| 岛屿问题 | 中等:130、1020、1254、200、695、16 | 130,1020题意大致一样,1254和200题型一样,但200默认被水包围,少一个边界判定条件。695吗6,19岛屿的面积题型一样。 |
|---|---|---|
| 困难:827、778、417、934、749 | ||
| 地图问题 | 中等:offer13.offer12 | 12寻找单词, |
中等
剑指 Offer 13. 机器人的运动范围
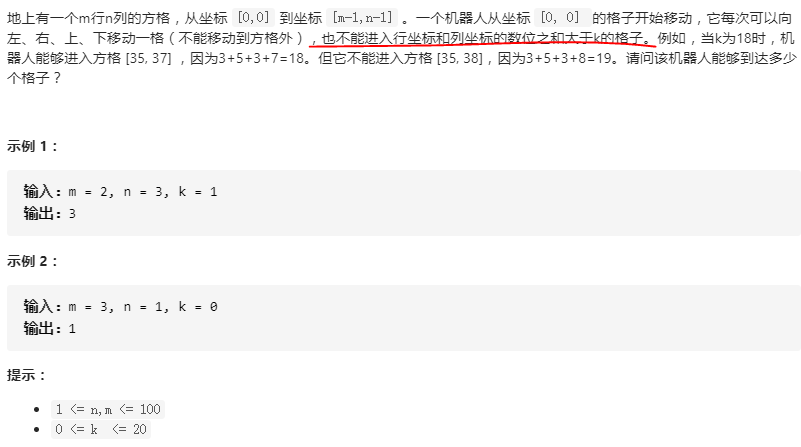
思路:将方格值全部设置为1,把数位和满足要求的设置为0,然后从0开始遍历,遍历过的设置为1,以防重复计算。
class Solution:def movingCount(self, m: int, n: int, k: int) -> int:visited = [[1] * n for _ in range(m)]for i in range(m):for j in range(n):# 可抵达节点设置为0if i // 10 + i % 10 + j // 10 + j % 10 <= k: # 注意,题里只包括两位数visited[i][j] = 0def dfs(x, y):if x < 0 or x >= m or y < 0 or y >= n or visited[x][y]: # 超出数组范围或者已访问过return 0visited[x][y] = 1return 1 + dfs(x + 1, y) + dfs(x, y + 1)return dfs(0, 0)
class Solution:def movingCount(self, m: int, n: int, k: int) -> int:visited = [[1] * n for _ in range(m)]for i in range(m):for j in range(n):if i // 10 + i % 10 + j // 10 + j % 10 <= k:visited[i][j] = 0queue = collections.deque([(0, 0)])res = 0while queue:x, y = queue.popleft()res += 1for dx, dy in ((1, 0), (0, 1)):nx, ny = x + dx, y + dyif 0 <= nx < m and 0 <= ny < n and not visited[nx][ny]:visited[nx][ny] = 1queue.append((nx, ny))return res
√剑指 Offer 12. 矩阵中的路径

class Solution:def exist(self, board: List[List[str]], word: str) -> bool:def dfs(i,j,w):if w==len(word):return Truefor d in [[-1,0],[0,1],[1,0],[0,-1]]:ni=i+d[0]nj=j+d[1]if 0<=ni<m and 0<=nj<n and board[ni][nj]==word[w]:tmp=board[i][j]board[i][j]='0' # 防止重复访问if dfs(ni,nj,w+1): # 注意,这里要加判断跳出循环。return Trueboard[i][j]=tmp # 恢复# print(board)return Falsem=len(board)n=len(board[0])for i in range(m):for j in range(n):if board[i][j]==word[0]:board[i][j] = '0'if dfs(i, j, 1):return Trueboard[i][j] = word[0]return False
√130.被围绕的区域


先边界DFS,找出不被围绕的区域(和1020相同),将它复制为B,之后将O换成X,将B换回O
