex'Vue.use(Vuex)const store = new Vuex.Store({state: {count: 0},mutations: {increment (state) {state.count++}}})
以上用的是标准的Vue 插件模式,所以很容易推测Vuex会有一个install的值,下面就是对vuex源码的具体解析,vuex源码地址 链接。
vuex/src/index.js 文件如下,他导出了我们熟悉的Store, install, mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions。
import { Store, install } from './store'import { mapState, mapMutations, mapGetters, mapActions, createNamespacedHelpers } from './helpers'import createLogger from './plugins/logger'export default {Store,install,version: '__VERSION__',mapState,mapMutations,mapGetters,mapActions,createNamespacedHelpers,createLogger}export {Store,install,mapState,mapMutations,mapGetters,mapActions,createNamespacedHelpers,createLogger}
install
我们先从导出的install函数看起(下面提到的Vue只是一个变量,不是我们引入的vue)
vue/src/store.js 该文件重要的只有两句话(直接忽略掉__DEV相关的判断,看主干内容)
- (14)将传入的
_vue赋值给Vue参数 - (15)
applyMixin(Vue)给Vue Mixin一些内容(继续后面内容) ```javascript let Vue
// … … 展示省略中间的很多内容,只保留当前相关的内容
export function install (Vue) { if (Vue && Vue === Vue) { if (__DEV) { console.error( ‘[vuex] already installed. Vue.use(Vuex) should be called only once.’ ) } return } Vue = _Vue applyMixin(Vue) }
**vuex/src/mixins.js**(上面提到的applyMixin函数)下面代码可以看出,vuex针对不同的vue版本进行了处理:- vue的版本≥2时(4-5),是通过mixin混入beforeCreate钩子,将vuex初始化进来的- vue的版本<2时(9-14),是透过Vue的原型链,将vuex初始化进来的```javascriptexport default function (Vue) {const version = Number(Vue.version.split('.')[0])if (version >= 2) {Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate: vuexInit })} else {// override init and inject vuex init procedure// for 1.x backwards compatibility.const _init = Vue.prototype._initVue.prototype._init = function (options = {}) {options.init = options.init? [vuexInit].concat(options.init): vuexInit_init.call(this, options)}}
具体我们也可以看到(9-11),我们是将options.store挂到了vue实例的this.$store身上。
/*** Vuex init hook, injected into each instances init hooks list.*/function vuexInit () {const options = this.$options// store injectionif (options.store) {this.$store = typeof options.store === 'function'? options.store(): options.store} else if (options.parent && options.parent.$store) {this.$store = options.parent.$store}}}
所以在实例化vue的时候,我们会把之前定义的store作为参数引入进来(即options.store),所以在vue初始化的时候,vuex也就通过插件模式融入进vue实例了。
new Vue({el: '#app',store: store,})
Store
接下来我们主要研究下vuex内部的一些处理机制。
先从我们对store的初始化开始,最开始官网的例子,我们通过new Vuex.Store实例化了一个根store。
const store = new Vuex.Store({state: {count: 0},mutations: {increment (state) {state.count++}}})
紧接着就是进入vuex/src/store.js内看一下new实例时,都做了一些什么。
内容非常多,我们同样是看主干内容,在构造函数(constructor)中:
(8-9)首先检查Vue(此处是自己定义的变量Vue)是否存在,如果Vue变量为“空”,且window对象中有引入Vue(此处的为window.Vue)时,就会通过插件模式将vuex初始化的内容挂载到
beforeCreate钩子上(上一章的内容install)。(24-33)初始化了一些store内的参数
- (29)
**this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options)**实例化了modules(请 先 看 下一章ModuleCollection),此处其实就是初始化了各个模块(根模块、子模块) - (32)
this._watcherVM为一个实例化的Vue
- (29)
(38-43)初始化了
dispatch和commit函数(53)
**installModule(this, state, [], this._modules.root)**(重点,详见后面)(57)
**resetStoreVM(this, state)**(重点,详见后面)(60)
plugins.forEach(plugin => plugin(this))执行 options.plugins里的内容(此例子中plugins为空,先不管)- (62-65)与devTool有关,暂时忽略(不是重点) ```javascript let Vue
export class Store {
constructor (options = {}) {
// Auto install if it is not done yet and window has Vue.
