本篇博文主要对asp.net mvc开发需要撑握的C#语言知识点进行简单回顾,尤其是C# 3.0才有的一些C#语言特性。对于正在学asp.net mvc的童鞋,不防花个几分钟浏览一下。本文要回顾的C#知识点有:特性、自动属性、对象集合初始化器、扩展方法、Lambda表达式和Linq查询。C#资深“玩家”可路过。
1.特性(Attributes)
特性(Attributes),MSDN的定义是:公共语言运行时允许你添加类似关键字的描述声明,叫做attributes, 它对程序中的元素进行标注,如类型、字段、方法和属性等。Attributes和Microsoft .NET Framework文件的元数据保存在一起,可以用来向运行时描述你的代码,或者在程序运行的时候影响应用程序的行为。
例如,在一个方法前标注[Obsolete]特性,则调用该方法时VS则会提示该方法已过期的警告,如下图: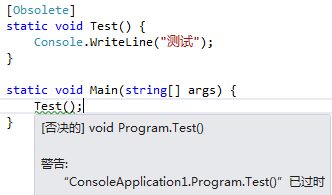
又如,在.Net Remoting的远程对象中,如果要调用或传递某个对象,例如类,或者结构,则该类或结构则必须标注[Serializable]特性。还有,我们在构建XML Web服务时用得很多的一个特性就是[WebMegthod],它可让通过HTTP请求的公开方法的返回值编码成XML进行传递。
特性实际上就是一个类,[Obsolete]特性的实际类名是ObsoleteAttribute,但我们在标注的时候可以不带Attribute后缀,系统在名称转换时会自动给我们加上。
上面说的都是些.NET系统定义的一些特性,当然还有很多。了解如何自定义特性,有利有我们更好的在ASP.NET MVC编程使用特性,比如给Model类的属性标注特性来验证表单输入的合法性(以后进行介绍)。
下面我们来模拟一个ASP.NET MVC经常要用到的StringLenth特性,它用于判断用户输入是否超出长度限制。我们现在来模拟它。先定义一个MyStringLenth特性:

[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property | AttributeTargets.Field)]
public sealed class MyStringLenthAttribute : Attribute {
<font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> MyStringLenthAttribute(<font style="color:#0000FF;">string</font> displayName, <font style="color:#0000FF;">int</font><font style="color:#000000;"> maxLength) {</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">this</font>.MaxLength =<font style="color:#000000;"> maxLength;</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">this</font>.DisplayName =<font style="color:#000000;"> displayName;</font>}<font style="color:#008000;">//</font><font style="color:#008000;">显示的名称,对外是只读的,所以不能通过可选参数来赋值,必须在构造函数中对其初始化。</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">string</font> DisplayName { <font style="color:#0000FF;">get</font>; <font style="color:#0000FF;">private</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">set</font><font style="color:#000000;">; }</font><font style="color:#008000;">//</font><font style="color:#008000;">长度最大值,对外是只读的,所以不能通过可选参数来赋值,必须在构造函数中对其初始化。</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">int</font> MaxLength { <font style="color:#0000FF;">get</font>; <font style="color:#0000FF;">private</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">set</font><font style="color:#000000;">; }</font><font style="color:#008000;">//</font><font style="color:#008000;">错误信息,标注时可作为可选命名参数来使用。</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">string</font> ErrorMessage { <font style="color:#0000FF;">get</font>; <font style="color:#0000FF;">set</font><font style="color:#000000;">; }</font><font style="color:#008000;">//</font><font style="color:#008000;">长度最小值,标注时可作为可选命名参数来使用。</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">int</font> MinLength { <font style="color:#0000FF;">get</font>; <font style="color:#0000FF;">set</font><font style="color:#000000;">; }</font>
}

上面若不加AttributeUsage限制,特性可以声明在类型(如结构、类、枚举、委托)和成员(如方法,字段,事件,属性,索引)的前面。
然后我们把这个特性应用在下面的Order类之上:

[MyStringLenth(<font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">订单号</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, <font style="color:#800080;">6</font>,MinLength = <font style="color:#800080;">3</font>, ErrorMessage = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">{0}的长度必须在{1}和{2}之间,请重新输入!</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#000000;">)]</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">string</font> OrderID { <font style="color:#0000FF;">get</font>; <font style="color:#0000FF;">set</font><font style="color:#000000;">; }</font>
}

最后我们看看如何使用MyStringLenth特性验证用户输入字符串的长度:

