

内存图详解: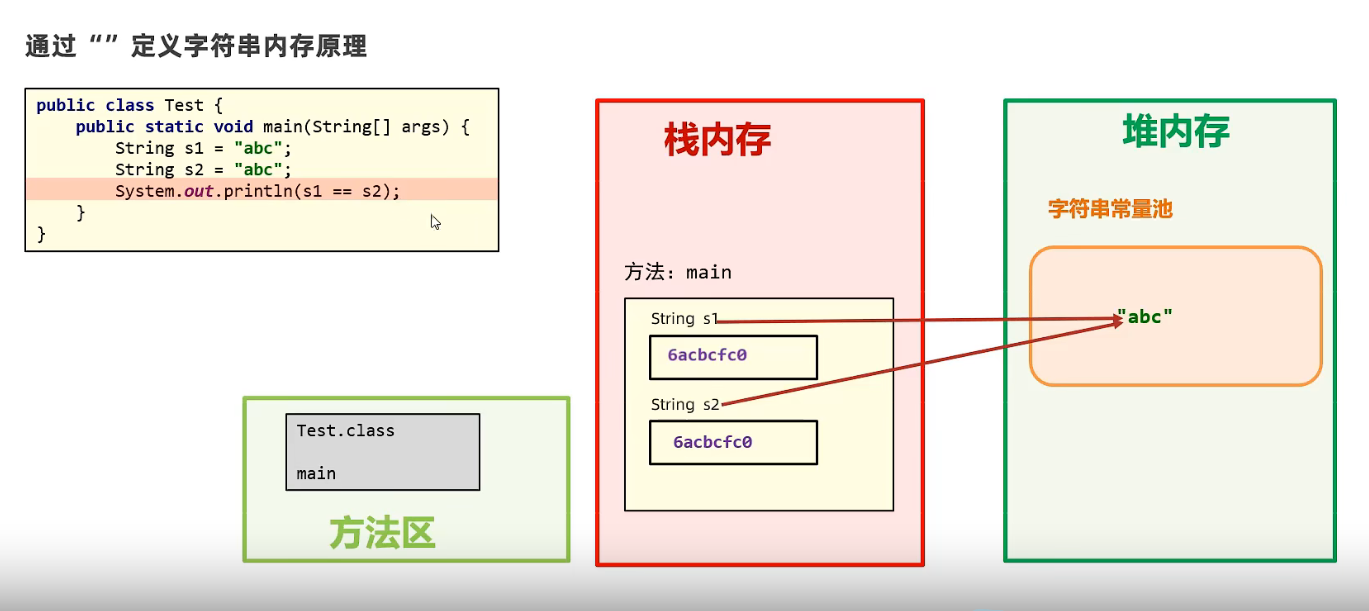
动态数组和静态数组的元素是放在堆内存中的,数组变量名(数组地址)是放在栈内存中 — new出来的都是在堆内存(静态数组缩写了new)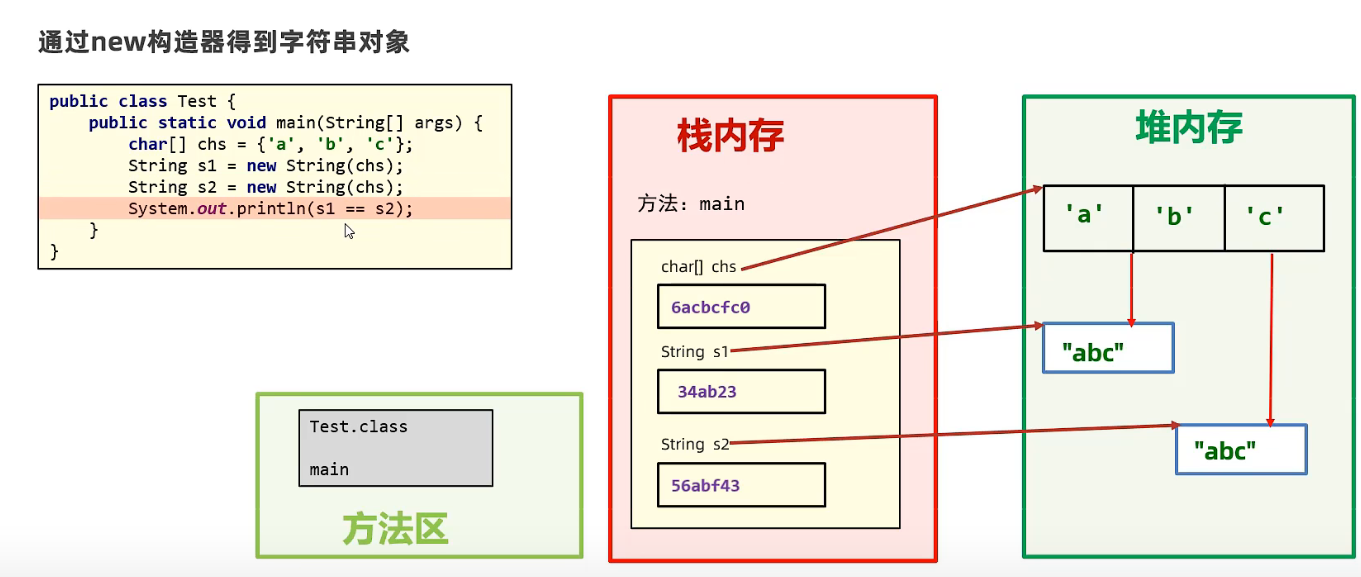
package com.itheima.string;/*目标:String类创建字符串对象的两种方式 一种是直接双引号,另一种是调用构造器*/public class StringDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 方式一:直接使用双引号得到字符串对象String name = "我爱你中国";System.out.println(name); // 根据这个字符串name地址找到的内容// 方式二:// 1.public String(): 创建一个空白字符串对象,不含有任何内容(几乎不用)String s1 = new String(); // s1 = ""; 等于调用了String类中的无参构造器System.out.println(s1);// 2.public String(String): 根据传入的字符串内容,来创建字符串对象(几乎不用)String s2 = new String("我是中国人"); // 等于是String类里面有一个有参构造器System.out.println(s2);// 3.public String(char[] c): 根据字符数组的内容,来创建字符串对象char[] chars = {'a','b','中','国'};// new String(chars); 先new一个String类的对象,然后将字符数组传入String有参构造器中String s3 = new String(chars); // 将char字符数组转换为字符串对象System.out.println(s3);// ab中国// 4.public String(byte[] b): 根据字节数组的内容,来创建字符串对象byte[] bytes = {97,98,99,65,66,67};String s4 = new String(bytes); // 将byte字节数组传入String有参构造器,将byte数组(byte是整型)转换为String对象(变成字符串的ABC,对应ASCII码)System.out.println(s4); // abcABCSystem.out.println("-------------------");String ss1 = "abc";String ss2 = "abc";System.out.println(ss1 == ss2); // 结果是true,他们的地址相同,都是指向字符串常量池中的“abc”char[] chars1 = {'a','b','c'};String ss3 = new String(chars1);String ss4 = new String(chars1);System.out.println(ss3 == ss4); // 结果为false,因为创建了两个新的对象,对象不同,地址就不同,为false}}

