微服务三要素:业务建模、技术组件和研发过程
- 业务建模
针对服务建模,首先需要明确服务类别,以及服务与业务之间的关系,尽可能的明确领域的边界;针对服务建模,使用领域驱动设计方法(DDD),通过识别领域中各个子域、判断这些子域是否独立、考虑子域与子域的交互关系,从而明确各个界限上下文之间的边界。在业界对于领域的划分:核心子域、支撑子域和通用子域三种类型,其中系统中的
- 技术组件
- 研发过程
注册中心(Eureka)
Eureka服务器端(服务注册服务端)
对于注册中心服务器而言,服务注册、续约、取消和剔除等不同的操作所执行的工作流程基本一致,即都是对服务存储的操作,并把这一操作同步到其他Eureka节点。
单机注册中心的注册调用类 AbstractInstanceRegistry.class
/*** Registers a new instance with a given duration.* 在一定时间内注册一个新实例* @see com.netflix.eureka.lease.LeaseManager#register(java.lang.Object, int, boolean)*/public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) {try {read.lock();//从已存储的registry获取一个服务定义Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(registrant.getAppName());REGISTER.increment(isReplication);if (gMap == null) {//初始化一个ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>,并放入registry中final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gNewMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>();gMap = registry.putIfAbsent(registrant.getAppName(), gNewMap);if (gMap == null) {gMap = gNewMap;}}//根据当前注册的ID找到对应的LeaseLease<InstanceInfo> existingLease = gMap.get(registrant.getId());// Retain the last dirty timestamp without overwriting it, if there is already a lease//如果Lease能找到,根据当前节点的最新更新时间和注册节点的最新更新时间比较,如果前者的时间//晚于后者的时间,那么注册实例就以存在的实例为准if (existingLease != null && (existingLease.getHolder() != null)) {Long existingLastDirtyTimestamp = existingLease.getHolder().getLastDirtyTimestamp();Long registrationLastDirtyTimestamp = registrant.getLastDirtyTimestamp();logger.debug("Existing lease found (existing={}, provided={}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp);// this is a > instead of a >= because if the timestamps are equal, we still take the remote transmitted// InstanceInfo instead of the server local copy.if (existingLastDirtyTimestamp > registrationLastDirtyTimestamp) {logger.warn("There is an existing lease and the existing lease's dirty timestamp {} is greater" +" than the one that is being registered {}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp);logger.warn("Using the existing instanceInfo instead of the new instanceInfo as the registrant");registrant = existingLease.getHolder();}} else {// The lease does not exist and hence it is a new registration//如果找不到,代表是一个新注册,则更新其每分钟期望得续约数量及其阈值synchronized (lock) {if (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews > 0) {// Since the client wants to register it, increase the number of clients sending renewsthis.