一、题目描述
题目一:N 皇后问题
题目要求:分别采用随机重启爬山法、最小冲突法和遗传算法求解 n 皇后问题
题目二:Wumpus World
题目三:采用 α-β 剪枝算法实现井字棋游戏
题目要求:
- 图形化界面。
- 随机选取先手后手。
- 可以人-计算机或计算机-计算机
二、基本思想
题目一:N 皇后问题
随机重启爬山法
随机爬山法为爬山法的一种变形,它在上山移动中随机地选择下一步;被选中的概率可能随着上山移动的陡峭程度不同而不同。这种算法通常比最陡上升算法的收敛速度慢不少,但是在某些状态空间地形图上它能找到更好的解。首选爬山法实现了随机爬山法,随机地生成后继结点直到生成一一个优于当前结点的后继。这个算法在后继结点很多的时候(例如上千个)是个好策略。
但到随机爬山法是不完备的——它们经常会在目标存在的情况下因为被局部极大值卡住而找不到目标。随机重启爬山法( random restart hill climbing)吸纳了
这种思想:“如果一开始没有成功,那么尝试,再尝试(重新开始搜索)”。它通过随机生成初始状态来导引爬山法搜索,直到找到目标。这个算法完备的概率接近于1。
爬山选择节点种类:
- 简单爬山(Simple Hill climbing): 它逐个检查相邻节点,并选择第一个相邻节点作为下一个节点,优化当前开销。
- 评估初始状态。如果它是一个目标状态,那么停止并返回成功。否则,将初始状态设置为当前状态。
- 循环,直到找到解决方案状态,或者没有新的可以应用于当前状态的运算符。
- 选择一个尚未应用于当前状态的状态,并应用它来生成一个新状态。
- 执行这些操作来评估新的状态。
- 如果当前状态是目标状态,那么停止并返回成功。
- 如果它优于当前状态,那么将其设置为当前状态并进一步处理。
- 如果它不比当前状态好,那么继续循环,直到找到解决方案。
- 退出
- 最速爬山(Steepest-Ascent Hill climbing): 它首先检查所有相邻的节点,然后选择下一个节点最接近解状态的节点。
- 评估初始状态。
- 重复这些步骤,直到找到解决方案或者当前状态不变为止。
- 假设“目标”为一种状态,以使当前状态的任何后继者都比它更好。
- 对于适用于当前状态的每个运算符
- 应用新的操作符并创建一个新的状态
- 评估新状态
- 如果此状态是目标状态,则退出,否则与“目标”比较
- 如果这个状态比“目标”要好,就把这个状态设为“目标”
- 如果目标优于当前状态,将当前状态设置为目标
- 随机爬山(Stochastic hill climbing): 在决定选择哪个节点之前,它不会检查所有相邻的节点。它只是随机选择一个邻近节点,然后决定(基于该邻居的改进量)是移动到该邻居还是检查另一个邻居。
最小冲突法
最小冲突算法是一种搜索算法或启发式方法来解决约束补偿问题。为 CSP 的所有变量分配一个初始值 ,该算法会从一组变量中随机选择一个冲突违反CSP约束的变量。然后它将最小化冲突次数的值赋给这个变量。如果有一个以上具有最少数量冲突的值,则会随机选择一个。重复进行随机变量选择和最小冲突值分配的过程,直到找到解决方案或达到预选的最大迭代次数为止。因为当所有变量都有一个赋值(称为完全状态,complete state)时,CSP 可以被解释为一个局部搜索问题,所以最小冲突算法可以被看作是一个修复启发式算法,它选择冲突次数最少的状态。
尽管算法中未指定,但良好的初始分配对于快速解决问题至关重要。使用具有一定程度随机性的贪婪算法,并在其他分配均无法满足要求时允许变量分配打破约束。这种随机性有助于最小冲突避免贪婪算法初始分配创建的局部最小值。事实上,对最小冲突解决方案反应最好的约束补偿问题在贪婪算法几乎能解决问题的情况下表现得很好。
遗传算法
遗传算法(genetic algorithm, GA)是随机束搜索的一个变形,它通过把两个父状态结合来生成后继,而不是通过修改单一状态进行。这和随机剪枝搜索一样,与自然选择
类似,除了我们现在处理的是有性繁殖而不是无性繁殖。像束搜索一样,遗传算法也是从 k 个随机生成的状态开始,我们称之为种群。每个状态,或称个体,用一个有限长度的字符串表示一通常是0、1串。
遗传算法的每个状态都由它的目标函数或(用遗传算法术语)适应度函数给出评估值。对于好的状态,适应度函数应返回较高的值,所以在八皇后问题中,我们用不相互攻击的皇后对的数目来表示。并按照设置的概率随机地选择两对进行繁殖。请注意其中一个个体被选中两次而有一个一次也没被选中。对于要配对的每对个体,在字符串中随机选择一个位置作为杂交点。
像随机束搜索一样,遗传算法结合了上山趋势、随机探索和在并行搜索线程之间交换信息。遗传算法最主要的优点,如果算是,来自于杂交操作。然而可以在数学上证明,如果基因编码的位置在初始的时候就允许随机转换,杂交就没有优势了。直观上说,杂交的优势在于它能够将独立发展出来的能执行有用功能的字符区域结合起来,因此提高了搜索的粒度。例如,将前三个皇后分别放在位置2、4和6 (互不攻击)就组成了一个有用的区域,它可以和其他有用的区域组合起来形成问题的解。
题目二:Wumpus World
Wumpus World PEAS 描述:
- 性能度量:
- 带着金子爬出洞口 +1000
- 掉入洞或者被Wumpus吃掉 -1000
- 每采用一个行动得-1
- 用掉箭 -10
- 游戏在 Agent 死亡 或 Agent 出洞时结束。
- 环境:
4X4的房间网格。Agent 每次都从标号为[1, 1]的方格出发,面向右方。
金子和 Wumpus 的位置按均匀分布随机选择除了起始方格以外的方格。另外,除了起始方格以外的任一方格都可能是无底洞,概率为0.2。
- 执行器:
- Agent 可以向前移动、左转90°或者右转90°。
- 如果它碰上无底洞或者活着的Wumpus, 它将悲惨地死去(进入死Wumpus的方格是安全的)。
- 如果Agent前方是一堵墙,那么不能向前移动。
- 行动Grab可以用于捡起 Agent 所处方格内的物体。
- 行动Shoot可以用于向 Agent 所正对的方向射箭,箭向前运动直到击中 Wumpus (此时Wumpus将被杀死)或者击中墙。Agent 只有一支箭,因此只有第一个 Shoot 行动有效。
- 行动Climb用于爬出洞口,只能从方格[1, 1]中爬出。
- 传感器: Agent 具有五个传感器,每个都可以提供一些单一信息,这5种感知信息以符号列表形式提供给 Agent。
- 在Wumpus 所在之处以及与之直接相邻(非对角的)的方格内,Agent 可以感知到臭气。
- 在与无底洞直接相邻的方格内,Agent 能感知到微风。
- 在金子所处的方格内,Agent 感知到闪闪金光。
- 当Agent撞到墙时,它感知到撞击。
- 当Wumpus被杀死时,它发出的悲惨嚎叫在洞穴内的任何地方都可以感知到。
联机搜索
联机搜索问题只能通过 Agent 执行行动来求解,它不是纯粹的计算过程。
我们假设环境是确定的和完全可观察的,我们规定 Agent 只知道以下信息:
- ACTIONS(s),返回状态s下可能进行的行动列表;单步耗散函数c(s, a, s’)——注意 Agent 知道行动的结果为状态s’时才能用;
- GOAL-TEST(s)。
需要注意的是,Agent 并不知道 RESULT(s, a) 的值,除非 Agent 确实是在状态 s 下执行了行动 a。
