ArrayList
类图
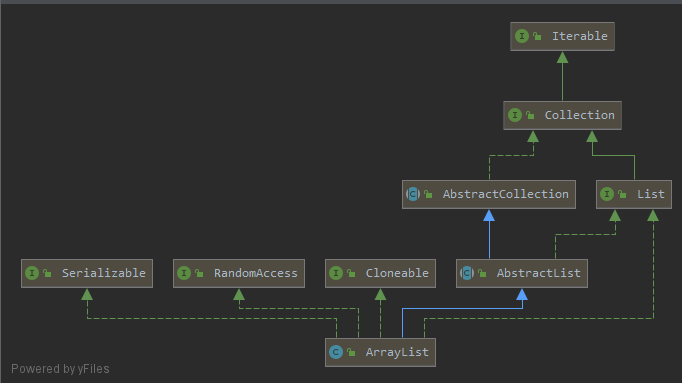
List: 提供增、删、迭代遍历等方法要求RandomAccess: 提供可随机访问的功能Serializable: 提供可序列化的功能AbstractList: 提供了List接口的骨架实现,尤其是实现 迭代遍历 相关的代码- 不过对于
ArrayList来说没啥用,前者又重写了很多方法
- 不过对于
几个概念
- index: 数组下标
transient Object[] elementData;数组本身,默认为 nullprivate int size;已使用了elementData的数量,没有volatile修饰, 非线程安全private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;初始容量,默认 10protected transient int modCount = 0;版本号,当前数组被修改的版本次数,数组结构变动,就会 +1
初始化
- 无参构造,则
elementData依然为 null- 需要进行 内部扩容
- 有参构造,接收 ```java // 空数组, 首次扩容为 10 private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 空数组,扩容会按照 1.5 倍扩容 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
//无参数直接初始化,数组大小为空 public ArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; }
// 指定大小初始化 public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0) { // 初始化数组 this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { // 为0,则为空数组 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException(“Illegal Capacity: “+ initialCapacity); } }
//指定初始数据初始化 public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { //elementData 是保存数组的容器,默认为 null elementData = c.toArray(); //如果给定的集合(c)数据有值 if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) { // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) // 如果集合元素类型不是 Object 类型,我们会转成 Object if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) { elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } } else { // 给定集合(c)无值,则默认空数组 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } }
- `<A>`: jdk9 修复 bug<a name="39AZB"></a>## 增加```javapublic boolean add(E e) {// <A>ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!// <B>elementData[size++] = e;return true;}
<A>: 判断是否需要扩容,传入 请求索引值<B>: 将元素进行添加,此处线程不安全
内部扩容
如果 当前list 是无参构造而来的
- 那么需要进行内部扩容,将其扩容为 10
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {// <A>if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);}// <B>ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);}
- 那么需要进行内部扩容,将其扩容为 10
<A>: 内部扩容 如果是空数组,则在 minCapacity(size + 1[对应add()] 或者size + number对应addAll()) 和DEFAULT_CAPACITY(默认值,10) 中取最大值- 一般结果是设置为
DEFAULT_CAPACITY,即 10
- 一般结果是设置为
<B>: 进行扩容判断
扩容判断
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {// <A>modCount++;// overflow-conscious code// <B>if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)grow(minCapacity);}
<A>: 版本号 + 1<B>: 如果 最小容量 比当前数组长度大,则进行扩容
扩容
private void grow(int minCapacity) {// 1int oldCapacity = elementData.length;// 2int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);// 3if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)newCapacity = minCapacity;// 4if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)// 4.anewCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:// 5elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);}
- 获取当前数组长度
- 获取预期扩容值,数字为当前数组长度*1.5的 (
>>1表示除以 2) - 如果预期扩容值 小于 请求索引值,直接设置预期扩容值为请求索引值
- 预期扩容值要么 ==
elementData.length, 要么 ==minCapacity
- 预期扩容值要么 ==
- 如果预期扩容值 大于 jvm 所能分配的数组的最大值(
Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8) 则进行<DD>- 预计扩容值设置为
Integer.MAX_VALUE
- 预计扩容值设置为
- 真正的扩容,底部调用
System.arraycopy进行拷贝
删除
// 按值删除public boolean remove(Object o) {if (o == null) {// 1.for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)// 1.aif (elementData[index] == null) {fastRemove(index);return true;}} else {// 2.for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)// 2.aif (o.equals(elementData[index])) {fastRemove(index);return true;}}return false;}
- 如果值为
null, 则在elementData[index, size)中查找值为null的位置,进行 快速删除- 进行
elementData[index] == null判断
- 进行
- 如果值不为
null,则在elementData[index, size)中查找指定值的位置,进行 快速删除- 进行
指定值.equals(elementData[index]判断
- 进行
快速删除
private void fastRemove(int index) {// 1.modCount++;// 2.int numMoved = size - index - 1;// 2.aif (numMoved > 0)System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,numMoved);// 3elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work}
- 版本号 + 1
- 计算往前挪的数值
- 如果步骤2中的数值大于0,说明需要对数组进行向前整体移动
- 否则说明将移除的
index是最后一位
- 将数组的最后一位置
null,且size - 1
- 步骤2 和 步骤3 可以看成
- 如果
迭代器
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {int cursor; // index of next element to returnint lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no suchint expectedModCount = modCount;// other method}
参数
int cursor; // index of next element to return 迭代中的下个元素的索引,默认 0int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such 迭代中最后一个元素的索引, -1 表示么得了int expectedModCount = modCount; // 迭代中期望的版本号
hasNext
public boolean hasNext() {return cursor != size;}
- 迭代中的下一个元素的索引不为数组的大小,返回 true
next
public E next() {// 1.checkForComodification();// 2.int i = cursor;if (i >= size)throw new NoSuchElementException();// 3.Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;if (i >= elementData.length)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();// 4cursor = i + 1;// 5.return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];}
- 检查版本号
- 获取 cursor 的值
- 获取当前数组
- cursor +1
- 返回
elementData[curosr], 并且设置 lastRet 为最新的 cursorremove
```java public void remove() { // 1. if (lastRet < 0)
// 2. checkForComodification();throw new IllegalStateException();
try {// 3.ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);// 4.cursor = lastRet;lastRet = -1;expectedModCount = modCount;} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}
}
```
- lastRet 小于 0, 说明是没有元素了
- 检查版本号
- 删除该元素
// 删除元素时 modCount 的值已经发生变化,在此赋值给 expectedModCount
// 这样下次迭代时,两者的值是一致的了

