一.搭建jdk源码环境
1.1找到jdk安装目录
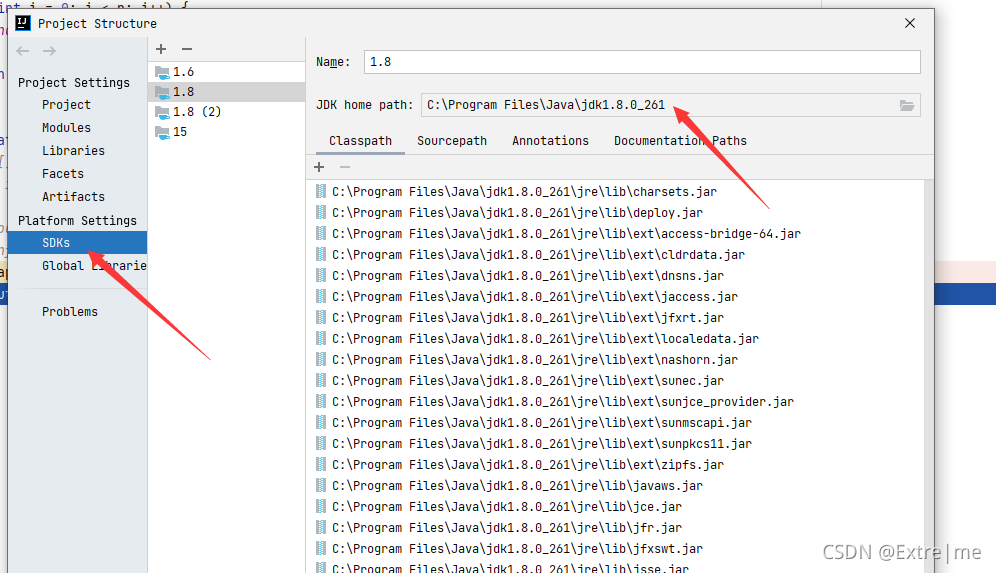
1.2.获取jdk下src安装包
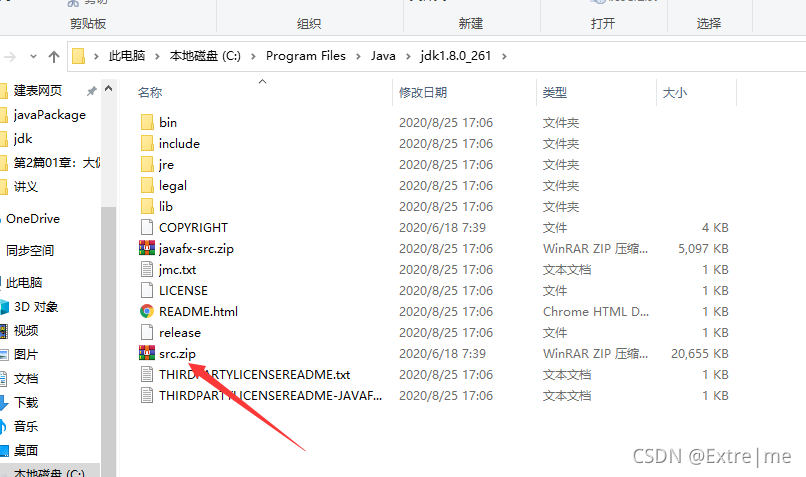
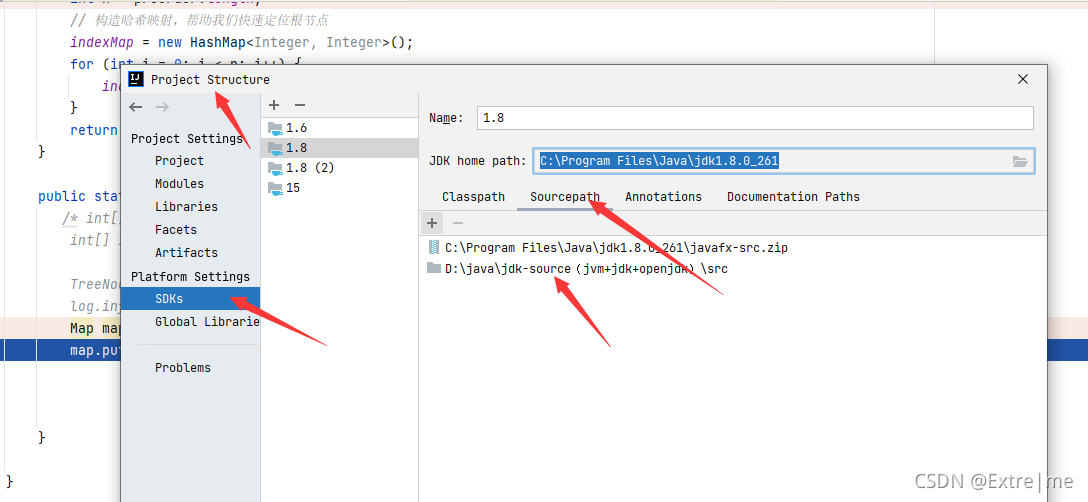
1.3将src复制到其他目录并解压,然后在ideal中配置原源码路径
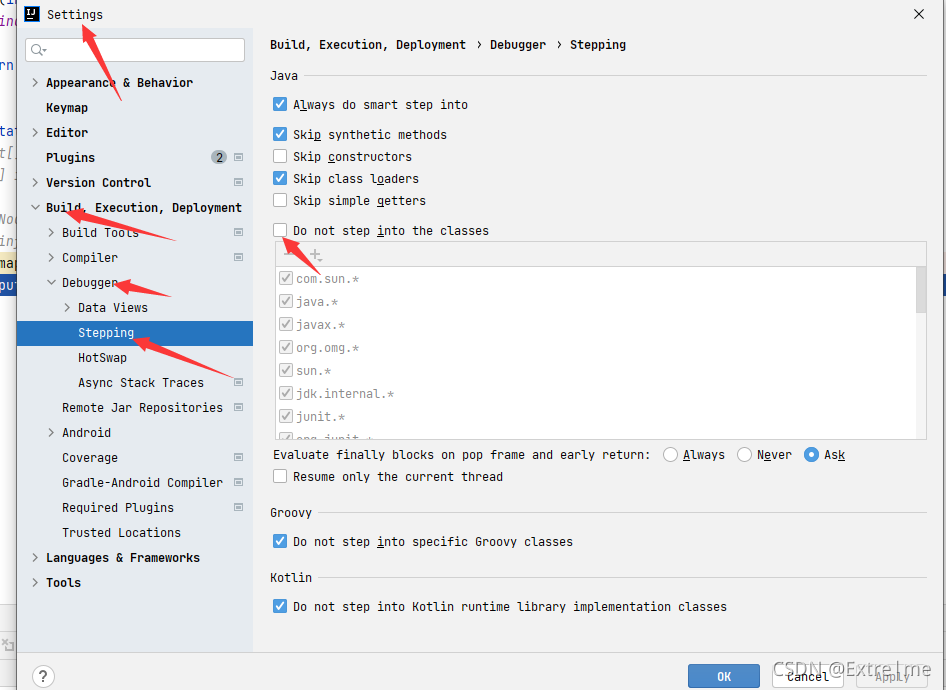
1.4去除源码保护
1.5debug调试源码
二.Object类
2.1 Oject是如何织入的
jdk1.6以及之前Object通过继承的方式织入jdk1.6之后是通过虚拟机织入的我们使用ideal能够直接调用Object类中的方法是因为里面的插件

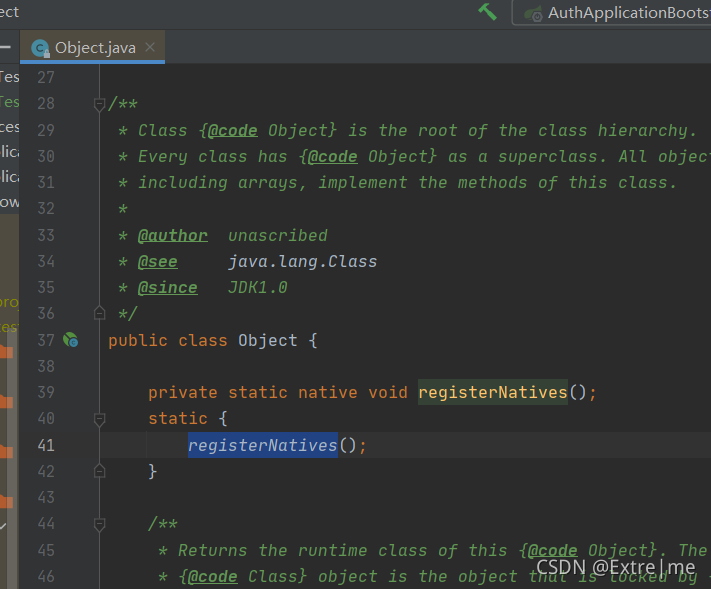
2.2 Obect中native方法是如果调用的
native 是调用底层c c++语言的方法,源码包地址链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1rW6UYVAO4LKcdQtZxCUxVQ提取码:1111
在加载静态代码块的时候,会通过registerNatives()加载,通过method函数对java和c++方法做映射


2.3 hashcode
查看java对象的内存地址需要导入jdk工具包,调用方法VM.current().addressOf(java对象)
<!--jdk工具 能够查看对象的内存地址--><dependency><groupId>org.openjdk.jol</groupId><artifactId>jol-core</artifactId><version>0.9</version></dependency>
