Spring Boot 官方提供了以RESTful API接口方式提供性能数据的功能 Actuator(详见官方文档),直接查看这些接口的返回信息过于繁琐也不直观。而当需要监控的服务器过多的时候则更加麻烦。为此解决此问题,有人专门编写了 Web 应用程序来集中管理 Spring Boot 的性能信息。
41.1 概述
Spring Boot Admin (简称 SBA)是一个管理和监控 Spring Boot 应用程序的(非官方)开源项目。它分为Admin-Server 和Admin-Client 两个组件。多个应用程序作为Spring Boot Admin Client向为Spring Boot Admin Server注册(通过HTTP)或使用本章未涉及到的 SpringCloud 注册中心(例如Eureka,Consul)自动发现客户端。 他的展示部分是Angular JS 应用程序,以可视化的方式呈现Spring Boot Admin Client的Actuator端点上的内容,并且可以动态切换日志级别、导出日志、导出Heapdump、监控各项指标等。
Spring Boot Admin在对单一服务监控的同时也提供了集群监控方案,支持通过Eureka、Consul、ZooKeeper等注册中心的方式实现多服务监控与管理
41.2 设置监控管理服务器
尽管我们的教程和你学习的时候可以在一台机器上同时运行 Admin-Server 和 Admin-Client,但在实际的环境中,Spring Boot Admin Server 应该独立运行。
构造一个 Admin Server 非常简单:用 start.spring.io (或 IDEA)直接用初始化一个最基本的应用程序,选择 JDK 11、类型为 JAR,不需要选择任何依赖,项目生成完成后,只需要做2件事情。
41.2.1 添加依赖项
型 pom.xml 中添加 Spring Boot Admin Server starter
<dependency><groupId>de.codecentric</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-server</artifactId><version>2.5.4</version></dependency>
最新的版本可以查看 MVN Repository
之所以不需要选择任何依赖,是因为在 spring-boot-admin-server 中已经定义了下面全部必须的依赖:
- spring-boot-starter
- spring-boot-starter-webflux
- spring-boot-starter-web
- spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
- spring-boot-starter-actuator
- spring-boot-autoconfigure-processor
- spring-boot-configuration-processor
- httpclient
- reactor-extra
- lombok
- jsr305
- spring-boot-starter-mail
- hazelcast
41.2.2 添加 Admin Server 注解
在 main 加方法所在添加 @EnableAdminServer 注解引入Spring Boot Admin服务器配置
package com.longser.adminserver;import de.codecentric.boot.admin.server.config.EnableAdminServer;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;@SpringBootApplication@EnableAdminServerpublic class AdminServerApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(AdminServerApplication.class, args);}}
