拼接操作
- 常量与常量的拼接结果在常量池,原理是编译期优化。
- 常量池中不会存在相同内容的常量。
- 多个字符串相加+,只要其中有一个是变量,结果就在堆中。变量拼接的原理是StringBuilder。
- 如果拼接的结果调用intern()方法,则主动将常量池中还没有的字符串对象放入池中,并返回此对象地址。
public void test1() {String s1 = "a" + "b" + "c";//编译期优化:等同于"abc"String s2 = "abc"; //"abc"一定是放在字符串常量池中,将此地址赋给s2/** 最终.java编译成.class,再执行.class* String s1 = "abc";* String s2 = "abc"*/System.out.println(s1 == s2); //trueSystem.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); //true}public void test2() {String s1 = "javaEE";String s2 = "hadoop";String s3 = "javaEEhadoop";String s4 = "javaEE" + "hadoop";//编译期优化//如果拼接符号的前后出现了变量,则相当于在堆空间中new String(),具体的内容为拼接的结果:javaEEhadoopString s5 = s1 + "hadoop";String s6 = "javaEE" + s2;String s7 = s1 + s2;System.out.println(s3 == s4);//trueSystem.out.println(s3 == s5);//falseSystem.out.println(s3 == s6);//falseSystem.out.println(s3 == s7);//falseSystem.out.println(s5 == s6);//falseSystem.out.println(s5 == s7);//falseSystem.out.println(s6 == s7);//false//intern():判断字符串常量池中是否存在javaEEhadoop值,如果存在,则返回常量池中javaEEhadoop的地址;//如果字符串常量池中不存在javaEEhadoop,则在常量池中加载一份javaEEhadoop,并返回次对象的地址。String s8 = s6.intern();System.out.println(s3 == s8);//true}
intern()的使用
如果不是用双引号声明的 String 对象,可以使用 String 提供的intern方法: intern方法会从字符串常量池中查询当前字符串是否存在,若不存在就会将当前字符串放入常量池中。
比如: String myInfo = new String("I love u").intern();
也就是说,如果在任意字符串上调用String. intern方法,那么其返回结果所指向的那个类实例,必须和直接以常量形式出现的字符串实例完全相同。因此,下列表达式的值必定是true: ("a" + "b" + "c").intern() == "abc";
通俗点讲,Interned String就是确保字符串在内存里只有一份拷贝,这样可以节约内存空间,加快字符串操作任务的执行速度。注意,这个值会被存放在字符串内部池(String Intern Pool)。
public class StringIntern1 {public static void main(String[] args) {//StringIntern.java中练习的拓展:String s3 = new String("1") + new String("1");//new String("11")//执行完上一行代码以后,字符串常量池中,是否存在"11"呢?答案:不存在!!String s4 = "11";//在字符串常量池中生成对象"11"String s5 = s3.intern();System.out.println(s3 == s4);//falseSystem.out.println(s5 == s4);//true}}
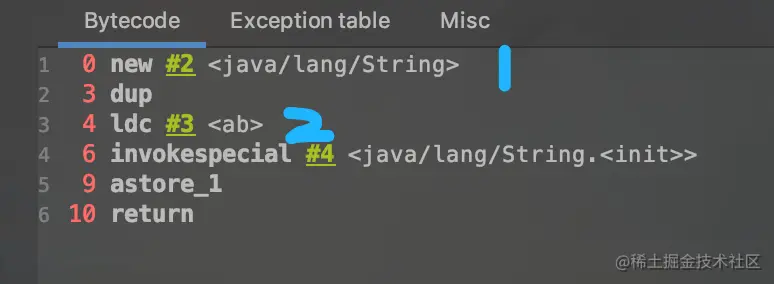
**new String("ab")**会创建几个对象,**new String("a")+new String("b")**呢?new String("ab")会创建几个对象?看字节码,就知道是两个。
- 一个对象是:new关键字在堆空间创建的
- 另一个对象是:字符串常量池中的对象”ab”。 字节码指令:ldc
new String("a") + new String("b")呢?
- 对象1:new StringBuilder()
- 对象2: new String(“a”)
- 对象3: 常量池中的”a”
- 对象4: new String(“b”)
- 对象5: 常量池中的”b”

深入剖析: StringBuilder的toString():
- 对象6 :new String(“ab”)
- 强调一下,toString()的调用,在字符串常量池中,没有生成”ab”

