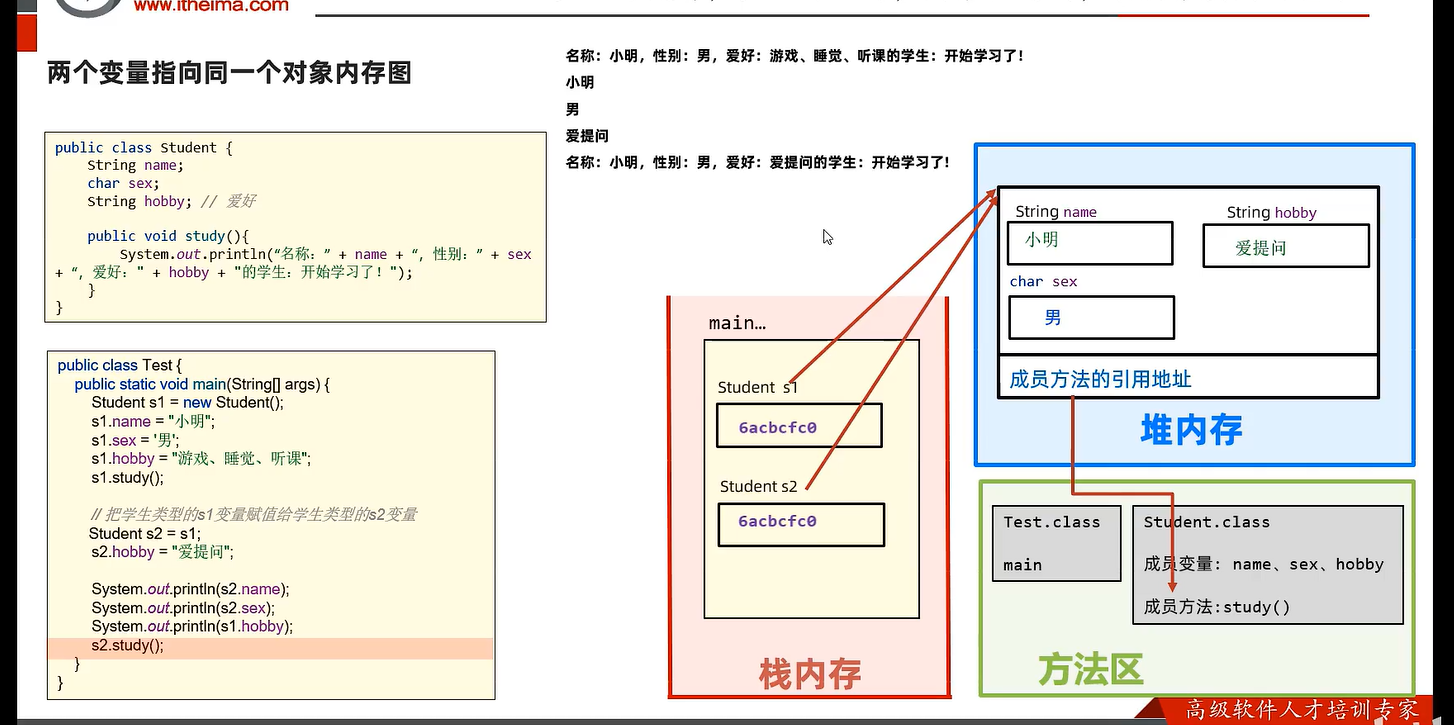
package com.itheima.memory;/*目标:理解2个变量指向同一个对象的内存运行机制*/public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建学生对象Student s1 = new Student();s1.name = "小明";s1.sex = '男';s1.hobby = "睡觉,游戏,学习";s1.study();// 把s1变量赋值给一个学生类的变量s2Student s2 = s1; // 赋值的是对象的地址,创建的对象名类型一定是”类"System.out.println(s2);System.out.println(s1);//com.itheima.memory.Student@5f184fc6// 改变学生类Student的成员变量的值s2.hobby = "爱提问";System.out.println(s2.name);System.out.println(s2.sex);System.out.println(s1.hobby);// 由于s1和s2都是同一个对象地址,所以s1访问hobby的值被改变s2.study();}}(这是一个新定义的类)package com.itheima.memory;public class Student {String name;char sex;String hobby;public void study(){System.out.println("名称:" + name + ",性别" + sex + ",爱好:" + hobby + "开始学习了!");}}
垃圾回收机制:
当对象名为null时(相当于连接堆内存的那根线断了),无法指向堆内存的方法和成员变量,这个时候这个对象就会被回收,给别人使用,提示程序的性能