41.2.3 访问管理服务器
如果想要指定标准 80 以外的端口,可以在 applicaion.propertis 或者 application.yml 中指定端口号。当然这不是必须的步骤。
把自动生成的 application.propertis 改成 application.yml,然后做如下的设置
server:port: 8188
启动应用系统,用浏览器访问管理服务器,可以看到如下的界面: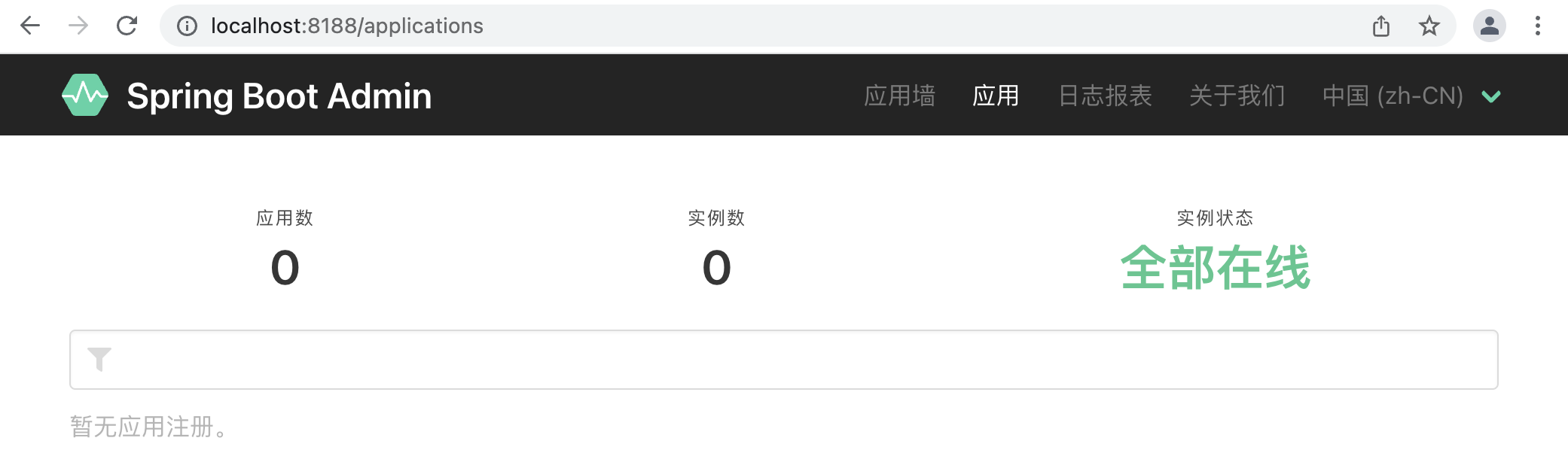
如果要通过在Servlet容器中进行 War Deployment来设置Spring Boot Admin服务器,请查看相关的示例 spring-boot-admin-sample-war。
41.3 设置客户端应用程序
41.3.1 注册客户端应用程序
Spring Boot Admin客户端在Admin Server上注册应用程序。这是通过定期向服务器发出HTTP Post请求,提供有关应用程序的信息来完成的。它还将 Jolokia 添加到您的应用程序中,以便可以通过HTTP访问JMX-bean。
你可以在服务器端直接静态配置客户端的信息(详见官方文档)。此外,还可以使用本章未涉及到的 SpringCloud 注册中心(例如Eureka,Consul)由服务器自动发现客户端。
每个要注册的应用程序都必须包含 Spring Boot Admin 客户端。为了保护暴露信息的端点(Endpoint),还需要 Spring Boot Security 保护信息安全。
1. 添加 Admin Client 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-client</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jolokia</groupId>
<artifactId>jolokia-core</artifactId>
<version>1.7.1</version>
</dependency>
最新的版本可以查看 MVN Repository
2. 指定 Admin Server 地址
在 application.yml 中添加下面的配置,指定 Admin Server 的地址
spring:
boot:
admin:
client:
url: http://localhost:8188
3. 设置暴露出的信息
在 application.yml 中添加下面的配置,定义当前应用暴露出的 Actuator 内容
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
实际上线运行的应用系统要小心选择暴露的内容,(详见Actuator官方文档)
4. 放行Actuator地址
在 SecurityConfig 中放行Actuator地址(一直放行)
private final String[] publicAPI = {
+ "/actuator/**",
5. 不对actuator的输出进行封装
默认的,我们对所有API的返回信息都进行了封装,这这会导致管理服务器无法识别的actuator输出的信息,因此需要把改成如下的样子
@Override
public boolean supports(MethodParameter returnType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) {
if(returnType.getExecutable().getDeclaringClass().getName().contains("org.springframework.boot.actuate")) {
return false;
}
return !returnType.hasMethodAnnotation(IgnoreRestful.class);
