一、redis实现分布式锁
问题一:释放了不是自己加的锁
1.客户 1 获取锁成功并设置设置 30 秒超时;2.客户 1 因为一些原因导致执行很慢(网络问题、发生 FullGC……),过了 30 秒依然没执行完,但是锁过期「自动释放了」;3.客户 2 申请加锁成功;4.客户 1 执行完成,执行 DEL 释放锁指令,这个时候就把客户 2 的锁给释放了。
解决:
在加锁的时候设置一个「唯一标识」作为 value 代表加锁的客户端。SET resource_name random_value NX PX 30000在释放锁的时候,客户端将自己的「唯一标识」与锁上的「标识」比较是否相等,匹配上则删除,否则没有权利释放锁。
具体实现:为保证原子性使用lua脚本
// 获取锁的 value 与 ARGV[1] 是否匹配,匹配则执行 delif redis.call("get",KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] thenreturn redis.call("del",KEYS[1])elsereturn 0end
问题二:设置锁的超时时间(超时时间设置多久合适)
根据在测试环境多次测试,然后压测多轮之后,比如计算出平均执行时间 200 ms。因为如果锁的操作逻辑中有网络 IO 操作、JVM FullGC 等,线上的网络不会总一帆风顺,我们要给网络抖动留有缓冲时间,那么锁的超时时间就放大为平均执行时间的 3~5 倍。设置短了导致锁提前释放,设置长了导致锁长期被占有,不管时间怎么设置都不大合适。
解决
可以让获得锁的线程开启一个守护线程,用来给快要过期的锁「续航」。加锁的时候设置一个过期时间,同时客户端开启一个「守护线程」,定时去检测这个锁的失效时间。如果快要过期,但是业务逻辑还没执行完成,自动对这个锁进行续期,重新设置过期时间。
二、springboot集成Redisson
依赖
<!--redisson--><dependency><groupId>org.redisson</groupId><artifactId>redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId><version>3.13.6</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId><version>2.3.2.RELEASE</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId><version>1.18.12</version></dependency>
配置文件
spring:## Redis配置redis:password:cluster:nodes: 127.0.0.1:6379jedis:pool:#最大连接数max-active: 8#最大阻塞等待时间(负数表示没限制)max-wait: -1#最小空闲min-idle: 0#最大空闲max-idle: 8#连接超时时间timeout: 10000##Redisson配置redisson:enable: truecluster-servers-config:cluster-nodes: ${spring.redis.cluster.nodes}load-balancer-mode: RADOMpassword: ${spring.redis.password}slave-connection-minimum-idle-size: 8slave-connection-pool-size: 16sslEnableEndpointIdentification: falsethreads: 8nettyThreads: 8transportMode: NIO
使用redisson每隔10秒会自动续期
@RestController@Slf4jpublic class RedissonTestController {@Autowiredprivate RedissonClient redissonClient;@RequestMapping(value = "/redisson")public void redissonTest() {RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("9999");try {log.info("开始上锁了");lock.lock();Thread.sleep(40000);} catch (Exception e) {} finally {lock.unlock();}log.info("已解锁");}}
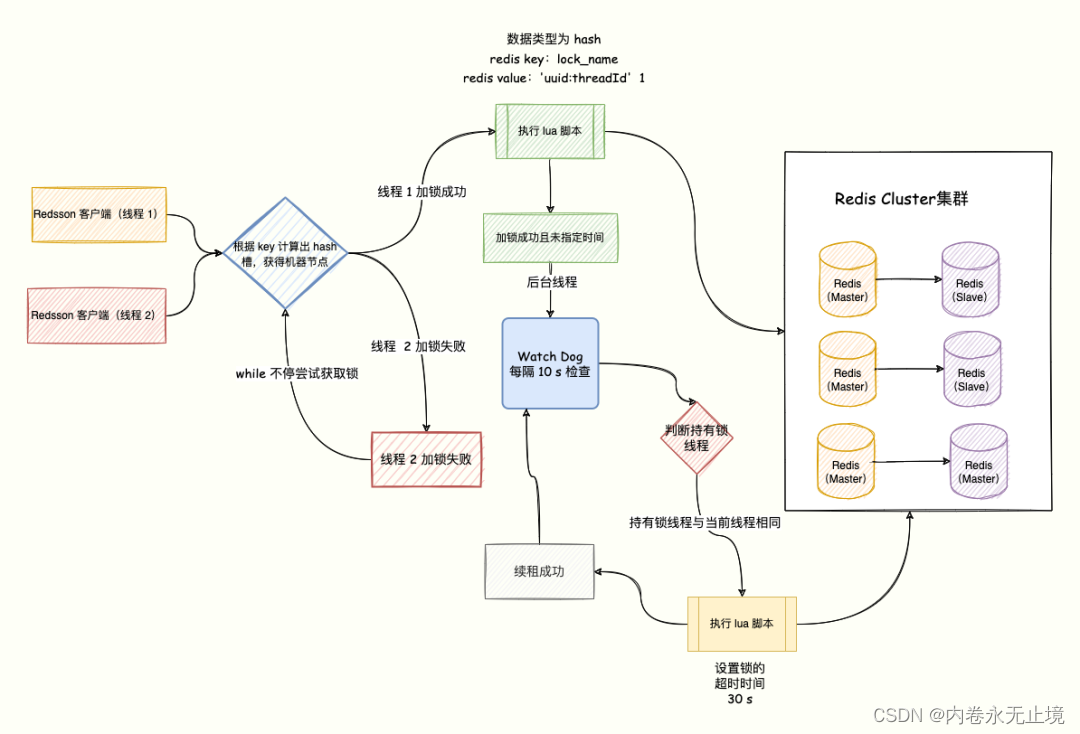
redisson续约源码