class Solution:def solve(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> None:"""Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead."""len_x = len(board)len_y = len(board[0])def dfs(x, y):board[x][y] = 'B' # 注意,与边界相连的都可以离开directions = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, 1), (0, -1)]for _x, _y in directions:dx,dy=x + _x,y+_yif dx >= 0 and dx < len_x and dy >= 0 and dy < len_y and board[dx][dy]=='O' :dfs(dx, dy)for i in range(len_x):for j in range(len_y):if (i in [0, len_x - 1] or j in [0, len_y - 1]) and board[i][j]=='O': #注意边界DFSdfs(i,j)for i in range(len_x):for j in range(len_y):if board[i][j]=='O':board[i][j]='X'elif board[i][j]=='B':board[i][j]='O'
√1020.飞地的数量(边界DFS)

class Solution:def numEnclaves(self, A: List[List[int]]) -> int:if not A:return 0len_x = len(A)len_y = len(A[0])def dfs(x, y):A[x][y] = 0 # 注意,与边界相连的都可以离开directions = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, 1), (0, -1)]for _x, _y in directions:dx,dy=x + _x,y+_yif dx >= 0 and dx < len_x and dy >= 0 and dy < len_y and A[dx][dy] :dfs(dx, dy)for i in range(len_x):for j in range(len_y):if (i in [0, len_x - 1] or j in [0, len_y - 1]) and A[i][j]: #注意边界DFSdfs(i,j)return sum([sum(A[i]) for i in range(len_x)])
√1254.统计封闭岛屿的数目(flag记录)

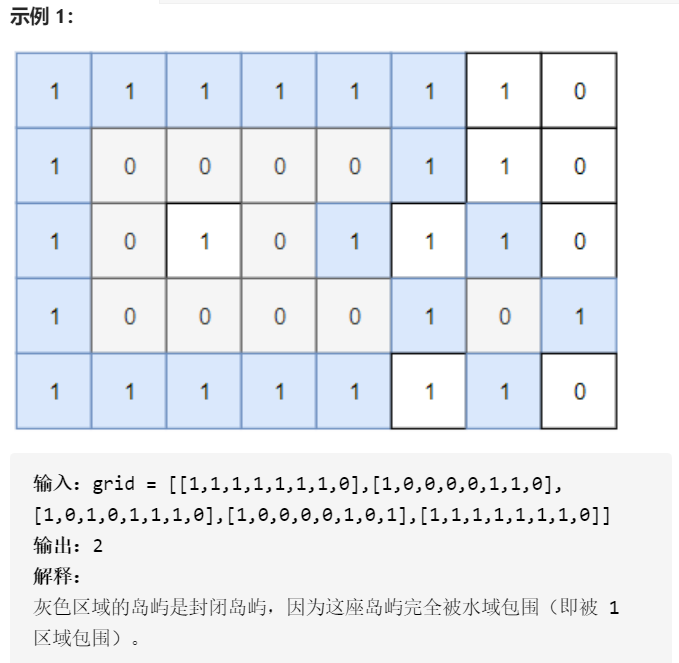
(这里DFS也可以结合695返回值为1 ,FLAG为TRUE时加上这个数,就代表1020无法离开的数量)
class Solution:def closedIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])def dfs(i, j):grid[i][j] = 1 # 注意,防止重复遍历for di, dj in ((1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, 1), (0, -1)):x, y = i + di, j + djif 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and grid[x][y]==0:dfs(x, y)else: # 注意,如果到达边界, 说明不封闭。nonlocal flag # 使它能够修变量flag = Falseans = 0for i, j in itertools.product(range(m), range(n)):flag = Trueif not grid[i][j]:dfs(i, j)ans += flagreturn ans
√200.岛屿数量
不用考虑边界条件,这里是字符不是数字