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews + 1;updateRenewsPerMinThreshold();}}logger.debug("No previous lease information found; it is new registration");}//创建一个新的Lease并放入Map中Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = new Lease<InstanceInfo>(registrant, leaseDuration);if (existingLease != null) {lease.setServiceUpTimestamp(existingLease.getServiceUpTimestamp());}gMap.put(registrant.getId(), lease);synchronized (recentRegisteredQueue) {recentRegisteredQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>(System.currentTimeMillis(),registrant.getAppName() + "(" + registrant.getId() + ")"));}// This is where the initial state transfer of overridden status happensif (!InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN.equals(registrant.getOverriddenStatus())) {logger.debug("Found overridden status {} for instance {}. Checking to see if needs to be add to the "+ "overrides", registrant.getOverriddenStatus(), registrant.getId());if (!overriddenInstanceStatusMap.containsKey(registrant.getId())) {logger.info("Not found overridden id {} and hence adding it", registrant.getId());overriddenInstanceStatusMap.put(registrant.getId(), registrant.getOverriddenStatus());}}InstanceStatus overriddenStatusFromMap = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.get(registrant.getId());if (overriddenStatusFromMap != null) {logger.info("Storing overridden status {} from map", overriddenStatusFromMap);registrant.setOverriddenStatus(overriddenStatusFromMap);}// Set the status based on the overridden status rulesInstanceStatus overriddenInstanceStatus = getOverriddenInstanceStatus(registrant, existingLease, isReplication);registrant.setStatusWithoutDirty(overriddenInstanceStatus);// If the lease is registered with UP status, set lease service up timestampif (InstanceStatus.UP.equals(registrant.getStatus())) {lease.serviceUp();}//处理服务的InstanceStatusregistrant.setActionType(ActionType.ADDED);recentlyChangedQueue.add(new RecentlyChangedItem(lease));//更新服务最新 更新时间registrant.setLastUpdatedTimestamp();//刷新缓存invalidateCache(registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getVIPAddress(), registrant.getSecureVipAddress());logger.info("Registered instance {}/{} with status {} (replication={})",registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getId(), registrant.getStatus(), isReplication);} finally {read.unlock();}}
在注册集群下,使用的注册类为PeerAwareInstanceRegistry.class
//继承了注册类通用接口,public interface PeerAwareInstanceRegistry extends InstanceRegistry {void init(PeerEurekaNodes peerEurekaNodes) throws Exception;/*** Populates the registry information from a peer eureka node. This* operation fails over to other nodes until the list is exhausted if the* communication fails.