boot 版本:2.4.4
它的作用范围(根据传递的语言获取对应的信息)目前笔者发现的有:
- 可以手动获取资源文件中对应 code 的信息
@Validated验证抛出的信息
依赖
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
默认已经有资源文件的自动配置了
# 自动配置类是这个org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfigurationspring:messages:# messages 是默认的资源包前缀,意味着只能在 classpath 下存在 messages[_en].properties 这样的文件# 想要放到其他路径下可以这样写 i18n/messagesbasename: 'messages' # 这个是默认的资源包前缀
首先准备两个资源文件
# messages.propertiesusername=张三 {0}# messages_en.propertiesusername=zhangsan {0}
编写工具类
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Componentpublic class I18nServices {// 直接注入资源包@Autowiredprivate MessageSource messageSource;public String get(String code, Object... args) {// LocaleContextHolder 会拿到相关的解析器获取到的 local// 关于这个解析器参考下面的说明return messageSource.getMessage(code, args, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());}public String get(String code) {return messageSource.getMessage(code, null, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());}}
Locale 有几种解析器,可以查看 官方文档,有一个默认配置好的 请求头解析器( org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver ),它只能通过 Accept-Language 头来改变当前访问接口的语言信息。
前端请求的时候如下携带上指定的语言信息,就能被解析到
GET {{host}}/test/i18nAuthorization: bearer {{access_token}}Accept-Language: en
对应的 controller 测试
@Autowiredprivate I18nServices i18nServices;@ApiOperation("测试")@GetMapping("i18n")public Result i18n() {final String username = i18nServices.get("username", 2);return ResultHelper.ok(username);}
这里的语言信息与资源文件的对应关系是:
messages_[en].properties# 方括号中的就是标头携带的# 很多文档都定义的是 en_US ,那么如果要想找到这个资源,你的标头就必须写 en_US
IDEA 中的 i18n 支持
idea 提供了一个 Resource Bundle Editor(资源编辑器),这个是需要我们自己在插件市场中安装的,它提供的功能就是方便你编辑多个语言版本,如下图所示
从属性文件进入
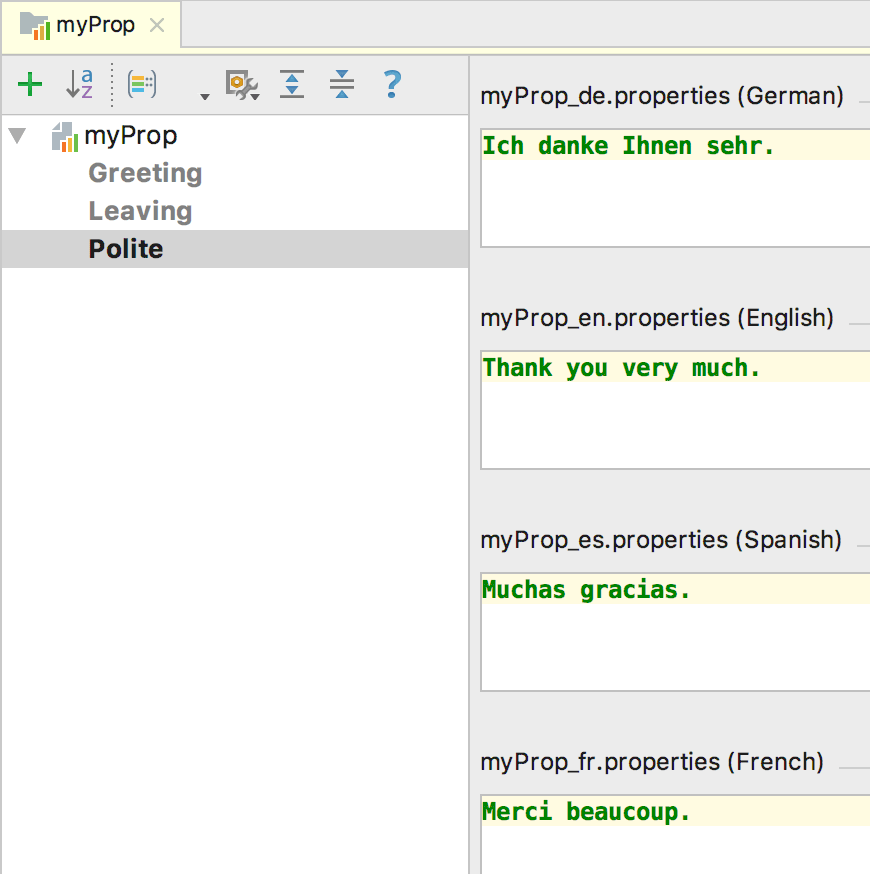