<font style="color:#0000FF;">foreach</font> (<font style="color:#0000FF;">object</font> attribute <font style="color:#0000FF;">in</font> member.GetCustomAttributes(<font style="color:#0000FF;">true</font><font style="color:#000000;">)) {</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">if</font> (attribute <font style="color:#0000FF;">is</font><font style="color:#000000;"> MyStringLenthAttribute) {</font>MyStringLenthAttribute attr=<font style="color:#000000;">(MyStringLenthAttribute)attribute;</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">string</font> displayName =<font style="color:#000000;"> attr.DisplayName;</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">int</font> maxLength =<font style="color:#000000;"> attr.MaxLength;</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">int</font> minLength =<font style="color:#000000;"> attr.MinLength;</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">string</font> msg =<font style="color:#000000;"> attr.ErrorMessage;</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">if</font> (inputLength < minLength || inputLength ><font style="color:#000000;"> maxLength) {</font>Console.WriteLine(msg, displayName, minLength, maxLength);<font style="color:#0000FF;">return</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">false</font><font style="color:#000000;">;</font>}<font style="color:#0000FF;">else</font><font style="color:#000000;"> {</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">return</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">true</font><font style="color:#000000;">;</font>}}}<font style="color:#0000FF;">return</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">false</font><font style="color:#000000;">;</font>
}
//验证输入是否合法 private static bool IsValid(Order order) {
<font style="color:#0000FF;">if</font> (order == <font style="color:#0000FF;">null</font>) <font style="color:#0000FF;">return</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">false</font><font style="color:#000000;">;</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">foreach</font> (PropertyInfo p <font style="color:#0000FF;">in</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">typeof</font><font style="color:#000000;">(Order).GetProperties()) {</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">if</font><font style="color:#000000;"> (IsMemberValid(order.OrderID.Length, p))</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">return</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">true</font><font style="color:#000000;">;</font>}<font style="color:#0000FF;">return</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">false</font><font style="color:#000000;">;</font>
}
public static void Main() {
<font style="color:#0000FF;">string</font> input=<font style="color:#0000FF;">string</font><font style="color:#000000;">.Empty;</font>Order order;<font style="color:#0000FF;">do</font><font style="color:#000000;"> {</font>Console.WriteLine(<font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">请输入订单号:</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#000000;">);</font>input =<font style="color:#000000;"> Console.ReadLine();</font>order = <font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Order { OrderID =<font style="color:#000000;"> input };</font>}<font style="color:#0000FF;">while</font> (!<font style="color:#000000;">IsValid(order));</font>Console.WriteLine(<font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">订单号输入正确,按任意键退出!</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#000000;">);</font>Console.ReadKey();
}

输出效果如下: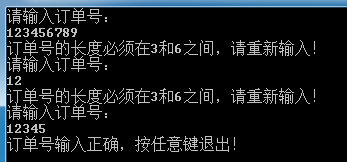
2.自动属性
在 C# 3.0 和更高版本中,当属性的访问器中不需要其他逻辑时,自动实现的属性可使属性声明更加简洁。
下面示例演示了属性的标准实现和自动实现:

<font style="color:#0000FF;">class</font><font style="color:#000000;"> Person {</font><font style="color:#008000;">//</font><font style="color:#008000;">标准实现的属性</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">int</font><font style="color:#000000;"> _age;</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">int</font><font style="color:#000000;"> Age {</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">get</font> { <font style="color:#0000FF;">return</font><font style="color:#000000;"> _age; }</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">set</font><font style="color:#000000;"> {</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">if</font> (value < <font style="color:#800080;">0</font> || value > <font style="color:#800080;">130</font><font style="color:#000000;">) {</font>Console.WriteLine(<font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">设置的年龄有误!</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#000000;">);</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">return</font><font style="color:#000000;">;</font>}_age =<font style="color:#000000;"> value;</font>}}<font style="color:#008000;">//</font><font style="color:#008000;">自动实现的属性</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">string</font> Name { <font style="color:#0000FF;">get</font>; <font style="color:#0000FF;">set</font><font style="color:#000000;">; }</font>}<font style="color:#0000FF;">static</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">void</font> Main(<font style="color:#0000FF;">string</font><font style="color:#000000;">[] args) {</font>Person p = <font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font><font style="color:#000000;"> Person();</font>p.Age = <font style="color:#800080;">180</font><font style="color:#000000;">;</font>p.Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">小王</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#000000;">;</font>Console.WriteLine(<font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">{0}今年{1}岁。</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#000000;">,p.Name,p.Age);</font>Console.ReadKey();}
}

