1.生命周期钩子函数(旧)
1.1 组件挂载
import React from 'react'class App extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props)console.log('constructor')}//初始化状态state = {count: 0,}add = () => {let { count } = this.statethis.setState({count: ++count,})}// 組件挂在之前執行componentWillMount(){console.log('componentWillMount')}// 组件挂载之后执行componentDidMount(){console.log('componentDidMount');}render() {console.log('render');return (<div><h2>count当前的值:{this.state.count}</h2><button onClick={this.add}>+</button></div>)}}export default App
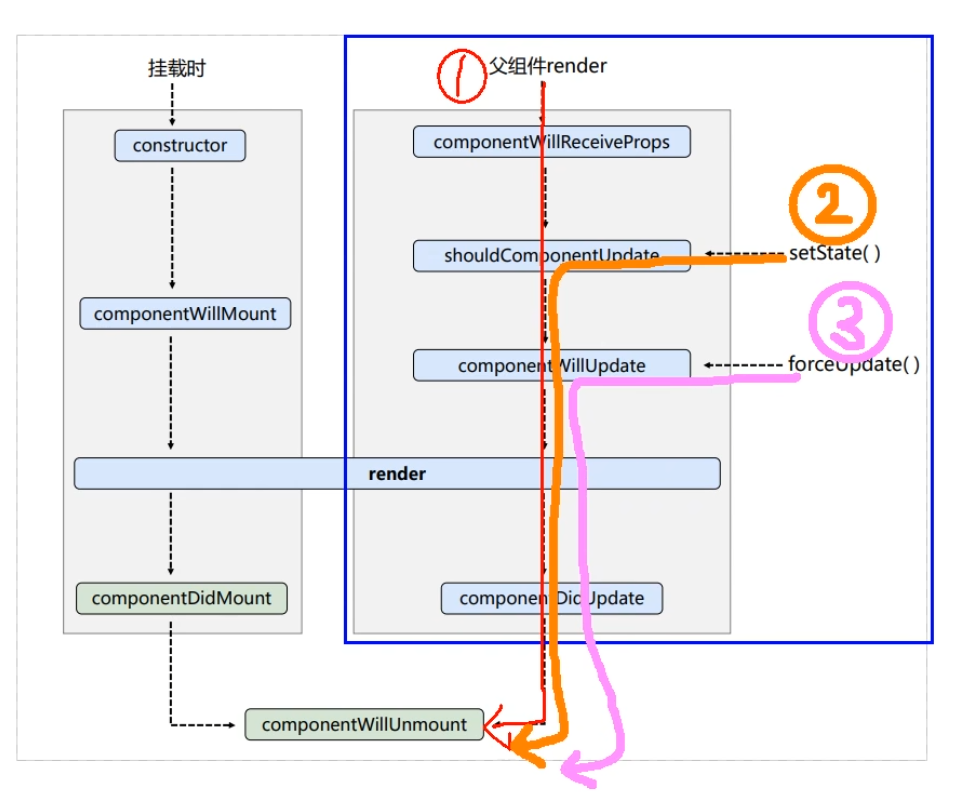
:::success 页面初始化阶段: 由ReactDOM.render()触发 ——初次渲染
- constructor
- componentWillMount
- render
- componentDidMount
:::
1.2组件更新
```javascript import React from ‘react’ class App extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props) console.log(‘constructor’) } //初始化状态 state = { count: 0, } add = () => { let { count } = this.state this.setState({
}) } // 卸载组件的方法 death = () => { // React.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById(‘app’)); } // 組件挂在之前執行 componentWillMount(){ console.log(‘componentWillMount’) } // 组件挂载之后执行 componentDidMount(){ console.log(‘componentDidMount’); } // 组件卸载之后 componentWillUnmount(){ console.log(‘componentWillUnmount’) } // 组件是否需要更新 shouldComponentUpdate(){ console.log(‘shouldComponentUpdate’); return true } // 组件将要更新 componentWillUpdate(){ console.log(‘componentWillUpdate’); } // 组件更新之后 componentDidUpdate(){ console.log(‘componentDidUpdate’) } render() { console.log(‘render’); return (count: ++count,
) } } export default App<div id='app'><h2>count当前的值:{this.state.count}</h2><button onClick={this.add}>+</button><button onClick={this.death}>卸载组件</button></div>