}
重新启动应用系统,在启动信息的最后看类似如下的信息代表客户端已经注册成功
[gistrationTask1] d.c.b.a.c.r.ApplicationRegistrator : Application registered itself as f7a66ade5253
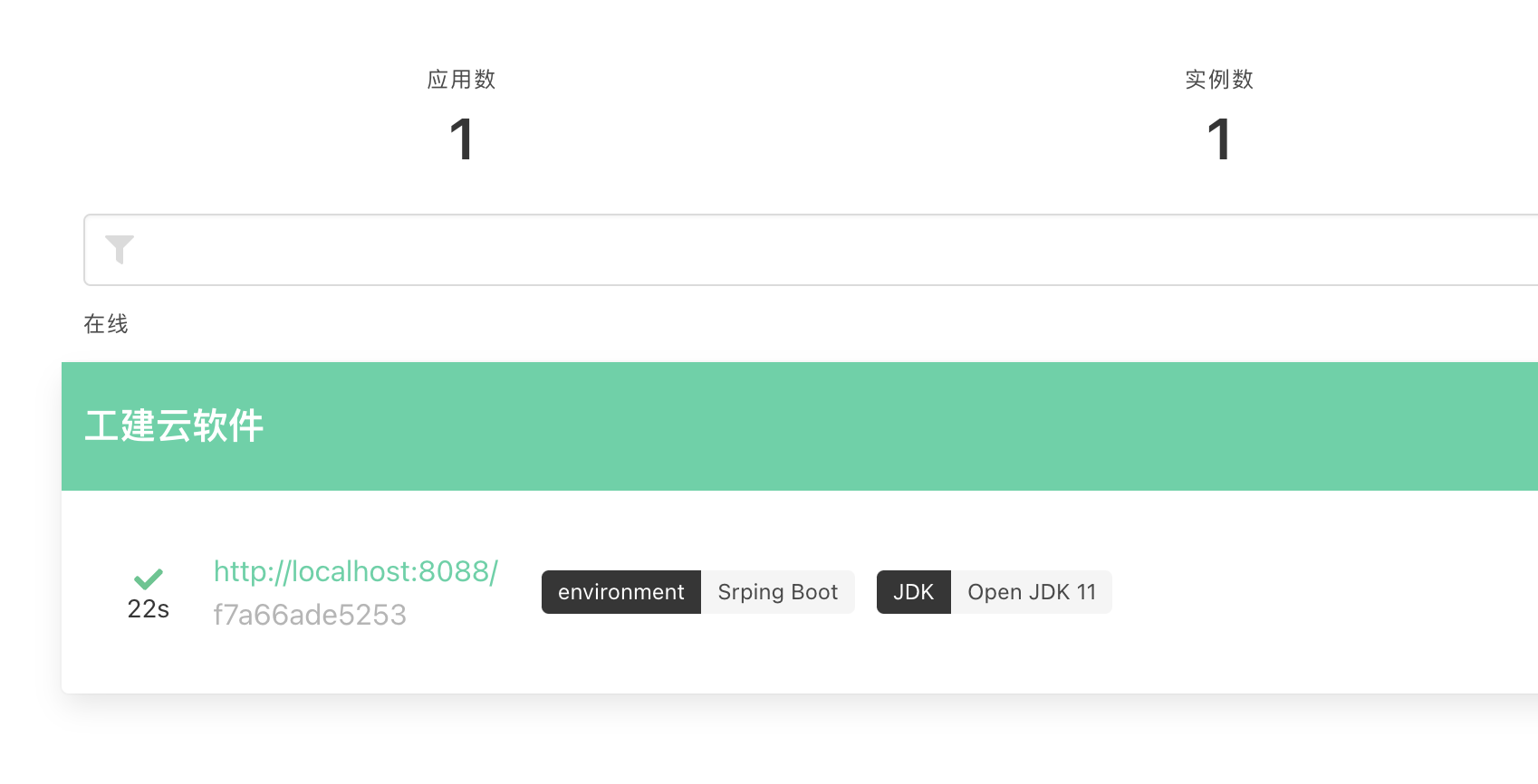
等候管理服务器页面自动刷新(或者手动刷新)可以看到应用系统列表发生了变化: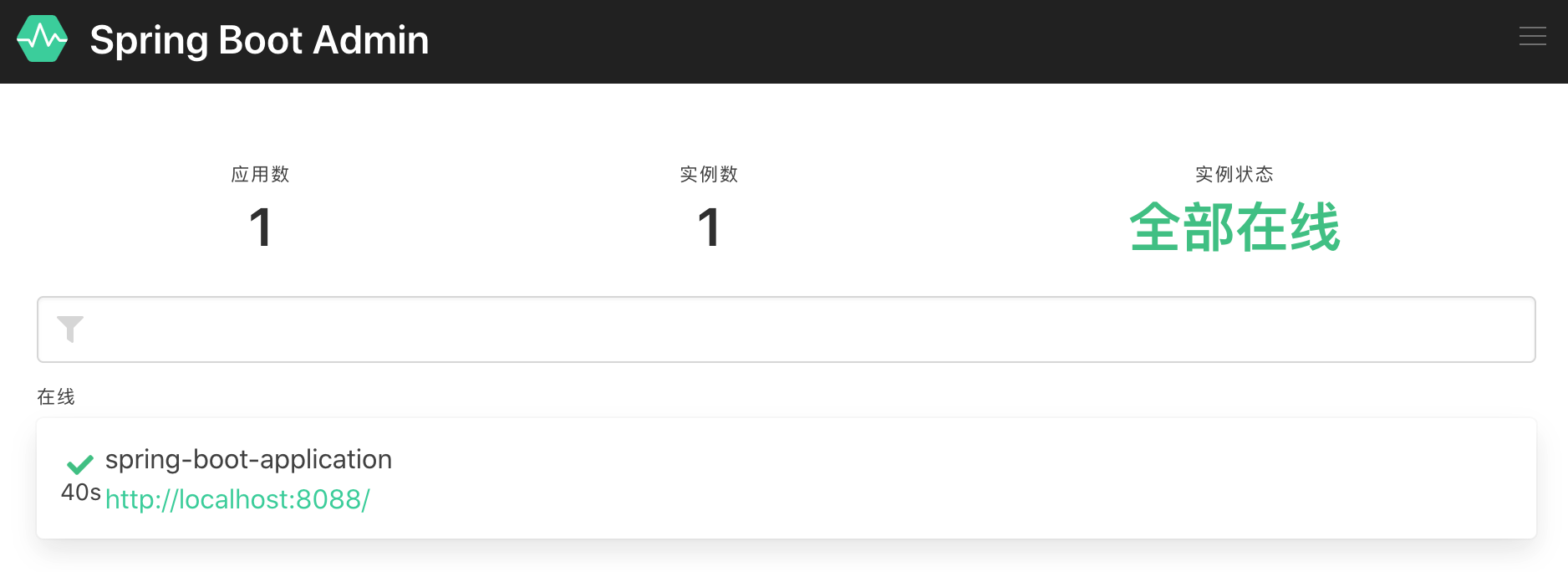
点击页面右上角“日志报表”菜单可以看到应用系统注册的信息
在列表上点击应用系统,可以看到详细的监控信息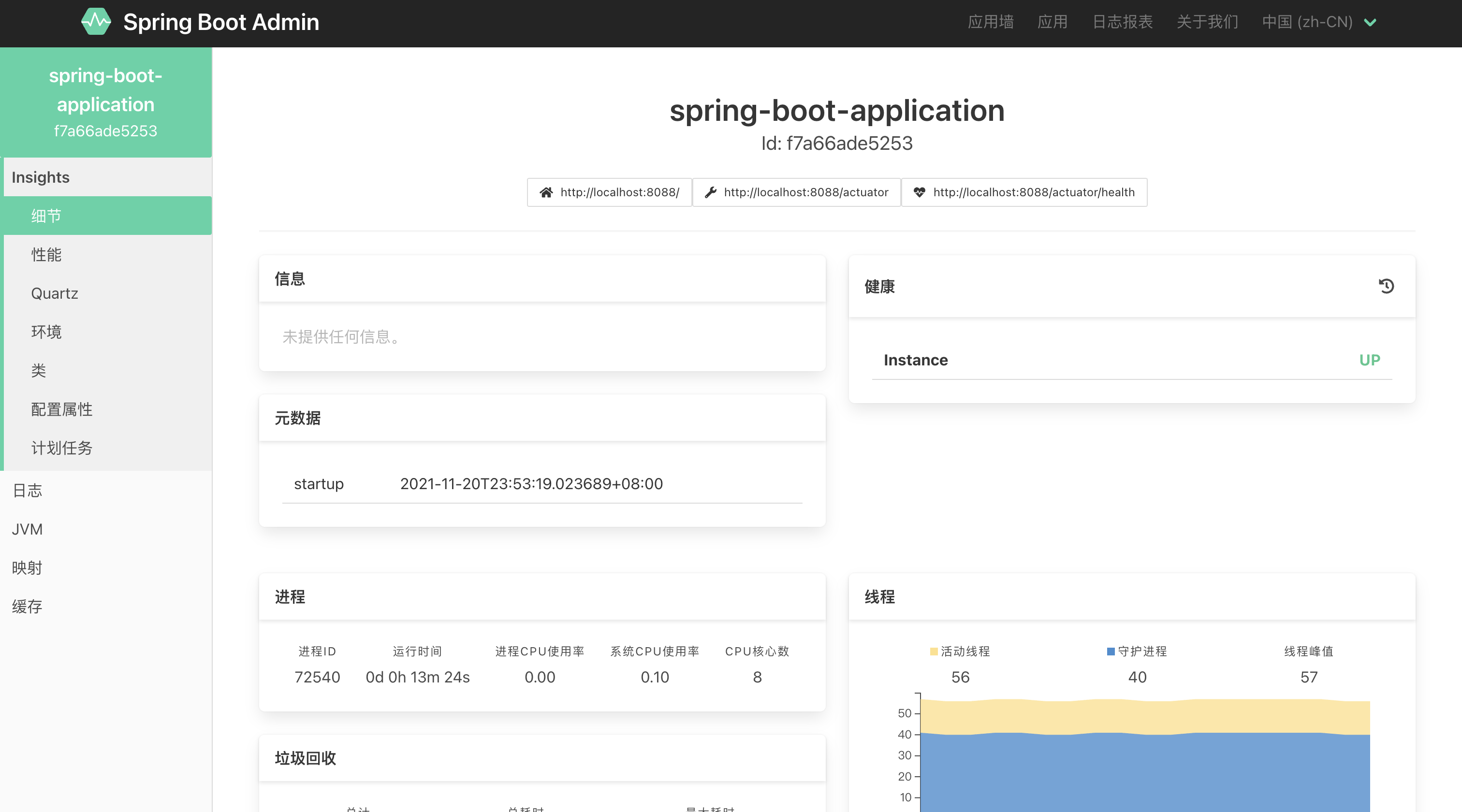
Spring Boot Admin Server 可以监控的功能很多,使用起来没有难度,下面是可以监测的部分内容:
- 应用运行状态,如时间、垃圾回收次数,线程数量,内存使用走势。
- 应用性能监测,通过选择 JVM 或者 Tomcat 参数,查看当前数值。
- 应用环境监测,查看系统环境变量,应用配置参数,自动配置参数。
- 应用 bean 管理,查看 Spring Bean ,并且可以查看是否单例。
- 应用计划任务,查看应用的计划任务列表。
- 应用日志管理,动态更改日志级别,查看日志。
- 应用 JVM 管理,查看当前线程运行情况,dump 内存堆栈信息。
- 应用映射管理,查看应用接口调用方法、返回类型、处理类等信息。
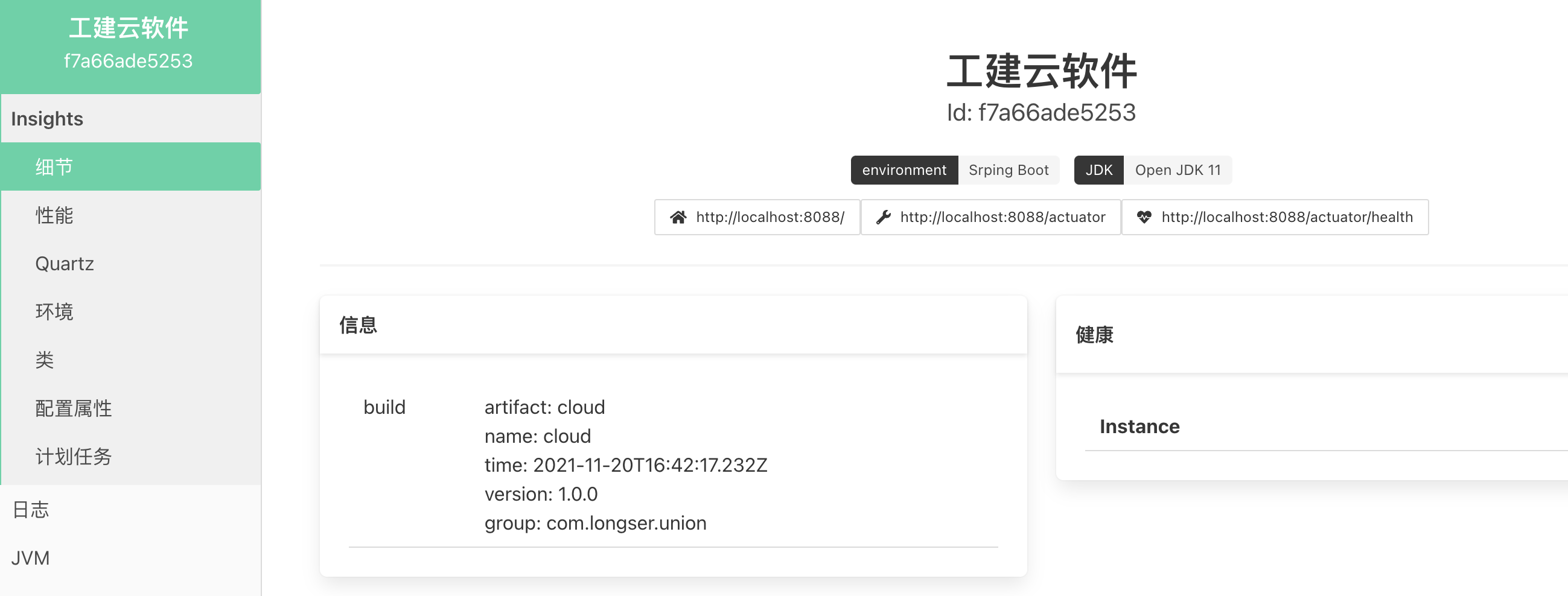
41.3.2 应用系统启动版本信息
在 Spring Boot 应用系统中添加 spring-boot-maven-plugin 并且设置 build-info 。<build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> <executions> <execution> <goals> <goal>build-info</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> </plugin> ..... 其他插件 ..... </plugins> </build>注意:这个直接放在
中,不要错放到
执行 maven build-info,会在 target/classes/META-INF 目录下生成 build-info.properties 文件,重启应用系统,在管理服务器刷新数据后查看应用系统信息,可以看到自动生成的信息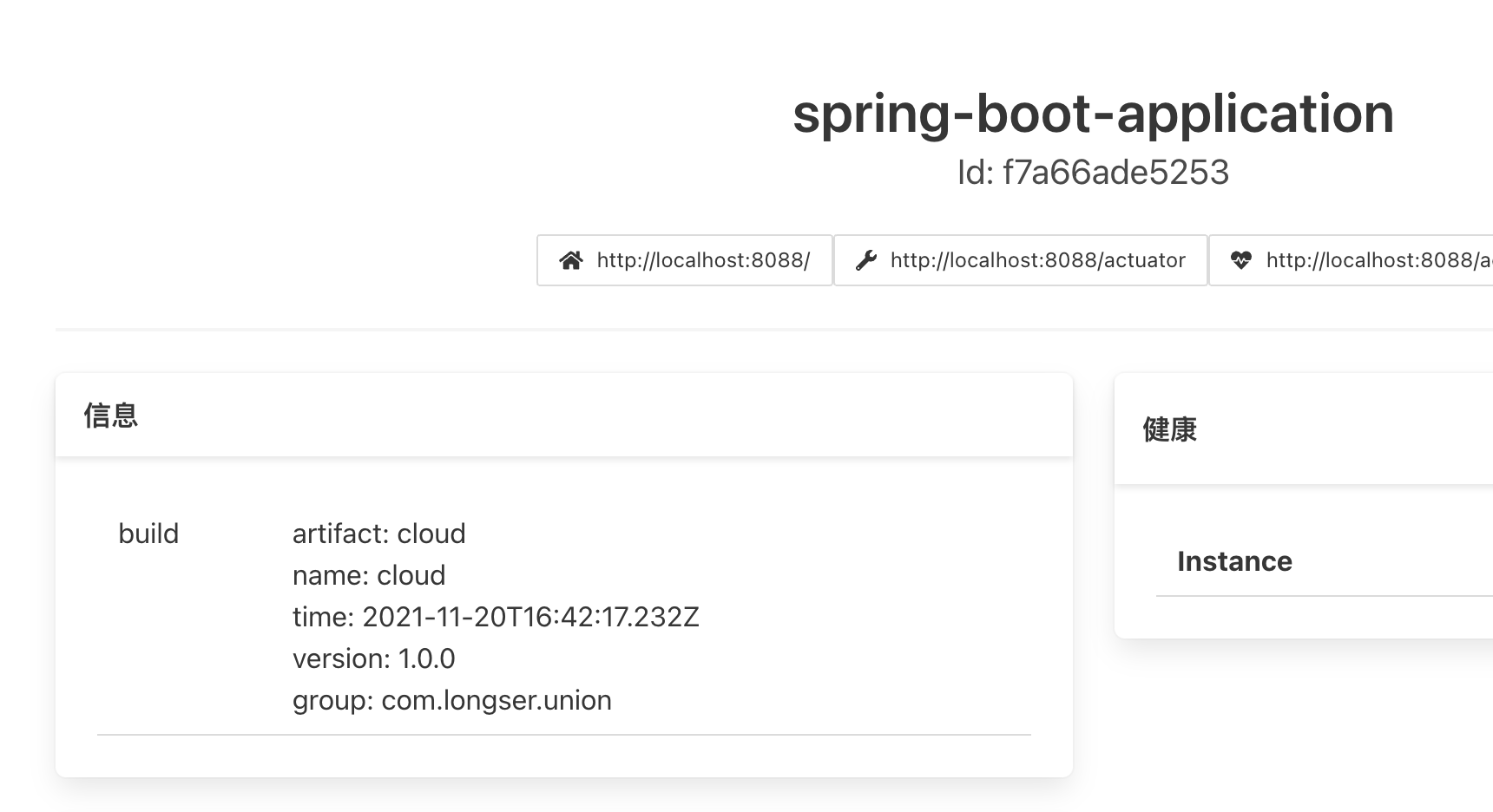
41.3.3 为应用程序定义名称和标签
默认的,应用程序在管理服务器的页面中的名称都是 spring-boot-application,你可以自己定义一个有意义有区别度的名字。
定义标签是则在每个实例中添加可视标记的一种方法,它们将显示在应用程序列表和实例视图中。默认情况下,应用程序的实例并没有标签,需要你在客户端配置里自己配置。
下面是一个配置实例:
spring:
boot:
admin:
client:
url: http://localhost:8188
instance:
name: 工建云软件
metadata:
tags:
environment: Srping Boot
JDK: Open JDK 11
这里也可以不设置 spring.boot.admin.client.instance.name,而是设置 spring.application.name。或者说如果设置了后者,那就不要单独设置 instance.name,这样便于统一。
标签的名称没有限制,你可以自己按需求定义,这里的只是举例。
41.3.4 应查看用程序日志
如果在应用程序中你已经按照教程 “21.6 输出到日志文件”中的方法做好了日志文件的我配置,那么你在管理服务器中可以看到日志的内容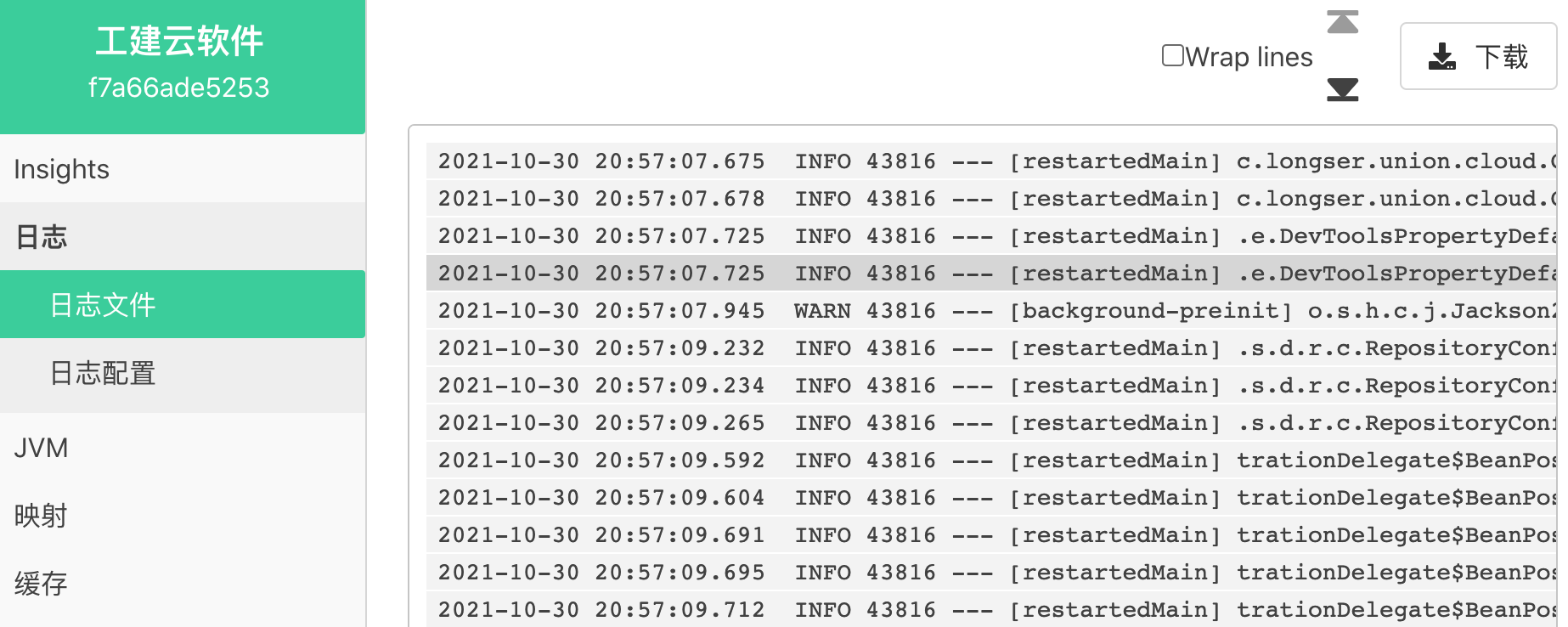