在每个活动之后,联机 Agent 都能接收到感知信息,告诉它到达的当前状态;根据此信息,Agent 可以扩展自己的环境地图。可以用当前地图来决定下一步往哪里走。这种规划和活动的交替是联机搜索算法和前面讲的脱机搜索算法的不同点。另一方面,联机算法只会扩展它实际占据的结点。为了避免遍历整个搜索树去扩展下一个结点,按照局部顺序扩展结点看来更好一些。
题目三:采用 α-β 剪枝算法实现井字棋游戏
α-β 剪枝算法
α-β 剪枝可以应用于任何深度的树,很多情况下可以剪裁整个子树,而不仅仅是剪裁叶结点。一般原则是:考虑在树中某处的结点 n, 选手选择移动到该结点。如果选手在n的父结点或者更上层的任何选择点有更好的选择m,那么在实际的博弈中就永远不会到达 n。所以一旦发现关于n的足够信息(通过检查它的某些后代),能够得到上述结论,我们就可以裁剪它。
极小极大搜索是深度优先的,所以任何时候只需考虑树中某条单一路径上的结点。α-β剪枝的名称取自描述这条路径.上的回传值的两个参数:
- α = 到目前为止路径上发现的MAX的最佳选择(即极大值)
- β = 到目前为止路径上发现的MIN的最佳选择(即极小值)
- α-β 搜索中不断更新 α 和 β 的值,并且当某个结点的值分别比目前的 MAX 的 α 或者 MIN 的 β 值更差的时候剪裁此结点剩下的分支(即终止递归调用)。
三、软件设计
3.1 需求分析
题目一:N 皇后问题
分别采用随机重启爬山法、最小冲突法和遗传算法求解 n 皇后问题,并对其进行不同数据规模的性能测试,分析比较不同情况下算法的性能优劣(如运行时间、运行空间等)。题目二:Wumpus World
使用联机搜索求解 Wumpus 怪兽世界问题,使 Agent 尽可能获取高的分数。题目三:采用 α-β 剪枝算法实现井字棋游戏
采用 α-β 剪枝算法实现井字棋游戏,要求实现如下功能:
题目一:N 皇后问题
具体功能
分别实现随机重启爬山法、最小冲突法和遗传算法解决 n 皇后问题,并分析算法在不同数据规模下的性能优劣。
处理流程
- QueenChess :存储 N 皇后的棋盘数据。
- QueenTool:存储解决 N 皇后问题时要使用的一些基础函数。
- HillClimbingRandomRestart:随机爬山法算法主程序。
- MinConflictsSolver:最小冲突法主程序。
- GeneticAlgorithm:遗传算法主程序。
题目二:Wumpus World
具体功能
处理流程
- Agent:Agent 类,用于判断 agent 下一步如何执行。
- Area:存储地图上的区域信息。
- Path:查找回去的最短路径。
- WumpusGame:游戏的交互和输出。
- WumpusWorld:存储 Wumpus 世界的数据。
题目三:采用 α-β 剪枝算法实现井字棋游戏
具体功能
通过图形化界面实现人机对战或计算机-计算机对战,并实现计算机随机选取先后手。
处理流程
- Algorithms: 不同算法的封装。
- MiniMax:MiniMax 算法实现 。
- AlphaBetaPruning:α-β 剪枝算法时间。
- AlphaBetaAdvanced:α-β 剪枝算法优化(加入层数指标,防止递归过深)。
- Board:棋盘数据与规则。
-
3.3 详细设计
题目一:N 皇后问题
随机重启爬山法详细设计
随机重启爬山法通过逐列遍历棋子,并将其移动到相邻的冲突减小的行来解决 N 皇后问题,当冲突值无法通过移动行减小时,则认为已经处在了局部最小值,对棋盘进行随机重启来解决问题,出于性能考虑,当移动步数大于所设定的最大步数后,程序选择退出,避免出现陷入死循环或数据量过大,程序卡死的情况。程序运行结束后,将运行结果输出给用户。
最小冲突法函数设计
最小冲突法通过逐列遍历棋子,并将其移动到冲突最小的行来解决 N 皇后问题,同样的,出于性能考虑,当移动步数大于所设定的最大步数后,程序选择退出,避免出现陷入死循环或数据量过大,程序卡死的情况。程序运行结束后,将运行结果输出给用户。
遗传算法函数设计
遗传算法通过若干随机生成棋子布局,并选择其中冲突值较少的布局,进行交叉和变异,并对子代重复上述过程直至冲突值减少为0或遗传代数超过所设最大代数。
题目二:Wumpus World
agent 通过已经观察到的区域,对其邻接的区域进行收益判断,选择邻接区域中死亡率最低的区域,当死亡率小于可接受范围,则移动至该区域,否则返回上一区域,发现金子则取得胜利,回到起点,若剩余未访问区域的死亡率都大于可接受范围,则放弃本局游戏。最后将游戏结果输出给用户。
题目三:采用 α-β 剪枝算法实现井字棋游戏
算法在 MiniMax 算法的基础上,对不必处理的分支进行剪枝处理,加快算法执行速度,同时加入了迭代深度作为参数,防止游戏层数过深,加快游戏结束速度。
3.4 代码实现
题目一:N 皇后问题
随机重启爬山法 ```java public class HillClimbingRandomRestart { private static int n; private static int stepsClimbedAfterLastRestart = 0; private static int totalStepsClimbed = 0; private static int heuristic = 0; private static int randomRestarts = 0; private static final int MAX_STEPS = 10000000;
public static void main(String[] args) {
n = QueenTool.getNum();long startTime = System.nanoTime();run();long endTime = System.nanoTime();System.out.println("hill climbing random restart program run time: " + (endTime - startTime) / 1000000.0 + "ms");
}
public static void run() {
int presentHeuristic;// creating the initial BoardQueenChess[] presentBoard = QueenTool.generateBoard(n);// test if the present board is the solution boardpresentHeuristic = QueenTool.findHeuristic(presentBoard);while ((presentHeuristic != 0) && (totalStepsClimbed < MAX_STEPS)) {// get the next boardpresentBoard = hillClimbing(presentBoard);presentHeuristic = heuristic;}if (totalStepsClimbed < MAX_STEPS) {//Printing the solutionSystem.out.println("Solution to " + n + " queens using hill climbing with random restart:");QueenTool.printBoard(presentBoard);System.out.println("\nTotal number of Steps Climbed: " + totalStepsClimbed);System.out.println("Number of random restarts: " + randomRestarts);System.out.println("Steps Climbed after last restart: " + stepsClimbedAfterLastRestart);} else {System.out.println("Total Steps is bigger than max Steps!");}