自动属性也可以有不同的访问权限,如:
public string Name { get;private set; } 注意,自动属性不能定义只读或者只写的属性,必须同时提供get和set访问器: public string Name { get; }//编译出错 public string PetName { set; }//编译出错3.对象和集合的初始化器
上面我们演示自动属性的时候给对象的实例初始化时是一个一个属性进行赋值的,有多少个属性就需要多少句代码。C# 3.0和更高版本中有了对象集合初始化器,有了它,只需一句代码就可初始化一个对象或一个对象集合的所有属性。这在里先创建一个“商品”类,用于后面的示例演示:

<font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"><summary></font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font><font style="color:#008000;"> 商品编号</font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"></summary></font><font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">int</font> ProductID { <font style="color:#0000FF;">get</font>; <font style="color:#0000FF;">set</font><font style="color:#000000;">; }</font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"><summary></font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font><font style="color:#008000;"> 商品名称</font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"></summary></font><font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">string</font> Name { <font style="color:#0000FF;">get</font>; <font style="color:#0000FF;">set</font><font style="color:#000000;">; }</font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"><summary></font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font><font style="color:#008000;"> 商品描述</font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"></summary></font><font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">string</font> Description { <font style="color:#0000FF;">get</font>; <font style="color:#0000FF;">set</font><font style="color:#000000;">; }</font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"><summary></font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font><font style="color:#008000;"> 商品价格</font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"></summary></font><font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">decimal</font> Price { <font style="color:#0000FF;">get</font>; <font style="color:#0000FF;">set</font><font style="color:#000000;">; }</font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"><summary></font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font><font style="color:#008000;"> 商品分类</font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"></summary></font><font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">string</font> Category { <font style="color:#0000FF;">set</font>; <font style="color:#0000FF;">get</font><font style="color:#000000;">; }</font>
}

基于上面定义好的商品类,下面代码演示了如何通过初始化器来创建商品类的实例对象和集合:

<font style="color:#008000;">//</font><font style="color:#008000;">对象初始化器的使用 (可只给部分字段赋值)</font>Product product = <font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product { ProductID = <font style="color:#800080;">1234</font>, Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">西瓜</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">2.3M</font> };<font style="color:#008000;">//</font><font style="color:#008000;">创建并初始化一个实例</font><font style="color:#008000;">//</font><font style="color:#008000;">集合初始化器的使用</font>List<Product> proList = <font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> List<Product><font style="color:#000000;"> { </font><font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product { ProductID = <font style="color:#800080;">1234</font>, Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">西瓜</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">2.3M</font><font style="color:#000000;"> },</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product { ProductID = <font style="color:#800080;">2345</font>, Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">苹果</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">5.9M</font><font style="color:#000000;"> },</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product { ProductID = <font style="color:#800080;">3456</font>, Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">樱桃</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">4.6M</font><font style="color:#000000;"> }</font>};<font style="color:#008000;">//</font><font style="color:#008000;">打印</font>Console.WriteLine(<font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">对象初始化器:{0} {1} {2}</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#000000;">, product.ProductID, product.Name, product.Price);</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">foreach</font> (Product p <font style="color:#0000FF;">in</font><font style="color:#000000;"> proList) {</font>Console.WriteLine(<font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">集合初始化器:{0} {1} {2}</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#000000;">, p.ProductID, p.Name, p.Price);</font>}Console.ReadKey();
}

另外还有一些其它类型也可以使用初始化器,如下:

Dictionary<string, int> fruitDic = new Dictionary<string, int>() {
{ <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">apple</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, <font style="color:#800080;">10</font><font style="color:#000000;"> },</font>{ <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">orange</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, <font style="color:#800080;">20</font><font style="color:#000000;"> },</font>{ <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">plum</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, <font style="color:#800080;">30</font><font style="color:#000000;"> }</font>
};

4.扩展方法
扩展方法使您能够向现有类型“添加”方法,而无需创建新的派生类型或修改原始类型。扩展方法是一种特殊的静态方法,但可以像扩展类型上的实例方法一样进行调用。例如,我们可以让Random类的所有实例对象拥有一个返回随机bool值的方法。我们不能对Random类本身进行修改,但可以对它进行扩展,如下代码所示:

<font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"><summary></font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font><font style="color:#008000;"> 随机返回 true 或 false</font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"></summary></font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"><param name="random"></font><font style="color:#008000;">this参数自动指定到Random的实例</font><font style="color:#808080;"></param></font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"><returns></returns></font><font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">static</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">bool</font> NextBool(<font style="color:#0000FF;">this</font><font style="color:#000000;"> Random random) {</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">return</font> random.NextDouble() > <font style="color:#800080;">0.5</font><font style="color:#000000;">;</font>}<font style="color:#0000FF;">static</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">void</font> Main(<font style="color:#0000FF;">string</font><font style="color:#000000;">[] args) {</font><font style="color:#008000;">//</font><font style="color:#008000;">调用扩展方法</font>Random rd = <font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font><font style="color:#000000;"> Random();</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">bool</font> bl =<font style="color:#000000;"> rd.NextBool();</font>Console.WriteLine(bl.ToString());Console.ReadKey();}
}

注意,扩展方法必须在非泛型的静态类中定义,上面的Program类如不加static修饰符则会报错。
我们可以创建一个接口的扩展方法,这样实现该接口的类都可以调用该扩展方法。看下面一个完整示例:

<font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> List<Product> Products { <font style="color:#0000FF;">get</font>; <font style="color:#0000FF;">set</font><font style="color:#000000;">; }</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> IEnumerator<Product><font style="color:#000000;"> GetEnumerator() {</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">return</font><font style="color:#000000;"> Products.GetEnumerator();</font>}IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator() {<font style="color:#0000FF;">return</font><font style="color:#000000;"> GetEnumerator();</font>}
}
///
<font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"><summary></font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font><font style="color:#008000;"> 计算商品总价钱</font><font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"></summary></font><font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">static</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">decimal</font> TotalPrices(<font style="color:#0000FF;">this</font> IEnumerable<Product><font style="color:#000000;"> productEnum) {</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">decimal</font> total = <font style="color:#800080;">0</font><font style="color:#000000;">;</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">foreach</font> (Product prod <font style="color:#0000FF;">in</font><font style="color:#000000;"> productEnum) {</font>total +=<font style="color:#000000;"> prod.Price;</font>}<font style="color:#0000FF;">return</font><font style="color:#000000;"> total;</font>}
}
class Program {
<font style="color:#0000FF;">static</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">void</font> Main(<font style="color:#0000FF;">string</font><font style="color:#000000;">[] args) {</font><font style="color:#008000;">//</font><font style="color:#008000;"> 创建并初始化ShoppingCart实例,注入IEnumerable<Product></font>IEnumerable<Product> products = <font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font><font style="color:#000000;"> ShoppingCart {</font>Products = <font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> List<Product><font style="color:#000000;"> { </font><font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product {Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">Kayak</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">275</font><font style="color:#000000;">}, </font><font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product {Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">Lifejacket</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">48.95M</font><font style="color:#000000;">}, </font><font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product {Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">Soccer ball</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">19.50M</font><font style="color:#000000;">}, </font><font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product {Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">Corner flag</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">34.95M</font><font style="color:#000000;">}</font>}};<font style="color:#008000;">//</font><font style="color:#008000;"> 创建并初始化一个普通的Product数组</font>Product[] productArray =<font style="color:#000000;"> { </font><font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product {Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">Kayak</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price =<font style="color:#000000;"> 275M}, </font><font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product {Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">Lifejacket</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">48.95M</font><font style="color:#000000;">}, </font><font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product {Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">Soccer ball</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">19.50M</font><font style="color:#000000;">}, </font><font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product {Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">Corner flag</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">34.95M</font><font style="color:#000000;">} </font>};<font style="color:#008000;">//</font><font style="color:#008000;"> 取得商品总价钱:用接口的方式调用TotalPrices扩展方法。</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">decimal</font> cartTotal =<font style="color:#000000;"> products.TotalPrices();</font><font style="color:#008000;">//</font><font style="color:#008000;"> 取得商品总价钱:用普通数组的方式调用TotalPrices扩展方法。</font><font style="color:#0000FF;">decimal</font> arrayTotal =<font style="color:#000000;"> productArray.TotalPrices();</font>Console.WriteLine(<font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">Cart Total: {0:c}</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#000000;">, cartTotal);</font>Console.WriteLine(<font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">Array Total: {0:c}</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#000000;">, arrayTotal);</font>Console.ReadKey();}
}