class Solution:def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])def dfs(x, y):grid[x][y] = '0' # 注意,防止重复遍历for di, dj in ((1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, 1), (0, -1)):dx, dy = x + di, y + djif 0 <= dx < m and 0 <= dy < n and grid[dx][dy]=='1':dfs(dx, dy)ans = 0for i, j in itertools.product(range(m), range(n)):if grid[i][j]=='1':dfs(i, j)ans += 1return ans
√695.岛屿的最大面积(计算DFS遍历了多少个节点)
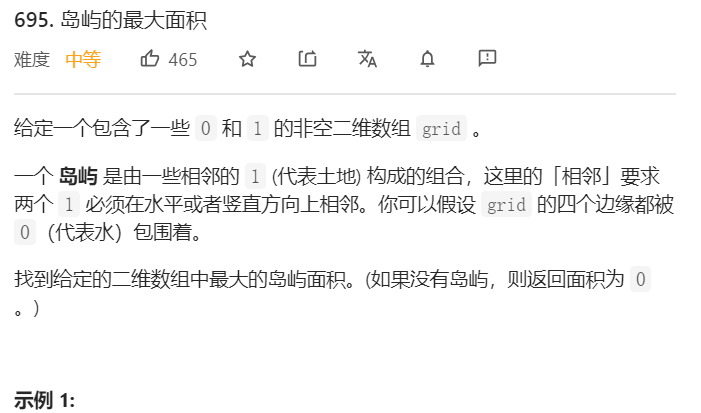

可以根据下一题,返回数组最后一个数,但要注意为了防止数组为空,需要初始化rst=[0],return res[-1] ,另一种解法就是拿一个变量记录当前值,然后和前一个值对比取最大值。没有排序时间上会更快一点。
class Solution:def maxAreaOfIsland(self, land: List[List[int]]) -> int:n = len(land)m = len(land[0])ans = 0 # 给一个初始值,防止数组为空def dfs(i,j):land[i][j]=0area = 1for (dx,dy) in [(i+1,j),(i-1,j),(i,j+1),(i,j-1)]:if dx>=0 and dx<n and dy>=0 and dy<m and land[dx][dy]==1:area+=dfs(dx,dy)return areafor i in range(n):for j in range(m):if land[i][j]==1:num=dfs(i,j) # 注意ans=max(ans,num) # 注意return ans
√16.19水域大小 (排序)

class Solution:def pondSizes(self, land: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:n = len(land)m = len(land[0])rst = []def dfs(i,j):land[i][j]=1area = 1 # 注意for (dx,dy) in [(i+1,j),(i-1,j),(i,j+1),(i,j-1),(i+1,j+1),(i+1,j-1),(i-1,j+1),(i-1,j-1)]:if dx>=0 and dx<n and dy>=0 and dy<m and land[dx][dy]==0:area+=dfs(dx,dy) # 注意return area # 注意for i in range(n):for j in range(m):if land[i][j]==0:rst.append(dfs(i,j))rst.sort()return rst
困难
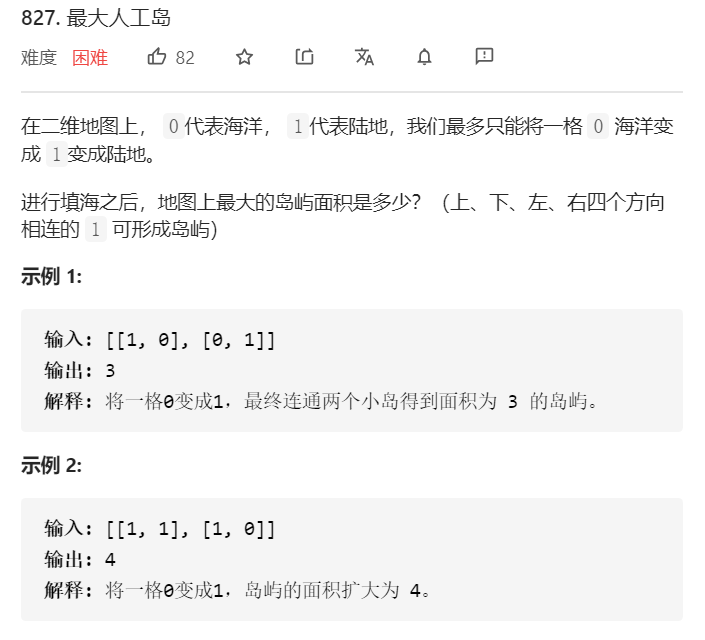
√827.最大人工岛
重新赋值为岛屿面积,对0点遍历
将每个岛屿进行重新赋值,利用哈希表存储岛屿对应的数值和面积。然后对0点四周进行遍历,相邻岛屿面积相加。最后比较最大值
class Solution:def largestIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:def dfs(i,j,grid,newnumber):if i<0 or i>m-1 or j<0 or j>n-1:return 0if grid[i][j] != 1:return 0grid[i][j] = newnumberreturn 1+dfs(i-1,j,grid,newnumber)+dfs(i,j-1,grid,newnumber)+dfs(i+1,j,grid,newnumber)+dfs(i,j+1,grid,newnumber)m = len(grid)n = len(grid[0])newnumber = 1area = {}maxarea = 0for i in range(m):for j in range(n):if grid[i][j] == 1:newnumber+=1area[newnumber] = dfs(i,j,grid,newnumber)maxarea = max(maxarea,area[newnumber])maxareares = 0for i in