private void renewExpiration() {RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry ee = (RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry)EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(this.getEntryName());if (ee != null) {Timeout task = this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry ent = (RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry)RedissonLock.EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(RedissonLock.this.getEntryName());if (ent != null) {Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId();if (threadId != null) {RFuture<Boolean> future = RedissonLock.this.renewExpirationAsync(threadId);future.onComplete((res, e) -> {if (e != null) {RedissonLock.log.error("Can't update lock " + RedissonLock.this.getName() + " expiration", e);} else {if (res) {RedissonLock.this.renewExpiration();}}});}}}}, this.internalLockLeaseTime / 3L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);ee.setTimeout(task);}}private void scheduleExpirationRenewal(long threadId) {RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry entry = new RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry();RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry oldEntry = (RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry)EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.putIfAbsent(this.getEntryName(), entry);if (oldEntry != null) {oldEntry.addThreadId(threadId);} else {entry.addThreadId(threadId);this.renewExpiration();}}protected RFuture<Boolean> renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {return this.evalWriteAsync(this.getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN, "if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return 1; end; return 0;", Collections.singletonList(this.getName()), this.internalLockLeaseTime, this.getLockName(threadId));}protected <T> RFuture<T> evalWriteAsync(String key, Codec codec, RedisCommand<T> evalCommandType, String script, List<Object> keys, Object... params) {CommandBatchService executorService = this.createCommandBatchService();RFuture<T> result = executorService.evalWriteAsync(key, codec, evalCommandType, script, keys, params);if (!(this.commandExecutor instanceof CommandBatchService)) {executorService.executeAsync();}return result;}
1.独享(相互排斥)。在任意一个时刻,只有一个客户端持有锁。2无死锁。即便持有锁的客户端崩溃(crashed)或者网络被分裂(gets parttioned),锁仍然可以被获取。3.容错。只要大部分Redis节点都活着,客户端就可以获取和释放锁
问题:
1.客户端A从master获取到锁2.在master将锁同步到slave之前,master宕掉了。3. slave节点被晋级为master节点4.客户端B取得了同一个资源被客户端A已经获取到的另外一个锁。安全失效!