*/int syncUp();/*** Checks to see if the registry access is allowed or the server is in a* situation where it does not all getting registry information. The server* does not return registry information for a period specified in* {@link com.netflix.eureka.EurekaServerConfig#getWaitTimeInMsWhenSyncEmpty()}, if it cannot* get the registry information from the peer eureka nodes at start up.** @return false - if the instances count from a replica transfer returned* zero and if the wait time has not elapsed, otherwise returns true*/boolean shouldAllowAccess(boolean remoteRegionRequired);//在注册集群下,使用的注册方法void register(InstanceInfo info, boolean isReplication);void statusUpdate(final String asgName, final ASGResource.ASGStatus newStatus, final boolean isReplication);}
/*** Registers the information about the {@link InstanceInfo} and replicates* this information to all peer eureka nodes. If this is replication event* from other replica nodes then it is not replicated.** @param info* the {@link InstanceInfo} to be registered and replicated.* @param isReplication* true if this is a replication event from other replica nodes,* false otherwise.*/@Overridepublic void register(final InstanceInfo info, final boolean isReplication) {int leaseDuration = Lease.DEFAULT_DURATION_IN_SECS;if (info.getLeaseInfo() != null && info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs() > 0) {leaseDuration = info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs();}super.register(info, leaseDuration, isReplication);//注册中心集群节点间注册信息同步replicateToPeers(Action.Register, info.getAppName(), info.getId(), info, null, isReplication);}/*** Replicates all eureka actions to peer eureka nodes except for replication* traffic to this node.* 节点间进行同步*/private void replicateToPeers(Action action, String appName, String id,InstanceInfo info /* optional */,InstanceStatus newStatus /* optional */, boolean isReplication) {Stopwatch tracer = action.getTimer().start();try {if (isReplication) {numberOfReplicationsLastMin.increment();}// If it is a replication already, do not replicate again as this will create a poison replicationif (peerEurekaNodes == Collections.EMPTY_LIST || isReplication) {return;}for (final PeerEurekaNode node : peerEurekaNodes.getPeerEurekaNodes()) {// If the url represents this host, do not replicate to yourself.if (peerEurekaNodes.isThisMyUrl(node.getServiceUrl())) {continue;}replicateInstanceActionsToPeers(action, appName, id, info, newStatus, node);}} finally {tracer.stop();}}
Eureka的设计与实现上的技巧,也就是high level api 和low level api,如下图所示: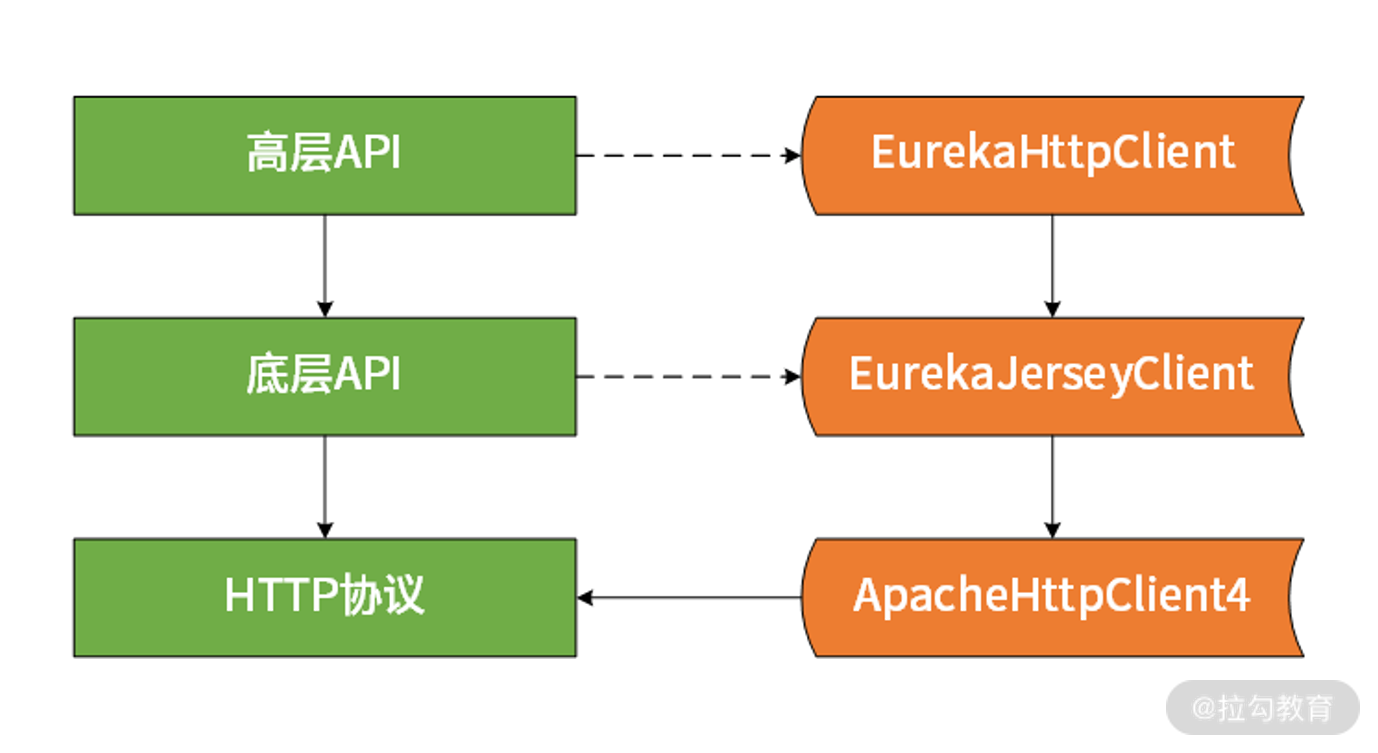
针对high level api,主要是通过装饰器模式进行一系列包装,从而创建目标EurekaHttpClient。关于low level api的话,主要是HTTP远程调用的实现,Netflix提供的是基于Jersey的版本,而Spring Cloud则是提供了基于RestTemplate的版本。
服务消费者操作源码解析
对于Eureka而言,作为客户端组件的DiscoveryClient同样具备这种缓存功能。
Eureka客户端通过定时任务完成缓存刷新操作,在DiscoveryClient中的initScheduledTasks方法用于初始化各种调度任务,对于缓存刷新,调度器的初始化过程如下:
/*** Initializes all scheduled tasks.*/private void initScheduledTasks() {if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) {// registry cache refresh timerint registryFetchIntervalSeconds = clientConfig.getRegistryFetchIntervalSeconds();int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();scheduler.schedule(new TimedSupervisorTask("cacheRefresh",scheduler,cacheRefreshExecutor,registryFetchIntervalSeconds,TimeUnit.SECONDS,expBackOffBound,new CacheRefreshThread()),registryFetchIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);}if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) {int renewalIntervalInSecs = instanceInfo.getLeaseInfo().getRenewalIntervalInSecs();int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();logger.info("Starting heartbeat executor: " + "renew interval is: {}", renewalIntervalInSecs);// Heartbeat timerscheduler.schedule(new TimedSupervisorTask("heartbeat",scheduler,heartbeatExecutor,renewalIntervalInSecs,TimeUnit.SECONDS,expBackOffBound,new HeartbeatThread()),renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS);// InstanceInfo replicatorinstanceInfoReplicator = new InstanceInfoReplicator(this,instanceInfo,clientConfig.getInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds(),2); // burstSizestatusChangeListener = new ApplicationInfoManager.StatusChangeListener() {@Overridepublic String getId() {return "statusChangeListener";}@Overridepublic void notify(StatusChangeEvent statusChangeEvent) {if (InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getStatus() ||InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getPreviousStatus()) {// log at warn level if DOWN was involvedlogger.warn("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent);} else {logger.info("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent);}instanceInfoReplicator.onDemandUpdate();}};if (clientConfig.shouldOnDemandUpdateStatusChange()) {applicationInfoManager.registerStatusChangeListener(statusChangeListener);}instanceInfoReplicator.start(clientConfig.getInitialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds());} else {logger.info("Not registering with Eureka server per configuration");}}
显然,这里启动了一个调度任务并通过CacheRefreshThread线程完成具体操作,CacheRefreshThread线程定义如下:
/*** The task that fetches the registry information at specified intervals.**/class CacheRefreshThread implements Runnable {public void run() {refreshRegistry();}}
对于服务消费者,最重要的操作是获取服务注册信息。在这里的refreshRegistry方法中,在进行一系列的校验后,最终调用fetchRegistry方法完成注册信息更新,该方法代码如下:
/*** Fetches the registry information.** <p>* This method tries to get only deltas after the first fetch unless there* is an issue in reconciling eureka server and client registry information.* </p>** @param forceFullRegistryFetch Forces a full registry fetch.** @return true if the registry was fetched*/private boolean fetchRegistry(boolean forceFullRegistryFetch) {Stopwatch tracer = FETCH_REGISTRY_TIMER.start();try {// If the delta is disabled or if it is the first time, get all// applications 获取应用Applications applications = getApplications();//如果满足全部条件,则会全量拉取服务实例数据if (clientConfig.shouldDisableDelta()|| (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress()))|| forceFullRegistryFetch|| (applications == null)|| (applications.getRegisteredApplications().size() == 0)|| (applications.getVersion() == -1)) //Client application does not have latest library supporting delta{logger.info("Disable delta property : {}", clientConfig.shouldDisableDelta());logger.info("Single vip registry refresh property : {}", clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress());logger.info("Force full registry fetch : {}", forceFullRegistryFetch);logger.info("Application is null : {}", (applications == null));logger.info("Registered Applications size is zero : {}",(applications.getRegisteredApplications().size() == 0));logger.info("Application version is -1: {}", (applications.getVersion() == -1));getAndStoreFullRegistry();} else {//增量拉取服务实例数据getAndUpdateDelta(applications);}//重新计算和设置一致性hashcodeapplications.setAppsHashCode(applications.getReconcileHashCode());logTotalInstances();} catch (Throwable e) {logger.error(PREFIX + "{} - was unable to refresh its cache! status = {}", appPathIdentifier, e.getMessage(), e);return false;} finally {if (tracer != null) {tracer.stop();}}// Notify about cache refresh before updating the instance remote status//刷新本地缓存onCacheRefreshed();// Update remote status based on refreshed data held in the cache//更新远程服务实例运行状态updateInstanceRemoteStatus();// registry was fetched successfully, so return truereturn true;}
全量更新方法如下:
/*** Gets the full registry information from the eureka server and stores it locally.* When applying the full registry, the following flow is observed:** if (update generation have not advanced (due to another thread))* atomically set the registry to the new registry* fi** @return the full registry information.* @throws Throwable* on error.*/private void getAndStoreFullRegistry() throws Throwable {long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get();logger.info("Getting all instance registry info from the eureka server");Applications apps = null;EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress() == null? eurekaTransport.queryClient.getApplications(remoteRegionsRef.get()): eurekaTransport.queryClient.getVip(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress(), remoteRegionsRef.get());if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode()) {apps = httpResponse.getEntity();}logger.info("The response status is {}", httpResponse.getStatusCode());if (apps == null) {logger.error("The application is null for some reason. Not storing this information");} else if (fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1)) {localRegionApps.set(this.filterAndShuffle(apps));logger.debug("Got full registry with apps hashcode {}", apps.getAppsHashCode());} else {logger.warn("Not updating applications as another thread is updating it already");}}
以下我们重点介绍一下getAndUpdateDelta()方法,重点学习一下eureka中如何实现增量数据更新的设计技巧,方法代码如下:
/*** Get the delta registry information from the eureka server and update it locally.* When applying the delta, the following flow is observed:** if (update generation have not advanced (due to another thread))* atomically try to: update application with the delta and get reconcileHashCode* abort entire processing otherwise* do reconciliation if reconcileHashCode clash* fi** @return the client response* @throws Throwable on error*/private void getAndUpdateDelta(Applications applications) throws Throwable {long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get();Applications delta = null;//通过eurekaTransport.queryClient获取增量信息EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = eurekaTransport.queryClient.getDelta(remoteRegionsRef.get());if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode()) {delta = httpResponse.getEntity();}if (delta == null) {logger.warn("The server does not allow the delta revision to be applied because it is not safe. "+ "Hence got the full registry.");//如果增量信息为空,就直接发起一次全量更新getAndStoreFullRegistry();} else if (fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1)) {logger.debug("Got delta update with apps hashcode {}", delta.getAppsHashCode());String reconcileHashCode = "";if (fetchRegistryUpdateLock.tryLock()) {try {//比对从服务器端返回的增量数据和本地数据,合并两者的差异数据updateDelta(delta);//用合并了增量数据之后的本地数据生成一致性hashcodereconcileHashCode = getReconcileHashCode(applications);} finally {fetchRegistryUpdateLock.unlock();}} else {logger.warn("Cannot acquire update lock, aborting getAndUpdateDelta");}// There is a diff in number of instances for some reason//比较本地数据中的hashcode和来自服务器端的hashcodeif (!reconcileHashCode.equals(delta.getAppsHashCode()) || clientConfig.shouldLogDeltaDiff()) {//如果hashcode不一致,就触发远程调用进行全量更新reconcileAndLogDifference(delta, reconcileHashCode); // this makes a remoteCall}} else {logger.warn("Not updating application delta as another thread is updating it already");logger.debug("Ignoring delta update with apps hashcode {}, as another thread is updating it already", delta.getAppsHashCode());}}
