IOPS
IOPS 衡量指标
- random performance
- sequential performance
- random performance and sequential performance
IOPS calculations
- Rotational speed
Measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), most disks you’ll consider for enterprise storage rotate at speeds of 7,200, 10,000 or 15,000 RPM with the latter two being the most common. A higher rotational speed is associated with a higher performing disk.
- Average latency
The time it takes for the sector of the disk being accessed to rotate into position under a read/write head. - Average seek time
The time (in ms) it takes for the hard drive’s read/write head to position itself over the track being read or written.
IOPS 计算公式
Average IOPS: Divide 1 by the sum of the average latency in ms and the average seek time in ms (1 / (average latency in ms + average seek time in ms).
- Model: Western Digital VelociRaptor 2.5” SATA hard drive
- Rotational speed: 10,000 RPM
- Average latency: 3 ms (0.003 seconds)
- Average seek time: 4.2 (r)/4.7 (w) = 4.45 ms (0.0045 seconds)
- Calculated IOPS for this disk: 1/(0.003 + 0.0045) = about 133 IOPS
IOPS 合并
| 卷类型 | 来自应用程序的 I/O 操作 | 最大 I/O 大小 | IOPS 数量 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSD | 256 KiB | 1 个 1024 KiB I/O 操作 | 4 (1,024÷256=4) | Amazon EBS 将 1,024 个 I/O 操作拆分为四个较小的 256 KiB 操作。 |
| 8 个连续 32 KB I/O 操作 | 1 (8x32=256) | Amazon EBS 将 8 个连续 32 KiB I/O 操作合并为一个 256 KiB 操作。 | ||
| 8 个随机 32 KiB I/O 操作 | 8 | Amazon EBS 分别计算随机 I/O 操作。 | ||
| HDD | 1024 KiB | 1 个 1024 KiB I/O 操作 | 1 | I/O 操作已经等于最大 I/O 大小。它不会被合并或拆分。 |
| 8 个连续 128 KB I/O 操作 | 1 (8x128=1,024) | Amazon EBS 将 8 个连续 128 KiB I/O 操作合并为一个 256 KiB I/O 操作。 | ||
| 8 个随机 32 KiB I/O 操作 | 8 | Amazon EBS 分别计算随机 I/O 操作。 |
RAID Summary
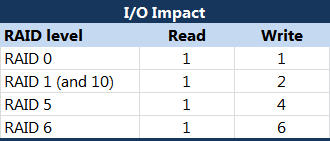
Parity-based RAID systems also introduce other additional processing that result from the need to calculate parity information. The more parity protection you add to a system, the more processing overhead you incur.
(Total Workload IOPS Percentage of workload that is read operations) + (Total Workload IOPS Percentage of workload that is read operations * RAID IO Penalty)
- Total IOPS need: 250 IOPS
- Read workload: 50%
- Write workload: 50%
- RAID level: 6 (IO penalty of 6)
Result: You would need an array that could support 875 IOPS to support a 250 IOPS RAID 6-based workload that is 50% writes.
The transport choice
The transport choice is an important one, but it’s not the primary choice that many would make it out to be.
队列长度
卷队列长度是指等待设备处理的 I/O 请求的数量。Disk Queue Length每个硬盘长时间大于2,可能会产生系统瓶颈。如果您的 RAID 系统有 8 个磁盘,则 Avg. 磁盘队列长度不应超过 16延迟为 I/O 操作的实际端到端客户端时间,也就是说,从将 I/O 发送到 EBS 到接收来自 EBS 的确认以表示 I/O 读取或写入完成所经过的时间。
参考链接:
https://www.techrepublic.com/blog/the-enterprise-cloud/calculate-iops-in-a-storage-array/
IOWait
•What can be done about high I/O wait percentages?
•https://access.redhat.com/solutions/2045
•How do I determine what processes are contributing to iowait?
•https://access.redhat.com/solutions/288803
•Understanding iostat -x output
•https://access.redhat.com/articles/524333
•How can I perform per process I/O monitoring on Red Hat Enterprise Linux?
•https://access.redhat.com/solutions/20456
磁盘调度算法
CFQ [cfq](完全公平队列)是 Linux 内核的 I/O 调度程序,在许多 Linux 发行版下都是默认设置。
Noop调度器(noop)是基于FIFO队列概念的Linux内核最简单的I/O调度器。
预期调度器(anticipatory)是一种用于调度硬盘输入/输出以及被CFQ取代的旧调度器的算法
截止时间调度程序(deadline)——它试图保证一个请求的开始服务时间。
cat /sys/block/{DEVICE-NAME}/queue/scheduler
# cat /sys/block/sda/queue/scheduler
参考链接:
https://lonesysadmin.net/2013/12/06/use-elevator-noop-for-linux-virtual-machines/
https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/linux-change-io-scheduler-for-harddisk/