:::success**页面更新阶段:**由组件内部this.setSate()或父组件重新render触发,且shouldComponentUpdate返回true, 则执行顺序为:- **shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState)**- **componentWillUpdate**- **render**- **componentDidUpdate**:::**注意:**- 如果shouldComponentUpdate返回false,则不执行下面的钩子函数;- 如果组件中不屑shouldComponentUpdate,那么组件会默认的加这个钩子, 且返回值是true;<a name="tXD17"></a>## 1.3强制更新组件```javascriptimport React from 'react'class App extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props)console.log('constructor')}//初始化状态state = {count: 0,}add = () => {let { count } = this.statethis.setState({count: ++count,})}// 卸载组件的方法death = () => {// React.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById('app'));}//强制更新组件force = () => {console.log('强制更新');this.forceUpdate()}// 組件挂在之前執行componentWillMount(){console.log('componentWillMount')}// 组件挂载之后执行componentDidMount(){console.log('componentDidMount');}// 组件卸载之后componentWillUnmount(){console.log('componentWillUnmount')}// 组件是否需要更新shouldComponentUpdate(){console.log('shouldComponentUpdate');return true}// 组件将要更新componentWillUpdate(){console.log('componentWillUpdate');}// 组件更新之后componentDidUpdate(){console.log('componentDidUpdate')}render() {console.log('render');return (<div id='app'><h2>count当前的值:{this.state.count}</h2><button onClick={this.add}>+</button><button onClick={this.death}>卸载组件</button><button onClick={this.force}>强制刷新页面</button></div>)}}export default App
:::success 强制更新:forceUpdate()
- componentWillUpdate
- render
-
1.4 componentWillReceiveProps:
componentWillReceiveProps在初始的时候不会被调用, 它在组件接收到新的props时调用。 一般用于父组件更新状态时子组件重新渲染。
在React6.3之前,componentWillReceiveProps是在不进行额外render的前提下,相应props中改变并更新state的唯一方式。componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps){//通过this.props来获取旧的外部状态, 初始props不会被调用//通过对比新旧状态, 来判断是否执行其他方法}
2. 生命周期钩子函数(新)
2.1 新版本中废弃掉3个旧版本的钩子函数:
componentWillMount
- componentWillUpdate
- componentWillReceiveProps
注意:现在使用会出现警告, 下一个版本需要加上UNSAFE_前缀才能使用, 以后会彻底废弃, 不建议使用。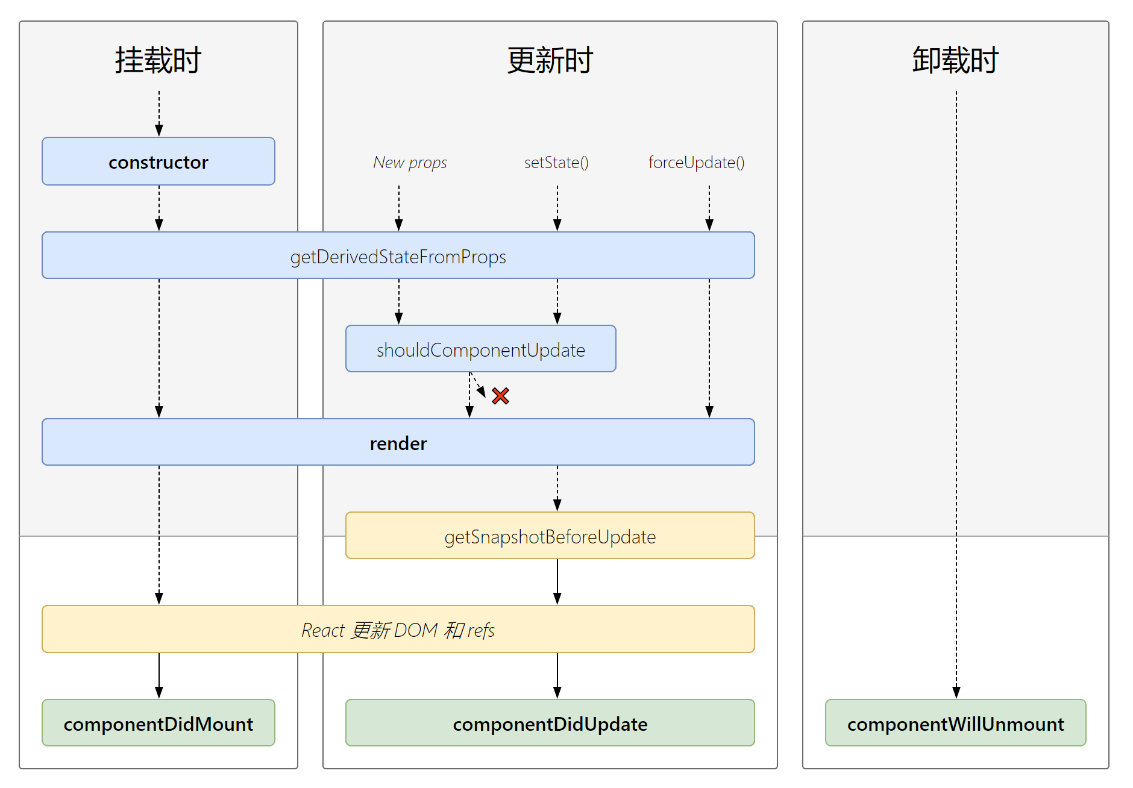
2.2 getDerivedStateFromProps:
getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state): 会在调用render方法之前调用, 并且在初始挂载及后续更新时都会被调用, 它应该返回一个对象来更新state, 如果返回null则不更新任何内容。
此方法使用场景:state的值在任何时候都取决于props.
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state){}
2.3 getSnapShotBeforeUpdate():
getSnapShotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState): 在最近一次渲染输出(提交到DOM节点)之前调用。 它使得组件在发生改变之前从DOM中捕获一些信息(例如: 滚动位置)。此生命周期方法的任何返回值将作为参数传递给componentDidUpdate
import React from 'react';import './index.css'class Home extends React.Component {constructor(props){super(props)console.log('count:constructor ');}state = {newsArr:[]}componentDidMount(){setInterval(() => {const { newsArr } = this.state;//模拟一条新闻const news = '新闻'+(newsArr.length + 1)//更新状态this.setState({newsArr:[news, ...newsArr]})},1000)}//组件更新前getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(){return this.list.scrollHeight}//组件已经更新componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState,height){console.log('count:componentDidUpdate', height);this.list.scrollTop += this.list.scrollHeight - height}render() {const { newsArr } = this.state;console.log('count:render' )return (<ul className='list' ref={ c => this.list = c}>{newsArr?.map( (item ,index) => {return <li key={index} className='listItem'>{item}</li>})}</ul>);}}export default Home;
2.4 新版生命周期钩子函数的三个阶段:
1. 初始化阶段: 由ReactDOM.render()触发——初次渲染 :::success
- constructor()
- getDerivedStateFromProps
- render()
componentDidMount() ::: 2. 更新阶段: 由组件内部的this.setState()或父组件重新render触发 :::success
getDerivedStateFromProps
- shouldComponentUpdate()
- render()
- getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()
- componentDidUpdate
:::
3. 卸载组件: 由ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode()触发
:::success
componentWillUnmonunt()
:::
3. 总结
总结:有三个重要的钩子:
1. render: 初始化渲染或者组件更新调用
2. componentDIdMount: 开始监听, 发送Ajax请求
3. componentWillUnmount: 做一些收尾工作: 比如清理定时器;