}
/*** Method to get the next board with lower heuristic** @param presentBoard p* @return lower heuristic chess board*/public static QueenChess[] hillClimbing(QueenChess[] presentBoard) {QueenChess[] nextBoard = new QueenChess[n];QueenChess[] tmpBoard = new QueenChess[n];int presentHeuristic = QueenTool.findHeuristic(presentBoard);int bestHeuristic = presentHeuristic;int tempHeuristic;// Copy present board as best board and temp boardfor (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {nextBoard[i] = new QueenChess(presentBoard[i].getRow(), presentBoard[i].getColumn());tmpBoard[i] = nextBoard[i];}// Iterate each columnfor (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {// recovery the previous column and traverse the current column to find the function with the smallest heuristic valueint col = (i - 1 + n) % n;tmpBoard[col] = new QueenChess(presentBoard[col].getRow(), presentBoard[col].getColumn());tmpBoard[i] = new QueenChess(0, tmpBoard[i].getColumn());// Iterate each rowfor (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {tempHeuristic = QueenTool.findHeuristic(tmpBoard);if (tempHeuristic < bestHeuristic) {bestHeuristic = tempHeuristic;for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {nextBoard[k] = new QueenChess(tmpBoard[k].getRow(), tmpBoard[k].getColumn());}}//Move the queenif (tmpBoard[i].getRow() != n - 1) {tmpBoard[i].move(1, n);}}}//Check whether the present bord and the best board found have same heuristic//Then randomly generate new board and assign it to best boardif (bestHeuristic == presentHeuristic) {randomRestarts++;stepsClimbedAfterLastRestart = 0;nextBoard = QueenTool.generateBoard(n);heuristic = QueenTool.findHeuristic(nextBoard);} else {heuristic = bestHeuristic;}totalStepsClimbed++;stepsClimbedAfterLastRestart++;return nextBoard;}
}
- 遗传算法```javapublic class GeneticAlgorithm {private static int n;private static final double MUTATE_RATE = 0.02;private static final int TIMES = 10000;public static void main(String[] args) {n = QueenTool.getNum();long startTime = System.nanoTime();run();long endTime = System.nanoTime();System.out.println("genetic algorithm program run time: " + (endTime - startTime) / 1000000.0 + "ms");}public static void run() {int[] father = init();int[] mother = init();for (int i = 0; i < TIMES; i++) {List<Integer[]> son = new ArrayList<>();for (int j = 0; j < 4 * n; j++) {son.add(Arrays.stream(crossover(father, mother)).boxed().toArray(Integer[]::new));}mutate(son);Map<Integer[], Integer> res = select(son);for (Map.Entry<Integer[], Integer> c : res.entrySet()) {if (c.getValue() == 0) {System.out.println("Solution to " + n + " queens using genetic algorithm:");QueenTool.printBoard(c.getKey());return;}}father = Arrays.stream(res.entrySet().iterator().next().getKey()).mapToInt(k -> k).toArray();mother = Arrays.stream(res.entrySet().iterator().next().getKey()).mapToInt(k -> k).toArray();}System.out.println("Generations