回顾Eureka服务器端基本原理,我们知道Eureka服务器端会保存一个服务注册列表缓存。Eureka官方文档提到这个数据保留时间是三分钟,而Eureka客户端的定时调度机制会每个30秒刷新本地缓存。原则上,只要Eureka客户端不停地获取服务器端的更新数据,就能保证自己的数据和Eureka服务器端保持一致。但如果客户端没有在3分钟之内没有获取更新数据,就会导致自身与服务器端的数据不一致。这就是这种更新机制所必须考虑的问题,在设计此类场景时需要注意的一个点。
对于上述产生的问题,Eureka采用了一致性hashcode方法解决。Eureka服务器端每次返回的增量数据中都会带有一个一致性hashcode,这个hashcode会与eureka客户端本地服务列表数据算出的hashcode进行对比,如果不一致则表示增量更新出了问题,这时候需要执行一次全量更新。
在eureka中,计算一致性hashcode的方法如下所示,该方法基于服务注册实例信息完成编码计算过程,最终返回一个String类型的计算结果:
private String getReconcileHashCode(Applications applications) {TreeMap<String, AtomicInteger> instanceCountMap = new TreeMap<String, AtomicInteger>();if (isFetchingRemoteRegionRegistries()) {for (Applications remoteApp : remoteRegionVsApps.values()) {remoteApp.populateInstanceCountMap(instanceCountMap);}}applications.populateInstanceCountMap(instanceCountMap);return Applications.getReconcileHashCode(instanceCountMap);}
总结
Eureka客户端缓存定时更新流程如下图所示,可以看到他与服务注册的流程基本一致,也就是说在Eureka中,服务提供者和服务消费者作为Eureka服务器的客户端采用了同一套体系完成与服务器端的交互。
**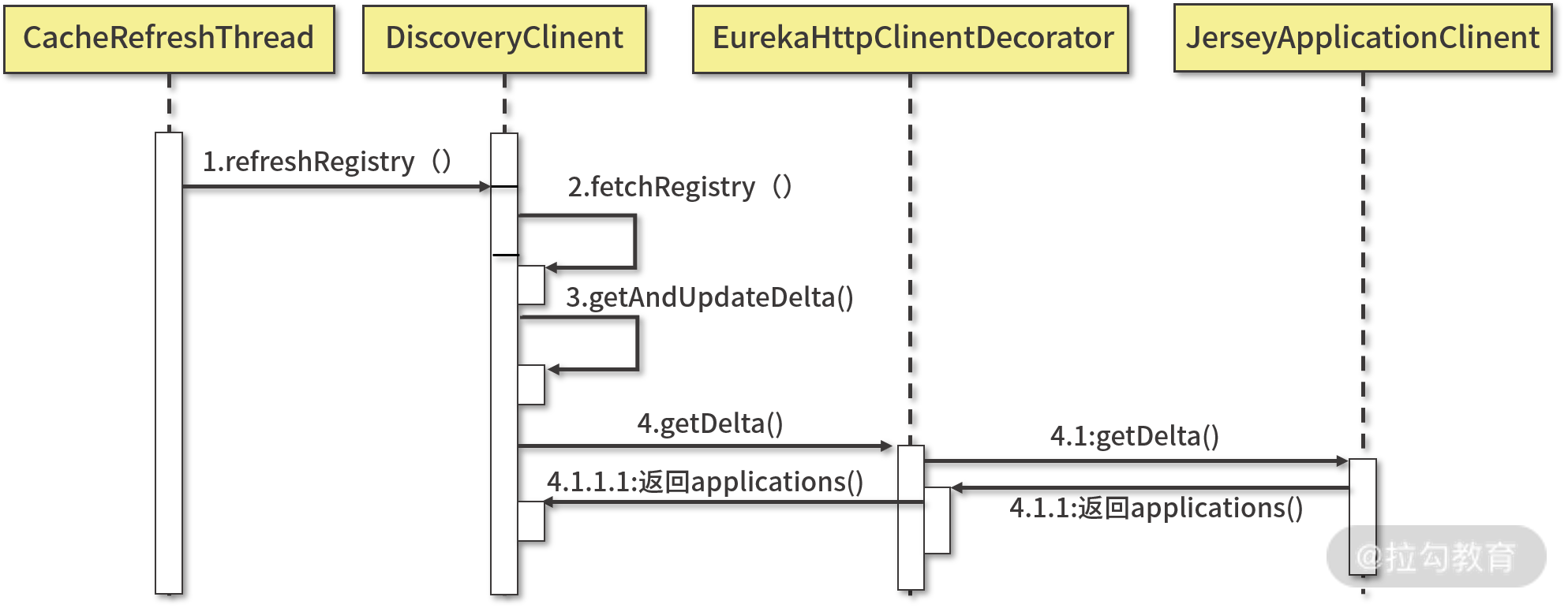
Eureka缓存刷新流程时序图
负载均衡(Ribbon)
使用Ribbon实现客户端负载均衡
Ribbon组件是客户端的一个负载均衡器,Ribbon会自动基于内置的负载均衡算法去连接服务实例,需要嵌入到服务消费者内部使用。
基于Ribbon实现负载均衡的方式主要包括两种:
- 使用@LoadBalanced注解
该注解使用于修饰发起Http请求的RestTemplate(org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate)工具类,并在该工具类中自动嵌入客户端负载均衡功能。开发人员不需要针对负载均衡做特殊开发或配置。以下是使用@LoadBalanced注解样例:
@SpringBootApplication@EnableEurekaClientpublic class InterventionApplication {@LoadBalanced@Beanpublic RestTemplate getRestTemplate(){return new RestTemplate();}public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(InterventionApplication.class, args);}}
- 使用@RibbonClient注解
开发人员使用该注解可以针对负载均衡做特殊的开发或配置,可以选择使用的负载均衡算法,@LoadBalanced注解默认使用Ribbon组件提供的轮询策略进行负载均衡。
使用@RibbonClient注解,首先需要创建一个独立的配置类,用来制定具体的负载均衡规则。
@Configurationpublic class SpringHealthLoadBalanceConfig{@AutowiredIClientConfig config;@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic IRule springHealthRule(IClientConfig config) {return new RandomRule();}}
然后在RestTemplate上使用@RibbonCient注解制定自己定义的负载均衡规则。
@SpringBootApplication@EnableEurekaClient@RibbonClient(name = "userservice", configuration = SpringHealthLoadBalanceConfig.class)public class InterventionApplication{@Bean@LoadBalancedpublic RestTemplate restTemplate(){return new RestTemplate();}public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(InterventionApplication.class, args);}}
Ribbon中负载均衡策略
Ribbon中的负载均衡策略,分为两大类,一种是静态负载均衡算法,另一种是动态负载均衡算法。
静态负载均衡算法
主要包含随机(Random)、轮询(Round Ribbon)和加权轮询(Weighted Round Ribbon)算法
动态负载均衡算法
静态的算法设计权重,就可以转化为动态算法,典型的动态算法有 IP哈希算法、最少连接数算法、服务调用时延算法等
BestAvailableRule算法
选择一个并发请求量最小的服务器,逐个考察服务器然后选择其中活跃请求数最小的服务器。