// To allow users to avoid auto-installation in some cases,
// this code should be placed here. See #731
if (!Vue && typeof window !== ‘undefined’ && window.Vue) {
install(window.Vue)
}
if (__DEV__) {assert(Vue, `must call Vue.use(Vuex) before creating a store instance.`)assert(typeof Promise !== 'undefined', `vuex requires a Promise polyfill in this browser.`)assert(this instanceof Store, `store must be called with the new operator.`)}const {plugins = [],strict = false} = options// store internal statethis._committing = falsethis._actions = Object.create(null)this._actionSubscribers = []this._mutations = Object.create(null)this._wrappedGetters = Object.create(null)this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options)this._modulesNamespaceMap = Object.create(null)this._subscribers = []this._watcherVM = new Vue()this._makeLocalGettersCache = Object.create(null)// bind commit and dispatch to selfconst store = thisconst { dispatch, commit } = thisthis.dispatch = function boundDispatch (type, payload) {return dispatch.call(store, type, payload)}this.commit = function boundCommit (type, payload, options) {return commit.call(store, type, payload, options)}// strict modethis.strict = strictconst state = this._modules.root.state// init root module.// this also recursively registers all sub-modules// and collects all module getters inside this._wrappedGettersinstallModule(this, state, [], this._modules.root)// initialize the store vm, which is responsible for the reactivity// (also registers _wrappedGetters as computed properties)resetStoreVM(this, state)// apply pluginsplugins.forEach(plugin => plugin(this))const useDevtools = options.devtools !== undefined ? options.devtools : Vue.config.devtoolsif (useDevtools) {devtoolPlugin(this)}
}
// … … 展示省略中间的很多内容,只保留当前相关的内容 }
<a name="rC82j"></a>## installModule如函数名所言,此处是对各个模块的“安装”、“设置”,我们把上面的主要相关的代码拿下来分析:```javascriptconst state = this._modules.root.stateinstallModule(this, state, [], this._modules.root)
- 首先得到state的值 (我们在Module章节已经分析过了 为
{count: 0 }) - 我们将例子中的参数带进去看后,如下
vuex/src/store.jsinstallModule(this, // 第一个参数,对应下面的 store{ count: 0 }, // 第二个参数,对应下面的 rootState[], // 第三个参数,对应下面的 pathmodule类实例 // 第四个参数,对应下面的 module)
- (2)
isRoot用来判断是否为根模块(此例子![].length = true,isRoot为true) - (3)获取当前模块的命名空间值
namespace,此处为根模块,所以命名空间值为''(初始值)。 - (6-11)如果当前模块存在命名空间,则在store的_modulesNamespaceMap中以key-value的形式记录下来
- (14-27)主要是为非根模块设置state值(暂时忽略)
(29-49)这里就是重头戏了,为模块注册mutation,action,getter和组装子模块的内容(继续往下看即可)
function installModule (store, rootState, path, module, hot) {const isRoot = !path.lengthconst namespace = store._modules.getNamespace(path)// register in namespace mapif (module.namespaced) {if (store._modulesNamespaceMap[namespace] && __DEV__) {console.error(`[vuex] duplicate namespace ${namespace} for the namespaced module ${path.join('/')}`)}store._modulesNamespaceMap[namespace] = module}// set stateif (!isRoot && !hot) {const parentState = getNestedState(rootState, path.slice(0, -1))const moduleName = path[path.length - 1]store._withCommit(() => {if (__DEV__) {if (moduleName in parentState) {console.warn(`[vuex] state field "${moduleName}" was overridden by a module with the same name at "${path.join('.')}"`)}}Vue.set(parentState, moduleName, module.state)})}const local = module.context = makeLocalContext(store, namespace, path)module.forEachMutation((mutation, key) => {const namespacedType = namespace + keyregisterMutation(store, namespacedType, mutation, local)})module.forEachAction((action, key) => {const type = action.root ? key : namespace + keyconst handler = action.handler || actionregisterAction(store, type, handler, local)})module.forEachGetter((getter, key) => {const namespacedType = namespace + keyregisterGetter(store, namespacedType, getter, local)})module.forEachChild((child, key) => {installModule(store, rootState, path.concat(key), child, hot)})}
local
我们看看local是什么?