Obejct中hashcode底层是通过xor算法得出的随机数,以下是hashcode的计算方法 默认为5product(intx, hashCode, 5, \"(Unstable) select hashCode generation algorithm") \OpenJDK8 默认hashCode的计算方法是通过和当前线程有关的一个随机数+三个确定值,运用Marsaglia's xorshift scheme随机数算法得到的一个随机数。和对象内存地址无关具体算法解释可以看下这俩篇大佬的文章https://urlify.cn/URzeuahttps://www.jianshu.com/p/be943b4958f4
static inline intptr_t get_next_hash(Thread * Self, oop obj) {intptr_t value = 0 ;if (hashCode == 0) {// This form uses an unguarded global Park-Miller RNG,// so it's possible for two threads to race and generate the same RNG.// On MP system we'll have lots of RW access to a global, so the// mechanism induces lots of coherency traffic.value = os::random() ;} elseif (hashCode == 1) {// This variation has the property of being stable (idempotent)// between STW operations. This can be useful in some of the 1-0// synchronization schemes.intptr_t addrBits = intptr_t(obj) >> 3 ;value = addrBits ^ (addrBits >> 5) ^ GVars.stwRandom ;} elseif (hashCode == 2) {value = 1 ; // for sensitivity testing} elseif (hashCode == 3) {value = ++GVars.hcSequence ;} elseif (hashCode == 4) {value = intptr_t(obj) ;} else {// Marsaglia's xor-shift scheme with thread-specific state// This is probably the best overall implementation -- we'll// likely make this the default in future releases.unsigned t = Self->_hashStateX ;t ^= (t << 11) ;Self->_hashStateX = Self->_hashStateY ;Self->_hashStateY = Self->_hashStateZ ;Self->_hashStateZ = Self->_hashStateW ;unsigned v = Self->_hashStateW ;v = (v ^ (v >> 19)) ^ (t ^ (t >> 8)) ;Self->_hashStateW = v ;value = v ;}value &= markOopDesc::hash_mask;if (value == 0) value = 0xBAD ;assert (value != markOopDesc::no_hash, "invariant") ;TEVENT (hashCode: GENERATE) ;return value;}
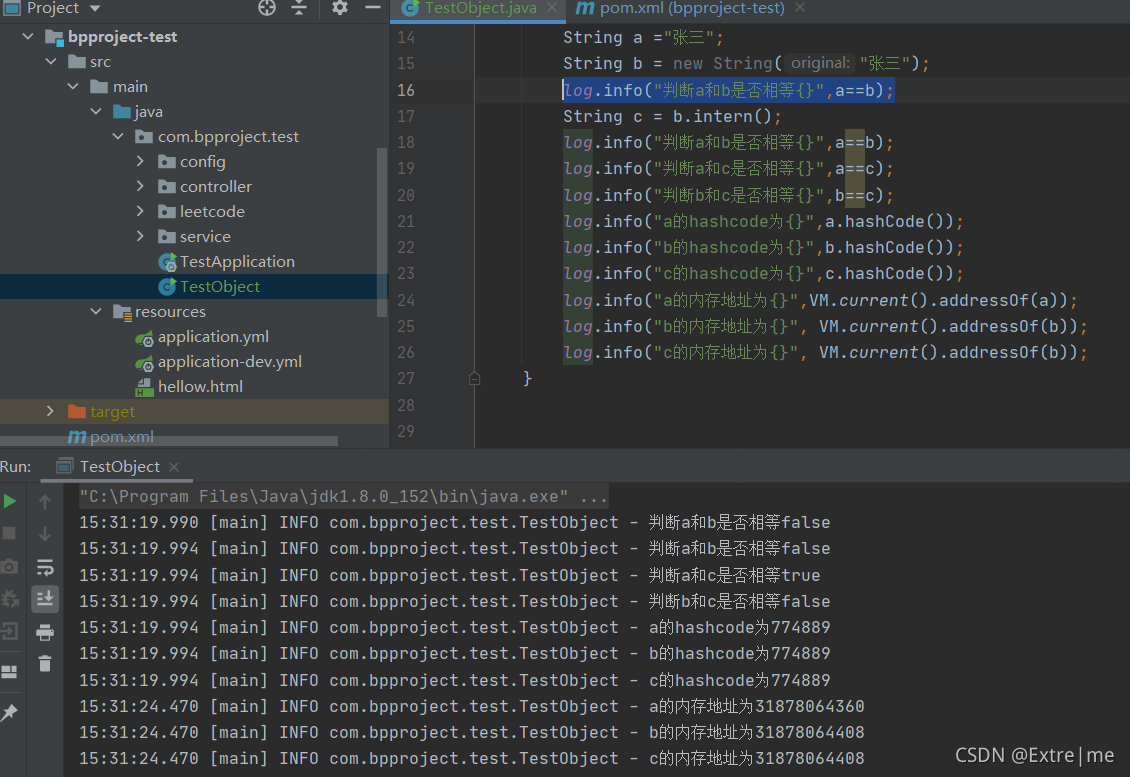
hashcode并不是内存地址,串池中的内存地址和堆中的内存地址并不一样,当使用intern()方法是当串池中有当前字符串会将串池中对象地址返回回来,如果没有会将堆中对象地址放入串池并返回
2.4 为什么要同时重写hashcode和equals方法
个人理解:对象的hashcode是有可能重复的,当前重复的时候我们需要去根据字段的属性判断两个对象是否相等 这个时候需要对对象各个属性的值进行判断,就需要重新equals方法(object的equals方法是比较的内存地址)