are more than the max number of iterations!");}/*** use List to shuffle and trans to array to return** @return a random array of the queens chess board*/private static int[] init() {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {list.add(i);}Collections.shuffle(list);return list.stream().mapToInt(i -> i).toArray();}/*** Chromosomal crossover for genetic recombination** @param originFather father of the son* @param originMother mother of the son* @return the son*/private static int[] crossover(int[] originFather, int[] originMother) {int[] father = Arrays.copyOf(originFather, n);int[] mother = Arrays.copyOf(originMother, n);int[] son = new int[n];int[] rend = new int[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {rend[i] = Math.random() >= 0.5 ? 0 : 1;}int f = 0, m = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {// move the point of chromosomalif (rend[i] == 0) {for (f = 0; f < n; f++) {if (father[f] != 0) {break;}}} else {for (m = 0; m < n; m++) {if (mother[m] != 0) {break;}}}// Inherit parents' genesson[i] = rend[i] == 0 ? father[f] : mother[m];// Set the inherited genes to 0for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {if (father[j] == son[i]) {father[j] = 0;}if (mother[j] == son[i]) {mother[j] = 0;}}}return son;}/*** mutate to suit for the env* for the chromosome in chromosomes* choose two gene randomly to mutate** @param chromosomes chromosomes of the obj*/private static void mutate(List<Integer[]> chromosomes) {for (Integer[] chromosome : chromosomes) {if (Math.random() > MUTATE_RATE) {continue;}int i = (int) (Math.random() * n);int j = (int) (Math.random() * n);if (i == j) {continue;}// three times xor to swap two numbers to hybridizechromosome[i] ^= chromosome[j];chromosome[j] ^= chromosome[i];chromosome[i] ^= chromosome[j];}}private static Integer fit(Integer[] result) {int res = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {if (Math.abs(result[i] - result[j]) == j - i || result[i].equals(result[j])) {res++;}}}return res;}/*** method to choose the best individual** @param son subgroup of the population* @return the best individual of the subgroup*/private static Map<Integer[], Integer> select(List<Integer[]> son) {Map<Integer[], Integer> result = son.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(x -> x, GeneticAlgorithm::fit));result = result.entrySet().stream().sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByValue()).collect(Collectors.toMap(Map.Entry::getKey, Map.Entry::getValue, (oldValue, newValue) -> oldValue, LinkedHashMap::new));return result;}}
最小冲突法 ```java public class MinConflictsSolver { private static int n; private static int totalStepsMoved = 0; private static final int MAX_STEPS = 100000;
/**
- row[i] shows the queen of the i row,col[i] shows the queen of the i col
- mainDiag[i] shows the queen of the i main diag
- secondaryDiag[i] shows the queen of the i secondary diag
- Additional explanation
- The row-col values on the diagonal from top left to bottom right are the same,use this as the index of the diag
Plus n - 1 to avoid the value is negative value */
static int[] row; static int[] col; static int[] mainDiag; static int[] secondaryDiag;