const local = module.context = makeLocalContext(store, namespace, path)
从代码里看,这里的
local是一个包含dispatch、commit、getters和state这些键的key-value对象。
vue/src/store.js
由于我们是根模块,noNamespace为true,所以我们只考虑true的情况,所以这里获取到的local对象的dispatch、commit、getters、state的值都为store对应的值,所以local.state= { count: 0 }
function makeLocalContext (store, namespace, path) {const noNamespace = namespace === ''const local = {dispatch: noNamespace ? store.dispatch : (_type, _payload, _options) => {// ... ... 展示省略中间的很多内容,只保留当前相关的内容},commit: noNamespace ? store.commit : (_type, _payload, _options) => {// ... ... 展示省略中间的很多内容,只保留当前相关的内容}}// getters and state object must be gotten lazily// because they will be changed by vm updateObject.defineProperties(local, {getters: {get: noNamespace? () => store.getters: () => makeLocalGetters(store, namespace)},state: {get: () => getNestedState(store.state, path)}})return local}
registerMutation
由于我们的例子只有mutation,后面我就先深入module.forEachMutation来叙述:
module.forEachMutation((mutation, key) => {const namespacedType = namespace + keyregisterMutation(store, namespacedType, mutation, local)})
先看module.forEachMutation,此处的module是之前提到的module类的实例,forEachMutation参数中的fn则对应此处的 (mutation, key)=>{const namespacedType = namespace + key ... }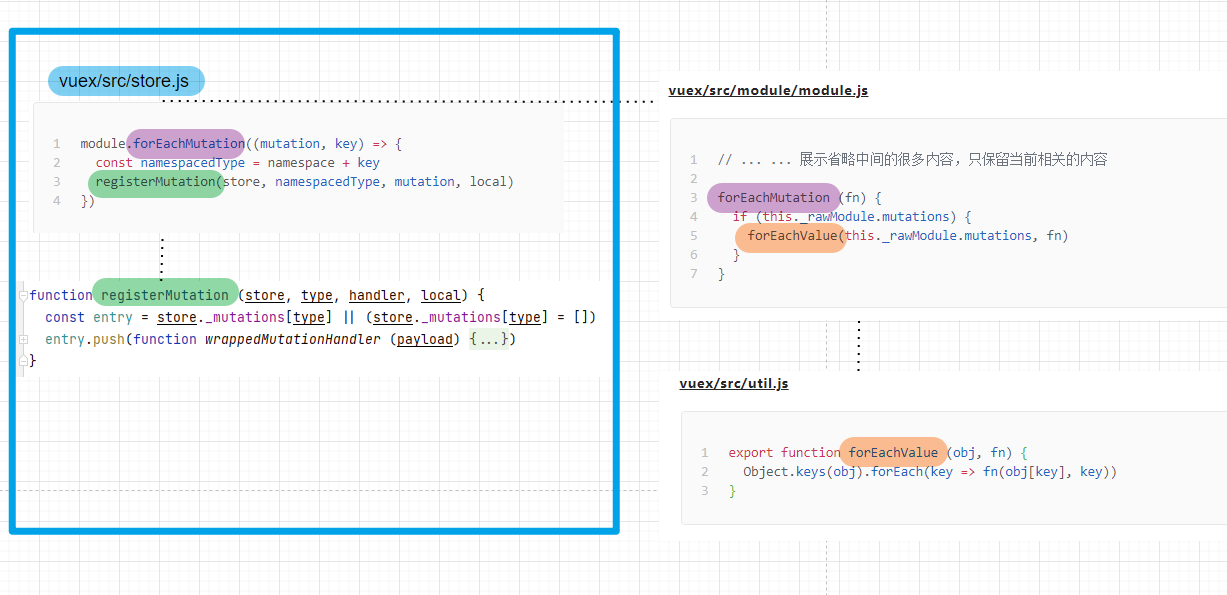
将所有参数带进去后,内容如下
- 根据(24-33)我们可以看出
store._mutations是一个对象,他会按(8)forEach的index值,初始化一个array数组,然后把对应的mutation封装在函数wrappedMutationHandler内后push进去。
vue/src/store.js
forEachMutation () {const mutations = {increment: function (state) { state.count++ }}Object.keys(mutations).forEach((key) => {(mutations[key], index) => {const namespacedType = namespace + index(store, namespacedType, mutation=mutations[key], local)=>{const entry = store._mutations[namespacedType] || (store._mutations[namespacedType] = [])entry.push(function wrappedMutationHandler (payload) {mutation.call(store, local.state, payload)})}()}})}/*(10-17)带入参数后如下const namespacedType = '0'const entry = store._mutations[namespacedType] = []entry.push(function wrappedMutationHandler (payload) {mutations['increment'].call(store, local.state, payload)})*/
即最后store._mutations的值为:
store._mutations = {0: [function wrappedMutationHandler (payload) {mutations['increment'].call(store, local.state, payload)})],}
registerGetter(待完善)
vue/src/store.js