执行后输出如下结果:
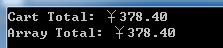
5.Lambda 表达式
Lambda 表达式和匿名函数其实是一件事情。不同是,他们语法表现形式不同,Lambda 表达式在语法上实际上就是匿名函数的简写。直接介绍匿名函数和Lambda表达式的用法没什么意思,在这里,我要根据实际应用来讲一个两者用法的例子,这样在介绍知识点的同时也能和大家分享一下解决问题的思想。
假如我们要实现一个功能强大的商品查询方法,这个商品查询方法如何查询商品是可以由用户自己来决定的,用户可以根据价格来查询商品,也可以根据分类来查询商品等等,也就是说用户可以把自己的查询逻辑传递给这个查询方法。要编写这样一个方法,我们很自然的会想到用一个委托来作为这个方法的参数,这个委托就是用户处理商品查询的逻辑。 我们不防把这个查询方法称为“商品查询器”。我们可以用静态的扩展方法来实现这个“商品查询器“,这样每个商品集合对象(如 IEnumerable

<font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"><summary></font>
<font style="color:#808080;">///</font><font style="color:#008000;"> 商品查询器</font>
<font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"></summary></font>
<font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"><param name="productEnum"></font><font style="color:#008000;">扩展类型的实例引用</font><font style="color:#808080;"></param></font>
<font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"><param name="selectorParam"></font><font style="color:#008000;">一个参数类型为Product,返回值为bool的委托</font><font style="color:#808080;"></param></font>
<font style="color:#808080;">///</font> <font style="color:#808080;"><returns></font><font style="color:#008000;">查询结果</font><font style="color:#808080;"></returns></font>
<font style="color:#0000FF;">public</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">static</font> IEnumerable<Product> Filter(<font style="color:#0000FF;">this</font> IEnumerable<Product> productEnum, Func<Product, <font style="color:#0000FF;">bool</font>><font style="color:#000000;"> selectorParam) {</font>
<font style="color:#0000FF;">foreach</font> (Product prod <font style="color:#0000FF;">in</font><font style="color:#000000;"> productEnum) {</font>
<font style="color:#0000FF;">if</font><font style="color:#000000;"> (selectorParam(prod)) {</font>
<font style="color:#0000FF;">yield</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">return</font><font style="color:#000000;"> prod;</font>
}
}
}
}

没错,我们就是用这么简短的Filter方法来满足各种需求的查询。上面Product类使用的是前文定义的。这里也再一次见证了扩展方法的功效。为了演示Filter查询方法的调用,我们先来造一批数据:

<font style="color:#008000;">//</font><font style="color:#008000;"> 创建商品集合</font>
IEnumerable<Product> products = <font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font><font style="color:#000000;"> ShoppingCart {</font>
Products = <font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> List<Product><font style="color:#000000;"> { </font>
<font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product {Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">西瓜</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Category = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">水果</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">2.3M</font><font style="color:#000000;">}, </font>
<font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product {Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">苹果</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Category = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">水果</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">4.9M</font><font style="color:#000000;">}, </font>
<font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product {Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">ASP.NET MCV 入门</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Category = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">书籍</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">19.5M</font><font style="color:#000000;">}, </font>
<font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product {Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">ASP.NET MCV 提高</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Category = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">书籍</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">34.9M</font><font style="color:#000000;">} </font>
}
};
}

接下来我们继续在上面Main方法中来调用查询方法Filter:

Func
<font style="color:#0000FF;">return</font> prod.Category == <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">水果</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#000000;">;</font>
};
//调用Filter,查询分类为“水果”的商品IEnumerable
Console.WriteLine(<font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">商品名称: {0}, 单价: {1:c}</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#000000;">, prod.Name, prod.Price);</font>
}
Console.ReadKey();

输出结果为:
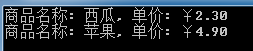
上面我们使用的是委托和匿名函数来处理用户查询逻辑,并把它传递给Filter方法,满足了前面所说的需求。但若使用Lambda表达式代替上面的匿名函数能使上面的代码看上去更简洁更人性化,如下代码所示:
Func
IEnumerable
没有了delegate关键字,没有了大小括号,看上去更舒服。当然上面两行代码可以继续简化为一行:
IEnumerable
这三种方式输出结果都是一样的。然后,我们还可以通过Lambda表达式实现各种需求的查询:
//查询分类为“水果”或者单价大于30元的商品IEnumerable
prod.Category == <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">水果</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font> || prod.Price > <font style="color:#800080;">30</font>
);
通过这个示例,相信大家已经清晰的了解并撑握了Lambda表达式的简单应用,而这就足够了:)。
6.LINQ
最后简单回顾一下LINQ。LINQ(Language Integrated Query语言集成查询)是 VS 2008 和 .NET Framework 3.5 版中一项突破性的创新,它在对象领域和数据领域之间架起了一座桥梁。
上面讲Lambda表达式时,用到的查询结果集的方式未免还是有点麻烦(因为自定义了一个Filter扩展方法),而Linq本身就集合了很多扩展方法,我们可以直接使用,大大的简化了编写查询代码的工作。例如,对于这样一个数据集合:

Product[] products = {
<font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product {Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">西瓜</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Category = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">水果</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">2.3M</font><font style="color:#000000;">}, </font>
<font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product {Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">苹果</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Category = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">水果</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">4.9M</font><font style="color:#000000;">}, </font>
<font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product {Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">空心菜</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Category = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">蔬菜</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">2.2M</font><font style="color:#000000;">}, </font>
<font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font> Product {Name = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">地瓜</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Category = <font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">蔬菜</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font>, Price = <font style="color:#800080;">1.9M</font><font style="color:#000000;">} </font>
};

如果要查询得到价钱最高的三个商品信息,如果不使用Linq,我们可能会先写一个排序方法,对products根据价钱由高到低进行排序,排序时需要创建一个新的Product[]对象用于存储排序好的数据。但用Linq可大大减少工作量,一两句代码就能搞定。如下代码所示,查出价钱最高的三个商品:

<font style="color:#0000FF;">orderby</font><font style="color:#000000;"> product.Price descending</font>
<font style="color:#0000FF;">select</font> <font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font><font style="color:#000000;"> {</font>
product.Name,
product.Price
};
Console.WriteLine(<font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">商品:{0},价钱:{1}</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#000000;">, p.Name, p.Price);</font>
<font style="color:#0000FF;">if</font> (++count == <font style="color:#800080;">3</font>) <font style="color:#0000FF;">break</font><font style="color:#000000;">;</font>
}
Console.ReadKey();

输出结果:
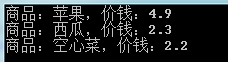
能熟练使用Linq是一件很爽的事情。上面的Linq语句和我们熟悉的SQL查询语句类似,看上去非常整洁且易懂。但并不是每一种SQL查询语句在C#都有对应的关键字,有时候我们需要使用另外一种Linq查询方式,即“点号”方式的Linq查询方式,这种方式中的Linq查询方法都是扩展方法。如下面这段代码和上面实现的效果是一样的:

.OrderByDescending(e =><font style="color:#000000;"> e.Price)</font>
.Take(<font style="color:#800080;">3</font><font style="color:#000000;">)</font>
.Select(e => <font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font><font style="color:#000000;"> { e.Name,e.Price});</font>
Console.WriteLine(<font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">商品:{0},价钱:{1}</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#000000;">, p.Name, p.Price);</font>
}
Console.ReadKey();

虽然类SQL的Linq查询方式比这种方式看上去更一目了然,但并不是每一种SQL查询语句在C#都有对应的关键字,比如这里的Take扩展方法就是类SQL的Linq查询语法没有的功能。
注意,有些Linq扩展方法分为“延后查询”(deferred)和“即时查询”(immediate)。延后查询意思是拥有“延后查询”扩展方法的Linq语句只有当调用结果集对象的时候才开始真正执行查询,即时查询则是立即得到结果。比如上面的Linq语句的OrderByDescending扩展方法就是一个“延后查询”方法,当程序执行到Linq语句定义部分时并没有查询出结果并放到results对象中,而是当程序执行到foreach循环时才真正执行Linq查询语句得到查询结果。我们可以做个测试,在Ling语句之后,我们再将products[1]对象重新赋值,如下代码所示:

.OrderByDescending(e =><font style="color:#000000;"> e.Price)</font>
.Take(<font style="color:#800080;">3</font><font style="color:#000000;">)</font>
.Select(e => <font style="color:#0000FF;">new</font><font style="color:#000000;"> { e.Name, e.Price });</font>
products[1] = new Product { Name = “榴莲“, Category = “水果“, Price = 22.6M };
//打印 foreach (var p in results) {Console.WriteLine(<font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#800000;">商品:{0},价钱:{1}</font><font style="color:#800000;">"</font><font style="color:#000000;">, p.Name, p.Price);</font>
}
Console.ReadKey();

输出结果为:
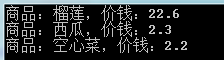
我们发现results是重新赋值之后的结果。可想而知,查询语句是在results被调用之后才真正执行的。
Linq非常强大也非常好用,这里只是把它当作一个学习ASP.NET MVC之前需掌握的知识点进行简单回顾。要灵活熟练地使用Linq还需要经常使用才行。