public static void main(String[] args) { n = QueenTool.getNum(); long startTime = System.nanoTime(); run(); long endTime = System.nanoTime(); System.out.println(“min conflicts program run time: “ + (endTime - startTime) / 1000000.0 + “ms”); }
public static void run() { row = new int[n]; col = new int[n]; mainDiag = new int[2 n]; secondaryDiag = new int[2 n];
System.out.println(“n is: “ + n); // creating the initial Board QueenChess[] board = QueenTool.generateBoard(n); update(board, row, col, mainDiag, secondaryDiag);
int heuristic = QueenTool.findHeuristic(board); if (heuristic != 0) {
minConflictsSolve(board);
}
if (totalStepsMoved < MAX_STEPS) {
//Printing the solutionSystem.out.println("Solution to " + n + " queens using min conflicts Solver");QueenTool.printBoard(board);System.out.println("Total number of Steps Moved: " + totalStepsMoved);
} else {
System.out.println("Total Steps is bigger than max Steps!");
} }
public static void minConflictsSolve(QueenChess[] board) { boolean isGood = false; while (!isGood && totalStepsMoved < MAX_STEPS) {
// Iterate each columnfor (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {totalStepsMoved++;if (adjustRow(i, board)) {isGood = true;break;}}
} }
/**
- @param column adjust row for this column
@return is adjust good */ public static boolean adjustRow(int column, QueenChess[] board) { // 通过列得到行 int curRow = board[column].getRow(); // 最佳行号,设置为当前行,然后更新 int bestRow = curRow;
// row 不减一的原因是交换任然保证每行每列都有一个而已 // 现在还没移过去 // 对角线冲突数为当前对角线皇后数减一 int minConflict =
row[bestRow]+ mainDiag[getP(bestRow, column, n)] - 1+ secondaryDiag[getC(bestRow, column)] - 1;
// Iterate through each row for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i == curRow) {continue;}int conflict = row[i] + mainDiag[getP(i, column, n)] + secondaryDiag[getC(i, column)];// update dataif (conflict < minConflict) {minConflict = conflict;bestRow = i;}
}
// update col, mainDiag, secondaryDiag if (bestRow != curRow) {
// minus current row queenrow[curRow]--;mainDiag[getP(curRow, column, n)]--;secondaryDiag[getC(curRow, column)]--;// add best row queenrow[bestRow]++;mainDiag[getP(bestRow, column, n)]++;secondaryDiag[getC(bestRow, column)]++;// 注意,这里我们没有移动 在这个列上的之前的那个行上的皇后// move chessboard[column].row = bestRow;// return is this col move successfulif (row[curRow] == 1 && row[bestRow] == 1&& mainDiag[getP(bestRow, column, n)] == 1&& secondaryDiag[getC(bestRow, column)] == 1) {return satisfy(board);}
}
// any else return false; }
public static boolean satisfy(QueenChess[] board) { // Iterate through each row for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (row[board[i].getRow()] != 1 ||mainDiag[getP(board[i].getRow(), i, n)] != 1 ||secondaryDiag[getC(board[i].getRow(), i)] != 1) {return false;}
} return true; }
public static void update(QueenChess[] board, int[] row, int[] col, int[] mainDiag, int[] secondaryDiag) { int n = row.length; // 每列恰好一个皇后 // 行后续再做初始化 for (int point = 0; point < n; point++) {
col[point] = 1;row[point] = 0;
} // 初始化 diag 皇后数 for (int point = 0; point < 2 * n - 1; point++) {
mainDiag[point] = 0;secondaryDiag[point] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