function registerAction (store, type, handler, local) {const entry = store._actions[type] || (store._actions[type] = [])entry.push(function wrappedActionHandler (payload) {let res = handler.call(store, {dispatch: local.dispatch,commit: local.commit,getters: local.getters,state: local.state,rootGetters: store.getters,rootState: store.state}, payload)if (!isPromise(res)) {res = Promise.resolve(res)}if (store._devtoolHook) {return res.catch(err => {store._devtoolHook.emit('vuex:error', err)throw err})} else {return res}})}
registerAction(待完善)
vue/src/store.js
function registerGetter (store, type, rawGetter, local) {if (store._wrappedGetters[type]) {if (__DEV__) {console.error(`[vuex] duplicate getter key: ${type}`)}return}store._wrappedGetters[type] = function wrappedGetter (store) {return rawGetter(local.state, // local statelocal.getters, // local gettersstore.state, // root statestore.getters // root getters)}}
resetStoreVM
上面的步骤中我们已经将module初始化完成,并且组装好了module(根模块和子模块)和其内的getters、mutations和actions,接下来我们看看resetStoreVM都做了些什么。
resetStoreVM(this, state)
vue/src/store.js
function resetStoreVM (store, state, hot) {const oldVm = store._vm// bind store public gettersstore.getters = {}// reset local getters cachestore._makeLocalGettersCache = Object.create(null)const wrappedGetters = store._wrappedGettersconst computed = {}forEachValue(wrappedGetters, (fn, key) => {// use computed to leverage its lazy-caching mechanism// direct inline function use will lead to closure preserving oldVm.// using partial to return function with only arguments preserved in closure environment.computed[key] = partial(fn, store)Object.defineProperty(store.getters, key, {get: () => store._vm[key],enumerable: true // for local getters})})// use a Vue instance to store the state tree// suppress warnings just in case the user has added// some funky global mixinsconst silent = Vue.config.silentVue.config.silent = truestore._vm = new Vue({data: {$$state: state},computed})Vue.config.silent = silent// enable strict mode for new vmif (store.strict) {enableStrictMode(store)}if (oldVm) {if (hot) {// dispatch changes in all subscribed watchers// to force getter re-evaluation for hot reloading.store._withCommit(() => {oldVm._data.$$state = null})}Vue.nextTick(() => oldVm.$destroy())}}
ModuleCollection
在实例化store的时候,我们注意到store中的_this.modules是ModuleCollection的实例化,通过名字我们很容易猜测到这里和模块有什么关系,也许模块、命名空间相关的内容我们都可以在这里找到。
this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options)
主要内容
- 实例化的第一步自然是走constrcutor的过程,这里执行了(4)
this.register([], rawRootModule, false) 深入到(15-34)的register函数,我们可以把参数具体化了看