WeightedResponseTimeRule算法
根据服务器响应时间加权重,服务器响应时间与权重成反比。服务器响应时间越长,权重越小;反之,服务器响应时间越短,权重越大。响应时间的计算依赖于ILoadBalancer接口中的LoadBalancerStats。WeightedResponseTimeRule会定时从LoadBalancerStats读取平均响应时间,为每个服务更新权重。权重的计算,每次请求的响应时间减去每个服务自己平均的响应时间就是该服务的权重。
该算法核心代码如下:
class ServerWeight {ServerWeight() {}public void maintainWeights() {ILoadBalancer lb = WeightedResponseTimeRule.this.getLoadBalancer();if (lb != null) {if (WeightedResponseTimeRule.this.serverWeightAssignmentInProgress.compareAndSet(false, true)) {try {WeightedResponseTimeRule.logger.info("Weight adjusting job started");AbstractLoadBalancer nlb = (AbstractLoadBalancer)lb;//从ILoadBalancer获取LoadBalancerStatsLoadBalancerStats stats = nlb.getLoadBalancerStats();if (stats != null) {double totalResponseTime = 0.0D;ServerStats ss;for(Iterator var6 = nlb.getAllServers().iterator(); var6.hasNext(); totalResponseTime += ss.getResponseTimeAvg()) {Server server = (Server)var6.next();ss = stats.getSingleServerStat(server);}Double weightSoFar = 0.0D;List<Double> finalWeights = new ArrayList();Iterator var20 = nlb.getAllServers().iterator();while(var20.hasNext()) {Server serverx = (Server)var20.next();ServerStats ssx = stats.getSingleServerStat(serverx);//计算权重double weight = totalResponseTime - ssx.getResponseTimeAvg();weightSoFar = weightSoFar + weight;finalWeights.add(weightSoFar);}WeightedResponseTimeRule.this.setWeights(finalWeights);return;}} catch (Exception var16) {WeightedResponseTimeRule.logger.error("Error calculating server weights", var16);return;} finally {WeightedResponseTimeRule.this.serverWeightAssignmentInProgress.set(false);}}}}}
AvailabilityFilteringRule算法
通过检查LoadBalancerStats中记录的各个服务器的运行状态,过滤掉那些处于一直连接失败或处于高并发状态下的服务器。
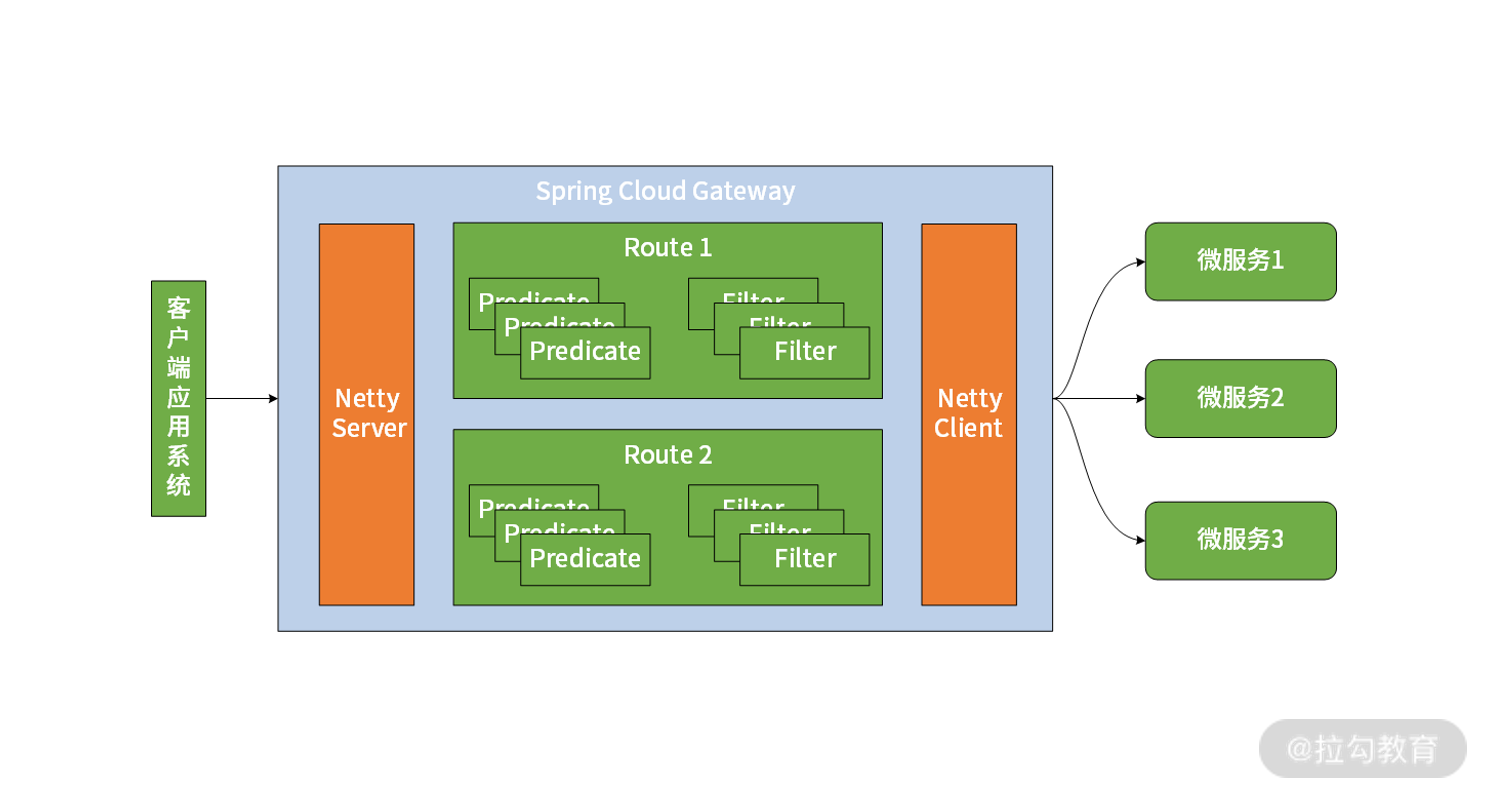
API网关
网关是Spring Cloud核心组件,在微服务架构中,API 网关起到了客户端与微服务之间的隔离作用。在Spring Cloud中,针对API网关的实现提供了两种解决方案,一种是集成Netflix中的Zuul网关,另一种是自研的Spring Cloud Gateway。
Zuul
使用Zuul如何构建一个网关
引入maven依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-zuul</artifactId></dependency>
创建启动类
@SpringBootApplication@EnableZuulProxypublic class ZuulServerApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(ZuulServerApplication.class, args);}}
如何使用Zuul实现服务路由
对于API网关,最重要的功能就是服务路由。即通过zuul网关的请求会路由并转发到对应的后端服务。
格式如下:http://zuulservice:5555/service //其中zuulservice是zuul的服务地址,service是所对应的后端服务
基于服务发现映射服务路由
Zuul可以基于服务注册中心的服务发现机制实现自动化服务路由功能。所以使用zuul实现路由服务最常见的、最推荐的做法就是利用这种自动化的路由映射关系来确定路由信息。这种方式借助注册中心,注册中心上注册的服务信息透明可见。
基于动态配置映射服务路由
这种方式对于开发人员或运维人员在系统映射上有定制化要求时使用,弥补基于服务发现映射服务路由的不足之处。
这种方式是在application.yml配置文件中设置自定义的路由名称,如下:
zuul:# 服务前缀名称prefix: /springhealthroutes:# 忽略由注册中心发现映射服务路由ignored-services: 'userservice'userservice: /user/**
基于静态配置映射服务路由
ApiGateway
- zuul与spring cloud gateway对比