Spring Boot Admin 将检测所有看起来像URL的内容,并将其呈现为超链接。它也支持 ANSI color-escapes 的指令。您需要设置自定义文件日志模式,因为Spring Boot的默认模式不使用颜色。
如可以做如下的配置
loggin:
pattern:
file: "%clr(%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS}){faint} %clr(%5p) %clr(${PID}){magenta} %clr(---){faint} %clr([%15.15t]){faint} %clr(%-40.40logger{39}){cyan} %clr(:){faint} %m%n%wEx"
重启应用系统,在管理服务器可以看到日志开始有了颜色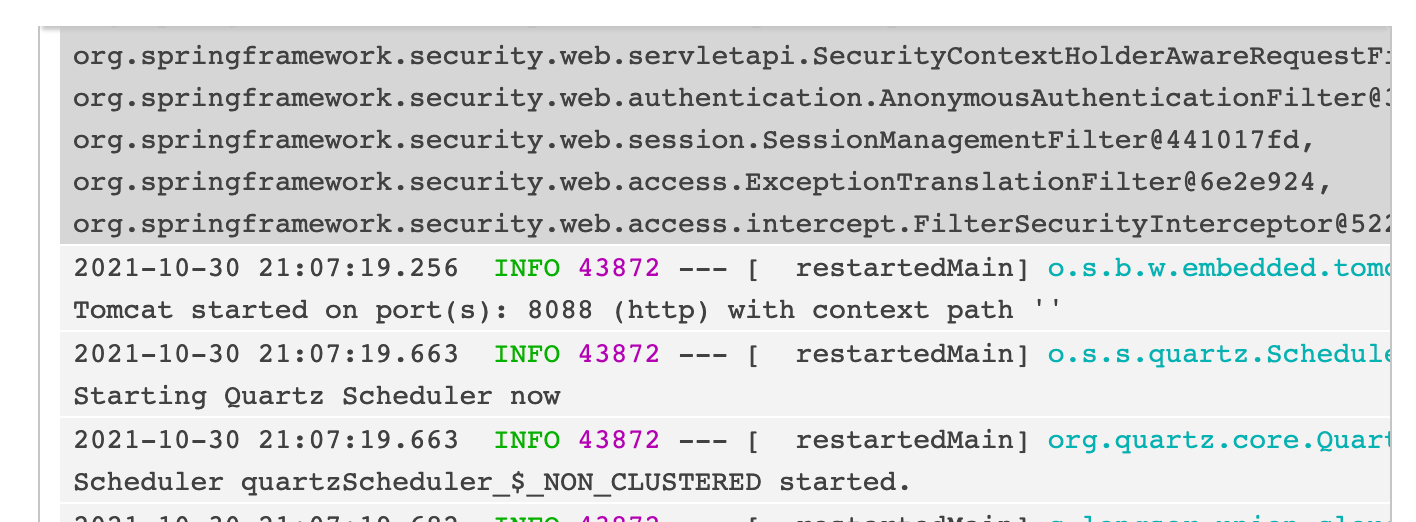
需要说明的是,这种功能使用起来比较积累。因为设置了这个以后,日志的实际内容变成了下面这个样子
为了定义颜色,日志中被加入了太多影响阅读的内容。所以如果你希望能够比较方便地直接阅读日志,那么还是不要做这个关于颜色的配置为好。
41.4 客户端的属性参数
有很多属性可以影响SBA客户端注册应用程序的方式。如果不符合您的需求,您可以提供自己的实现的 AppliationFactory 。
| 属性名称 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| spring.boot.admin.client.enabled | 启用Spring Boot Admin客户端。 | true |
| spring.boot.admin.client.url | Comma separated ordered list of URLs of the Spring Boot Admin server to register at. This triggers the AutoConfiguration. Mandatory. 以逗号分隔的要注册的Spring Boot Admin服务器的url的有序列表。这将触发自动配置。必须设置。 |
|
| spring.boot.admin.client.api-path | 在管理员服务器上注册的端点HTTP路径。 | “instances” |
| spring.boot.admin.client.username spring.boot.admin.client.password |
当SBA服务器api受到HTTP基本身份验证保护时的用户名和密码。 | |
| spring.boot.admin.client.period | 重复注册的时间间隔 (以毫秒为单位)。 | 10,000 |
| spring.boot.admin.client.connect-timeout | 连接注册超时时间 (以毫秒为单位)。 | 5,000 |
| spring.boot.admin.client.read-timeout | 注册的读取超时时间(以毫秒为单位)。 | 5,000 |
| spring.boot.admin.client.auto-registration | 如果设置为true,则在应用程序准备就绪后自动安排用于注册应用程序的定期任务。 | true |
| spring.boot.admin.client.auto-deregistration | 切换以在关闭上下文时在Spring Boot Admin server上启用自动注销。如果未设置该值,则在检测到正在运行的云平台时,该功能处于活动状态。 | null |
| spring.boot.admin.client.register-once | 如果设置为true,则客户端将仅针对一个管理服务器注册,如果该管理服务器出现故障,将自动向下一个管理服务器注册。如果为false,将针对所有管理服务器进行注册。 | true |