row[board[i].getRow()]++;mainDiag[getP(board[i].getRow(), board[i].getColumn(), n)]++;secondaryDiag[getC(board[i].getRow(), board[i].getColumn())]++;
} }
/**
- 给定二维矩阵的一个点坐标
- 返回其对应的右上到左下的对角线编号 *
@return the index of the Diag */ public static int getP(int row, int column, int n) { return row - column + n - 1; }
public static int getC(int row, int column) { return row + column; } }
<a name="ZUmDG"></a>#### 题目二:Wumpus World```javapublic class Agent {WumpusWorld world;int deathArea = 3;int unknownAreas;double acceptableRisk = 0.5;double[][] deathProbability;boolean[][] isTagged;Area agentArea;int score = 0;int steps;boolean isAgentAlive = true;boolean isGiveUp = false;boolean isWumpusAlive = true;boolean isGrabGold = false;/*** the 4 different directions of the agent at a specific time(step)*/final static int NORTH = 0;final static int EAST = 1;final static int SOUTH = 2;final static int WEST = 3;String[] printDirection = {"↑", "→", "↓", "←"};/*** default direction is east*/private int direction = 1;/*** init agents*/public Agent(WumpusWorld wumpusWorld) {this.world = wumpusWorld;int size = world.getSize();unknownAreas = size * size;deathProbability = new double[size + 2][size + 2];isTagged = new boolean[size + 2][size + 2];agentArea = wumpusWorld.getArea(size, 1);freshDeathProbability();freshDeathProbability();markArea(agentArea);}/*** start auto playing the game*/public void simulate() {if (!go(think())) {isGiveUp = true;}}// 搜寻 area 找死亡率小于可接受风险的概率的区域,未找到则放弃private int think() {int row = agentArea.getRow();int col = agentArea.getCol();double bestHeuristic = Integer.MAX_VALUE;int bestDirection = -1;if (!world.getArea(row - 1, col).getHasWall()&& !world.getArea(row - 1, col).getVisited()&& deathProbability[row - 1][col] < bestHeuristic) {bestHeuristic = deathProbability[row - 1][col];bestDirection = NORTH;}if (!world.getArea(row + 1, col).getHasWall()&& !world.getArea(row + 1, col).getVisited()&& deathProbability[row + 1][col] < bestHeuristic) {bestHeuristic = deathProbability[row + 1][col];bestDirection = SOUTH;}if (!world.getArea(row, col + 1).getHasWall()&& !world.getArea(row, col + 1).getVisited()&& deathProbability[row][col + 1] < bestHeuristic) {bestHeuristic = deathProbability[row][col + 1];bestDirection = EAST;}if (!world.getArea(row, col - 1).getHasWall()&& !world.getArea(row, col - 1).getVisited()&& deathProbability[row][col - 1] < bestHeuristic) {bestHeuristic = deathProbability[row][col - 1];bestDirection = WEST;}if (steps > world.getSize() * world.getSize() * 2.5) {isGiveUp = true;}// String pd = bestDirection == -1 ? "@" : printDirection[bestDirection];// System.out.println("deathProbability: " + bestHeuristic);// System.out.println("bestDirection: " + pd);return bestHeuristic >= acceptableRisk ? -1 : bestDirection;}public boolean go(int direction) {...}public void printWorld(boolean isKonwn) {...}public void turnLeft() {...}public void turnRight() {...}public boolean moveForward() {...}public boolean goEast() {...}public boolean goWest() {...}public boolean goNorth() {...}public boolean goSouth() {...}public boolean goBack() {...}public void markArea(Area area) {...}private void markAreaDangerous(int row, int col) {...}private void markAreaSafe(int row, int col) {...