上面的界面在任意一个资源文件下侧部分都有入口,点击级可切换到对照页面 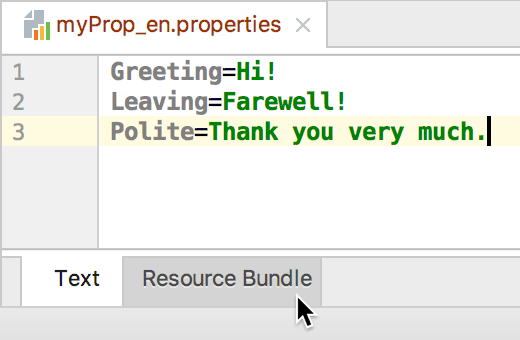
但是这种资源包的方式感觉体验要好一点,可以检测到没有对应翻译的编码,如下图所示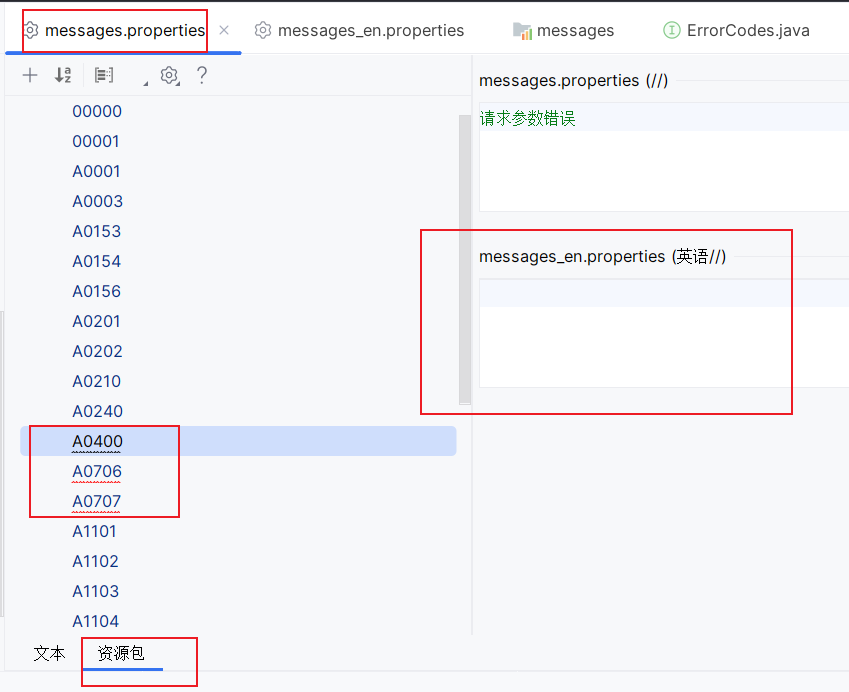
专门的的编辑器界面
上面的方式和专门的编辑器还不太一样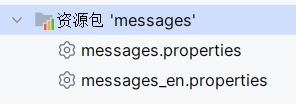 在资源包上按 F4 键可以进入
在资源包上按 F4 键可以进入
注意事项
前面虽然说资源文件中间的名称可以随意,但是其实是有标准语言的,就拿默认语言来说:当你没有传递任何语言的时候,会使用默认语言来获取对应的信息
// org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder#getLocale(org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContext)public static Locale getLocale(@Nullable LocaleContext localeContext) {if (localeContext != null) {Locale locale = localeContext.getLocale();if (locale != null) {return locale;}}return (defaultLocale != null ? defaultLocale : Locale.getDefault());}
而 Locale.getDefault() 是与当前系统环境有关系的。 如果你不设置默认语言环境,有可能在 win 系统中获取到的就是中文,在 linux 下获取到的默认语言就是英文的。
如何设置默认语言?在程序启动时,任意时机设置好默认语言就好,如下所示(最好是在启动时就设置)
@Autowiredprivate MessageSource messageSource;@PostConstructpublic void init() {if (messageSource instanceof ResourceBundleMessageSource) {((ResourceBundleMessageSource) messageSource).setDefaultLocale(Locale.CHINA);} else {// org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder#setDefaultLocaleLocaleContextHolder.setDefaultLocale(Locale.CHINA);}}
上面说到资源文件中间的语言是有标准的,这其实就是从 Locale 中获取的,比如 Locale 中的成员变量有如下
/** Useful constant for language.*/static public final Locale ENGLISH = createConstant("en", "");/** Useful constant for language.*/static public final Locale CHINESE = createConstant("zh", "");/** Useful constant for language.*/static public final Locale SIMPLIFIED_CHINESE = createConstant("zh", "CN");/** Useful constant for language.*/static public final Locale TRADITIONAL_CHINESE = createConstant("zh", "TW");
createConstant方法中,第一个是 语言,第二个参数是 国家,语言和国家都有值得话,合起来就是 语言_国家 比如中国中文:zh_CN