| spring.boot.admin.client.instance.health-url | 要注册的health-url。如果可访问的URL不同 (例如Docker),则可以覆盖。在注册表中必须是唯一的。 | 基于猜测的management-url 和 endpoints.health.id |
| spring.boot.admin.client.instance.management-base-url | 用于计算要注册的management-url的基本url。路径在运行时推断,并附加到基本url。 | 基于猜测的management.port、service-url 和 server.servlet-path |
| spring.boot.admin.client.instance.management-url | 要注册的management-url。如果可访问的url不同 (例如Docker),则可以覆盖。 | 基于猜测的management-base-url 和 management.context-path |
| spring.boot.admin.client.instance.service-base-url | 用于计算要注册的service-url的基本url。路径在运行时推断,并附加到基本url。 | 基于猜测的hostname和 server.port |
| spring.boot.admin.client.instance.service-url | 要注册的service-url。如果可访问的url不同 (例如Docker),则可以覆盖。 | 基于猜测的service-base-url 和 server.context-path. |
| spring.boot.admin.client.instance.name | 要注册的名称。 | 如果设置了spring.application.name,那么就取它的值,否则就是 spring-boot-applicatio |
| spring.boot.admin.client.instance.prefer-ip | 在猜测的url中使用ip地址而不是主机名。 如果设置了server.address 或 management.address ,那么使用它。否则使用 InetAddress.getLocalHost() 返回的地址。 |
false |
| spring.boot.admin.client.instance.metadata.* | 要与此实例关联的元数据键值对。 | |
| spring.boot.admin.client.instance.metadata.tags.* | 标记为要与此实例关联的键值对。 |
下面是实例元数据选项
| Key | Value | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| user.name user.password |
用于访问端点的凭据。 |
38.5 管理服务器的属性参数
下面是管理服务器可以配置的属性参数
| 属性名称 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| spring.boot.admin.context-path | 管理服务器的静态资产和API的上下文路径前缀。相对于Dispatcher-Servlet. | |
| spring.boot.admin.monitor.period | 以毫秒为单位的时间间隔,用于更新应用程序的过期状态。 |
10,000 |
| spring.boot.admin.monitor.status-lifetime | 应用程序状态的生命周期 (以ms为单位)。在生命周期到期之前,不会查询应用程序的 /health-endpoint。 |
10,000 |
| spring.boot.admin.monitor.connect-timeout | 在查询应用程序的状态和信息时,以ms为单位连接超时。 | 2,000 |
