作用
语法格式
cy.request(url)cy.request(url, body)cy.request(method, url)cy.request(method, url, body)cy.request(options)
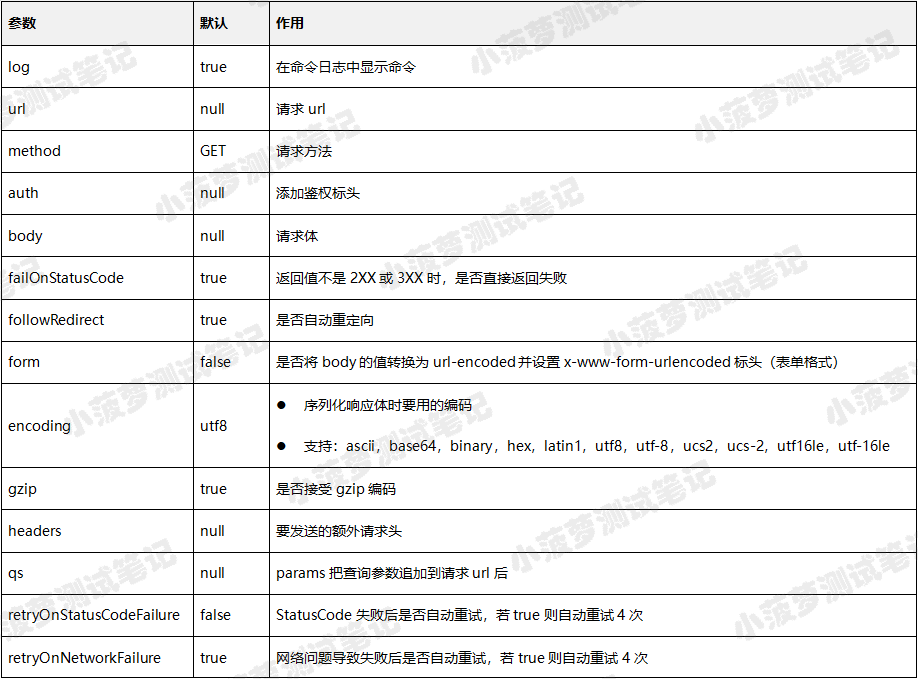
参数说明
url
cy.request() 在 cy.visit() 后面
// 先访问某个 urlcy.visit('http://localhost:8080/app')// 请求 url 是 http://localhost:8080/users/1.jsoncy.request('users/1.json')
设置了 baseUrl,且 cy.request() 在 cy.visit() 前面
cypress.json
// cypress.json{"baseUrl": "http://localhost:1234"}
测试代码
// url 是 http://localhost:1234/seed/admincy.request('seed/admin')
备注
body
- 请求正文,不同接口内容,body 会有不同的形式
- Cypress 设置了 Accepts 请求头,并通过 encoding 选项序列化响应体
method
options
GET 请求的栗子
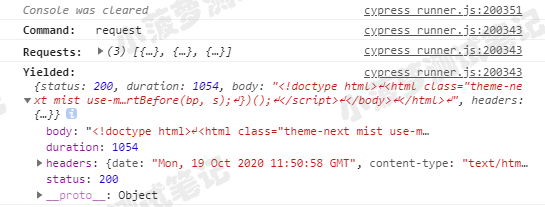
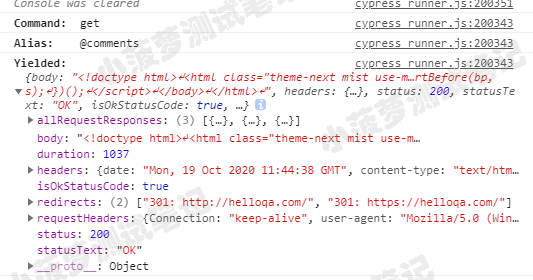
context('get请求', function () {it('默认访问方式', function () {cy.request('http://www.helloqa.com')});it('使用 options', function () {cy.request({method: 'get',url: 'http://www.helloqa.com'})});// .request() 常常和别名 .as() 一起使用,用来进行接口返回值的断言it('真实测试', function () {cy.request({method: 'get',url: 'https://www.helloqa.com'}).as('comments')cy.get('@comments').then((response) => {expect(response.status).to.be.eq(200)})});})
测试结果
.request() 返回值
- status
- body
- headers
- duration
.request() 别名后通过 .get() 的返回值
- status
- body
- headers
- duration
- statusText
- allRequestResponses
- requestHeaders
- redirects
- isOkStatusCode
使用 .request() 代替 .visit() 的栗子
官方有那么一句话
有时候,cy.request() 测试页面的内容要比 cy.visit() 更快,然后等待整个页面加载所有资源
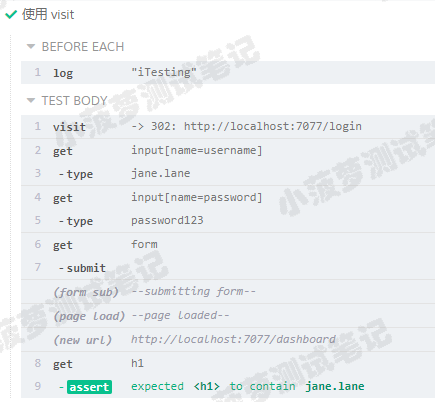
通过 .visit() 测试需要登录才能访问的页面