}/*** prepare to optimize the probability of hitting wumpus* undo*/public void chooseDirectionToShoot() {if (isWumpusAlive()) {shootWumpus();}}public boolean shootWumpus() {...}public void grabGold() {}public boolean isAlive() {...}public boolean isGiveUp() {return isGiveUp;}public boolean isGrabGold() {return isGrabGold;}public boolean isWumpusAlive() {return isWumpusAlive;}public void wumpusScream() {...}public void setAcceptableRisk(double acceptableRisk) {this.acceptableRisk = acceptableRisk;}public void printDeathP() {...}private int updateUnknownArea(){...}public void goBackHome() {...}}
题目三:采用 α-β 剪枝算法实现井字棋游戏
class AlphaBetaAdvanced {private static double maxDepth;/*** AlphaBetaAdvanced cannot be instantiated.*/private AlphaBetaAdvanced() {}/*** Execute the algorithm.** @param player the player that the AI will identify as* @param board the Tic Tac Toe board to play on* @param maxDepth the maximum depth*/static void run(Board.State player, Board board, double maxDepth) {if (maxDepth < 1) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Maximum depth must be greater than 0.");}AlphaBetaAdvanced.maxDepth = maxDepth;alphaBetaPruning(player, board, Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY, Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY, 0);}/*** The meat of the algorithm.** @param player the player that the AI will identify as* @param board the Tic Tac Toe board to play on* @param alpha the alpha value* @param beta the beta value* @param currentDepth the current depth* @return the score of the board*/private static int alphaBetaPruning(Board.State player, Board board, double alpha, double beta, int currentDepth) {if (currentDepth++ == maxDepth || board.isGameOver()) {return score(player, board, currentDepth);}if (board.getTurn() == player) {return getMax(player, board, alpha, beta, currentDepth);} else {return getMin(player, board, alpha, beta, currentDepth);}}/*** Play the move with the highest score.** @param player the player that the AI will identify as* @param board the Tic Tac Toe board to play on* @param alpha the alpha value* @param beta the beta value* @param currentDepth the current depth* @return the score of the board*/private static int getMax(Board.State player, Board board, double alpha, double beta, int currentDepth) {int indexOfBestMove = -1;for (Integer theMove : board.getAvailableMoves()) {Board modifiedBoard = board.getDeepCopy();modifiedBoard.move(theMove);int score = alphaBetaPruning(player, modifiedBoard, alpha, beta, currentDepth);if (score > alpha) {alpha = score;indexOfBestMove = theMove;}if (alpha >= beta) {break;}}if (indexOfBestMove != -1) {board.move(indexOfBestMove);}return (int) alpha;}/*** Play the move with the lowest score.** @param player the player that the AI will identify as* @param board the Tic Tac Toe board to play on* @param alpha the alpha value* @param beta the beta value* @param currentDepth the current depth* @return the score of the board*/private static int getMin(Board.State player, Board board, double alpha, double beta, int currentDepth) {int indexOfBestMove = -1;for (Integer theMove : board.getAvailableMoves()) {Board modifiedBoard = board.getDeepCopy();modifiedBoard.move(theMove);int score = alphaBetaPruning(player, modifiedBoard, alpha, beta, currentDepth);if (score < beta) {beta = score;indexOfBestMove = theMove;}if (alpha >= beta) {break;}}if (indexOfBestMove != -1) {board.move(indexOfBestMove);}return (int) beta;}/*** Get the score of the board. Takes depth into account.