| spring.boot.admin.monitor.read-timeout | 在查询应用程序的状态和信息时,以ms为单位读取超时。 | 10,000 |
| spring.boot.admin.monitor.default-retries | 失败请求的默认重试次数。修改类的请求(PUT, POST, PATCH, DELETE)永远不会重试。 | 0 |
| spring.boot.admin.monitor.retries.* | 键值对,每个endpointId的重试次数。默认为default-retries。修改类的请求(PUT, POST, PATCH, DELETE)永远不会重试。 | |
| spring.boot.admin.metadata-keys-to-sanitize | 与这些正则表达式模式匹配的键的元数据值将在所有json输出中进行清理。 | “.password$”, “.secret$”, “.key$”, “.$token$”, “.credentials.“, “.*vcap_services$” |
| spring.boot.admin.probed-endpoints | 对于Spring Boot 1.X客户端应用程序,SBA使用OPTIONS请求探测指定的端点。如果路径与id不同,则可以将其指定为id:path (例如,health:ping)。 |
“health”, “env”, “metrics”, “httptrace:trace”, “threaddump:dump”, “jolokia”, “info”, “logfile”, “refresh”, “flyway”, “liquibase”, “heapdump”, “loggers”, “auditevents” |
| spring.boot.admin.instance-proxy.ignored-headers | 向客户端发出请求时不转发的 Header 项。 | `”Cookie”, “Set-Cookie”, “Authorization” |
| spring.boot.admin.ui.brand | 在导航条中显示的标记。 | “ |
| spring.boot.admin.ui.title | 显示的页面标题 | “Spring Boot Admin” |
在 application.yml 中增加如下的设置
spring:
boot:
admin:
ui:
title: 朗思云网监控服务器
brand: <img src="http://www.longser.com.cn/images/logo-w.png"><span>朗思云网</span>
41.6 管理服务的提醒通知
41.6.1 提醒通知
应用程序停机/离线R的时候,RemindingNotifier 将提醒通知的发送委托给另一个通知程序。
默认情况下,当注册的应用程序停机或离线的时候会触发一个提醒。当状态变为非触发状态或相关应用程序被注销时,提醒结束。
默认情况下,提醒每10分钟发送一次,可以使用 setReminderPeriod() 更改提醒周期。RemindingNotifier 本身不会启动后台线程来发送提醒,您需要注意这一点,如下面的示例所示;
@Configuration
public class NotifierConfiguration {
@Autowired
private Notifier notifier;
@Primary
@Bean(initMethod = "start", destroyMethod = "stop")
public RemindingNotifier remindingNotifier() {
RemindingNotifier notifier = new RemindingNotifier(notifier, repository);
// The reminders will be sent every 10 minutes.