const username = 'jane.lane'const password = 'password123'it('使用 visit', function () {// 相当于 UI 界面操作cy.visit('')// 登录操作cy.get("input[name=username]").type(username)cy.get("input[name=password]").type(password)cy.get("form").submit()// 会跳转至需要登录才能访问的页面cy.get("h1").should("contain", "jane.lane") });
测试结果
通过 .request() 测试需要登录才能访问的页面
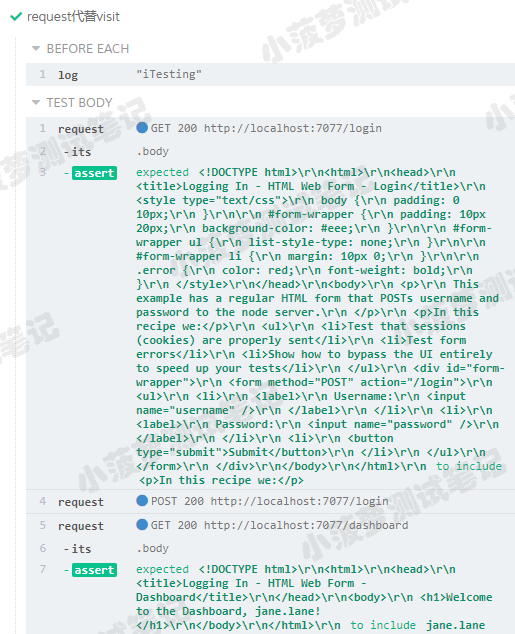
it('request代替visit', function () {// 通过接口层面去访问页面// 请求页面cy.request('/login').its('body').should('include', '<p>In this recipe we:</p>')// 登录请求cy.request({method: 'post',url: '/login',// 表单格式的请求form: true,body: {username: 'jane.lane',password: 'password123'}})// 访问需要登录之后才能访问的页面cy.request('/dashboard').its('body').should('include', 'jane.lane')});
测试结果
官方重点
通常,一旦对登录进行了适当的e2e测试,就没有理由继续使用 cy.visit() 登录并等待整个页面加载所有关联的资源,然后再运行其他命令,这样做可能会减慢我们整个测试套件的速度
轮询发出请求的栗子
背景
- 当轮询服务器以获取可能需要一段时间才能完成的响应时,此功能很有用
- 如何做:创建一个递归函数
测试代码
function req() {cy.request('/').then((resp) => {if (resp.status === 200)// 请求成功则退出轮询return// 递归req()})}context('轮询request', function () {it('默认访问方式', function () {cy.visit('http://localhost:7077/')// 轮询前的操作cy.get("form").click()// 轮询请求.then(() => {req()})});})
关于 .request() 的注意事项
Debugging
- 通过 .request() 发出的请求不会出现在开发者工具(F12)网络一栏中
- Cypress 实际上并未从浏览器发出XHR请求
- 实际上是从 Cypress Test Runner(在Node中)发出HTTP请求
- 因此,不会在开发人员工具中看到该请求
Cookie
- 通过 .request() 发出的请求,Cypress 会自动发送和接收 Cookie
- 在发送 HTTP 请求之前,如果请求来自浏览器,Cypress 会自动附加本应附加的 Cookie
- 此外,如果响应具有 Set-Cookie 标头,则这些标头将自动在浏览器 Cookie 上重新设置
- 换句话说,cy.request() 透明地执行所有基础功能,就好像它来自浏览器一样