range(m):for j in range(n):if grid[i][j] == 0:areares = 1res = []if i+1<m :res.append(grid[i+1][j])if i-1>=0:res.append(grid[i-1][j])if j+1<n:res.append(grid[i][j+1])if j-1>=0:res.append(grid[i][j-1])res = list(set(res))for k in range(len(res)):areares += area.get(res[k],0)maxareares = max(maxareares,areares)return max(maxareares,maxarea)
√778.水位上升的泳池中游泳
相同类型:1631. 最小体力消耗路径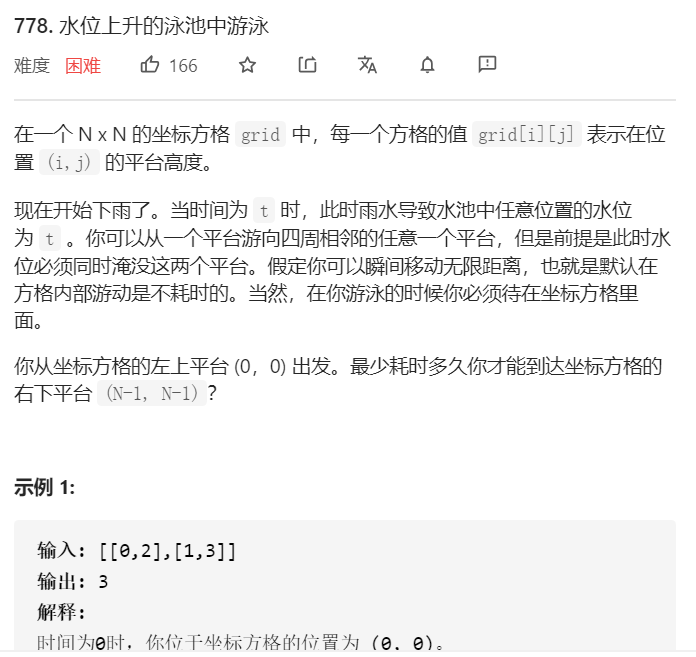

保存所有结果,选最小值。
class Solution:def swimInWater(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:dir=[1,0,-1,0,0,1,0,-1]max_grid = max(max(row) for row in grid)ans=max_grid+1 # 这个不知道为什么参数不能传递res=[]def dfs(x,y,val,ans):if val>=ans: # 在这里剪枝returnfor i in range(4):nx = x+dir[2*i]ny = y+dir[2*i+1]if nx>=0 and nx<n and ny>=0 and ny<n:nowVal = max(grid[nx][ny],val)if times[nx][ny]>nowVal and nowVal<ans:times[nx][ny]=nowValif nx==ny and nx==n-1:ans = nowValres.append(ans)returndfs(nx,ny,nowVal,ans)n = len(grid)times = [[max_grid+1]*n for _ in range (n)]times[0][0]=grid[0][0]dfs(0,0,times[0][0],ans)return min(res)
二分法加DFS
class Solution:def swimInWater(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:n = len(grid)def dfs(t, x, y, visited):if x == y == n - 1:return Truevisited[x][y] = Truefor dx, dy in ((-1,0),(1,0),(0,-1),(0,1)):nx, ny = x + dx, y + dyif 0 <= nx < n and 0 <= ny < n and not visited[nx][ny] and grid[nx][ny] <= t:if dfs(t, nx, ny, visited):return Truereturn Falseleft = max(grid[0][0], grid[-1][-1])right = n * n - 1 # 注意题意,数组是排列,最大值就是N*N-1while left <= right: # 闭区间[left,right]mid = (left + right) // 2visited = [[False] * n for _ in range(n)]if dfs(mid, 0, 0, visited): # 如果这个值可以到边界,可以缩小区域right = mid - 1else:left = mid + 1return left # 这里为什么返回left
BFS不是很懂