notifier.setReminderPeriod(Duration.ofMinutes(10));
// Schedules sending of due reminders every 10 seconds.
notifier.setCheckReminderInverval(Duration.ofSeconds(10));
return notifier;
}
}
41.6.2 过滤通知Filtering notifications
FilteringNotifier允许您根据规则在运行时添加/删除的规则过滤某些通知。它将通知的发送委托给另一个通知者。
如果您不想在部署应用程序时接收通知,此通知程序非常有用。在停止应用程序之前,您可以通过 POST请求添加一个 (expiring) 过滤器。
@Configuration
public static class NotifierConfig {
private final InstanceRepository repository;
private final ObjectProvider<List<Notifier>> otherNotifiers;
public NotifierConfig(InstanceRepository repository,
ObjectProvider<List<Notifier>> otherNotifiers) {
this.repository = repository;
this.otherNotifiers = otherNotifiers;
}
@Bean
// Add the FilteringNotifier bean using a delegate
// (e.g. MailNotifier when configured)
public FilteringNotifier filteringNotifier() {
CompositeNotifier delegate = new CompositeNotifier(otherNotifiers.getIfAvailable(Collections::emptyList));
return new FilteringNotifier(delegate, repository);
}
@Primary
@Bean(initMethod = "start", destroyMethod = "stop")
// Add the RemindingNotifier as primary bean using the
// FilteringNotifier as delegate.
public RemindingNotifier remindingNotifier() {
RemindingNotifier notifier = new RemindingNotifier(filteringNotifier(), repository);
notifier.setReminderPeriod(Duration.ofMinutes(10));
notifier.setCheckReminderInverval(Duration.ofSeconds(10));
return notifier;
}
}
此示例结合了提醒和过滤通知器。这允许您在部署的应用程序在一定时间内 (直到过滤器过期)没有重新启动的话 获得通知。
41.6.3 邮件通知
邮件通知使用 Thymeleaf 模板发送 HTML 邮件。要启用邮件通知,请使用 spring-boot-starter-mail 配置 JavaMailSender 并设置收件人。
下面是一个邮件的示例: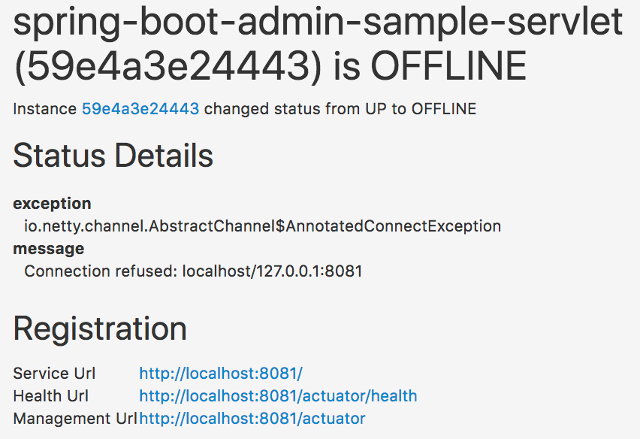
为了防止敏感信息泄露,默认邮件模板不显示实例的任何元数据。如果要显示一些元数据,可以使用自定义模板。
如前文所述,你需要单独添加 spring-boot-starter-mail 依赖,他已经包含在 spring-boot-admin-server 中。
1. 配置JavaMailSender
spring:
mail:
host: smtp.example.com
boot:
admin:
notify:
mail:
to: admin@example.com
2. 使用以下选项配置邮件
| 属性名称 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| spring.boot.admin.notify.mail.enabled | Enable mail notifications | true |
| spring.boot.admin.notify.mail.ignore-changes | 逗号分隔的要忽略的更改状态的列表: “ |
“UNKNOWN:UP” |
| spring.boot.admin.notify.mail.template | 用于渲染的Thyelef模板的资源路径。 | “classpath:/META-INF/spring-boot-admin-server/mail/status-changed.html” |
| spring.boot.admin.notify.mail.to | 逗号分隔的邮件收件人列表 | “root@localhost” |
| spring.boot.admin.notify.mail.cc | 逗号分隔的抄送接收人名单 | |
| spring.boot.admin.notify.mail.from | 邮件发送者 | “Spring Boot Admin noreply@localhost“ |
| spring.boot.admin.notify.mail.additional-properties | 可从模板访问的其他属性 |
41.7 监控过程的安全防护
41.7.1 管理服务器的安全
由于在分布式web应用程序中有几种解决身份验证和授权的方法,Spring Boot Admin不会提供默认方法。默认情况下 spring-boot-admin-server-ui 提供登录页面和注销按钮。
Spring安全配置可能如下所示
@Configuration
public static class SecuritySecureConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
private final String adminContextPath;
public SecuritySecureConfig(AdminServerProperties adminServerProperties) {
this.adminContextPath = adminServerProperties.getContextPath();
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler successHandler = new SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler();
successHandler.setTargetUrlParameter("redirectTo");
successHandler.setDefaultTargetUrl(adminContextPath + "/");
http.authorizeRequests()
// Grants public access to all static assets and the login page.
.antMatchers(adminContextPath + "/assets/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers(adminContextPath + "/login").permitAll()
// Every other request must be authenticated.
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
// Configures login and logout.
.formLogin().loginPage(adminContextPath + "/login").successHandler(successHandler).and()
.logout().logoutUrl(adminContextPath + "/logout").and()
// Enables HTTP-Basic support. This is needed for
// the Spring Boot Admin Client to register.
.httpBasic().and()
.csrf()
// Enables CSRF-Protection using Cookies
.csrfTokenRepository(CookieCsrfTokenRepository.withHttpOnlyFalse())
.ignoringAntMatchers(
// Disables CRSF-Protection the endpoint the Spring
// Boot Admin Client uses to register.
adminContextPath + "/instances",
// Disables CRSF-Protection for the actuator endpoints.
adminContextPath + "/actuator/**"
);
}
}
要获得完整的例子,请看 spring-boot-admin-sample-servlet.