this.register([], // 第一个参数,对应下面的path{ // 第二个参数,对应下面的rawModulestate: {count: 0},mutations: {increment (state) {state.count++}}}, // 即后面的rawModule对象false // 第三个参数,对应下面的runtime)
(20)
const newModule = new Module(rawModule, true)这里是将Module实例化了,这里涉及到了Module类(后面有图解ModuleCollection和Module的关系图)- (21)满足条件
[].length === 0所以当前module-collection实例(也就是上面的this._modules)的root值就为这里的newModule了 - (29-33)由于官方的例子没有子模块(即没有rawModule.modules),所以这里的内容就可以忽略了,其实这里就是注册(遍历)子模块,过程与根模块类似。
vuex/src/module/module-collection.js
export default class ModuleCollection {constructor (rawRootModule) {// register root module (Vuex.Store options)this.register([], rawRootModule, false)}get (path) {return path.reduce((module, key) => {return module.getChild(key)}, this.root)}// ... ... 展示省略中间的很多内容,只保留当前相关的内容register (path, rawModule, runtime = true) {if (__DEV__) {assertRawModule(path, rawModule)}const newModule = new Module(rawModule, runtime)if (path.length === 0) {this.root = newModule} else {const parent = this.get(path.slice(0, -1))parent.addChild(path[path.length - 1], newModule)}// register nested modulesif (rawModule.modules) {forEachValue(rawModule.modules, (rawChildModule, key) => {this.register(path.concat(key), rawChildModule, runtime)})}}// ... ... 展示省略中间的很多内容,只保留当前相关的内容}
获取命名空间值
vuex/src/module/module-collection.js
getNamespace (path) {let module = this.rootreturn path.reduce((namespace, key) => {module = module.getChild(key)return namespace + (module.namespaced ? key + '/' : '')}, '')}
Module
这里用图片表示一下ModuleCollection和Module的联系: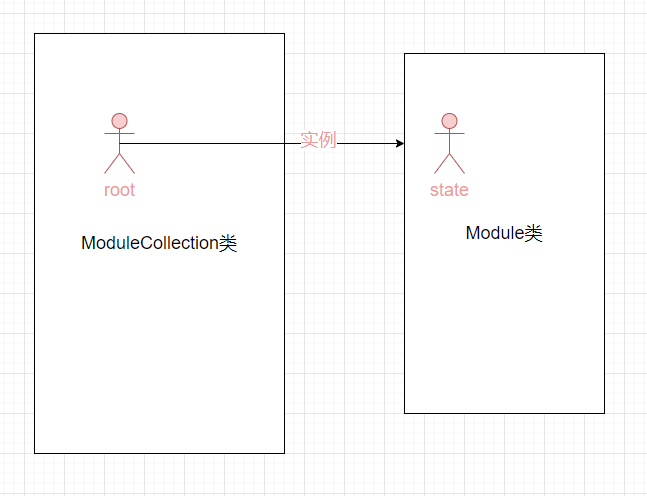
/*此处传递的 rawModule 值为{state: {count: 0},mutations: {increment (state) {state.count++}}}*/const newModule = new Module(rawModule, runtime)
vuex/src/module/module.js 如下,
- (11)所以此处newModule.state的值为
{count: 0 } - (10)
this._rawModule的值为{ state: {count: 0}, mutation: {...} }```javascript import { forEachValue } from ‘../util’
// Base data struct for store’s module, package with some attribute and method export default class Module { constructor (rawModule, runtime) { this.runtime = runtime // Store some children item this._children = Object.create(null) // Store the origin module object which passed by programmer this._rawModule = rawModule const rawState = rawModule.state
// Store the origin module's statethis.state = (typeof rawState === 'function' ? rawState() : rawState) || {}
}
// … … 展示省略中间的很多内容,只保留当前相关的内容
}
```