class Solution:def swimInWater(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:res = 0n = len(grid)heap = [(grid[0][0],0,0)]visited = set([(0,0)])while heap:height,x,y = heapq.heappop(heap)res = max(res,height)if x == n-1 and y == n-1:return resfor dx,dy in [(0,1),(0,-1),(1,0),(-1,0)]:new_x,new_y = x + dx,y + dyif 0 <= new_x < n and 0 <= new_y < n and (new_x,new_y) not in visited:visited.add((new_x,new_y))heapq.heappush(heap,(grid[new_x][new_y],new_x,new_y))return -1
√417.太平洋大西洋水流问题


个人版答案,从边界遍历,分别从太平洋和大西洋边界位置出发遍历,同时被它们两遍历到的,就是答案
遍历方法,就是按高度,找下一个大于等于此时遍历的点
class Solution:def pacificAtlantic(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:def dfs(x,y,point):point.append((x,y)) #注意,这里必须是(),不能是[],集合求交集,必须是hashtable格式direction = [[-1,0],[1,0],[0,1],[0,-1]]for d in direction:nx=x+d[0]ny=y+d[1]if nx>=0 and ny>=0 and nx<len(heights) and ny<len(heights[0]) and heights[nx][ny]>=heights[x][y] and (nx,ny) not in point:dfs(nx,ny,point)point=[]for i in range (len(heights[0])): # 第一行dfs(0,i,point)for i in range (len(heights)): # 第一列dfs(i,0,point)print(point)point2=[]for i in range (len(heights[0])): # 最后一行dfs(len(heights)-1,i,point2)for i in range (len(heights)): # 最后一列dfs(i,len(heights[0])-1,point2)print(point2)print(set(point2) & set(point))return list(set(point2) & set(point))
大佬版,思路一样
class Solution:def pacificAtlantic(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:if not matrix or not matrix[0]: return []# 流向太平洋的位置res1 = set()# 流向大西洋的位置res2 = set()row = len(matrix)col = len(matrix[0])# 从边界遍历def dfs(i, j, cur, res):res.add((i, j))for x, y in [[1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1]]:tmp_i = i + xtmp_j = j + yif 0 <= tmp_i < row and 0 <= tmp_j < col and matrix[i][j] <= matrix[tmp_i][tmp_j] and (tmp_i, tmp_j) not in res:dfs(tmp_i, tmp_j, matrix[i][j], res)# 太平洋for i in range(row):dfs(i, 0, 0, res1)# 太平洋for j in range(col):dfs(0, j, 0, res1)# 大西洋for i in range(row):dfs(i, col - 1, 0, res2)# 大西洋for j in range(col):dfs(row - 1, j, 0, res2)return list(res1 & res2)
速度慢的原因可能是集合判断那里,个人版答案不知道为什么有重复结果。
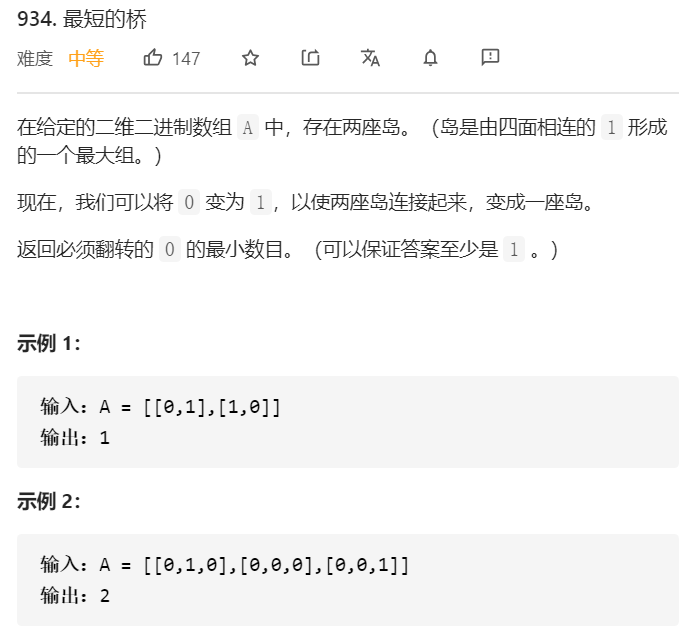
√934.最短的桥
×749.隔离病毒