** @param player the play that the AI will identify as* @param board the Tic Tac Toe board to play on* @param currentPly the current depth* @return the score of the board*/private static int score(Board.State player, Board board, int currentPly) {if (player == Board.State.Blank) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Player must be X or O.");}Board.State opponent = (player == Board.State.X) ? Board.State.O : Board.State.X;if (board.isGameOver() && board.getWinner() == player) {return 10 - currentPly;} else if (board.isGameOver() && board.getWinner() == opponent) {return -10 + currentPly;} else {return 0;}}}
3.5 测试
运行环境
随机重启爬山法、最小冲突法和遗传算法均能解决 N 皇后问题,但随机重启爬山法和遗传算法解决速度较慢。
- 题目二:Wumpus World
agent 可以在游戏中取得平均260以上的分数,即超过 1/4 以上取得胜利。
- 题目三:采用 α-β 剪枝算法实现井字棋游戏
α-β 剪枝算法可以达到人机对战中机器不会失落败,即机器只会出现胜利和平局两种情况。
四、运行结果及分析
题目一:N 皇后问题
随机重启爬山法、最小冲突法和遗传算法分别在 n = 10、n = 50、 n = 100、 n = 1000的运行时间如下表所示:
| 算法/数据规模 | n = 10 | n = 50 | n = 100 | n = 1000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 随机重启爬山法 | 8.1840ms | 3703.4996ms | NaN | NaN |
| 最小冲突法 | 5.4067ms | 7.1119ms | 7.9116ms | 27.0772ms |
| 遗传算法 | 313.9565ms | 9051.1581ms | 71101.8417ms | NaN |
通过上表可以看出,最小冲突法是解决 N 皇后最快的方法,且运行时间基本不受数据规模的影响,相比之下,随机重启爬山法随着数据规模的提升,运行时间迅速上升,在 n = 100 时短时间内已经无法获得问题的解。
遗传算法速度较最小冲突法较慢,但比随机重启爬山法要好一点,但是遗传算法在 n 取值较小时运行时间同样较慢。
题目二:Wumpus World
wumpus world 在随机初始世界并运行 10000 次后,得到的数据如下:
- score: 268.0
- win times: 2791
- failed times: 0
- give up times: 7209
从数据可以看出, agent 采取了保守的策略,即放弃探索收益较低(死亡率高)的区域,在这样的策略下,agent 获取了平均 260 以上的成绩。
程序详细运行结果如下:
- 启动后,初始化地图及 agent 界面和 agent 判断的每个区域的死亡概率。
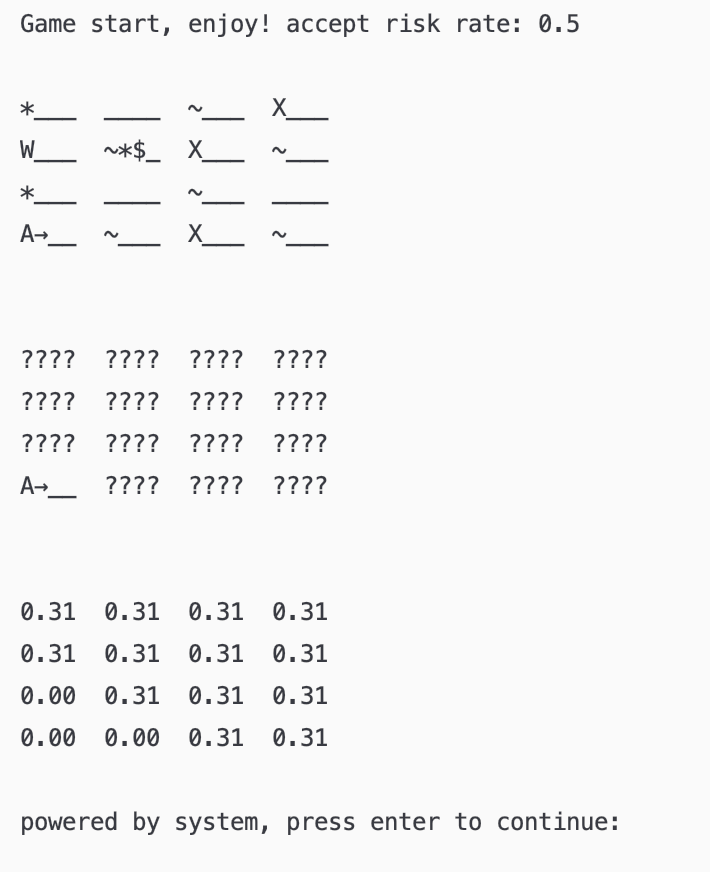
- 感受到臭味,射箭

- 捡到金子获胜
题目三:采用 α-β 剪枝算法实现井字棋游戏
- 程序启动并在左上角选择人机模式
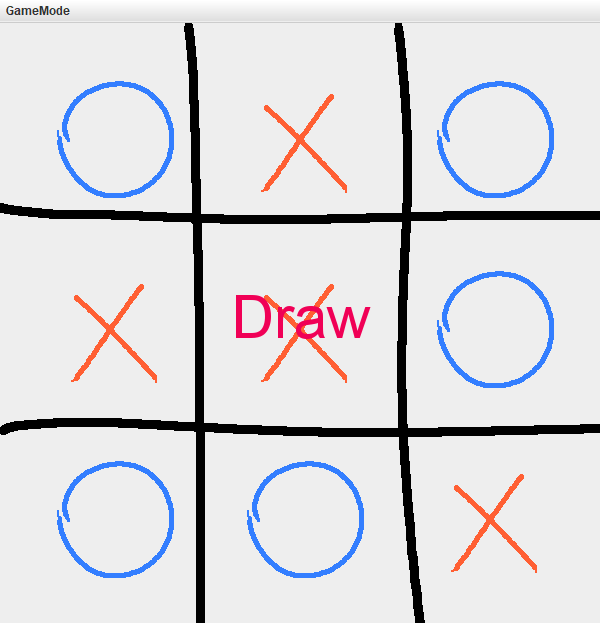
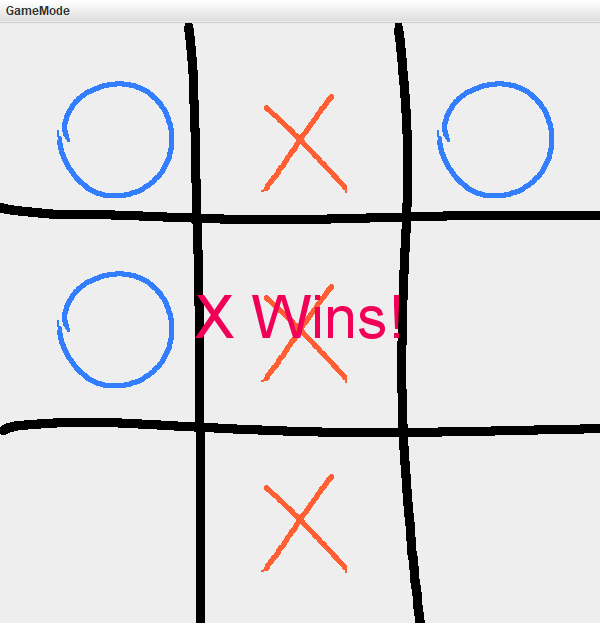
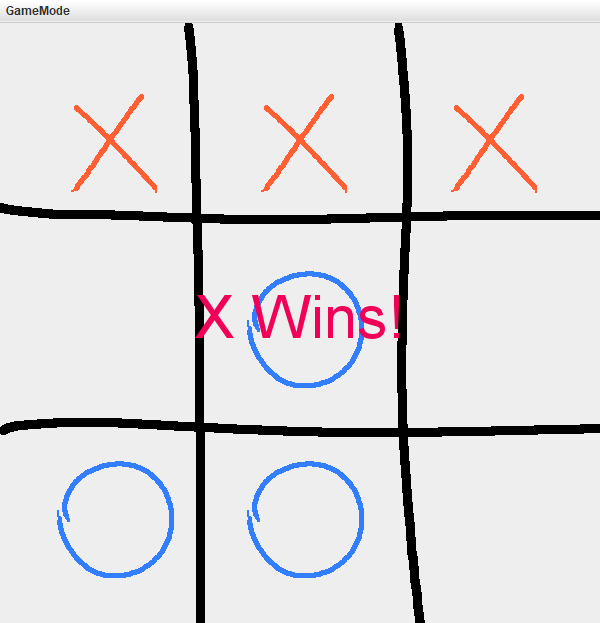
- 几局人机对战示例 (均为人(O)先手)
五、使用说明
- 推荐运行环境:
- Windows 10 64位系统
- 安装有 Java Runtime Environment 8.0 及以上
- 根据程序提示进行相应操作即可。
六、小结
题目一:N 皇后问题
验收测试时,本应性能表现最好且基本不受 N 大小影响的最小冲突法在 N=1000时却无法在有效时间内得到运行结果,经过 JProfiler 进行性能分析,发现查找冲突数的函数调用次数最多,经过分析原来简单实现的最小冲突法会在每次可能的调整都进行冲突次数查找,并且简单实现的冲突次数也要访问整个棋盘(n^2),所以导致算法性能表现极差,随后根据一篇博客,将查找冲突数的函数由 n^2 复杂度优化到线性复杂度,同时也优化了调用查找冲突的次数。代码修改后可以看出随机重启爬山法、最小冲突法和遗传算法中最小冲突法的性能表现最好,且基本不受 N 大小的影响。题目二:Wumpus World
Wumpus World 问题选择使用死亡概率作为启发值来判断移动到相邻的具体区域或选择返回,考虑到游戏目标是获取尽可能高的分数,而死亡失去的分数和得到金子后获取的分数是相等的,所以 agent 采取了保守的策略,尽量避免死亡,在测试中可以做到平均分约有260+分(10000 次测试)。题目三:采用 α-β 剪枝算法实现井字棋游戏
α-β 剪枝算法在 MiniMax 算法的基础上改进,并且又加入了层数进行优化,减少算法的运行时间同时也防止对局进行过长的时间。算法可以实现 AI 在下棋时立于不败之地。七、参考文献
[1] Norvig P . Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 4rd Edition[M].Pearson, 2020.
[2] Tanvir Sojal.Computing number of conflicting pairs in N-Queen board in Linear Time and Space Complexity[EB/OL].https://towardsdatascience.com/computing-number-of-conflicting-pairs-in-a-n-queen-board-in-linear-time-and-space-complexity-e9554c0e0645,2018-11-28.