如果您保护
/instances端点别忘了在 SBA 客户端使用 spring.boot.admin.client.username 和spring.boot.admin.client.password 配置用户名和密码。
41.7.2 保护客户端Actuator
当使用HTTP基本身份验证保护actuator端点时,SBA服务器需要凭据才能访问它们。注册应用程序时,您可以在元数据中提交凭据。访问应用程序的actuator端点时,BasicAuthHttpHeaderProvider 使用此元数据把 Authorization 添加到请求的 Header。您可以提供自己的 HttpHeadersProvider 改变这个行为 (例如添加一些解密) 或添加额外的 Header。
使用SBA客户端提交凭证(仅为示例)
spring.boot.admin.client:
instance:
metadata:
user.name: ${spring.security.user.name}
user.password: ${spring.security.user.password}
使用Eureka提交凭证:(仅为示例)
eureka:
instance:
metadata-map:
user.name: ${spring.security.user.name}
user.password: ${spring.security.user.password}
- SBA服务器在HTTP接口中屏蔽某些元数据,以防止敏感信息泄露。
- 通过元数据提交凭据时,应为SBA服务器或 (服务注册表) 配置HTTPS。
- 使用Spring Cloud Discovery时,您必须知道,任何可以查询您的服务注册表的人都可以获得凭据。
- 当使用这种方法时,SBA服务器决定用户是否可以访问注册的应用程序。有更复杂的解决方案可能 (使用OAuth2) 让客户端决定用户是否可以访问端点。为此,请查看示例 joshiste/spring-boot-admin-samples
一些actuator端点 (例如/loggers) 支持发布请求。使用Spring Security时,您需要忽略 CSRF-Protection 的actuator端点,因为Spring Boot Admin服务器当前缺乏支持。
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf()
.ignoringAntMatchers("/actuator/**");
}
41.7.3 更多的示例内容
等多的示例内容请仔细阅读示例的代码 spring-boot-admin-sample-servlet 。
41.8 定制
41.8.1 自定义通知程序
你可以添加实现了 Notifier 接口的 SpringBean 来添加自己的Notifiers。最好通过扩展 AbstractEventNotifier
或者 AbstractStatusChangeNotifier 来做。
public class CustomNotifier extends AbstractEventNotifier {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoggingNotifier.class);
public CustomNotifier(InstanceRepository repository) {
super(repository);
}
@Override
protected Mono<Void> doNotify(InstanceEvent event, Instance instance) {
return Mono.fromRunnable(() -> {
if (event instanceof InstanceStatusChangedEvent) {
LOGGER.info("Instance {} ({}) is {}", instance.getRegistration().getName(), event.getInstance(),
((InstanceStatusChangedEvent) event).getStatusInfo().getStatus());
} else {
LOGGER.info("Instance {} ({}) {}", instance.getRegistration().getName(), event.getInstance(),
event.getType());
}
});
}
}
41.8.2 注入自定义HTTP标头
如果您需要将自定义HTTP标头注入到对受监控应用程序的actuator端点的请求中,您可以轻松地通过添加HttpHeadersProvider来实现:
@Bean
public HttpHeadersProvider customHttpHeadersProvider() {
return instance -> {
HttpHeaders httpHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
httpHeaders.add("X-CUSTOM", "My Custom Value");
return httpHeaders;
};
}
41.8.3 拦截请求和响应
你可以通过实现执行 InstanceExchangeFilterFunction 接口拦来截和修改发往被监测应用系统 actuator 端点的请求和响应的。这对于审计或添加一些额外的安全检查很有用。
@Bean
public InstanceExchangeFilterFunction auditLog() {
return (instance, request, next) -> {
if (HttpMethod.DELETE.equals(request.method()) || HttpMethod.POST.equals(request.method())) {
log.info("{} for {} on {}", request.method(), instance.getId(), request.url());
}
return next.exchange(request);
};
}
41.8.4 自定义视图
可以向用户界面中添加自定义视图。视图必须是Vue.js组件。Javascript-Bundle和Css-Stlysheet必须放置在classpath的/META-INF/spring-boot-admin-server-ui/extension/{name}/,这样服务器就可以找到它们。
spring-boot-admin-sample-custom-ui 模块包含一个示例,该示例具有构建此类模块所需的maven设置。
调用 SBA.use() 可以自定义扩展通过调用来注册自身,并且需要暴露一个在设置路由时由 UI调用的install() 函数。这更嗯 install() 函数接收viewRegistry 和 applicationStore 引用的参数对象,以便注册视图和/或回调。
41.8.4.1 添加顶级视图
下面是一个简单的顶级视图,仅列出所有注册的应用程序:
<template>
<pre v-text="stringify(applications, null, 4)"/>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
applications: {
type: Array,
required: true
}
},
methods: {
stringify: JSON.stringify
}
};
</script>
如果你定义了一个 application props,组件将接收所有注册的应用程序(的申请)。
在应用程序和实例对象上有一些有用的方法可用。具体的可以看一下 application.js 和 instance.js。
这就是注册顶级视图的方式。
SBA.use({
install({viewRegistry}) {
viewRegistry.addView({
name: 'custom',
path: '/custom',
component: custom,
label: 'Custom',
order: 1000,
});
}
});
| 参数名 | 参数释义 |
|---|---|
| name | 视图的名称和到视图的路由 |
| path | 可访问视图的路径 |
| component | 导入的自定义组件,它将在路由上呈现。 |
| label | 要在顶部导航栏中显示的自定义视图的标签。 |
| order | 视图顺序。顶部导航栏中的视图按升序排序。 |
41.8.4.2 可视化自定义端点
以下是显示自定义端点的视图:
<template>
<div class="custom">
Instance: <span v-text="instance.id"/>
Output: <span v-text="text"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
instance: {
type: Object,
required: true
}
},
data: () => ({
text: ''
}),
async created() {
const response = await this.instance.axios.get('actuator/custom');
this.text = response.data;
}
};
</script>
<style>
.custom {
font-size: 20px;
width: 80%;
}
</style>
- 如果你定义了一个 instance props,组件将接收视图应呈现的实例。
- 每个实例都有一个预配置的 axios 实例,用来使用正确的路径和标头访问端点。
注册实例视图适用于具有一些附加属性的顶级视图:
SBA.use({
install({viewRegistry}) {
viewRegistry.addView({
name: 'instances/custom',
parent: 'instances',
path: 'custom',
component: customEndpoint,
label: 'Custom',
order: 1000,
isEnabled: ({instance}) => instance.hasEndpoint('custom')
});
}
});
- 父级必须是 “实例”,以便为单个实例呈现新的自定义视图。
- 如果添加了 isEnabled 回调,你可以动态确定是否应针对特定实例显示视图。
41.8.5 自定义标题徽标和标题
您可以在标题中设置自定义信息 (即通过使用以下配置属性显示暂存信息或公司名称):
- spring.boot.admin.ui.brand
- spring.boot.admin.ui.title
41.9 重要问题讨论
问:可以将 spring-boot-admin 包含到业务应用程序中吗?
答:你做得到,但你绝对不应该这么做!
您可以设置 spring.boot.admin.context-path 更改提供 UI 和 REST-API 的路径,但是根据应用程序的复杂性,您可能会遇到麻烦。另一方面,应用程序自我监控是没有意义的。如果把他们组合在一起,一旦应用程序出现故障,监控工具也会出现故障。
更详细的内容推荐阅读关于 Spring Boot Admin 和 Spring Boot Actuator 的官方文档
- https://codecentric.github.io/spring-boot-admin/2.1.0/
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/actuator.html
版权说明:本文由北京朗思云网科技股份有限公司原创,向互联网开放全部内容但保留所有权力。


